Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 viewsClimate
Climate
Uploaded by
Fikir FikirThe document discusses the effects of global warming on biodiversity. It notes that both long term actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and short term actions to establish nature reserves are needed. It also describes four methods to forecast the impacts: models of individual species, niche-theory models, general circulation models, and species-area curve models. The author identifies key points like the need for accurate biodiversity definition and data collection to inform policymaking.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- EAP Reading Worksheet Week 10 - Summary Practice 2Document4 pagesEAP Reading Worksheet Week 10 - Summary Practice 2Thu Phương VũNo ratings yet
- Englishix Reading PartialiiiDocument4 pagesEnglishix Reading PartialiiiCesar UA100% (1)
- Robert Guttmann - Eco-Capitalism-Springer International Publishing - Palgrave Macmillan (2018)Document321 pagesRobert Guttmann - Eco-Capitalism-Springer International Publishing - Palgrave Macmillan (2018)Renato Tavares100% (1)
- Introduction To Statistics Assignment II: Median 4.25Document5 pagesIntroduction To Statistics Assignment II: Median 4.25Fikir FikirNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Definition of Budget: Literature ReviewDocument10 pages2.1 Definition of Budget: Literature ReviewFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Call For Virtual Workshop On Aerospace, Digital Transformation, & Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesCall For Virtual Workshop On Aerospace, Digital Transformation, & Artificial IntelligenceFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Re-Circulation Loop: PC AttDocument5 pagesRe-Circulation Loop: PC AttFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Your Palm Reading Results!Document3 pagesYour Palm Reading Results!Fikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Interesting Facts About AquariusDocument9 pagesInteresting Facts About AquariusFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Description of Job For Marie Curie 5GWireless ProjectDocument3 pagesDescription of Job For Marie Curie 5GWireless ProjectFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- TC GSM OverviewDocument80 pagesTC GSM OverviewFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method and Its ApplicationsDocument34 pagesFinite-Difference Time-Domain Method and Its ApplicationsFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Digital Aerial Cameras: NtroductionDocument5 pagesDigital Aerial Cameras: NtroductionFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- MartinezDocument20 pagesMartinezdbramNo ratings yet
- EI247 Global Maritime Trends 2050Document1 pageEI247 Global Maritime Trends 2050rauljuganaruNo ratings yet
- Lynn Et Al. 2013 PDFDocument12 pagesLynn Et Al. 2013 PDFจิรกิตติ์ อาษากิจNo ratings yet
- Urban Flood Management Project Report - 240404 - 194444Document88 pagesUrban Flood Management Project Report - 240404 - 194444drlikhithrajNo ratings yet
- Climate - Change Book PDFDocument283 pagesClimate - Change Book PDFPantulu MurtyNo ratings yet
- Warning On Global WarmingDocument2 pagesWarning On Global WarmingLô Vỹ Vy VyNo ratings yet
- Climate Risk Country Profile: ThailandDocument32 pagesClimate Risk Country Profile: ThailandKrit YodpraditNo ratings yet
- Climate Change by EBCDocument11 pagesClimate Change by EBCMd Saidunnabi JohaNo ratings yet
- 25 Things You Need To Know About The FutureDocument227 pages25 Things You Need To Know About The FuturejamesNo ratings yet
- Assessing Coastal Vulnerability and Governance in Ma - 2022 - Progress in DisastDocument13 pagesAssessing Coastal Vulnerability and Governance in Ma - 2022 - Progress in DisastHiền TrầnNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is Now A Critical StageDocument3 pagesGlobal Warming Is Now A Critical StageSocial PhenomenaNo ratings yet
- GE 1001 Foundations of Geography The Atmosphere and Hydrosphere of The EarthDocument6 pagesGE 1001 Foundations of Geography The Atmosphere and Hydrosphere of The EarthPhani KumarNo ratings yet
- Coastal LandformsDocument46 pagesCoastal LandformsShreya YugalNo ratings yet
- Tatm 1 - Midterm2021Document8 pagesTatm 1 - Midterm2021Phuc DangNo ratings yet
- Property Information Pack - 15C Ngatiawa StreetDocument82 pagesProperty Information Pack - 15C Ngatiawa StreetYanci LNo ratings yet
- Fugro (2017) Geohazard Quantification Landslides in Deepwater Development AreasDocument44 pagesFugro (2017) Geohazard Quantification Landslides in Deepwater Development AreasJoeNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Group 2 Section MDocument3 pagesCase Study - Group 2 Section MًNo ratings yet
- Impact of The Climate Change On The Coastal Areas of Pakistan Mansoor Moin RealDocument33 pagesImpact of The Climate Change On The Coastal Areas of Pakistan Mansoor Moin RealMansoor Moin100% (1)
- Energy and Climate Change (ESE-832) : Dr. Warda AjazDocument59 pagesEnergy and Climate Change (ESE-832) : Dr. Warda AjazAffan RaufNo ratings yet
- (Dank Cho Thisinh Thi Chuyen Nga, PHDP, Trung) : Thai Gian Lam Bai: 180 Phut, Fchong K I Then Gian Giao deDocument8 pages(Dank Cho Thisinh Thi Chuyen Nga, PHDP, Trung) : Thai Gian Lam Bai: 180 Phut, Fchong K I Then Gian Giao deNguyên Hà Nguyễn100% (1)
- Climate Change Information KitDocument66 pagesClimate Change Information Kitnephila100% (2)
- Carbon Capture & StorageDocument52 pagesCarbon Capture & StorageJuniar Arya PrajakaNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Guidelines For Mainstreaming CC-DRR in The CLUP - CDRA PDFDocument318 pagesSupplemental Guidelines For Mainstreaming CC-DRR in The CLUP - CDRA PDFjamesNo ratings yet
- Presentation (PPT) - Climate Change & Groundwater (2020feb) MyintTheinDocument22 pagesPresentation (PPT) - Climate Change & Groundwater (2020feb) MyintTheinMyint Thein100% (1)
- FINAL REPORT - Case Study Jamaica - Spandana NakkaDocument30 pagesFINAL REPORT - Case Study Jamaica - Spandana Nakkaandreonife4736No ratings yet
- The Coming Ice Age - Harper's Magazine-1958Document11 pagesThe Coming Ice Age - Harper's Magazine-1958Michael RobertsNo ratings yet
- World Bank Essay From The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesWorld Bank Essay From The PhilippinesDavid Michael San JuanNo ratings yet
Climate
Climate
Uploaded by
Fikir Fikir0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views13 pagesThe document discusses the effects of global warming on biodiversity. It notes that both long term actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and short term actions to establish nature reserves are needed. It also describes four methods to forecast the impacts: models of individual species, niche-theory models, general circulation models, and species-area curve models. The author identifies key points like the need for accurate biodiversity definition and data collection to inform policymaking.
Original Description:
climate science
Original Title
climate
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the effects of global warming on biodiversity. It notes that both long term actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and short term actions to establish nature reserves are needed. It also describes four methods to forecast the impacts: models of individual species, niche-theory models, general circulation models, and species-area curve models. The author identifies key points like the need for accurate biodiversity definition and data collection to inform policymaking.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views13 pagesClimate
Climate
Uploaded by
Fikir FikirThe document discusses the effects of global warming on biodiversity. It notes that both long term actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and short term actions to establish nature reserves are needed. It also describes four methods to forecast the impacts: models of individual species, niche-theory models, general circulation models, and species-area curve models. The author identifies key points like the need for accurate biodiversity definition and data collection to inform policymaking.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Global warming effect on Biodiversity
• Understanding and modeling the effect of global warming on biodiversity is
vital for policy makers and general public
• To tackle the effect of global warming two approaches are necessary
1. Long-term action → Reduce green-house gas emissions
2. Short-term action → design vital natural reserves
• Fossil evidence and genetic & ecological study has limitation to accurately
estimate the extinction biodiversity.
• Effect of global warming on biodiversity can be forecasted using four methods
1. models that consider species individually
2. niche-theory models that group species by habitat
3. General circulation models and coupled ocean–atmosphere–biosphere models
4. species–area curve models that consider all species or large aggregates of species.
Global warming effect on Biodiversity
• The authors has identified several key points in forecasting effect of global
warming on biodiversity
Accurate definition of biodiversity is needed with great emphasis placed on DNA analysis
to determine genetically distinct units.
Validation of models for substantially prove the effect of global warming on biodiversity.
Develop a forecast that clearly integrate the environmental catastrophe and man-made ,
such as wild life trade, war, pollution, distraction of natural habitat, introducing invasive
species, and etc., effect on biodiversity.
Accurate and representative data collection and analysis for policy making.
Use of biodiversity preservation mechanism from quaternary fossil record to bridge
discrepancy between past few-extinction record and present large scale forecasted
extinction.
Global warming effect on Biodiversity
• The authors has identified several key points in forecasting effect of global
warming on biodiversity
Improve widely used models such as
Models of individuals: use individual as unit with fixed characteristics and forecast population & species
as sum of individuals.
Niche-theory models: use species and population as fixed characteristics to measure the environmental
variables that effect distribution of species.
Improved ecological principle embedded in general atmosphere-ocean-biotic coupled
circulation model. This circulation models take parameters such as influence of vegetation
on climate via albedo, surface roughness, water evaporation, exchange of green house gases
and aerosol. This relates the atmospheric greenhouse gas concentration and climate change.
Better model to forecast total biodiversity from area covered by species.
Summary
• Lewis
Binford (1968) point out that one key factor for human civilization and agricultural
development was sea level rise.
• Over past 200,000 years the global sea level has risen by 120 meters resulted in migrated shore
lines, separated continental mass to form islands, and ancient people resort to conflict and rising
tension between neighboring community.
• Currently, several hundred million people are living in costal area with sea level less than a
meter which pose treat to future flooding.
• The climate record indicate that the carbon concentration level in the atmosphere, which closely
related to increasing in the global temperature, has risen to level not seen in last two million
years.
• As a result of global warming, the sea levels are expected to rise between in century.
• Impact of human activity on oceans and cost lines has resulted in melting glaciers, warming
seas, rising sea, and collapsing marine ecosystem.
Summary
• Governments, environmental groups, insurance-companies, and non-governmental organization
are investing billions to predict the global warming effect on ecosystem and communities, and
mitigating the economic damage and cultural disruption caused by rising sea levels, intensified
storm cycles, and marine erosion.
• Little attention has been given to global warming induced damage on coastal historical and
archeological sites. Such loss add up to crisis of human history as more archeological records,
excavations, and dates are loss to coast line erosion.
• Close to nothing has been done by lawmakers and governments to protect sites and combat
global warming effect due to two reasons:
the size of the problem is already overwhelming if the agency responsible subject to budget cut and limited
resource.
miss guided belief that coastal erosions are natural process that requires no mitigation except under
extraordinary circumstances.
• Human activity such as damming of rivers, sand mining, ship traffic, and etc. has accelerates
the level of erosion and loss of such sites.
Summary
• The loss has destroyed information on how the past generation has survived huge devastation
and ways of handling sea level rise. As a results, current scientific community has little data to
develop comprehensive models to predict future devastation and warn policy-makers.
• A global discussion, collaboration, and effort is required to tackle the effect of global warming.
Summary
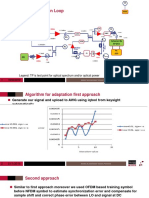
• The
severe acute respiratory syndrome–coronavirus 2 or SARS-CoV-2 has lead to travel
restriction that resulted in reduced GHG emission and air pollution as observed from satellite
data and ground-based observation.
• The data from Google and Apple is used to model and analyze emission trend during covid-19
locked-down. This include estimation of emission change from the mobility data.
• The Google mobility data from 114 countries indicate that population are under mobility
restriction which contributed to overall surface-transport emission change.
• Industrial, public, and residential sector emission change has also been observed from Google
residential, retail, and workplace movement data.
• Mobility data outside of surface-transport over estimates the emission. Specially industrial
emission is not correlated to mobility, due to automation of production line, baseline emission
of industries in absence of production, and alternative mode of work.
• The residential emission increment resulted from occupied vacant houses while at same time
energy consumption has increased.
Population-weighted histogram of surface-transport trends Violin plots of the distribution, minimum,
maximum and median levels of national trends
weighted by CO2 emissions
Estimates of emission changes for the datasets across four sectors
for April 2020 and the sum of the four sectors.
Summary
•• The
fossil fuel CO2 emission from surface transport, residential, power, industry, public and
aviation sectors from 123 countries has been assessed using a baseline from:
Countries climate action named nationally determined contributions (NDCs) by 2030. The
pathway accounts for both GHG and air pollution change.
• Change from such scenario are derived from three-stage process
1. 5-week Google mobility data used as reference.
2. The absolute emission is evaluated by multiplying this fractional change by the 2019 or
previous 2015 study data.
3. The absolute changes are then applied to steadily rising emission pathway before Covid-19.
• During the national lockdown the and emission peak showed reduction as much as driven by
surface –transport emission. Conversely, organic carbon emission has increased from residential
emission. Methane emission from power sector and emissio from industries has declined.
• Estimation of is challenging as has long atmospheric life time and different individual observation
don’t reflect global burden.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- EAP Reading Worksheet Week 10 - Summary Practice 2Document4 pagesEAP Reading Worksheet Week 10 - Summary Practice 2Thu Phương VũNo ratings yet
- Englishix Reading PartialiiiDocument4 pagesEnglishix Reading PartialiiiCesar UA100% (1)
- Robert Guttmann - Eco-Capitalism-Springer International Publishing - Palgrave Macmillan (2018)Document321 pagesRobert Guttmann - Eco-Capitalism-Springer International Publishing - Palgrave Macmillan (2018)Renato Tavares100% (1)
- Introduction To Statistics Assignment II: Median 4.25Document5 pagesIntroduction To Statistics Assignment II: Median 4.25Fikir FikirNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Definition of Budget: Literature ReviewDocument10 pages2.1 Definition of Budget: Literature ReviewFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Call For Virtual Workshop On Aerospace, Digital Transformation, & Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesCall For Virtual Workshop On Aerospace, Digital Transformation, & Artificial IntelligenceFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Re-Circulation Loop: PC AttDocument5 pagesRe-Circulation Loop: PC AttFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Your Palm Reading Results!Document3 pagesYour Palm Reading Results!Fikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Interesting Facts About AquariusDocument9 pagesInteresting Facts About AquariusFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Description of Job For Marie Curie 5GWireless ProjectDocument3 pagesDescription of Job For Marie Curie 5GWireless ProjectFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- TC GSM OverviewDocument80 pagesTC GSM OverviewFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Finite-Difference Time-Domain Method and Its ApplicationsDocument34 pagesFinite-Difference Time-Domain Method and Its ApplicationsFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- Digital Aerial Cameras: NtroductionDocument5 pagesDigital Aerial Cameras: NtroductionFikir FikirNo ratings yet
- MartinezDocument20 pagesMartinezdbramNo ratings yet
- EI247 Global Maritime Trends 2050Document1 pageEI247 Global Maritime Trends 2050rauljuganaruNo ratings yet
- Lynn Et Al. 2013 PDFDocument12 pagesLynn Et Al. 2013 PDFจิรกิตติ์ อาษากิจNo ratings yet
- Urban Flood Management Project Report - 240404 - 194444Document88 pagesUrban Flood Management Project Report - 240404 - 194444drlikhithrajNo ratings yet
- Climate - Change Book PDFDocument283 pagesClimate - Change Book PDFPantulu MurtyNo ratings yet
- Warning On Global WarmingDocument2 pagesWarning On Global WarmingLô Vỹ Vy VyNo ratings yet
- Climate Risk Country Profile: ThailandDocument32 pagesClimate Risk Country Profile: ThailandKrit YodpraditNo ratings yet
- Climate Change by EBCDocument11 pagesClimate Change by EBCMd Saidunnabi JohaNo ratings yet
- 25 Things You Need To Know About The FutureDocument227 pages25 Things You Need To Know About The FuturejamesNo ratings yet
- Assessing Coastal Vulnerability and Governance in Ma - 2022 - Progress in DisastDocument13 pagesAssessing Coastal Vulnerability and Governance in Ma - 2022 - Progress in DisastHiền TrầnNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Is Now A Critical StageDocument3 pagesGlobal Warming Is Now A Critical StageSocial PhenomenaNo ratings yet
- GE 1001 Foundations of Geography The Atmosphere and Hydrosphere of The EarthDocument6 pagesGE 1001 Foundations of Geography The Atmosphere and Hydrosphere of The EarthPhani KumarNo ratings yet
- Coastal LandformsDocument46 pagesCoastal LandformsShreya YugalNo ratings yet
- Tatm 1 - Midterm2021Document8 pagesTatm 1 - Midterm2021Phuc DangNo ratings yet
- Property Information Pack - 15C Ngatiawa StreetDocument82 pagesProperty Information Pack - 15C Ngatiawa StreetYanci LNo ratings yet
- Fugro (2017) Geohazard Quantification Landslides in Deepwater Development AreasDocument44 pagesFugro (2017) Geohazard Quantification Landslides in Deepwater Development AreasJoeNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Group 2 Section MDocument3 pagesCase Study - Group 2 Section MًNo ratings yet
- Impact of The Climate Change On The Coastal Areas of Pakistan Mansoor Moin RealDocument33 pagesImpact of The Climate Change On The Coastal Areas of Pakistan Mansoor Moin RealMansoor Moin100% (1)
- Energy and Climate Change (ESE-832) : Dr. Warda AjazDocument59 pagesEnergy and Climate Change (ESE-832) : Dr. Warda AjazAffan RaufNo ratings yet
- (Dank Cho Thisinh Thi Chuyen Nga, PHDP, Trung) : Thai Gian Lam Bai: 180 Phut, Fchong K I Then Gian Giao deDocument8 pages(Dank Cho Thisinh Thi Chuyen Nga, PHDP, Trung) : Thai Gian Lam Bai: 180 Phut, Fchong K I Then Gian Giao deNguyên Hà Nguyễn100% (1)
- Climate Change Information KitDocument66 pagesClimate Change Information Kitnephila100% (2)
- Carbon Capture & StorageDocument52 pagesCarbon Capture & StorageJuniar Arya PrajakaNo ratings yet
- Supplemental Guidelines For Mainstreaming CC-DRR in The CLUP - CDRA PDFDocument318 pagesSupplemental Guidelines For Mainstreaming CC-DRR in The CLUP - CDRA PDFjamesNo ratings yet
- Presentation (PPT) - Climate Change & Groundwater (2020feb) MyintTheinDocument22 pagesPresentation (PPT) - Climate Change & Groundwater (2020feb) MyintTheinMyint Thein100% (1)
- FINAL REPORT - Case Study Jamaica - Spandana NakkaDocument30 pagesFINAL REPORT - Case Study Jamaica - Spandana Nakkaandreonife4736No ratings yet
- The Coming Ice Age - Harper's Magazine-1958Document11 pagesThe Coming Ice Age - Harper's Magazine-1958Michael RobertsNo ratings yet
- World Bank Essay From The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesWorld Bank Essay From The PhilippinesDavid Michael San JuanNo ratings yet