Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsVisual and Vestibulocochlear Organs
Visual and Vestibulocochlear Organs
Uploaded by
Полина БауэрThe eyeball contains three layers - the outer fibrous tunic, middle vascular tunic, and inner retina. It also contains aqueous humor, vitreous body, and lens. The eyeball is surrounded by accessory organs like eyelids, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus, extraocular muscles, and connective tissue. The ear is divided into external, middle, and inner parts. The middle ear contains the tympanic cavity with ossicles, auditory tube, and mastoid cells. The inner ear's bony labyrinth contains cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals, while its membranous labyrinth contains cochlear duct, utricle, s
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Ent MCQDocument36 pagesEnt MCQDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Sheiko Universal Appropriate ProgramDocument12 pagesSheiko Universal Appropriate ProgramVukasinIgicNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument48 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanNaisy Magalona100% (2)
- Start Here Horizontal Pull Vertical Push Core Vertical Pull Handstand Horizontal Push Warm-UpDocument31 pagesStart Here Horizontal Pull Vertical Push Core Vertical Pull Handstand Horizontal Push Warm-Upfatima tu zahra100% (10)
- Eye and Ear HistologyDocument96 pagesEye and Ear HistologyErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (1)
- 21 Neural Control N Coordination-NCERT Questions N AnswersDocument6 pages21 Neural Control N Coordination-NCERT Questions N AnswersGuru SrinivaasNo ratings yet
- Ana 2 LecDocument32 pagesAna 2 LectuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahDocument36 pagesAnatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahRida ShahNo ratings yet
- Special Sense: Dr. Hanan EltumiDocument40 pagesSpecial Sense: Dr. Hanan EltumipraptaradikaltaNo ratings yet
- Less Sense OrgansDocument57 pagesLess Sense Organssambase420No ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument27 pagesAnatomy of EarKhush BakhtNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Structure of Eye and Ear OKDocument29 pagesMicroscopic Structure of Eye and Ear OKAn TonNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 2Document235 pagesOphthalmology 2yididiyagirma30No ratings yet
- Part 13 - Human Sensory Organs AnatomyDocument21 pagesPart 13 - Human Sensory Organs AnatomyAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Ear Lec-1-2Document41 pagesEar Lec-1-2adelremon24No ratings yet
- Snse Organs Ear EarDocument13 pagesSnse Organs Ear Earnitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- Ophtha - Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2007Document57 pagesOphtha - Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2007api-3856051100% (2)
- Histology Lecture. Histological Structure of URTDocument41 pagesHistology Lecture. Histological Structure of URTSounds of MindNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Unit IV For StdsDocument52 pagesSpecial Senses Unit IV For StdsanwarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EyeDocument13 pagesAnatomy of The EyeJerome GeronimoNo ratings yet
- 210 Chap 16Document25 pages210 Chap 16Sudip DevadasNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan THTDocument9 pagesPemeriksaan THTAtikah MuhamadNo ratings yet
- H.N P.gland, Scalp, Fossa, Tongue 3Document73 pagesH.N P.gland, Scalp, Fossa, Tongue 3cynthiabrinkley236No ratings yet
- ورق مذاكره PDFDocument100 pagesورق مذاكره PDFsalamred100% (1)
- ORGAN OF VISION. Clinical Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture by M. Bezugly MD, PH.D.)Document9 pagesORGAN OF VISION. Clinical Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture by M. Bezugly MD, PH.D.)Azra AzmunaNo ratings yet
- Orbital AnatomyDocument45 pagesOrbital AnatomyDevdutta NayakNo ratings yet
- Special Senses NotesDocument6 pagesSpecial Senses NotesajdNo ratings yet
- 2012 EarDocument7 pages2012 EarDinar Riny NvNo ratings yet
- Ana 2 LecDocument32 pagesAna 2 LecmalathiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Najah: Baghdad Medical CollegeDocument13 pagesDr. Najah: Baghdad Medical CollegeMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument18 pagesAnatomyالعراقي العراقيNo ratings yet
- 2-Inner Ear AnatomyDocument14 pages2-Inner Ear AnatomyM.IBRAHIM ALHAMECHNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument15 pagesAnatomyالعراقي العراقيNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 11Document40 pagesOphthalmology 11MAMA LALANo ratings yet
- Orbital and Ocular Anatomy: Abdulrahman Al-Muammar, MD, FRCSC King Saud UniversityDocument45 pagesOrbital and Ocular Anatomy: Abdulrahman Al-Muammar, MD, FRCSC King Saud UniversityAriyanie NurtaniaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Ear Histology 45Document48 pages3.3 Ear Histology 45Namomsa W.No ratings yet
- Anatomy EarDocument20 pagesAnatomy EarRod HilalNo ratings yet
- EAR General OrganizationDocument30 pagesEAR General OrganizationAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Ug Anatomy Dr.p.natarajanDocument234 pagesUg Anatomy Dr.p.natarajanDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Iner EarDocument51 pagesIner Earahmned A DOCTORNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial NervesDocument137 pagesAnatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial Nervesalhader libraryNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument53 pagesSpecial SensesPIOZRNo ratings yet
- Inner Ear PresentationDocument61 pagesInner Ear PresentationKarishma MishraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3, Presentations For The Final Exam MergedDocument165 pagesAnatomy 3, Presentations For The Final Exam Mergedemir krlpNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of External EyeDocument39 pagesAnatomy of External EyeUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- 25 10uhygtfcDocument91 pages25 10uhygtfcfdla rhmahNo ratings yet
- 1 AnatomyDocument58 pages1 AnatomyBemnet NuruNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Vestibular Organ and NeuralDocument56 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Vestibular Organ and NeuralVineet Chadha0% (1)
- OrbitDocument24 pagesOrbitsaifNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaDocument62 pagesAnatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaIin Widya Sari SiregarNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ Ear Eye and Skin NoteDocument29 pagesSense Organ Ear Eye and Skin NoteAnkit SubediNo ratings yet
- Ear AnatomyDocument25 pagesEar Anatomymohamed nadaaraNo ratings yet
- List The Neighboring Anatomical Regions and Structures Related To Each Wall of The OrbitDocument9 pagesList The Neighboring Anatomical Regions and Structures Related To Each Wall of The Orbitkep1313No ratings yet
- The Special Senses: Chapter ObjectivesDocument31 pagesThe Special Senses: Chapter ObjectivesSarmila Sathiya SeelanNo ratings yet
- 2019 Dr. Sahillah Anatomi Dan Fisiologi MataDocument29 pages2019 Dr. Sahillah Anatomi Dan Fisiologi MataWahyu FajarNo ratings yet
- Special Senses: Abu Ahmed 2021Document36 pagesSpecial Senses: Abu Ahmed 2021Khalid AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The EYEDocument50 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The EYEapi-19916399No ratings yet
- 2.eyes HistologyDocument23 pages2.eyes Histologyqty9jgkpnzNo ratings yet
- Suprachoroidal Space InterventionsFrom EverandSuprachoroidal Space InterventionsShohista SaidkasimovaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Cleft Lip or PalateDocument15 pagesClassification of Cleft Lip or Palatecempapi100% (1)
- Sa Node Action PotentialDocument2 pagesSa Node Action PotentialAljon AniesNo ratings yet
- 8-Open and Close Kinetic Chain ExercisesDocument24 pages8-Open and Close Kinetic Chain ExercisesMetin HakkanNo ratings yet
- Master Muscle ListDocument7 pagesMaster Muscle ListSyed AbudaheerNo ratings yet
- SGD Physiology Endocrine and MetabolismDocument7 pagesSGD Physiology Endocrine and MetabolismTinesh RajahNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)Document60 pagesNervous System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)DiazNo ratings yet
- Lab 22 The Eye VisionDocument12 pagesLab 22 The Eye Visionrhycelayon304100% (1)
- The Hard Gainer BodybuildingDocument30 pagesThe Hard Gainer Bodybuildingapi-3701884100% (3)
- R.jogi Basic Opthalmology PDFDocument512 pagesR.jogi Basic Opthalmology PDFLuhurulAmriNo ratings yet
- Neurodevelopmental Disabilities Among Children in India: An Inclen StudyDocument6 pagesNeurodevelopmental Disabilities Among Children in India: An Inclen Studyshruti kumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ST1Document2 pagesAnatomy ST1m_kudariNo ratings yet
- Tonsil EditDocument29 pagesTonsil EditDwi Utari PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 16 Easy Exercises To Burn Belly Fat FastDocument15 pages16 Easy Exercises To Burn Belly Fat FastTolu100% (1)
- Voice Disorder 2011 PDFDocument6 pagesVoice Disorder 2011 PDFfaidgustisyarifNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and ManagementDocument48 pagesSubarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and Managementesene1100% (1)
- Squat Mechanics Yp June 1951Document5 pagesSquat Mechanics Yp June 1951ʜзʀᴄᴜʟᴇѕNo ratings yet
- BL 8Document1 pageBL 8ray72roNo ratings yet
- How To Interpret Thyroid Function TestsDocument5 pagesHow To Interpret Thyroid Function TestsnonieshzNo ratings yet
- COT Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCOT Circulatory SystemMaria Monica BautistaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PDF People PDFDocument12 pagesUnit 1 PDF People PDFCosmic LatteNo ratings yet
- OSCE - Cranial Nerve ExaminationDocument2 pagesOSCE - Cranial Nerve ExaminationA.C.No ratings yet
- Figure FaultsDocument17 pagesFigure FaultsMichael SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Vestibular Neuritis Affects Both Superior and Inferior Vestibular NervesDocument10 pagesVestibular Neuritis Affects Both Superior and Inferior Vestibular NervesSabina BădilăNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - CirculatorySystem12052022Document1 pageKami Export - CirculatorySystem12052022Nyla ScottNo ratings yet
- (ANAT) P.05 Muscles of MasticationDocument3 pages(ANAT) P.05 Muscles of MasticationArthur NerickNo ratings yet
- AdvancedProtocol 012014Document1 pageAdvancedProtocol 012014martinpacenza32No ratings yet
- Breast Self ExamDocument40 pagesBreast Self ExamHoneylet Villanueva100% (1)
Visual and Vestibulocochlear Organs
Visual and Vestibulocochlear Organs
Uploaded by
Полина Бауэр0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views86 pagesThe eyeball contains three layers - the outer fibrous tunic, middle vascular tunic, and inner retina. It also contains aqueous humor, vitreous body, and lens. The eyeball is surrounded by accessory organs like eyelids, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus, extraocular muscles, and connective tissue. The ear is divided into external, middle, and inner parts. The middle ear contains the tympanic cavity with ossicles, auditory tube, and mastoid cells. The inner ear's bony labyrinth contains cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals, while its membranous labyrinth contains cochlear duct, utricle, s
Original Description:
Original Title
Visual and Vestibulocochlear organs
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe eyeball contains three layers - the outer fibrous tunic, middle vascular tunic, and inner retina. It also contains aqueous humor, vitreous body, and lens. The eyeball is surrounded by accessory organs like eyelids, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus, extraocular muscles, and connective tissue. The ear is divided into external, middle, and inner parts. The middle ear contains the tympanic cavity with ossicles, auditory tube, and mastoid cells. The inner ear's bony labyrinth contains cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals, while its membranous labyrinth contains cochlear duct, utricle, s
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views86 pagesVisual and Vestibulocochlear Organs
Visual and Vestibulocochlear Organs
Uploaded by
Полина БауэрThe eyeball contains three layers - the outer fibrous tunic, middle vascular tunic, and inner retina. It also contains aqueous humor, vitreous body, and lens. The eyeball is surrounded by accessory organs like eyelids, conjunctiva, lacrimal apparatus, extraocular muscles, and connective tissue. The ear is divided into external, middle, and inner parts. The middle ear contains the tympanic cavity with ossicles, auditory tube, and mastoid cells. The inner ear's bony labyrinth contains cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals, while its membranous labyrinth contains cochlear duct, utricle, s
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 86
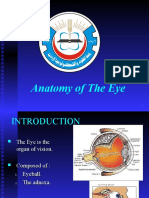
The sensory organs
The visual organ
consists of eyeball and accessory organs of eye.
The structure of eyeball
The eyeball comprises the wall of the
eyeball and the contents enclosed by it .
The Wall of Eyeball
It consists of three tunics(layers), from
outside inwards , which are the fibrous
tunic , the vascular tunic and retina .
1 The fibrous tunic(outer supporting layer)
consists of the sclera behind and the cornea in
front.
1) The sclera
a. features: posterior five-sixths of the outer
layer . strong , white and opaque
b. scleral venous sinus (Schlemm’ canal)
2) The cornea
a. features: anterior one-sixth of the outer layer.
transparent and non-vascular, but rich nerve
terminals
2. The vascular tunic
consists of the iris, the ciliary body and the
choroid
1) The iris
a. location and shape
b. pupil
c. sphincter and dilator pupillae
d. iridocorneal angle
e. colour : brown , dark , blue .depends upon the
number and placement of pigment cells
(melanocytes)
2) The ciliary body
a.location and shape
b.ciliary ring and ciliary processes
c.ciliary muscle
d.ciliary zonule(suspensory ligament)
e.function: produce aqueous humor
3) The choroid
a.location and shape : posterior two thirds
of choroid
b. features : numerous blood vessels and
pigment cells
3. The inner tunic (the retina)
1) Division: the optic part, ciliary part and iridial
part
2)Construction: two layers →outer pigmented
layer and inner neuroretina(photoreceptors:
rod and cone cells)
3) Optic disc (blind spot)
4) Macula lutea : fovea centralis→vision is
sharpest
The contents of the eyeball
include the aqueous humor, the vitreous
body and the lens .With the cornea
altogether to form the refractive media.
l. The chambers of the eye : between the
cornea and the lens; and divided into the
anterior and the posterior chambers by the
iris .It is filled with aqueous humor.
2. The aqueous humor : produced by the
capillaries of the ciliary processes. It is
colourless, transparent and watery fluid.
3. The lens
1) Location : lies between the iris and the
vitreous body.
2) Features: transparent and elastic, biconvex
body lacking vessels and nerves
3 ) Structures: outer cortex and inner
nucleus
4. The vitreous body
colourless, transparent and jelly-like
substance . It fills the space between the
lens and the retina (the vitreous chamber)
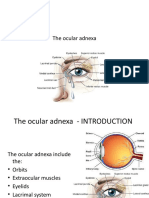
The accessory organs of eye
The accessory organs of the eye includes
the eyelid, the conjunctiva, the lacrimal
apparatus, the extraocular muscles and the
fasciae.
一 The eyelids (or palpebrae)
include the upper and lower eyelids
1Structures:Palpebral fissure, lacrimal papilla
and punctum
2 Layers: skin, subcutaneous areolar tissue,
orbicularis oculi, tarsus, and conjunctiva.
The conjunctiva
Division: bulbar conjunctiva , palpebral
conjunctiva and conjunctival fornix
The Lacrimal Apparatus
consists of the lacrimal gland and tbe
lacrimal passages
1 The lacrimal gland : lies in the lacrimal fossa
of the orbit
2 The lacrimal passages
1) The lacrimal punctum
2) The lacrimal ductule (canaliculus)
3) The lacrimal sac
4) The nasolacrimal duct
The extraocular muscles
1 The four rectus muscles
the medial and lateral rectuses, the superior
and posterior rectuses
2 The two oblique muscles
the superior obliquus (superior oblique m. )
and the inferior obliguus (inferior oblique
m. )
3 The levator palpebrae superioris
The connective tissue in the Orbit
1 The adipose body of orbit
2 The sheath of eyeball(the capsule of Tenon)
3 The episcleral space
The blood vessels of eye
The arteries of eye
supplied by the ophthalmic artery
1 The central artery of retina: superior and
inferior nasal retinal arteries, superior and
inferior temporal retinal arteries
2 The short posterior ciliary arteries: supply the
choroid coat and ciliary process
3 The long posterior ciliary arteries: supply the
iris
The veins of eye
1 The ophthalmic veins :the superior and the
inferior ophthalmic v.
2 The central vein of retina
The vestibulocochlear organ
The vestibulocochlear organ is divided into
three parts: the external, middle and
internal ears.
Section one the external ear
The external ear consists of
the auricle,
external acoustic meatus, and
tympanic membrane
1 The auricle
2 The external acoustic meatus
extends from the externa1 acoustic pore to the
tympanic membrane
1) Two parts: lateral part : the cartilaginous part (
one-third )
medial part : the bony part (two-thirds )
2) Direction: passes medially, its lateral part runs
forwards and upwards, and then backwards
and the medial part runs forwards and
downwards
3 The tympanic membrane
oval in form, thin and semi-transparent
1) Two parts: tense part (lower three fourths of
tympanic membrane) and flaccid part(upper
one fourth )
2) The umbo
3) Cone of light: lie anteroinferior to the tense
part of umbo
The middle ear
The middle ear lies between the external
and inner ears, and includes three parts:
the tympanic cavity, the auditory tube and
the mastoid cells.
1 The tympanic cavity
l) The walls of the tympanic cavity →six walls:
a. The tegmental wall (superior wall)
b. The jugular wall (inferior wall)
c. The carotid wall (anterior wall)
d. The mastoid wall (posterior wall)
e. The membranous wall (lateral wall)
f. The labyrinthine wall (medial wall)
2) The auditory ossicles
a.three ossicles: the malleus, incus and stapes
b. The muscles of the tympanic cavity :the
tensor tympani and the stapedius
2 The auditory tube (Eustachian tube)
the channel through which the tympanic
cavity communicates with the
nasopharynx.
3 The mastoid cells
spaces in the mastoid process of the
temporal bone
The internal ear
The internal (inner) ear lies in the petrous
part of the temporal bone and consists of
two parts:
the bony labyrinth and
the membranous labyrinth.
The bony labyrinth
three parts :
the cochlea ,
the vestibule and
the semicircular canals.
1 The cochlea:
looks like the shell of a snail and composed
of the bony canal
2 The vestibule: the central part of the bony
labyrinth. On its lateral wall, there are two
openings: the fenestra vestibuli and the
fenestra cochleae . On the posterior wall of the
vestibule there are the five openings of the
semicircular canals. On its anterior wall a
large opening communicates with the scala
vestibuli.
3 The semicircular canals
three in number, anterior (superior),
posterior and lateral semicircular canal
The membranous labyrinth
from before
backwards,
includes: the
cochlear duct,
the utricle and
saccule, and
the
membranous
semicircular
ducts.
1 The cochlear duct
a.Section of the cochlea:
shows three channels:
the scala tympani,
scala vestibuli and
the cochlear duct
b.the cochlear duct(transverse section)
three walls :
superior wall→the vestibular membrane
lateral wall→the thickend endosteum
inferior wall→ the basilar membrane(spiral
membrane) and the outer part of the lamina
of modiolus
The spiral organ on the basilar membrane
2 The utricle and saccule
The maculae are the organs of static balance.
3 The semicircular ducts
The ampullary crests are the organs of kinetic
balance.
The conduction of
sound
You might also like
- Ent MCQDocument36 pagesEnt MCQDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Sheiko Universal Appropriate ProgramDocument12 pagesSheiko Universal Appropriate ProgramVukasinIgicNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument48 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanNaisy Magalona100% (2)
- Start Here Horizontal Pull Vertical Push Core Vertical Pull Handstand Horizontal Push Warm-UpDocument31 pagesStart Here Horizontal Pull Vertical Push Core Vertical Pull Handstand Horizontal Push Warm-Upfatima tu zahra100% (10)
- Eye and Ear HistologyDocument96 pagesEye and Ear HistologyErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (1)
- 21 Neural Control N Coordination-NCERT Questions N AnswersDocument6 pages21 Neural Control N Coordination-NCERT Questions N AnswersGuru SrinivaasNo ratings yet
- Ana 2 LecDocument32 pagesAna 2 LectuhinsinghNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahDocument36 pagesAnatomy of Eye: By: Dr. Lubna ShahRida ShahNo ratings yet
- Special Sense: Dr. Hanan EltumiDocument40 pagesSpecial Sense: Dr. Hanan EltumipraptaradikaltaNo ratings yet
- Less Sense OrgansDocument57 pagesLess Sense Organssambase420No ratings yet
- Anatomy of EarDocument27 pagesAnatomy of EarKhush BakhtNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Structure of Eye and Ear OKDocument29 pagesMicroscopic Structure of Eye and Ear OKAn TonNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 2Document235 pagesOphthalmology 2yididiyagirma30No ratings yet
- Part 13 - Human Sensory Organs AnatomyDocument21 pagesPart 13 - Human Sensory Organs AnatomyAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet
- Ear Lec-1-2Document41 pagesEar Lec-1-2adelremon24No ratings yet
- Snse Organs Ear EarDocument13 pagesSnse Organs Ear Earnitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- Ophtha - Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2007Document57 pagesOphtha - Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye 2007api-3856051100% (2)
- Histology Lecture. Histological Structure of URTDocument41 pagesHistology Lecture. Histological Structure of URTSounds of MindNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Unit IV For StdsDocument52 pagesSpecial Senses Unit IV For StdsanwarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The EyeDocument13 pagesAnatomy of The EyeJerome GeronimoNo ratings yet
- 210 Chap 16Document25 pages210 Chap 16Sudip DevadasNo ratings yet
- Pemeriksaan THTDocument9 pagesPemeriksaan THTAtikah MuhamadNo ratings yet
- H.N P.gland, Scalp, Fossa, Tongue 3Document73 pagesH.N P.gland, Scalp, Fossa, Tongue 3cynthiabrinkley236No ratings yet
- ورق مذاكره PDFDocument100 pagesورق مذاكره PDFsalamred100% (1)
- ORGAN OF VISION. Clinical Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture by M. Bezugly MD, PH.D.)Document9 pagesORGAN OF VISION. Clinical Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture by M. Bezugly MD, PH.D.)Azra AzmunaNo ratings yet
- Orbital AnatomyDocument45 pagesOrbital AnatomyDevdutta NayakNo ratings yet
- Special Senses NotesDocument6 pagesSpecial Senses NotesajdNo ratings yet
- 2012 EarDocument7 pages2012 EarDinar Riny NvNo ratings yet
- Ana 2 LecDocument32 pagesAna 2 LecmalathiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Najah: Baghdad Medical CollegeDocument13 pagesDr. Najah: Baghdad Medical CollegeMariam QaisNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument18 pagesAnatomyالعراقي العراقيNo ratings yet
- 2-Inner Ear AnatomyDocument14 pages2-Inner Ear AnatomyM.IBRAHIM ALHAMECHNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument15 pagesAnatomyالعراقي العراقيNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology 11Document40 pagesOphthalmology 11MAMA LALANo ratings yet
- Orbital and Ocular Anatomy: Abdulrahman Al-Muammar, MD, FRCSC King Saud UniversityDocument45 pagesOrbital and Ocular Anatomy: Abdulrahman Al-Muammar, MD, FRCSC King Saud UniversityAriyanie NurtaniaNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Ear Histology 45Document48 pages3.3 Ear Histology 45Namomsa W.No ratings yet
- Anatomy EarDocument20 pagesAnatomy EarRod HilalNo ratings yet
- EAR General OrganizationDocument30 pagesEAR General OrganizationAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Ug Anatomy Dr.p.natarajanDocument234 pagesUg Anatomy Dr.p.natarajanDr.P.NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Iner EarDocument51 pagesIner Earahmned A DOCTORNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial NervesDocument137 pagesAnatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial Nervesalhader libraryNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument53 pagesSpecial SensesPIOZRNo ratings yet
- Inner Ear PresentationDocument61 pagesInner Ear PresentationKarishma MishraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 3, Presentations For The Final Exam MergedDocument165 pagesAnatomy 3, Presentations For The Final Exam Mergedemir krlpNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of External EyeDocument39 pagesAnatomy of External EyeUzma KhanNo ratings yet
- 25 10uhygtfcDocument91 pages25 10uhygtfcfdla rhmahNo ratings yet
- 1 AnatomyDocument58 pages1 AnatomyBemnet NuruNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Vestibular Organ and NeuralDocument56 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Vestibular Organ and NeuralVineet Chadha0% (1)
- OrbitDocument24 pagesOrbitsaifNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaDocument62 pagesAnatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaIin Widya Sari SiregarNo ratings yet
- Sense Organ Ear Eye and Skin NoteDocument29 pagesSense Organ Ear Eye and Skin NoteAnkit SubediNo ratings yet
- Ear AnatomyDocument25 pagesEar Anatomymohamed nadaaraNo ratings yet
- List The Neighboring Anatomical Regions and Structures Related To Each Wall of The OrbitDocument9 pagesList The Neighboring Anatomical Regions and Structures Related To Each Wall of The Orbitkep1313No ratings yet
- The Special Senses: Chapter ObjectivesDocument31 pagesThe Special Senses: Chapter ObjectivesSarmila Sathiya SeelanNo ratings yet
- 2019 Dr. Sahillah Anatomi Dan Fisiologi MataDocument29 pages2019 Dr. Sahillah Anatomi Dan Fisiologi MataWahyu FajarNo ratings yet
- Special Senses: Abu Ahmed 2021Document36 pagesSpecial Senses: Abu Ahmed 2021Khalid AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The EYEDocument50 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The EYEapi-19916399No ratings yet
- 2.eyes HistologyDocument23 pages2.eyes Histologyqty9jgkpnzNo ratings yet
- Suprachoroidal Space InterventionsFrom EverandSuprachoroidal Space InterventionsShohista SaidkasimovaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Cleft Lip or PalateDocument15 pagesClassification of Cleft Lip or Palatecempapi100% (1)
- Sa Node Action PotentialDocument2 pagesSa Node Action PotentialAljon AniesNo ratings yet
- 8-Open and Close Kinetic Chain ExercisesDocument24 pages8-Open and Close Kinetic Chain ExercisesMetin HakkanNo ratings yet
- Master Muscle ListDocument7 pagesMaster Muscle ListSyed AbudaheerNo ratings yet
- SGD Physiology Endocrine and MetabolismDocument7 pagesSGD Physiology Endocrine and MetabolismTinesh RajahNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)Document60 pagesNervous System (2015 - 06 - 09 22 - 21 - 55 Utc)DiazNo ratings yet
- Lab 22 The Eye VisionDocument12 pagesLab 22 The Eye Visionrhycelayon304100% (1)
- The Hard Gainer BodybuildingDocument30 pagesThe Hard Gainer Bodybuildingapi-3701884100% (3)
- R.jogi Basic Opthalmology PDFDocument512 pagesR.jogi Basic Opthalmology PDFLuhurulAmriNo ratings yet
- Neurodevelopmental Disabilities Among Children in India: An Inclen StudyDocument6 pagesNeurodevelopmental Disabilities Among Children in India: An Inclen Studyshruti kumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ST1Document2 pagesAnatomy ST1m_kudariNo ratings yet
- Tonsil EditDocument29 pagesTonsil EditDwi Utari PratiwiNo ratings yet
- 16 Easy Exercises To Burn Belly Fat FastDocument15 pages16 Easy Exercises To Burn Belly Fat FastTolu100% (1)
- Voice Disorder 2011 PDFDocument6 pagesVoice Disorder 2011 PDFfaidgustisyarifNo ratings yet
- Subarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and ManagementDocument48 pagesSubarachnoid Haemorrhage:Pathology, Clinical Features and Managementesene1100% (1)
- Squat Mechanics Yp June 1951Document5 pagesSquat Mechanics Yp June 1951ʜзʀᴄᴜʟᴇѕNo ratings yet
- BL 8Document1 pageBL 8ray72roNo ratings yet
- How To Interpret Thyroid Function TestsDocument5 pagesHow To Interpret Thyroid Function TestsnonieshzNo ratings yet
- COT Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCOT Circulatory SystemMaria Monica BautistaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 PDF People PDFDocument12 pagesUnit 1 PDF People PDFCosmic LatteNo ratings yet
- OSCE - Cranial Nerve ExaminationDocument2 pagesOSCE - Cranial Nerve ExaminationA.C.No ratings yet
- Figure FaultsDocument17 pagesFigure FaultsMichael SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Vestibular Neuritis Affects Both Superior and Inferior Vestibular NervesDocument10 pagesVestibular Neuritis Affects Both Superior and Inferior Vestibular NervesSabina BădilăNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - CirculatorySystem12052022Document1 pageKami Export - CirculatorySystem12052022Nyla ScottNo ratings yet
- (ANAT) P.05 Muscles of MasticationDocument3 pages(ANAT) P.05 Muscles of MasticationArthur NerickNo ratings yet
- AdvancedProtocol 012014Document1 pageAdvancedProtocol 012014martinpacenza32No ratings yet
- Breast Self ExamDocument40 pagesBreast Self ExamHoneylet Villanueva100% (1)