Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrochemistry: Electrolysis
Electrochemistry: Electrolysis
Uploaded by
Alishba ahmer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views33 pagesElectrolysis is the process of using an electric current to drive nonspontaneous chemical reactions. During electrolysis, electricity breaks down ionic compounds through oxidation and reduction reactions. The document discusses electrolysis of copper(II) chloride as an example, where copper ions are reduced at the cathode, depositing a pink metal, and chloride ions are oxidized at the anode, producing chlorine gas. An electrochemical cell is formed when two different reactive metals are placed in a conductive electrolyte solution, allowing electrons to flow through an external circuit and drive a redox reaction.
Original Description:
Original Title
Electrolysis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentElectrolysis is the process of using an electric current to drive nonspontaneous chemical reactions. During electrolysis, electricity breaks down ionic compounds through oxidation and reduction reactions. The document discusses electrolysis of copper(II) chloride as an example, where copper ions are reduced at the cathode, depositing a pink metal, and chloride ions are oxidized at the anode, producing chlorine gas. An electrochemical cell is formed when two different reactive metals are placed in a conductive electrolyte solution, allowing electrons to flow through an external circuit and drive a redox reaction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views33 pagesElectrochemistry: Electrolysis
Electrochemistry: Electrolysis
Uploaded by
Alishba ahmerElectrolysis is the process of using an electric current to drive nonspontaneous chemical reactions. During electrolysis, electricity breaks down ionic compounds through oxidation and reduction reactions. The document discusses electrolysis of copper(II) chloride as an example, where copper ions are reduced at the cathode, depositing a pink metal, and chloride ions are oxidized at the anode, producing chlorine gas. An electrochemical cell is formed when two different reactive metals are placed in a conductive electrolyte solution, allowing electrons to flow through an external circuit and drive a redox reaction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 33
Electrochemistry
Electrolysis
Electricity Chemical change
Electrolysis
• Breathing down by electricity
• Breaking down of ionic compounds
Ionic compounds
• Lattice arrangement( in solid state ions are fixed at their position)
• Solid
• High M.P and B.P
• Soluble in water
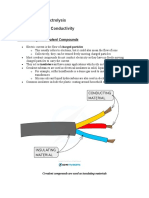
• Electrolytes ( can only conduct electricity when dissolve in water or in
molten state) due to presence of free ions.
Identity electrolytes/non
electrolytes/conductors/insulators
• Wood
• Copper(II)sulphate (s)
• Mercury
• Graphite
• Alcohol
• Plastic
• Sulfuric acid
• Sodium chloride (l)
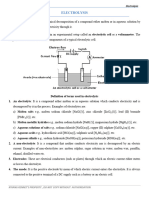
Components of electrolytic cells
Battery: to provide D.C current. It flows in one direction from
positive to negative terminal of the battery
Electrodes:: any conducting material e.g metals, graphite
Electrolyte: the ionic compound which we want to decompose.
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qqmKqpA61GI&t=11s
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qqmKqpA61GI&t=11s
Electrolysis of concentrated
copper(II)chloride
• Ions present Cu2+, Cl-, H+, OH-
• Ions discharge Cu2+, Cl-
• Reaction at cathode Cu2+ + 2e- = Cu
• Observation pink metal deposits at cathode
• Reaction at anode 2Cl- = 2e- + Cl2
• Observation yellowish green gas formed at cathode
• Test for identification of gas:
• Effect on electrolyte The blue color of electrolyte fades away
• Solution becomes dilute
An electrode becomes active when the
metal of which it is made of is dipped in
its own salt solution e.g Cu dipped in
CuSO4/CuCl2
Only anode becomes active electrode
Electroplating
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OxhCU_jBiOA electroplating
• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qqmKqpA61GI&t=11s
electrorefining
Reduction is the gain of electrons
And oxidation is the loss of electrons
Electrochemical cell
• simple electrochemical cell can be made
by dipping two different pieces of
metal (must be of different reactivity -
different potential), connected by a wire,
into a solution of ions e.g. a salt or dilute
acid which will act as an electrolyte
The more reactive metal, magnesium, dissolves in the
electrolyte and becomes Mg2+ ions, thereby producing
Sulfuric acid
electrons. As electrons are produced, the magnesium act
as negative electrode So, overall the overall redox reaction is ...
at the (–) electrode Mg(s) ==> Mg2+(aq) + 2e–(magnesium 2H+(aq) + Mg(s) ==> Mg2+(aq) + H2(g)
atoms oxidised) oxidation takes place at anode so it is
anode
The overall reaction is therefore the same as
These electrons travel to copper electrode and produce displacement reaction, and it is a redox reaction
bubbles of hydrogen gas at this electrode. As electrons are involving electron transfer and the movement of the
taken in, the copper is positive electrode. electrons through the external wire to the bulb or
at the (+) electrode 2H+(aq) + 2e– ==> H2(g) (hydrogen ions voltmeter etc. forms the working electric current.
reduced on the surface of the copper) reduction takes place
at cathode so it is cathode.
You might also like
- J. M. Haile Molecular Dynamics Simulation Elementary Methods 1992Document505 pagesJ. M. Haile Molecular Dynamics Simulation Elementary Methods 1992Anonymous HijNGQtN100% (4)
- Voltaic Cell Lab ReportDocument5 pagesVoltaic Cell Lab Reporthelia bazarganNo ratings yet
- Solution of Homework #4Document7 pagesSolution of Homework #4丁偉庭No ratings yet
- Symbols - STD 134Document32 pagesSymbols - STD 134Joaquim MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Electrochemsitry NotesDocument9 pagesElectrochemsitry NotesAhmad Shafiq ZiaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument52 pagesElectrochemistryBapu ThoratNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument23 pagesElectrolysisArhum KidwaiNo ratings yet
- Design Process in ElectrochemistryDocument92 pagesDesign Process in ElectrochemistryWulan SariNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Electrochemistry NotesDocument14 pagesIGCSE Electrochemistry Notestettehsackey100% (12)
- ElectrolysisDocument5 pagesElectrolysisbilldanit4fitzNo ratings yet
- Galvanic CellsDocument4 pagesGalvanic CellsshariziNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument33 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYr55088299No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Form 4Document14 pagesElectrochemistry Form 4Ct Sophie PheaNo ratings yet
- 20.2 Voltaic Cells: - Voltaic Cells Use To Convert Chemical Energy Into Electrical EnergyDocument18 pages20.2 Voltaic Cells: - Voltaic Cells Use To Convert Chemical Energy Into Electrical Energyaelinsmy93No ratings yet
- Electrolyte SolutionsDocument167 pagesElectrolyte Solutionszatty kimNo ratings yet
- 1 Energy SystemsDocument21 pages1 Energy Systemsadwar1807No ratings yet
- Investigatory Project ChemistryDocument17 pagesInvestigatory Project ChemistryRishav PatraNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument10 pagesElectrolysisFaithNo ratings yet
- Chap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument13 pagesChap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesMisbah Kamran0% (1)
- Chemistry Chapter 9.ABakshDocument16 pagesChemistry Chapter 9.ABakshNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Electricity and ChemistryDocument9 pagesElectricity and ChemistryFrancis EssilfieNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Lecture Notes 2018-2019Document69 pagesElectrochemistry Lecture Notes 2018-2019syed100% (1)
- أ - اندي محمد تجربه مختبرDocument9 pagesأ - اندي محمد تجربه مختبرMmm 123No ratings yet
- 12 ElectrochemistryDocument71 pages12 ElectrochemistryHunter DanielNo ratings yet
- Corrosion MergedDocument162 pagesCorrosion Mergedpraneesh reddyNo ratings yet
- Key Concept Chapter 10 ElectrolysisDocument20 pagesKey Concept Chapter 10 ElectrolysisKim KatNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument43 pagesElectrochemistryShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument152 pagesElectrochemistrypapaioasNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell OriginalDocument7 pagesElectrochemical Cell OriginalShajathi MNo ratings yet
- ECCDocument4 pagesECCSanat ChopraNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: H + F 2HFDocument41 pagesElectrochemistry: H + F 2HFtNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis PDFDocument13 pagesElectrolysis PDFShaikh Irad100% (1)
- Finding EMF of Electrochemical CellDocument4 pagesFinding EMF of Electrochemical CellVivek Singh Yadav100% (1)
- Chemistry - ElectrolysisDocument51 pagesChemistry - Electrolysisjoannavera2020No ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemical ChangeDocument20 pagesElectricity & Chemical ChangeGautam DayalNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell.Document9 pagesElectrochemical Cell.Maku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Electrochemistry and Energy Storage SystemsDocument25 pagesUnit-2 Electrochemistry and Energy Storage SystemsN x10No ratings yet
- Unit - Iii: Electrochemical Cells and CorrosionDocument25 pagesUnit - Iii: Electrochemical Cells and Corrosion320126512165 VSAICHARANGUPTANo ratings yet
- SudhanshuDocument14 pagesSudhanshusudhanshumishra8090No ratings yet
- Electrolysis 2015Document13 pagesElectrolysis 2015martinmbondjo062No ratings yet
- Introduction 1Document10 pagesIntroduction 1Boss of the worldNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument58 pagesElectrochemistryWatan SahuNo ratings yet
- s.4 Chem Notes On Electrlysis Corrected Copy.Document9 pagess.4 Chem Notes On Electrlysis Corrected Copy.Ronald RomNo ratings yet
- 7 +Electrolytic+CellsDocument17 pages7 +Electrolytic+Cellsadairyoung946No ratings yet
- Handout ElectroChemistry BY S.KDocument16 pagesHandout ElectroChemistry BY S.Katsats815No ratings yet
- El Ectrochemi Stry: H + F 2HFDocument39 pagesEl Ectrochemi Stry: H + F 2HFtNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Electrochemistry Unit IIIDocument8 pagesBasic Concept of Electrochemistry Unit IIItlata8954No ratings yet
- Chemistry - Notes Icse 10Document25 pagesChemistry - Notes Icse 10Suneet MohanNo ratings yet
- Report 2 ElectrolysisDocument19 pagesReport 2 ElectrolysisOmar SamirNo ratings yet
- The Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsDocument30 pagesThe Electrolysis of Aqueous SolutionsBayan O. Abu SaadaNo ratings yet
- 20electrochemistry Best Slides 2Document145 pages20electrochemistry Best Slides 2Muhammad Nauman KhalidNo ratings yet
- Electrode PotentialDocument24 pagesElectrode PotentialZoeNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument14 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- SS2 Note ElectrolysisDocument7 pagesSS2 Note ElectrolysisIbukun OlaitanNo ratings yet
- CH 6,7 NotesDocument18 pagesCH 6,7 NotesAishi GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Effect of An Electric Current On SubstancesDocument7 pages2.5 Effect of An Electric Current On Substancesgabrielsuva6No ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRYDocument3 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRYMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Notes 1Document3 pagesElectrochemistry Notes 1Joshika GNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument15 pagesChemistryTGC NINJANo ratings yet
- Lacture 10. ElectrochemistryDocument68 pagesLacture 10. ElectrochemistryHarish Kutty HariNo ratings yet
- Chemi G 10 Chap 3 HanoutDocument5 pagesChemi G 10 Chap 3 HanoutYISHAK ABRHAMNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Is The Study of The Relationship Between Chemical Reactions and ElectricalDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry Is The Study of The Relationship Between Chemical Reactions and ElectricalTudio GamingNo ratings yet
- Extractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesFrom EverandExtractive Metallurgy 2: Metallurgical Reaction ProcessesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Non - Rectangular Components: Prepared By: D.M.ODocument2 pagesNon - Rectangular Components: Prepared By: D.M.OCiero John MarkNo ratings yet
- Power and Distribution Transformers Catalog 2015Document17 pagesPower and Distribution Transformers Catalog 2015Pook ElvinNo ratings yet
- Daya Dan Gerakan: Force and MotionDocument21 pagesDaya Dan Gerakan: Force and MotionzinziemeewahNo ratings yet
- Aberrations Introduced in Off-Axis Testing of Spherical Surfaces - MalacaraDocument5 pagesAberrations Introduced in Off-Axis Testing of Spherical Surfaces - Malacarautente489133No ratings yet
- Circuit ElementsDocument81 pagesCircuit ElementsvidulaNo ratings yet
- Art 7series: Speaker SystemsDocument12 pagesArt 7series: Speaker SystemspalprodNo ratings yet
- BWE Brochure After ProofDocument12 pagesBWE Brochure After ProofNut AssanaiNo ratings yet
- Abaagalwa MwennaDocument2 pagesAbaagalwa Mwennasekyanzi pascalNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Surge-Transferred Overvoltages in Distribution TransformersDocument9 pagesEvaluation of Surge-Transferred Overvoltages in Distribution TransformersdankorankoNo ratings yet
- Brochure RESCONCEPT - 2019 - LowDocument8 pagesBrochure RESCONCEPT - 2019 - LowTrần Yến NhiNo ratings yet
- Oliver Heaviside Physical MathematicianDocument7 pagesOliver Heaviside Physical MathematicianAKHI9No ratings yet
- Ultradur® S 4090 G2Document4 pagesUltradur® S 4090 G2srinivasaNo ratings yet
- BG Barrier Gate User Instruction 20191104Document21 pagesBG Barrier Gate User Instruction 20191104Sigit TarioNo ratings yet
- Deliquescence, Efflorescence, and Phase Miscibility of Mixed Particles of Ammonium Sulfate and Isoprene-Derived Secondary Organic MaterialDocument17 pagesDeliquescence, Efflorescence, and Phase Miscibility of Mixed Particles of Ammonium Sulfate and Isoprene-Derived Secondary Organic MaterialFarid DelgaDoNo ratings yet
- 02 MoldedCaseCircuitBreakers LV10 042021 EN 202106011741229504Document94 pages02 MoldedCaseCircuitBreakers LV10 042021 EN 202106011741229504KajendranNo ratings yet
- Science X QP PB 2022-23 1-ADocument10 pagesScience X QP PB 2022-23 1-ADrone Max0% (1)
- STOKES DRAG Derivation PDFDocument4 pagesSTOKES DRAG Derivation PDFVadiraj HemadriNo ratings yet
- Kido DescriptionDocument7 pagesKido DescriptionAditya SamantrayNo ratings yet
- Poynting Vector E and BDocument4 pagesPoynting Vector E and BDao ZhangNo ratings yet
- Running Procedure 5Document2 pagesRunning Procedure 5Pesireron RoberthNo ratings yet
- Bolt Thread Coefficient of Friction TesterDocument48 pagesBolt Thread Coefficient of Friction TesterOwethu CibiNo ratings yet
- Maldservice ManualDocument452 pagesMaldservice ManualCarlos Alberto Ramirez GarciaNo ratings yet
- Reemplazo de IGBTs PDFDocument13 pagesReemplazo de IGBTs PDFRaul quispe quispeNo ratings yet
- Emulsion Types For Both Grade Cationic & AnionicDocument2 pagesEmulsion Types For Both Grade Cationic & AnionicSasanka SekharNo ratings yet
- Otonetics Tunics PR PRI ManualDocument41 pagesOtonetics Tunics PR PRI Manualtimothylee86No ratings yet
- Circuit Name: Sirajganj 225 MW Combined Cycle Power Plant Unit-1 (NWPGCL) Total Generation KWH by Fuel NGDocument1 pageCircuit Name: Sirajganj 225 MW Combined Cycle Power Plant Unit-1 (NWPGCL) Total Generation KWH by Fuel NGShakilNo ratings yet