Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Logarithms: © Department of Analytical Skills
Logarithms: © Department of Analytical Skills
Uploaded by
Sweety PrasadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Logarithms: © Department of Analytical Skills
Logarithms: © Department of Analytical Skills
Uploaded by
Sweety PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
LOGARITHMS
© Department of Analytical Skills
Content
1) Introduction
i.Properties of logarithms
2) Problems
i.Problems using properties
ii.Application (Finding number of digits of a number)
3) Solved problems
4)Practice problems
© Department of Analytical Skills
1) Introduction
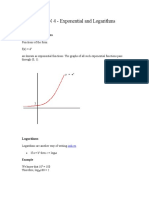
What is log?
Subtraction is the inverse operation to addition.
Ex: e + x = N ; x=N–e
Division is the inverse operation to multiplication
Ex: ex = N ; x = N/e
Likewise
Logarithm is the inverse operation to exponentiation.
Ex: ex = N : x = loge N
© Department of Analytical Skills
1.i) Properties of Logarithms:
Property LHS RHS
Addition property loga (xy) loga x + loga y
Subtraction property loga (x/y) loga x - loga y
Multiplication property loga (xn) n (loga x)
Inverse property loga x 1 / logx a
Application of multiplication loga^n (x) 1/n (loga x)
and inverse
Division property loga x logb x / logb a
Application of division logx x 1
property
a^0 = 1 property loga 1 0
Note: If no base value is mentioned in log, then it is
logarithms to the base 10 which are known as common
logarithms.
© Department of Analytical Skills
2.i) Problems using properties
Example: Simplify log9√3243
log9√3243 = log√243243
= log243^1/2243
= 1/½ log243243
= 2
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example 1. The value of log2 16 is:
A.1/8
B.4
C.8
D.16
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example: If log 27 = 1.431, then the value of log 9 is:
log 27 = 1.431
log 3^3 = 1.431
3 log 3 = 1.431
log 3 = 1.431/3
log 9 = log 3^2
= 2 log 3
= 2 (1.431/3)
= 0.954
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example 2. log √8 / log 8 is equal to:
A.1/8
B.1/4
C.1/2
D.8
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example: Simplify log 13 5+3log133-3log133-3log1315+2log1365
log 135+3log133-3log133-3log1315+2log1365
= log 135+log133^3-log133^3-log1315^3+log1365^2
= log 13 ( 5* 3^3 * 65^2 / 3^3 * 15^3)
= log 13 ( 5* 65^2 / 15^3)
= log 13 ( 5* 13^2 / 3^3)
= log 13 ( 169 / 27)
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example 3. 2log 7 – log 81 + log 189 – log 343
a)0
b) log 21
c) log 7
d) –log 3
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example: If log10 7 = a, then log10 (1/70) is equal to:
log10 (1/70) = log10 1 - log10 70
= log10 1 - log10 7 - log10 10
=0-a- 1
= - (a+1)
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example 4. If log10 2 = 0.3010, then log2 10 is equal to:
A.699/301
B.1000/301
C.0.3010
D.0.6990
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example: find x, if (log 6561)/(log 243) = log 32 x+2
(log 6561)/(log 243) = log 32 x+2
(log 3^8)/(log 3^5) = log 32 x+2
(8log 3)/(5log 3) = log 32 x+2
8/5 = log 32 x+2
32^8/5 = x+2
(2^5)^8/5 =x+2
2^8 =x+2
2^8 – 2 =x
x = 254
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example 5. Solve the following for x:
log 729 / log 81 = log x
a)100
b) √1000
c) 1000
d) 10
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example: If logx (9/16) = - 1/2 , then x is equal to:
A.- 3 4 B. 3 4 C. 81 256 D. 256 81
logx (9/16) = - 1/2
9/16 = x^(-1/2)
x = (9/16)^-2
= (16/9)^2
= 256/81
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example 6. If logx16 = 0.8, then find x
a)2
b) 4
c) 16
d) 32
© Department of Analytical Skills
2.ii) Application (Finding the number of digits
of a number)
Example: If log 3 = 0.4771, the number of digits in 324 is:
log 324 = 24 log 3
= 24 (0.4771)
log 324 = 11.45
324 = 1011.45
= 12 digits
(or)
Number of digits in 324 = characteristics+ 1 Characteristics is
= 11 + 1 the part
= 12 digits before decimal point
© Department of Analytical Skills
Example 7. If log 2 = 0.30103, the number of digits in 264
is:
A.18
B.19
C.20
D.21
© Department of Analytical Skills
3) Solved examples
© Department of Analytical skills
1. Find the value of x: log3(log2(log2(log5x))) = 0
Solution:
log3(log2(log2(log5x))) = 0
log2(log2(log5x)) = 3^0
log2(log2(log5x)) =1
(log2(log5x)) = 2^1
log2(log5x) =2
log5x = 2^2
log5x =4
x = 5^4
= 625
© Department of Analytical Skills
2. If log 2 = 0.3010 and log 3 = 0.4771, the value of log5 512 is:
Solution:
log5 512 = log5 2^9
= 9 log5 2
= 9 log 2 / log 5
= 9 log 2 / log (10/2)
= 9 log 2 / log 10 – log 2
= 9 log 2 / 1 – log 2
= 9 0.301/1-0.301
= 9 0.301/0.699
= 3.87
© Department of Analytical Skills
4) Practice problems
© Department of Analytical skills
1. If ax = by, then:
A.log a/b = x/y
B.log a/log b = x/y
C.log a/ log b = y/x
D.None of these
© Department of Analytical Skills
2. Simplify log3125525 + log125(25)60
a) 85
b) 145
c) 45
d) 145/4
© Department of Analytical Skills
3. Simplify log √32(1/1024)
a) 1
b) -1
c) -1/4
d) -4
© Department of Analytical Skills
4. Simplify log 7 + 3 log 2 – log 14 – log 4
a) 0
b) log 14
c) 2 log 56
d) 1
© Department of Analytical Skills
5. If log7(x-7) + log7(x^2+7x+49) =4
a)196
b) 7
c) 49
d) 14
© Department of Analytical Skills
You might also like
- 4 - Basic Maths and Error Analysis - 501552Document1 page4 - Basic Maths and Error Analysis - 501552shouryanarayan15No ratings yet
- Logarithm DPP For Class 11Document3 pagesLogarithm DPP For Class 11jhonanand80% (15)
- Index and LogDocument15 pagesIndex and LogSuresh Rao AppannahNo ratings yet
- Mhf4ub Unit 1 Lesson 02Document0 pagesMhf4ub Unit 1 Lesson 02Joseph ChoiNo ratings yet
- C3 Trigonometry D - QuestionsDocument2 pagesC3 Trigonometry D - QuestionsBenny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Logarithms ProblemsDocument9 pagesLogarithms Problemsluv_rustagi100% (1)
- Module 2Document9 pagesModule 2Uday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- M Log X: LogarithmDocument6 pagesM Log X: LogarithmAKASH JOEL DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Modul 5 Indices LogarithmsDocument14 pagesModul 5 Indices Logarithmsysheng98No ratings yet
- LogsDocument31 pagesLogssukriti dhimanNo ratings yet
- Logar I ThemDocument3 pagesLogar I Themjayonline_4uNo ratings yet
- MATHS 'A' LEVEL BOOK (Repaired) PDFDocument389 pagesMATHS 'A' LEVEL BOOK (Repaired) PDFMukwaya FelixNo ratings yet
- Logarithm WorksheetDocument3 pagesLogarithm WorksheetProfessor LassondeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - LogarithmsDocument5 pagesLesson 4 - LogarithmsAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Maths Ws 07Document10 pagesClass 9 Maths Ws 07mahisa agniNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 5 Indices&LogarithmsDocument12 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 5 Indices&LogarithmsManisha Sekaran Muniandy80% (5)
- Laws of Logarithms - SHSDocument5 pagesLaws of Logarithms - SHSPam G.No ratings yet
- Numerical Skills Exercise Topic 5: Indices & LogarithmDocument7 pagesNumerical Skills Exercise Topic 5: Indices & LogarithmLai Zhen WeiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes AlgebraDocument20 pagesLecture Notes Algebraagyabengmoses513No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Logarithmic and ExponentialDocument8 pagesTopic 2 - Logarithmic and Exponentialapi-258876060% (1)
- SAT ACT LogarithmsDocument7 pagesSAT ACT LogarithmsYb Andik Adi CahyonoNo ratings yet
- 01 Brahmastra LogarithmDocument7 pages01 Brahmastra LogarithmArnav SinghalNo ratings yet
- Test Mark Scheme - Logs and Exponents (2012) v2Document5 pagesTest Mark Scheme - Logs and Exponents (2012) v2makunjapNo ratings yet
- Faculty Workload GuidelinesDocument1 pageFaculty Workload GuidelinesAdNo ratings yet
- Ex 2.1-2.2 LogDocument3 pagesEx 2.1-2.2 Logapi-25887606100% (1)
- Exercise Chapter 5Document29 pagesExercise Chapter 5Samuel Sim Shien ShuangNo ratings yet
- Calculus Ii - Transcendental Function1.1Document21 pagesCalculus Ii - Transcendental Function1.1Feri AhsanNo ratings yet
- 16 LogDocument20 pages16 LogATIF ABDUL RAHEEMNo ratings yet
- Indeces PDFDocument12 pagesIndeces PDFzaedmohd100% (1)
- Indices LogDocument25 pagesIndices Logadeskitoku100% (1)
- Logarithm WorksheetDocument3 pagesLogarithm WorksheetquastardNo ratings yet
- Exponentials and Logarithms: MathematicsDocument16 pagesExponentials and Logarithms: MathematicsMahima AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Indices & LogarithmsDocument14 pagesChapter 5 - Indices & LogarithmsLai Weng KintNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument10 pagesMathsNeelamNo ratings yet
- Logarithms PDFDocument60 pagesLogarithms PDFsatyajitadrija100% (1)
- Listade Logaritmosv 2022Document5 pagesListade Logaritmosv 2022LauraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Indices & Logarithms: 1.1 Exponent 1.2 Logarithms 1.3 Exponent & Logarithms EquationDocument22 pagesChapter 1: Indices & Logarithms: 1.1 Exponent 1.2 Logarithms 1.3 Exponent & Logarithms EquationNur Suraya Shaarin100% (1)
- Logarithm PDFDocument5 pagesLogarithm PDFxxlaynamarie163No ratings yet
- Logarithms Worksheet Class 11Document1 pageLogarithms Worksheet Class 11devanshy949No ratings yet
- Rules of Logarithm: B BorDocument6 pagesRules of Logarithm: B Borkaziba stephenNo ratings yet
- Log Prashant SirDocument194 pagesLog Prashant SirHimanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- Logarithms: PrerequisitesDocument21 pagesLogarithms: PrerequisitesPrithviraj NetkeNo ratings yet
- Logrithan Gcse QuestionDocument7 pagesLogrithan Gcse QuestionAnonymous 1ONqWsq79No ratings yet
- Quantitative AbilityDocument20 pagesQuantitative AbilityAkash JinturkarNo ratings yet
- ) (Log Log: 2 Log 1 Log 3 Log Log 4 Log 2 LogDocument4 pages) (Log Log: 2 Log 1 Log 3 Log Log 4 Log 2 LogHéctor F BonillaNo ratings yet
- Logarithms: Learning Outcome: at The End of This Topic, Student Should Be Able ToDocument24 pagesLogarithms: Learning Outcome: at The End of This Topic, Student Should Be Able ToHelloNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Lecture Notes: 6.1 An Introduction To LogarithmsDocument19 pagesModule 6 Lecture Notes: 6.1 An Introduction To LogarithmsAlain LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29Document9 pagesChapter 29narasimhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Practice Problems: Logarithm: AnswersDocument2 pagesChapter Practice Problems: Logarithm: AnswersVedant PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Logaritma (P3)Document1 pageLogaritma (P3)DONI NUR HIDAYATNo ratings yet
- LogaritmiDocument36 pagesLogaritmiDinkaPajicNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Definition and Description of Finite Automata: Lecture #1Document83 pagesDefinition and Description of Finite Automata: Lecture #1Sweety PrasadNo ratings yet
- Conversion of CFG To PDA Conversion of PDA To CFGDocument22 pagesConversion of CFG To PDA Conversion of PDA To CFGSweety PrasadNo ratings yet
- Pea300 Basic MathematicsDocument8 pagesPea300 Basic MathematicsSweety PrasadNo ratings yet
- Notes 210227 102112 BecDocument20 pagesNotes 210227 102112 BecSweety PrasadNo ratings yet
- Aph881 L1Document19 pagesAph881 L1Sweety PrasadNo ratings yet
- Shirshasana: © LPU:: APH881 - YOGA AND WELLNESS: Amrinder KaurDocument17 pagesShirshasana: © LPU:: APH881 - YOGA AND WELLNESS: Amrinder KaurSweety PrasadNo ratings yet
- Basic 'Select' Exercises: Mysql Task 3Document4 pagesBasic 'Select' Exercises: Mysql Task 3Sweety PrasadNo ratings yet
- Sol 1Document4 pagesSol 1fofo100% (1)
- MCQ TEST IX ch-1Document2 pagesMCQ TEST IX ch-1puneet mangla50% (2)
- Modular Forms LARRY ROLEN.Document4 pagesModular Forms LARRY ROLEN.pedroagv08No ratings yet
- Set No: 2 R10Document6 pagesSet No: 2 R10Viswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- A4P-Inverse Trig FunctionsDocument3 pagesA4P-Inverse Trig FunctionsDEVIKA HARIHARAN100% (1)
- KubnaDocument5 pagesKubnawejnrooneyNo ratings yet
- CHP 2+3 Formula by Youth AcademyDocument2 pagesCHP 2+3 Formula by Youth Academybhattianas233No ratings yet
- Standard IntegrationDocument7 pagesStandard IntegrationChainarong TaepanichNo ratings yet
- Formulario de Derivadas - Lopez Michelini - MejoradoDocument3 pagesFormulario de Derivadas - Lopez Michelini - MejoradoJakori Huancas CoronelNo ratings yet
- XI Maths DPP (01) - Sets, Relations - Functions + Basic MathsDocument14 pagesXI Maths DPP (01) - Sets, Relations - Functions + Basic MathsvishnuNo ratings yet
- Differentiation Question FinalDocument19 pagesDifferentiation Question FinalAnubhav vaishNo ratings yet
- 5.3 The Unit Circle CAST RuleDocument5 pages5.3 The Unit Circle CAST RuleashleighNo ratings yet
- Exponential Integral Table PDFDocument2 pagesExponential Integral Table PDFTerry50% (2)
- Week5Lecture2 PDFDocument17 pagesWeek5Lecture2 PDFjayroldparcedeNo ratings yet
- AAMS1613 Chapter 1 NumberDocument12 pagesAAMS1613 Chapter 1 Number木木聪No ratings yet
- Math 9 Learning Plan ADocument10 pagesMath 9 Learning Plan AAquino UdtogNo ratings yet
- WQD10103 Chapter 1 LectureDocument19 pagesWQD10103 Chapter 1 LectureKedai KasutNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsDocument13 pagesLesson 7 - Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsEd Vill0% (1)
- Unit 1 - Convergence and DivergenceDocument20 pagesUnit 1 - Convergence and DivergenceDane SinclairNo ratings yet
- Control SystemDocument45 pagesControl SystemKelvin KongNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY 1 - Limit and ContuinityDocument48 pagesMATHEMATICS FOR ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY 1 - Limit and Contuinitysyaz lianaNo ratings yet
- Hyperbolic Angle Sum Formula: U U U UDocument3 pagesHyperbolic Angle Sum Formula: U U U UDavesh RaiNo ratings yet
- A Table of Laplace TransformsDocument1 pageA Table of Laplace TransformsEugene MartinNo ratings yet
- Midterm Complex AnalysisDocument16 pagesMidterm Complex AnalysisjhjoannaNo ratings yet
- M.SC - Mathematics Sem-I PDFDocument7 pagesM.SC - Mathematics Sem-I PDFWORLD OF FunNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry (Exercise For Cintya)Document6 pagesTrigonometry (Exercise For Cintya)ybandik adicahyonoNo ratings yet
- Series PDFDocument159 pagesSeries PDFtomdavis777No ratings yet
- L2s - Ratios For Angles Greater Than 90Document5 pagesL2s - Ratios For Angles Greater Than 90YoviNo ratings yet
- Integration Structured Exam Questions Part IDocument268 pagesIntegration Structured Exam Questions Part INur ShazzyNo ratings yet