Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 12
Chapter 12
Uploaded by
Hannah Buquiron0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views24 pagesOriginal Title
Chapter 12 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views24 pagesChapter 12
Chapter 12
Uploaded by
Hannah BuquironCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 24
Chapter 12:
Antiprotozoal Agents
Copyright © 2013 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Causes of Protozoal Infections
Insect Bites
o Malaria
o Trypanosomiasis
o Leishmaniasis
Ingestion or Contact with the Causal Organism
o Amebiasis
o Giardiasis
o Trichomoniasis
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Protozoal Parasites Identified as Causes
of Malaria
Plasmodium falciparum
o Considered the most dangerous type of protozoan
Plasmodium vivax
o Milder form of the disease; seldom results in death
Plasmodium malariae
o Endemic in tropical countries; mild symptoms
Plasmodium ovale
o Rarely seen; in the process of being eradicated
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Malaria
Signs and Symptoms
o Related to the destruction of red blood cells and
toxicity to the liver
Treatment
o Aims at attacking the parasite at the various stages
of its development inside and outside the human
body
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
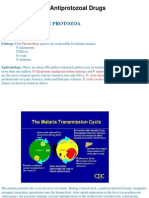
Life Cycle of Plasmodium
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Use of Antiprotozoal Therapy Across the
Life Span
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Antimalarials #1
Chloroquine (Aralen)
o Prevention and treatment of plasmodial malaria;
treatment of extraintestinal amebiasis
Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil)
o Treatment of plasmodial malaria in combination with
other drugs (particularly primaquin)
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Antimalarials #2
Mefloquine (Lariam)
o Prevention and treatment of plasmodial malaria in
combination with other drugs
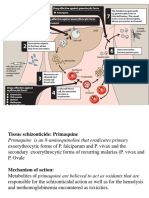
Primaquine (generic)
o Prevention of relapses of Plasmodium vivax and
Plasmodium malariae infections; radical cure of
P. vivax malaria
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Antimalarials #3
Pyrimethamine (Daraprim)
o Prevention of plasmodial malaria in combination with
other agents to suppress transmission; treatment of
toxoplasmosis
Quinine (generic)
o Treatment of chloroquine-resistant plasmodial
infections
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Antimalarials #4
Indications- Prevent the acute malarial reaction in
individuals who have been infected by the parasite, or
work against tissue schizonts as prophylactic or
antirelapse agents
Actions- Enters human red blood cells and changes the
metabolic pathways necessary for the reproduction of the
Plasmodium
Pharmacokinetics- Readily absorbed from the GI tract,
concentrated in the liver, spleen, kidney, and brain and is
excreted very slowly in the urine
Contraindications- Known allergy, liver disease,
alcoholism, pregnancy and lactation
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Antimalarials #5
Adverse effects- CNS, GI, hepatic dysfunction and
dermatological
Drug-to-drug interactions- Patient who is receiving
combinations of quinine derivative and quinine is at
increased risk for toxicity and convulsions
o Prototype - Quinine (generic)
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Nursing Considerations for
Antimalarial Agents
Assess:
o History of allergy to any of the antimalarials
o Physical status
o Ophthalmic and retinal examinations and auditory
screening
o Liver function, including liver function tests
o Blood culture to identify the causative, Inspect the
skin closely for color, temperature, texture, and
evidence of lesions
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Question #1
Please answer the following statements as true or false.
Chlorquine (Aralen) is an antimalarial drug used in the
treatment of plasmodial malaria. It is typically used in
combination with other drugs.
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Answer to Question #1
True
Rationale: (Aralen): Treatment of plasmodial malaria;
used in combination with other drugs
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Risk Factors for Protozoal Infections
Unsanitary Conditions
Poor Hygienic Practices
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Other Protozoal Infections
Amebiasis
Leishmaniasis
Trypanosomiasis
Trichomoniasis
Giardiasis
Pneumocystic carinii
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Common Other Antiprotozoal Agents
Atovaquone (Mepron)
o Especially active against PCP
Metronidazole (Flagyl, MetroGel, Noritate)
o Treats amebiasis, trichomoniasis, and giardiasis
Pentamidine (Pentam 300, NebuPent)
o Treats PCP, trypanosomiasis, and leishmaniasis
Tinidazole (Tindamax)
o Treats trichomoniasis, giardiasis, and amebiasis
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Other Antiprotozoal Drugs
Actions- Inhibit DNA synthesis in susceptible protozoa
Pharmokokinetics- Readily absorbed and highly protein
bound in circulation or metabolized in the liver and
excreted in the urine and feces
Contraindications- Known allergy, pregnancy, CNS
disease, hepatic disease
Adverse Reactions- Headache, dizziness, ataxia,
nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
Drug-to-drug interaction- Alcohol, anticoagulants,
disulfiram
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Nursing Considerations for Antiprotozoal
Agents
Assess:
o History of allergy to any of the antiprotozoals
o Perform a physical assessment
o CNS to check reflexes and muscle strength, skin and
mucous membranes to check for lesions, color,
temperature, and texture
o Evaluate liver function, including liver function tests
o Obtain cultures
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Prototype Antiprotozoal Agent
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Question #2
When are antiprotozoal medications contraindicated?
A. Renal disease
B. Anemia
C. CNS disease
D. Cardiovascular disease
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Answer to Question #2
C. CNS disease
Rationale: Contraindications are known allergy,
pregnancy, CNS disease, hepatic disease.
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Question #3
When are antimalarial medications contraindicated ?
A. Renal disease
B. Anemia
C. Alcoholism
D. Cardiovascular disease
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
Answer to Question #3
C. Alcoholism
Rationale: Because of the need for hepatic metabolism to
prevent toxicity
Copyright © 2017 Wolters Kluwer • All Rights Reserved
You might also like
- Community Health Nursing Exam 2Document7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 2Hannah Buquiron100% (1)
- Chapter 13 AntihilminticDocument20 pagesChapter 13 AntihilminticAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Anti InflammDocument36 pagesChapter 16 Anti InflammAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document23 pagesChapter 11Hannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 AntineoplasticDocument37 pagesChapter 14 AntineoplasticAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal AgentsDocument4 pagesAntiprotozoal AgentsReem NurNo ratings yet
- AntibioticsDocument84 pagesAntibioticsNandini GulurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09 AntibioticsDocument77 pagesChapter 09 AntibioticsAngela Joy AmparadoNo ratings yet
- Trichomoniasis: T. Vaginalis Is A Parasitic Protozoan, and The Taxonomic Position Is Based On The ClassificationDocument15 pagesTrichomoniasis: T. Vaginalis Is A Parasitic Protozoan, and The Taxonomic Position Is Based On The Classificationrave robNo ratings yet
- CORTEZ LoaloaDocument12 pagesCORTEZ LoaloaLouisa Marie Miranda100% (1)
- Levanthan Short Ans KeyDocument42 pagesLevanthan Short Ans Keyxyab.varga.swuNo ratings yet
- Blood Tissue and FlagellatesDocument15 pagesBlood Tissue and FlagellatesHughNo ratings yet
- HI Classmates!!!Document36 pagesHI Classmates!!!Alex SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Myiasis and Strike: Dr. Thahsin Farjana Associate Professor Dept. of Parasitology BAUDocument33 pagesMyiasis and Strike: Dr. Thahsin Farjana Associate Professor Dept. of Parasitology BAUChuramoni Saha100% (1)
- Arthropod-Borne Viruses Part OneDocument80 pagesArthropod-Borne Viruses Part Onetummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- TrematodesDocument56 pagesTrematodesrmukbelNo ratings yet
- AnthraxDocument20 pagesAnthraxanemenyeeNo ratings yet
- Marine Parasite EcologyDocument22 pagesMarine Parasite EcologyNura Omar AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Economic Importances of NematodesDocument5 pagesEconomic Importances of Nematodesyayeg raja100% (1)
- Chikungunya WDocument11 pagesChikungunya Wapi-378136896100% (1)
- Malaria FalciparumDocument35 pagesMalaria FalciparumAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- Phylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) : Important InformationDocument26 pagesPhylum Platyhelminthes (Flatworms) : Important InformationYoussef EmadNo ratings yet
- Provido Atlas in NematodesDocument33 pagesProvido Atlas in NematodesCatherine Kaye ProvidoNo ratings yet
- Filariasis 140310130022 Phpapp02Document18 pagesFilariasis 140310130022 Phpapp02알파No ratings yet
- Abortions in Dairy Cows PDFDocument4 pagesAbortions in Dairy Cows PDFransinghNo ratings yet
- Intro+Clini+Blood Film Malaria Balsam 2Document66 pagesIntro+Clini+Blood Film Malaria Balsam 2DaxNo ratings yet
- Illustrated Manual of Infectious Diseases of Livestock in AfghanistanDocument245 pagesIllustrated Manual of Infectious Diseases of Livestock in Afghanistanqadir-qadis100% (2)
- Q Fever ReviewsDocument13 pagesQ Fever ReviewspaswordnyalupaNo ratings yet
- Handouts in Communicable DiseasesDocument15 pagesHandouts in Communicable DiseasesArianne Bernardo100% (1)
- #Spirochaetes & Mycoplasma#Document28 pages#Spirochaetes & Mycoplasma#Sarah PavuNo ratings yet
- Clinically Important Pathogenic Bacteria and Their Infectious DiseasesDocument19 pagesClinically Important Pathogenic Bacteria and Their Infectious DiseasesanumNo ratings yet
- FluroquinolonesDocument29 pagesFluroquinolonestummalapalli venkateswara rao0% (1)
- LeishmaniaFilaria Part 1Document45 pagesLeishmaniaFilaria Part 1YS Nate100% (1)
- Viruses - Viroids - and PrionsDocument60 pagesViruses - Viroids - and Prionssanashar100% (1)
- Salmonellosis 2021Document36 pagesSalmonellosis 2021mehrshad Farahpour Gp5No ratings yet
- Adult ImmunizationDocument43 pagesAdult ImmunizationTris100% (2)
- TaeniasisDocument66 pagesTaeniasisM Lutfi Fanani100% (1)
- Rabies FinalDocument18 pagesRabies FinalPrem SinghNo ratings yet
- pm2 TREMATODESDocument39 pagespm2 TREMATODESshastaNo ratings yet
- Arboviruses: R.Varidianto Yudo T., Dr.,MkesDocument19 pagesArboviruses: R.Varidianto Yudo T., Dr.,MkesalbertmogNo ratings yet
- 23-Overstreet Et Al 2009-Trematoda of The GoMxDocument69 pages23-Overstreet Et Al 2009-Trematoda of The GoMxDinda Tiara Sukma50% (2)
- WK13 CDN - Meningitis, Poliomyelitis, Leprosy, Tetanus, Red TideDocument43 pagesWK13 CDN - Meningitis, Poliomyelitis, Leprosy, Tetanus, Red TidePotato PceeNo ratings yet
- Tapeworm Infections in PoultryDocument10 pagesTapeworm Infections in PoultryAmulyaVemulapadNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Helminthiasis and Filariasis - SGTDocument73 pagesIntestinal Helminthiasis and Filariasis - SGTLemathaNo ratings yet
- Trypanosoma: Sri SundariDocument37 pagesTrypanosoma: Sri SundariVaniaNo ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah, The Most Beneficent and MercifulDocument35 pagesIn The Name of Allah, The Most Beneficent and MercifulAhmedMenshawyNo ratings yet
- Rickettsia Coxiella: Prof. Khalifa Sifaw GhengheshDocument20 pagesRickettsia Coxiella: Prof. Khalifa Sifaw GhengheshKhalifa Sifaw GhengheshNo ratings yet
- Sandfly: Student Name:Ruaa Abduljabbar Hadi Grad:Second Stage Subject: Medical InsectsDocument19 pagesSandfly: Student Name:Ruaa Abduljabbar Hadi Grad:Second Stage Subject: Medical InsectsSara AlyousifNo ratings yet
- H.influenzae Modified 2012Document12 pagesH.influenzae Modified 2012MoonAIRNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument3 pagesParasitologyKCSotelo_xxviiNo ratings yet
- Host Parasite Relationship NotesDocument6 pagesHost Parasite Relationship NotesGrace ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument42 pagesRespiratory Tract InfectionsRoshana MallawaarachchiNo ratings yet
- General Veterinary MicrobiologyDocument73 pagesGeneral Veterinary MicrobiologySanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- OLFU College of Medicine Class 2015: ParasitologyDocument2 pagesOLFU College of Medicine Class 2015: Parasitologyrochelle_gNo ratings yet
- CephalosporinsDocument21 pagesCephalosporinsMoha Bin Ladiif75% (4)
- Dipylidium Caninum: Causal AgentDocument2 pagesDipylidium Caninum: Causal AgentPrincess Jovelyn GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Brucellosis: Dr.T.V.Rao MDDocument55 pagesBrucellosis: Dr.T.V.Rao MDsana shakeelNo ratings yet
- Trematodes of Wild BirdsDocument5 pagesTrematodes of Wild BirdsSunilNo ratings yet
- Disease Trasmitted From Fish To HumanDocument6 pagesDisease Trasmitted From Fish To HumanDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU Philippines100% (5)
- Introduction To Parasitology and Enterobiasis: Arnav Bhasin Roll No. - 14Document19 pagesIntroduction To Parasitology and Enterobiasis: Arnav Bhasin Roll No. - 14Arnav BhasinNo ratings yet
- The Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyFrom EverandThe Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyLawrence ChakrinNo ratings yet
- Using Antimicrobial Agents To Control Mirobial Growth in VivoDocument39 pagesUsing Antimicrobial Agents To Control Mirobial Growth in VivoHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument52 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyHannah Buquiron100% (1)
- Rregular Heartbeats. Nausea. Vomiting. Anxiety. Headache. Chills. Goosebumps. Shortness of BreathDocument4 pagesRregular Heartbeats. Nausea. Vomiting. Anxiety. Headache. Chills. Goosebumps. Shortness of BreathHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 ReviewerDocument2 pagesChapter 12 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Brand Name:: VasopressinDocument3 pagesBrand Name:: VasopressinHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Lidocaine 100 MG 5ml Syringes Brand Name - DosageDocument2 pagesLidocaine 100 MG 5ml Syringes Brand Name - DosageHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases of Skin and EarDocument56 pagesInfectious Diseases of Skin and EarHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Exam 1Document7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 1Hannah Buquiron100% (2)
- Sodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML SyringeDocument2 pagesSodium Bicarbonate 50meq/50 ML Syringe Calcium Chloride 1Gm/10 ML SyringeHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Exam 5: B. Liver CirrhosisDocument7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 5: B. Liver CirrhosisHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Exam 3Document7 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Exam 3Hannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 ReviewerDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 10 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Collecting Objective DataDocument14 pagesCollecting Objective DataHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document23 pagesChapter 11Hannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 ReviewerDocument4 pagesChapter 10 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cell Physiology Introduction To Cell PhysiologyDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Cell Physiology Introduction To Cell PhysiologyHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Validating and Documenting DataDocument14 pagesValidating and Documenting DataHannah Buquiron100% (1)
- CHAPTER 9 ReviewerDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 9 ReviewerHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Collecting Subjective DataDocument18 pagesCollecting Subjective DataHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Chem 205 Lecture 5 Nucleic AcidsDocument37 pagesChem 205 Lecture 5 Nucleic AcidsHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- Nursing SkillDocument1 pageNursing SkillHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHEM 205 LECTUREs 7 8 9 CARBOHYDRATES and Carb MetabDocument136 pagesCHEM 205 LECTUREs 7 8 9 CARBOHYDRATES and Carb MetabHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CHEM 205 LECTURE 4 Enzyme KineticsDocument47 pagesCHEM 205 LECTURE 4 Enzyme KineticsHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- CDC Malaria Hotline: (770) 488-7788 or (855) 856-4713 (Toll-Free) Monday-Friday 9am-5pm EST (770) 488-7100 After Hours, Weekends, and HolidaysDocument1 pageCDC Malaria Hotline: (770) 488-7788 or (855) 856-4713 (Toll-Free) Monday-Friday 9am-5pm EST (770) 488-7100 After Hours, Weekends, and HolidaysRaden febrian Dwi cahyoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology-Unit-III (F) AntimalarialdrugsDocument59 pagesPharmacology-Unit-III (F) Antimalarialdrugswebpixel services100% (1)
- 2 MalariaDocument79 pages2 MalariaSabyashashi SaikiaNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument61 pagesMalariaEscitalopram 5mgNo ratings yet
- Management MalariaDocument2 pagesManagement MalariaMuhammad NuansaNo ratings yet
- PSM PYP II (1) (1)-CopyDocument93 pagesPSM PYP II (1) (1)-Copyksaurabh027No ratings yet
- Anti-Protozoal Drugs FinalizedDocument54 pagesAnti-Protozoal Drugs FinalizedMoazama Fayyaz100% (1)
- IVMS Cell Biology and Pathology Flash Facts 2Document3,980 pagesIVMS Cell Biology and Pathology Flash Facts 2Marc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument74 pagesHandoutschayChay gapolNo ratings yet
- 420 062 Guideline MalariaDocument8 pages420 062 Guideline Malariazenagit123456No ratings yet
- Malaria Case PresentationDocument36 pagesMalaria Case Presentationkamal_zaidi04No ratings yet
- Clinical Pathways (Paediatric) 23 October 2019Document15 pagesClinical Pathways (Paediatric) 23 October 2019ommyleNo ratings yet
- Blood & Tissue ProtozoaDocument81 pagesBlood & Tissue ProtozoaMoses Tamba MomohNo ratings yet
- ChemotherapyDocument253 pagesChemotherapyalmskein100% (1)
- Antiprotozoal Drugs: Blood and Tissue ProtozoaDocument12 pagesAntiprotozoal Drugs: Blood and Tissue ProtozoaLuciano Rodrigues SimoesNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument45 pagesAntimalarial DrugsDeribe BekeleNo ratings yet
- Malaria Management AlgorithmDocument1 pageMalaria Management AlgorithmAdriel SebastianNo ratings yet
- Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency: G6Pd G6Pd E.G. G6Pd G6PdDocument42 pagesGlucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency: G6Pd G6Pd E.G. G6Pd G6PdAlina CodreanuNo ratings yet
- PRIMAQUINE PHOSPHATE-primaquine Phos Phate Tablet Bays Hore Pharmaceuticals, LLCDocument8 pagesPRIMAQUINE PHOSPHATE-primaquine Phos Phate Tablet Bays Hore Pharmaceuticals, LLCKulfi BarfiNo ratings yet
- Battery ExamsDocument71 pagesBattery ExamsJoana Grace CortezNo ratings yet
- Malaria Treatment Guideline 2012Document38 pagesMalaria Treatment Guideline 2012van_cristiano100% (3)
- Treatment of MalariaDocument49 pagesTreatment of MalariaShanza AmaanNo ratings yet
- Malaria: Michelle Carandang-Cuvin, M.D. FPPS, Fpidsp Pediatric Infectious Disease ConsultantDocument77 pagesMalaria: Michelle Carandang-Cuvin, M.D. FPPS, Fpidsp Pediatric Infectious Disease ConsultantHanako AranillaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Pharma 1dr Elsha3rDocument5 pagesMCQ Pharma 1dr Elsha3rsherif mamdoohNo ratings yet
- Malaria Operational Manual 2009Document275 pagesMalaria Operational Manual 2009Ram Mohan SNo ratings yet
- Malaria Prevention TimikaDocument41 pagesMalaria Prevention Timikastivana26No ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Antimalarial DrugsDocument14 pagesEffectiveness of Antimalarial DrugsMark Vertiz CernaNo ratings yet
- Alphaland Profile, 2016Document18 pagesAlphaland Profile, 2016Andres RomeroNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument14 pagesAntimalarial Drugstea jayNo ratings yet
- Malaria Case ManagementDocument48 pagesMalaria Case ManagementjamshaidjiNo ratings yet