Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture-15 Barotropic, Baroclinic Atmosphere - BSGIS - Morning - Section-A
Lecture-15 Barotropic, Baroclinic Atmosphere - BSGIS - Morning - Section-A
Uploaded by
adnan salikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture-15 Barotropic, Baroclinic Atmosphere - BSGIS - Morning - Section-A
Lecture-15 Barotropic, Baroclinic Atmosphere - BSGIS - Morning - Section-A
Uploaded by
adnan salikCopyright:
Available Formats
Barotropic, Baroclinic Atmosphere
Barotropic Atmosphere
• Barotropic Atmosphere: One in which density is a
function only of pressure
( p)
Significance:
1) Isobaric and constant density surfaces are the same
2) Isobaric surfaces are also isothermal (Ideal Gas Law)
3) Thus, no temperature gradient = no change in geostrophic wind
with height
Baroclinicity
• Baroclinic Atmosphere – Density is a function of
pressure and temperature
( p, T )
• Thermal wind equation applies, geostrophic wind
can have vertical shear
• Temperature gradients imply frontal systems
• Mid-latitudes are baroclinic
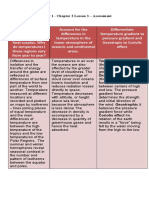
4. Baroclinic vs. Barotropic
Barotropic Baroclinic
=(p) only =(p,T)
Implications: Implications:
1) isobaric and isothermal surfaces 1) isobaric and isothermal surfaces
coincide intersect
2) no vertical wind shear 2) vertical wind shear
(thermal wind = 0) (thermal wind ≠ 0)
3) no tilt of pressure systems with height 3) pressure systems tilt with height
Seasons: Atmosphere is most baroclinic in winter.
Atmosphere is least baroclinic in summer.
Geographic: Atmosphere is most baroclinic in midlatitudes
Atmosphere is least baroclinic in the Tropics
You might also like
- Pertemuan_07 Dynamics 2 (1)Document21 pagesPertemuan_07 Dynamics 2 (1)Niken SyuaibNo ratings yet
- Global Atmosphere/Ocean/Ice Circulation I: Atmospheric Pressure and WindsDocument22 pagesGlobal Atmosphere/Ocean/Ice Circulation I: Atmospheric Pressure and WindsArun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Thermal WindsDocument16 pagesThermal Windsamanamu436No ratings yet
- Class5 2022Document16 pagesClass5 2022Ashish v PhilipNo ratings yet
- Temperature, Pressure and WindsDocument22 pagesTemperature, Pressure and WindssinanggipNo ratings yet
- Tananyag Fejlesztés Idegen Nyelven: Prevention of The AtmosphereDocument39 pagesTananyag Fejlesztés Idegen Nyelven: Prevention of The AtmospheremoxlindeNo ratings yet
- AtmosphereDocument93 pagesAtmosphereJohn Carlo Abala100% (1)
- Climatic Factor For Design of BuildingDocument66 pagesClimatic Factor For Design of Buildingarchitectneha614No ratings yet
- Climatology 1Document11 pagesClimatology 1Ritu RaniNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Models: Pave PilićDocument7 pagesAtmospheric Models: Pave Pilićtrstenik994No ratings yet
- L6 Air PressureDocument34 pagesL6 Air PressureVasuNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Part1Document15 pagesChapter1 Part1Richard TooheyNo ratings yet
- Presented By:: Anshereena Mae Arines Patricia Estrada Nica Malantic Kenneth ParasDocument20 pagesPresented By:: Anshereena Mae Arines Patricia Estrada Nica Malantic Kenneth ParasSh3eNa..No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Climate and Human ComfortDocument60 pagesUnit 1 - Climate and Human ComfortVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Concept of AgrometeorologyDocument43 pagesConcept of Agrometeorologybabloo08No ratings yet
- Atmospheric Circulation: F.6 GeographyDocument44 pagesAtmospheric Circulation: F.6 Geographyglorfindel123456No ratings yet
- UD 2 The Atmosphere 1º ESODocument10 pagesUD 2 The Atmosphere 1º ESONoelia Francisco PastorNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Density & TempDocument31 pagesPressure, Density & TempShariya Abu NomanNo ratings yet
- Part 5-1 - Meteorological Base of Atmospheric PollutionDocument8 pagesPart 5-1 - Meteorological Base of Atmospheric PollutionkontaintoNo ratings yet
- Physical Chapter 3 Lesson 3-ActivityDocument1 pagePhysical Chapter 3 Lesson 3-ActivityMaria Cristina ImportanteNo ratings yet
- Physical Chapter 3 Lesson 3-ActivityDocument1 pagePhysical Chapter 3 Lesson 3-ActivityMaria Cristina ImportanteNo ratings yet
- Onset Monsoon: Tuan B.MDocument21 pagesOnset Monsoon: Tuan B.MBùi Minh TuânNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate Students CopyDocument60 pagesWeather and Climate Students CopyRai PepitoNo ratings yet
- Climate: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument2 pagesClimate: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterNo ratings yet
- Air, Atmospheric Pressure and WindsDocument42 pagesAir, Atmospheric Pressure and WindsVishnu Prasad100% (1)
- Atmosphere Solar Energy and ClimateDocument14 pagesAtmosphere Solar Energy and ClimateRoy MapingereNo ratings yet
- Air Mass (Astronomy) : Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument15 pagesAir Mass (Astronomy) : Jump To Navigationjump To SearchSrynnENo ratings yet
- ED7837 Chapter7Document30 pagesED7837 Chapter7anthonyNo ratings yet
- Intro To Aero 1-2 AtmoshereDocument39 pagesIntro To Aero 1-2 Atmosherezohaibali30No ratings yet
- Climatology: Unit 1 - Climate and Human ComfortDocument60 pagesClimatology: Unit 1 - Climate and Human ComfortShyam Narayanan100% (1)
- AttachmentDocument16 pagesAttachmentRodrigo Uriona TerrazasNo ratings yet
- 3 Climate Full Notes - 1to5unitsDocument105 pages3 Climate Full Notes - 1to5unitsVinoth Kumar100% (1)
- ClimatologyDocument6 pagesClimatologyEyeVanNo ratings yet
- The Atmosphere: Composition and StructureDocument31 pagesThe Atmosphere: Composition and StructureDoods GaldoNo ratings yet
- NATS 101 Atmospheric Composition and Vertical StructureDocument32 pagesNATS 101 Atmospheric Composition and Vertical StructureTshiamo MatshekaNo ratings yet
- Chaptar 2 Hydrometerology (Final) PDFDocument35 pagesChaptar 2 Hydrometerology (Final) PDFHusnain WaleedNo ratings yet
- Climatology: AtmosphereDocument21 pagesClimatology: AtmosphereRaj DeepNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere: CyanobacteriaDocument11 pagesAtmosphere: CyanobacteriaNaser MahmudNo ratings yet
- 1.1.introduction To MeteorologyDocument52 pages1.1.introduction To Meteorologycrissa penaflorNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Unit 4Document22 pagesVocabulary Unit 4bego docencia100% (1)
- Lec 1 Int Atm PhysDocument45 pagesLec 1 Int Atm Physzahra raieNo ratings yet
- Environmental Chemistry: Atmosphere Atmospheric StructureDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry: Atmosphere Atmospheric StructureDc CheungNo ratings yet
- The Koppen's Climattic Classification System: December 2022Document9 pagesThe Koppen's Climattic Classification System: December 2022SwagatikaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Geography 1290Document14 pagesUnit 2 Geography 1290jaimal dhillonNo ratings yet
- E Climateresponsive Design I+II SummaryDocument40 pagesE Climateresponsive Design I+II Summarygandhi.sagar.234No ratings yet
- 3 Climate Full Notes - 1to5unitsDocument105 pages3 Climate Full Notes - 1to5unitsvibiloceym2000No ratings yet
- Interaksi Atmosfer LautanDocument55 pagesInteraksi Atmosfer Lautansyafrei adi iskandarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Coursework - For Group BDocument11 pagesChemistry Coursework - For Group Bwilson chandigaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of The WindDocument21 pagesThe Nature of The WindIjaz FazilNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities 2 MODULEDocument84 pagesEngineering Utilities 2 MODULEJoaneNo ratings yet
- AtmósferaDocument20 pagesAtmósferaPatrick CastleNo ratings yet
- Meteorology by Coleman and LawDocument7 pagesMeteorology by Coleman and LawAliah MosqueraNo ratings yet
- Climatology: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument11 pagesClimatology: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchLali HajzeriNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Atmos.Document7 pagesReviewer Atmos.JeahNo ratings yet
- Latitudnal Heat BalanceDocument2 pagesLatitudnal Heat BalanceNova ChronoNo ratings yet
- (BONUS) Session 1-2 Atmosphere (28 Days To MET)Document36 pages(BONUS) Session 1-2 Atmosphere (28 Days To MET)Priyadharshini sRNo ratings yet
- Air MassDocument13 pagesAir MassAnand raj Raja BabuNo ratings yet
- TNPSC Geography Study Material in English by GovtDocument105 pagesTNPSC Geography Study Material in English by GovtPriyanka KNo ratings yet
- New Chapter-3Document38 pagesNew Chapter-3hever7lru83No ratings yet