Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atmospheric Components and Ozone
Atmospheric Components and Ozone
Uploaded by
jsn_fCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Life Cycle Analysis of Cement IndustryDocument26 pagesLife Cycle Analysis of Cement IndustryJudy Ann BoseNo ratings yet
- Insuflex CatalogDocument15 pagesInsuflex Catalogmarceilinus devaluanto100% (1)
- Composition of AirDocument1 pageComposition of Airdr.ayishamufsiraNo ratings yet
- Composition of AirDocument2 pagesComposition of Airfatfrank3566No ratings yet
- Composition of AirDocument10 pagesComposition of AirAngelica DiazNo ratings yet
- Sidestream and Mainstream Deammonification - Opportunities and ChallengesDocument32 pagesSidestream and Mainstream Deammonification - Opportunities and ChallengesLuqmanNo ratings yet
- Air CompositionDocument2 pagesAir CompositionHarsh Vardhan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Che 521 NoteDocument39 pagesChe 521 NoteBenjamin IlesanmiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Environmental PollutionDocument71 pagesLecture 6 Environmental PollutionDulon ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Allowable DischargeDocument3 pagesAllowable DischargeTiago PhillipeNo ratings yet
- NewoneDocument18 pagesNewoneMustafa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 6 - Environmental PollutionDocument71 pagesLecture - 6 - Environmental PollutionСаманати СоринNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution: by Mrs. Vaibhavi ApteDocument71 pagesEnvironmental Pollution: by Mrs. Vaibhavi ApteNOT AkulNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry: Air Pollution: The Atmospheric PressureDocument42 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry: Air Pollution: The Atmospheric Pressuresayed Tamir janNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument68 pagesAir PollutionjohnnyNo ratings yet
- Theoryandoperationofmethanationcatalyst 130728222405 Phpapp01Document32 pagesTheoryandoperationofmethanationcatalyst 130728222405 Phpapp01yuriNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument56 pagesAir PollutionBinit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Environmental-PollutionDocument71 pagesLecture 6 Environmental-PollutionD V MaskarNo ratings yet
- Che 517 - Module 1Document55 pagesChe 517 - Module 1Precious JamesNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance (Final)Document26 pagesMass Balance (Final)Adeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Txgard & Flamgard Plus: Fixed Point Gas DetectorsDocument4 pagesTxgard & Flamgard Plus: Fixed Point Gas Detectorscasmadi casmadiNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument74 pagesAir PollutionAlok Gowda BmNo ratings yet
- 8a-Advanced Waste Water TreatmentDocument43 pages8a-Advanced Waste Water TreatmentSathish GlNo ratings yet
- 1-Mine GasesDocument74 pages1-Mine GasesNeha Sharma0% (1)
- Air CompositionDocument1 pageAir CompositionkausikrNo ratings yet
- AIR Natural ResourceDocument1 pageAIR Natural ResourceShreyansh JalonhaNo ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument66 pagesEnvironmental PollutionRAHUL JARARIYANo ratings yet
- Outdoor Air Quality MonitorDocument3 pagesOutdoor Air Quality MonitorZulfequar Ali AhmadNo ratings yet
- Semi Soft Coking Coal and PCI CoalDocument2 pagesSemi Soft Coking Coal and PCI CoalYusuff QuadrilateralNo ratings yet
- Che 517 - Module 1Document55 pagesChe 517 - Module 1Precious JamesNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument15 pagesAir PollutionM Favor PaulNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument24 pagesAir Pollutionইসলামিক টিভি100% (1)
- Module 2. - Air Pollution & EffectDocument53 pagesModule 2. - Air Pollution & EffectOluwagbenga OlasehindeNo ratings yet
- 4158 Alia 1 Metode SamplingDocument71 pages4158 Alia 1 Metode SamplingoliviaNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia Air CompositionDocument11 pagesWikipedia Air CompositionAzrul NizamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes (Air)Document2 pagesChemistry Notes (Air)Teo Jia Ming Nickolas100% (1)
- OREAS 60d DataPackDocument308 pagesOREAS 60d DataPackWidy macNo ratings yet
- OREAS 181 CertificateDocument10 pagesOREAS 181 CertificaterusdiansyahNo ratings yet
- 6th STEP Presentation TemplateDocument35 pages6th STEP Presentation TemplateSajjala SreedharreddyNo ratings yet
- Ozone Technology and ApplicationsDocument24 pagesOzone Technology and ApplicationsVũ TrựcNo ratings yet
- OREAS 194 Certificate PDFDocument9 pagesOREAS 194 Certificate PDFAndhika Manggal Putra PNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument20 pagesAir Pollutionjan isobel hidalgoNo ratings yet
- Apes Chapter 15 Notes (Mrs. Bauck) : Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone DepletionDocument24 pagesApes Chapter 15 Notes (Mrs. Bauck) : Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone DepletionMATTHEW STRASSMANNo ratings yet
- Municipal and Domestic Wastewater TreatmentDocument37 pagesMunicipal and Domestic Wastewater TreatmentBerlian SitorusNo ratings yet
- Kali Pyro Chlo ReDocument1 pageKali Pyro Chlo ReramzchileNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Acids, Bases, and Salts: Reaction With MetalsDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Acids, Bases, and Salts: Reaction With Metals22550No ratings yet
- EnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 02 Air Pollution Sources & ImpactsDocument100 pagesEnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 02 Air Pollution Sources & ImpactsAlexis Bryan RiveraNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric-Chemistry NRWDocument86 pagesAtmospheric-Chemistry NRWSherlyNo ratings yet
- Interconnectedness of Environmental Cycles: Systems of The EarthDocument23 pagesInterconnectedness of Environmental Cycles: Systems of The EarthMustafa UnsalNo ratings yet
- F CVEN9857 - Biological Nutrient Removal MMDocument80 pagesF CVEN9857 - Biological Nutrient Removal MMWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- OREAS 180 CertificateDocument10 pagesOREAS 180 CertificaterusdiansyahNo ratings yet
- OREAS 623 DatapackDocument304 pagesOREAS 623 DatapackGilang PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Composés Alimentation (T/H) Pet Coke (T/H) : SO3 0.84 0.87 K2O 0.816 0 CL 0.096 0.0012Document7 pagesComposés Alimentation (T/H) Pet Coke (T/H) : SO3 0.84 0.87 K2O 0.816 0 CL 0.096 0.0012Anonymous cZWSMZNo ratings yet
- Stratospheric Ozone: Sunlight. This Is Good Ozone. It Is Critical For Life Because It Protects All Life OnDocument35 pagesStratospheric Ozone: Sunlight. This Is Good Ozone. It Is Critical For Life Because It Protects All Life OnHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Mine GasesDocument68 pagesMine GasesAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Densities, Molecular Weight and Chemical Formulas of Some Common Gases Can Be Found in The Table BelowDocument9 pagesDensities, Molecular Weight and Chemical Formulas of Some Common Gases Can Be Found in The Table Belowkuruvillaj2217No ratings yet
- Compound Forming Extractants, Solvating Solvents and Inert Solvents: Iupac Chemical Data SeriesFrom EverandCompound Forming Extractants, Solvating Solvents and Inert Solvents: Iupac Chemical Data SeriesNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Estimating Atmospheric Ozone For Solar Radiation ModelsDocument6 pagesEstimating Atmospheric Ozone For Solar Radiation ModelsLuuutscherNo ratings yet
- What Is Corona Effect - Electrical NotesDocument17 pagesWhat Is Corona Effect - Electrical NotesNunna BaskarNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Flame: Jun Wang, Long Zhang, Yaofeng Mao, Feiyan GongDocument7 pagesCombustion and Flame: Jun Wang, Long Zhang, Yaofeng Mao, Feiyan GongKay WhiteNo ratings yet
- BZG05C15 Datasheet Diodo RGBDocument4 pagesBZG05C15 Datasheet Diodo RGBgeraldoNo ratings yet
- MSP Drillex BOP AnularDocument21 pagesMSP Drillex BOP AnularDavid GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Air QualityDocument24 pagesAir QualityNiño Jhim AndrewNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument19 pagesAir PollutionMika Hakimie100% (1)
- Accelerated AgingDocument198 pagesAccelerated Aginganbuchelvan100% (1)
- D 4325 - 02 Standard Test Methods For Nonmetallic Semi-Conducting and Electrically Insulating Rubber TapesDocument6 pagesD 4325 - 02 Standard Test Methods For Nonmetallic Semi-Conducting and Electrically Insulating Rubber TapesPaulo Heber Alves BrandaoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Hoses, Fittings and Equipment - ParkerDocument612 pagesHydraulic Hoses, Fittings and Equipment - ParkerRastko100% (1)
- Qbank EditedDocument20 pagesQbank EditedMithun Santhosh YuvarajanNo ratings yet
- Hong Kong Apes ReviewDocument13 pagesHong Kong Apes Reviewapi-263638354No ratings yet
- 1984 WhiteheadDocument19 pages1984 WhiteheadAnita yuliyantiNo ratings yet
- And Reactivity in Chemistry and How These Are Also ManDocument354 pagesAnd Reactivity in Chemistry and How These Are Also Manluiz13eduardoNo ratings yet
- Hayanon - What Is The Ozone Hole - Nagoya University, Japan (2006)Document16 pagesHayanon - What Is The Ozone Hole - Nagoya University, Japan (2006)hanif ahmadNo ratings yet
- ACE Salt Water Sanitizing SystemDocument16 pagesACE Salt Water Sanitizing SystemMichele Borselli0% (1)
- The Impacts of Air Pollution On GladstoneDocument20 pagesThe Impacts of Air Pollution On Gladstoneapi-300392659No ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 12Document21 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 12MfanafuthiNo ratings yet
- S 2 Why We Should Protect Our EnvironmentDocument9 pagesS 2 Why We Should Protect Our Environmentfadhli76No ratings yet
- Libelium IoTDocument84 pagesLibelium IoTverticalphoebusNo ratings yet
- Decomposition of Ozone in Water in The Presence of Organic Solutes Acting As Promoters and Imhibitors of Radical Chain ReactionsDocument8 pagesDecomposition of Ozone in Water in The Presence of Organic Solutes Acting As Promoters and Imhibitors of Radical Chain ReactionsSoukunNo ratings yet
- Water PurificationDocument317 pagesWater Purificationdocasadaku5651100% (1)
- Fenton Process Coupledto Ultrasoundand UVDocument9 pagesFenton Process Coupledto Ultrasoundand UVArpit MehtaNo ratings yet
- KCET 2024 Chemistry Paper With AnswerDocument9 pagesKCET 2024 Chemistry Paper With Answerthejasmath2005No ratings yet
- 4.2 (180 Marks) : MarkschemeDocument67 pages4.2 (180 Marks) : MarkschemeSemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- de Thi HSG Tinh Binh Phuoc 2023Document10 pagesde Thi HSG Tinh Binh Phuoc 2023Nguyễn Trần Hà AnhNo ratings yet
- Oxygen and OxidesDocument87 pagesOxygen and OxidesFatema Khatun100% (1)
- SM MP C2030 C2050 2530 2550 FSM DI-C1 Final PDFDocument832 pagesSM MP C2030 C2050 2530 2550 FSM DI-C1 Final PDFДмитрий РазуваевNo ratings yet
- APC Notes 2Document84 pagesAPC Notes 2srisuji14No ratings yet
Atmospheric Components and Ozone
Atmospheric Components and Ozone
Uploaded by
jsn_fOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atmospheric Components and Ozone
Atmospheric Components and Ozone
Uploaded by
jsn_fCopyright:
Available Formats
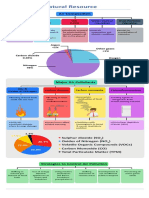
Earth’s Atmosphere
Constant Component
Nitrogen (N2) 78.08%
Oxygen (O2) 20.95%
Argon (Ar) 0.93%
Neon, Helium, 0.0001%
Krypton
Variable Components
Carbon dioxide (CO2) 0.038%
Water vapor (H20) 0-4%
Methane (CH4) trace
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) trace
Ozone (O3) trace
Nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2, N2O) trace
Composition of dry atmosphere, by volume[2]
Gas Volume
Nitrogen (N2) 780,840 ppmv (78.084%)
Oxygen (O2) 209,460 ppmv (20.946%)
Argon (Ar) 9,340 ppmv (0.9340%)
Carbon dioxide (CO2) 390 ppmv (0.039%)
Neon (Ne) 18.18 ppmv (0.001818%)
Helium (He) 5.24 ppmv (0.000524%)
Methane (CH4) 1.79 ppmv (0.000179%)
Krypton (Kr) 1.14 ppmv (0.000114%)
Hydrogen (H2) 0.55 ppmv (0.000055%)
Nitrous oxide (N2O) 0.3 ppmv (0.00003%)
Carbon monoxide (CO) 0.1 ppmv (0.00001%)
Xenon (Xe) 0.09 ppmv (9×10−6%) (0.000009%)
Ozone (O3) 0.0 to 0.07 ppmv (0 to 7×10−6%)
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) 0.02 ppmv (2×10−6%) (0.000002%)
Iodine (I2) 0.01 ppmv (1×10−6%) (0.000001%)
Ammonia (NH3) trace
Not included in above dry atmosphere:
Water vapor (H O) ~0.40% over full atmosphere, typically 1%-4% at
Argon
Rayleigh scattering
Figure 1: Craters on the far side of the moon (L) and
Manicouagan crater in Quebec (R). Image courtesy of NASA.
Ozone Molecule
What the Ozone Layer Does
Low level ozone
• Low level ozone (or tropospheric ozone) is an atmospheric
pollutant. It is not emitted directly bycar engines or by
industrial operations, but formed by the reaction of
sunlight on air containing hydrocarbons and nitrogen
oxides that react to form ozone directly at the source of
the pollution or many kilometers down wind.
• Ozone reacts directly with some hydrocarbons such
as aldehydes and thus begins their removal from the air,
but the products are themselves key components
of smog.
Usefulness of Ozone
• Disinfect laundry in hospitals, food factories, care homes etc
• Disinfect water in place of chlorine
• Deodorize air and objects, such as after a fire. This process is extensively
used in fabric restoration
• Kill bacteria on food or on contact surfaces
• Sanitize swimming pools and spas
• Kill insects in stored grain
• Scrub yeast and mold spores from the air in food processing plants;
• Wash fresh fruits and vegetables to kill yeast, mold and bacteria
• Manufacture chemical compounds via chemical synthesis
• Clean and bleach fabrics (the former use is utilized in fabric restoration;
the latter use is patented);
• Assist in processing plastics to allow adhesion of inks;
• Age rubber samples to determine the useful life of a batch of rubber;
• Eradicate water borne parasites
• DEGRADE PLASTICS
Propellant/Foam
Ozone Depletion
Ozone Hole
Carbon Dioxide
• A candy called Pop Rocks is pressurized with carbon
dioxide gas at about 40 bar
• Leavening agents produce carbon dioxide to cause
dough to rise. Baker's yeast produces carbon dioxide
by fermentation of sugars.
• arbon dioxide is used to produce carbonatedsoft
drinks and soda water
• Fire extinguisher
Toxicity
• 1% can cause drowsiness with prolonged exposure.
• At 2% it is mildly narcotic and causes increased blood
pressure and pulse rate, and causes reduced hearing.
• At about 5% it causes stimulation of the respiratory
center, dizziness, confusion and difficulty in breathing
accompanied by headache and shortness of breath.
Panic attacks may also occur at this concentration.
• At about 8% it causes headache, sweating, dim vision,
tremor and loss of consciousness after exposure for
between five and ten minutes.
You might also like
- Life Cycle Analysis of Cement IndustryDocument26 pagesLife Cycle Analysis of Cement IndustryJudy Ann BoseNo ratings yet
- Insuflex CatalogDocument15 pagesInsuflex Catalogmarceilinus devaluanto100% (1)
- Composition of AirDocument1 pageComposition of Airdr.ayishamufsiraNo ratings yet
- Composition of AirDocument2 pagesComposition of Airfatfrank3566No ratings yet
- Composition of AirDocument10 pagesComposition of AirAngelica DiazNo ratings yet
- Sidestream and Mainstream Deammonification - Opportunities and ChallengesDocument32 pagesSidestream and Mainstream Deammonification - Opportunities and ChallengesLuqmanNo ratings yet
- Air CompositionDocument2 pagesAir CompositionHarsh Vardhan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Che 521 NoteDocument39 pagesChe 521 NoteBenjamin IlesanmiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Environmental PollutionDocument71 pagesLecture 6 Environmental PollutionDulon ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Allowable DischargeDocument3 pagesAllowable DischargeTiago PhillipeNo ratings yet
- NewoneDocument18 pagesNewoneMustafa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 6 - Environmental PollutionDocument71 pagesLecture - 6 - Environmental PollutionСаманати СоринNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution: by Mrs. Vaibhavi ApteDocument71 pagesEnvironmental Pollution: by Mrs. Vaibhavi ApteNOT AkulNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry: Air Pollution: The Atmospheric PressureDocument42 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry: Air Pollution: The Atmospheric Pressuresayed Tamir janNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument68 pagesAir PollutionjohnnyNo ratings yet
- Theoryandoperationofmethanationcatalyst 130728222405 Phpapp01Document32 pagesTheoryandoperationofmethanationcatalyst 130728222405 Phpapp01yuriNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument56 pagesAir PollutionBinit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Environmental-PollutionDocument71 pagesLecture 6 Environmental-PollutionD V MaskarNo ratings yet
- Che 517 - Module 1Document55 pagesChe 517 - Module 1Precious JamesNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance (Final)Document26 pagesMass Balance (Final)Adeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Txgard & Flamgard Plus: Fixed Point Gas DetectorsDocument4 pagesTxgard & Flamgard Plus: Fixed Point Gas Detectorscasmadi casmadiNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument74 pagesAir PollutionAlok Gowda BmNo ratings yet
- 8a-Advanced Waste Water TreatmentDocument43 pages8a-Advanced Waste Water TreatmentSathish GlNo ratings yet
- 1-Mine GasesDocument74 pages1-Mine GasesNeha Sharma0% (1)
- Air CompositionDocument1 pageAir CompositionkausikrNo ratings yet
- AIR Natural ResourceDocument1 pageAIR Natural ResourceShreyansh JalonhaNo ratings yet
- Environmental PollutionDocument66 pagesEnvironmental PollutionRAHUL JARARIYANo ratings yet
- Outdoor Air Quality MonitorDocument3 pagesOutdoor Air Quality MonitorZulfequar Ali AhmadNo ratings yet
- Semi Soft Coking Coal and PCI CoalDocument2 pagesSemi Soft Coking Coal and PCI CoalYusuff QuadrilateralNo ratings yet
- Che 517 - Module 1Document55 pagesChe 517 - Module 1Precious JamesNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument15 pagesAir PollutionM Favor PaulNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument24 pagesAir Pollutionইসলামিক টিভি100% (1)
- Module 2. - Air Pollution & EffectDocument53 pagesModule 2. - Air Pollution & EffectOluwagbenga OlasehindeNo ratings yet
- 4158 Alia 1 Metode SamplingDocument71 pages4158 Alia 1 Metode SamplingoliviaNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia Air CompositionDocument11 pagesWikipedia Air CompositionAzrul NizamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes (Air)Document2 pagesChemistry Notes (Air)Teo Jia Ming Nickolas100% (1)
- OREAS 60d DataPackDocument308 pagesOREAS 60d DataPackWidy macNo ratings yet
- OREAS 181 CertificateDocument10 pagesOREAS 181 CertificaterusdiansyahNo ratings yet
- 6th STEP Presentation TemplateDocument35 pages6th STEP Presentation TemplateSajjala SreedharreddyNo ratings yet
- Ozone Technology and ApplicationsDocument24 pagesOzone Technology and ApplicationsVũ TrựcNo ratings yet
- OREAS 194 Certificate PDFDocument9 pagesOREAS 194 Certificate PDFAndhika Manggal Putra PNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument20 pagesAir Pollutionjan isobel hidalgoNo ratings yet
- Apes Chapter 15 Notes (Mrs. Bauck) : Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone DepletionDocument24 pagesApes Chapter 15 Notes (Mrs. Bauck) : Air Pollution and Stratospheric Ozone DepletionMATTHEW STRASSMANNo ratings yet
- Municipal and Domestic Wastewater TreatmentDocument37 pagesMunicipal and Domestic Wastewater TreatmentBerlian SitorusNo ratings yet
- Kali Pyro Chlo ReDocument1 pageKali Pyro Chlo ReramzchileNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Acids, Bases, and Salts: Reaction With MetalsDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Acids, Bases, and Salts: Reaction With Metals22550No ratings yet
- EnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 02 Air Pollution Sources & ImpactsDocument100 pagesEnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 02 Air Pollution Sources & ImpactsAlexis Bryan RiveraNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric-Chemistry NRWDocument86 pagesAtmospheric-Chemistry NRWSherlyNo ratings yet
- Interconnectedness of Environmental Cycles: Systems of The EarthDocument23 pagesInterconnectedness of Environmental Cycles: Systems of The EarthMustafa UnsalNo ratings yet
- F CVEN9857 - Biological Nutrient Removal MMDocument80 pagesF CVEN9857 - Biological Nutrient Removal MMWeixuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- OREAS 180 CertificateDocument10 pagesOREAS 180 CertificaterusdiansyahNo ratings yet
- OREAS 623 DatapackDocument304 pagesOREAS 623 DatapackGilang PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Composés Alimentation (T/H) Pet Coke (T/H) : SO3 0.84 0.87 K2O 0.816 0 CL 0.096 0.0012Document7 pagesComposés Alimentation (T/H) Pet Coke (T/H) : SO3 0.84 0.87 K2O 0.816 0 CL 0.096 0.0012Anonymous cZWSMZNo ratings yet
- Stratospheric Ozone: Sunlight. This Is Good Ozone. It Is Critical For Life Because It Protects All Life OnDocument35 pagesStratospheric Ozone: Sunlight. This Is Good Ozone. It Is Critical For Life Because It Protects All Life OnHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Mine GasesDocument68 pagesMine GasesAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Densities, Molecular Weight and Chemical Formulas of Some Common Gases Can Be Found in The Table BelowDocument9 pagesDensities, Molecular Weight and Chemical Formulas of Some Common Gases Can Be Found in The Table Belowkuruvillaj2217No ratings yet
- Compound Forming Extractants, Solvating Solvents and Inert Solvents: Iupac Chemical Data SeriesFrom EverandCompound Forming Extractants, Solvating Solvents and Inert Solvents: Iupac Chemical Data SeriesNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresFrom EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableFrom EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNo ratings yet
- Estimating Atmospheric Ozone For Solar Radiation ModelsDocument6 pagesEstimating Atmospheric Ozone For Solar Radiation ModelsLuuutscherNo ratings yet
- What Is Corona Effect - Electrical NotesDocument17 pagesWhat Is Corona Effect - Electrical NotesNunna BaskarNo ratings yet
- Combustion and Flame: Jun Wang, Long Zhang, Yaofeng Mao, Feiyan GongDocument7 pagesCombustion and Flame: Jun Wang, Long Zhang, Yaofeng Mao, Feiyan GongKay WhiteNo ratings yet
- BZG05C15 Datasheet Diodo RGBDocument4 pagesBZG05C15 Datasheet Diodo RGBgeraldoNo ratings yet
- MSP Drillex BOP AnularDocument21 pagesMSP Drillex BOP AnularDavid GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Air QualityDocument24 pagesAir QualityNiño Jhim AndrewNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument19 pagesAir PollutionMika Hakimie100% (1)
- Accelerated AgingDocument198 pagesAccelerated Aginganbuchelvan100% (1)
- D 4325 - 02 Standard Test Methods For Nonmetallic Semi-Conducting and Electrically Insulating Rubber TapesDocument6 pagesD 4325 - 02 Standard Test Methods For Nonmetallic Semi-Conducting and Electrically Insulating Rubber TapesPaulo Heber Alves BrandaoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Hoses, Fittings and Equipment - ParkerDocument612 pagesHydraulic Hoses, Fittings and Equipment - ParkerRastko100% (1)
- Qbank EditedDocument20 pagesQbank EditedMithun Santhosh YuvarajanNo ratings yet
- Hong Kong Apes ReviewDocument13 pagesHong Kong Apes Reviewapi-263638354No ratings yet
- 1984 WhiteheadDocument19 pages1984 WhiteheadAnita yuliyantiNo ratings yet
- And Reactivity in Chemistry and How These Are Also ManDocument354 pagesAnd Reactivity in Chemistry and How These Are Also Manluiz13eduardoNo ratings yet
- Hayanon - What Is The Ozone Hole - Nagoya University, Japan (2006)Document16 pagesHayanon - What Is The Ozone Hole - Nagoya University, Japan (2006)hanif ahmadNo ratings yet
- ACE Salt Water Sanitizing SystemDocument16 pagesACE Salt Water Sanitizing SystemMichele Borselli0% (1)
- The Impacts of Air Pollution On GladstoneDocument20 pagesThe Impacts of Air Pollution On Gladstoneapi-300392659No ratings yet
- National Senior Certificate: Grade 12Document21 pagesNational Senior Certificate: Grade 12MfanafuthiNo ratings yet
- S 2 Why We Should Protect Our EnvironmentDocument9 pagesS 2 Why We Should Protect Our Environmentfadhli76No ratings yet
- Libelium IoTDocument84 pagesLibelium IoTverticalphoebusNo ratings yet
- Decomposition of Ozone in Water in The Presence of Organic Solutes Acting As Promoters and Imhibitors of Radical Chain ReactionsDocument8 pagesDecomposition of Ozone in Water in The Presence of Organic Solutes Acting As Promoters and Imhibitors of Radical Chain ReactionsSoukunNo ratings yet
- Water PurificationDocument317 pagesWater Purificationdocasadaku5651100% (1)
- Fenton Process Coupledto Ultrasoundand UVDocument9 pagesFenton Process Coupledto Ultrasoundand UVArpit MehtaNo ratings yet
- KCET 2024 Chemistry Paper With AnswerDocument9 pagesKCET 2024 Chemistry Paper With Answerthejasmath2005No ratings yet
- 4.2 (180 Marks) : MarkschemeDocument67 pages4.2 (180 Marks) : MarkschemeSemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- de Thi HSG Tinh Binh Phuoc 2023Document10 pagesde Thi HSG Tinh Binh Phuoc 2023Nguyễn Trần Hà AnhNo ratings yet
- Oxygen and OxidesDocument87 pagesOxygen and OxidesFatema Khatun100% (1)
- SM MP C2030 C2050 2530 2550 FSM DI-C1 Final PDFDocument832 pagesSM MP C2030 C2050 2530 2550 FSM DI-C1 Final PDFДмитрий РазуваевNo ratings yet
- APC Notes 2Document84 pagesAPC Notes 2srisuji14No ratings yet