Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01 - Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet
01 - Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet
Uploaded by
Luis Miguel Lancho CastilloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
01 - Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet
01 - Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet
Uploaded by
Luis Miguel Lancho CastilloCopyright:
Available Formats
Industrial Ethernet Workshop
Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet,
Protocols, Addressing
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.1
What is a network ?
Computer 2,
e.g. in Germany
Computer 1,
e.g. in the USA
Physical
characteristics
?
Protocol?
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.2
What are the Internet, Intranet and Extranet ?
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.3
The protocols used in the model
ISO/OSI model 4 layers
of the TCP/IP
7 Topic, news 7 Application layer
Application
6 Language, Application-
6 Presentation layer oriented protocols:
e.g. German layer Telnet, FTP, SMTP
5 Communication
5 Behavior
layer
4 Extension requires Transport protocols:
4 Transport layer
external line TCP, UDP
3 Connection through Internet protocols:
3 Network layer
telecom. company Transport- IP, ICMP
oriented
2 Data link layer layer
2 Analog or digital
data transmission Network access
1 through telecom. protocol:
1 Physical Ethernet, token ring
company layer
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.4
The MAC address
08 : 00 : 06 : XX : XX : XX
Vendor-specific,
e.g. Siemens
Unique ID for each
manufactured product
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.5
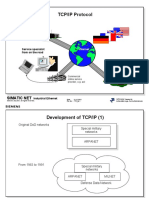
TCP / IP: What is it ?
• TCP/IP is a network protocol
• It is the foundation for many applications which must
exchange data beyond the boundaries of a single network.
• It comprises:
TCP: The transmission control protocol for secure data
transmission
IP: The Internet protocol for sending data across
network boundaries
• TCP/IP is one of many protocols used on the Internet
which is why the terms are often confused.
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.6
The IP address (1)
• A 32-bit IP address is represented by 4 decimal numbers which are
separated by a dot. e.g. 141.73.4.238
• The address is subdivided into the network ID (N) and host ID (H)
• The following network classes can be distinguished:
Class A: 1.0-127.0 about 16 million nodes/network
Class B: 128.0-191.255 about 65,000 nodes/network
Class C: 192.0-223.255.255 254 nodes/network
• Addresses must be unique across the network. InterNIC assigns
addresses for the network 'INTERNET'
• Since network addresses are hard to come by and this type of
classification does not use the address space effectively, names are
used instead (name services)
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.7
The IP address (2)
Class A: The first byte of the IP address is used for addressing
the network; the last three bytes address the network node
b31 b0
0Version
Network ID Host ID
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 00 0 0 1 0 1 1 1
100. 16. 232. 23
Class B: The first two bytes of the IP address are used for addressing
the network; the last two bytes address the network node 0
b31 b
1Version
0 Network ID Host ID
1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 00 0 0 1 0 1 1 1
180. 16. 232. 23
Class C: The first three bytes of the IP address are used for addressing
the network; the last byte addresses the network node
b31 b0
1Version
1 0 Network ID Host ID
1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 00 0 0 1 0 1 1 1
220. 16. 232. 23
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.8
Routing with TCP/IP
• To set up a WAN, LANs must be
linked with routers. They handle
142.20.10.1
the data transport at the interfaces
of the LANs.
LAN
• Routers are connected to two
142.20.10.2
networks and therefore have two
Router
IP addresses.
192.20.30.7 • Hosts and routers use routing
tables to make decisions for
LAN
sending datagrams beyond the
192.20.30.12 network.
Router
• Each host knows the router and
sends the datagram directly to the
134.218.30.7
LAN
router even if the address lies
outside the subnet.
134.218.30.16
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.9
ICMP: Very simple diagnostics with the PING function
ICMP stands for "Internet Control Message Protocol".
This protocol offers the simplest diagnostics option. By calling
the PING function on a computer, the connection to a remote
computer can be checked over IP.
The partner responds and the response time is displayed.
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.10
Example: The PING function
The physical connection to a remote station can
be checked by calling the PING function on the
programming device.
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.11
Active network components (1)
Repeater / hub (star hub) Application Application
- Refreshes and forwards the incoming Presentation Presentation
signals. Session Session
- Immediately forwards the information to all
Transport Transport
partners connected to the repeater/hub
Network Network
- No filtering, load separation or intervention in Repeater / Hub
Data Link Data Link
communication Physical Physical
Physical Physical
- The use of repeaters/hubs is restricted to a
single collision domain.
Bridge / switch
Application Application
- Connects collision domains. The maximum
Presentation Presentation
extension is only limited by the delay of the data
Session Session
packets between two nodes
Transport Transport
- Load separation: Data traffic can be spread over
different subsegments Network
Bridge / Switch
Network
- The data traffic is not interrupted if individual Data Link Data Link Data Link Data Link
stations fail. Physical Physical Physical Physical
- Parallel communication
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.12
Active network components (2)
Router Application Application
- Decouples networks on the basis of Layer 3 Presentation Presentation
Session Session
addresses (IP addresses)
Transport Router Transport
- Controls traffic between networks (routing)
Network Network Network Network
- Protocol-independent, offers routing functions
Data Link Data Link Data Link Data Link
and flow control
Physical Physical Physical Physical
Gateway Gateway
- A gateway converts services. Application Application Application Application
- Security mechanisms are possible Presentation Presentation Presentation Presentation
(firewall, proxy). Session Session Session Session
Transport Transport
- A gateway comprises hardware and software Transport Transport
Network Network Network Network
for connecting different networks whereby Data Link Data Link Data Link Data Link
all protocols can be converted Physical Physical Physical Physical
(all 7 OSI layers).
SIMATIC NET Date: 01.04.21 SITRAIN Training for
Automation and Industrial Solutions
Siemens AG, 2005. All rights reserved. File: Fundamentals of Industrial Ethernet.13
You might also like
- IMS Presentation V0.3 2008-10-28Document73 pagesIMS Presentation V0.3 2008-10-28Mohammed AnwarNo ratings yet
- Tbii TrainingDocument79 pagesTbii TrainingLuis Villarroel100% (2)
- TCP/IP Protocol: Simatic NetDocument43 pagesTCP/IP Protocol: Simatic NetEdsonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SIMATIC NET Industrial EthernetDocument56 pagesIntroduction To SIMATIC NET Industrial EthernetEdsonNo ratings yet
- CRI Reti 11 Industrial Networks RT EthernetDocument37 pagesCRI Reti 11 Industrial Networks RT EtherneterospatariniNo ratings yet
- PROFINET - The Industrial Ethernet Standard: © Siemens AG 2013. Alle Rechte VorbehaltenDocument22 pagesPROFINET - The Industrial Ethernet Standard: © Siemens AG 2013. Alle Rechte VorbehaltenKhaled Ouni100% (2)
- Reliable Industrial NetworksDocument96 pagesReliable Industrial Networkswangzhi8192No ratings yet
- The Future of TSN in Industrial NetworksDocument27 pagesThe Future of TSN in Industrial NetworksVishwa MohanNo ratings yet
- Ctrl-Eng Ethernet EssentialsDocument8 pagesCtrl-Eng Ethernet EssentialsCyrix.OneNo ratings yet
- Rockwell RfoukalDocument60 pagesRockwell RfoukalRuchirNo ratings yet
- Ethernet APL+Ethernet To The Field+en+FINAL+September 2020 1.1Document18 pagesEthernet APL+Ethernet To The Field+en+FINAL+September 2020 1.1Com DigfulNo ratings yet
- KANDH General-Catalog-V2 PDFDocument36 pagesKANDH General-Catalog-V2 PDFJorge SaNo ratings yet
- PUB00138R6 Tech Series EtherNetIPDocument8 pagesPUB00138R6 Tech Series EtherNetIPAnderson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Indusrial Ethernet: Powerlink Ou EtherCAT?Document36 pagesIndusrial Ethernet: Powerlink Ou EtherCAT?Marco Antonio100% (1)
- IP - Module1-Quo - Vadis v1.510-TOCDocument5 pagesIP - Module1-Quo - Vadis v1.510-TOCArun DubeyNo ratings yet
- Networking 61850 Belden-SEADocument62 pagesNetworking 61850 Belden-SEAErnesto A. WeiszNo ratings yet
- C172 - Network Security FoundationsDocument16 pagesC172 - Network Security FoundationsMichael ANo ratings yet
- Configuring Connections: Simatic NetDocument56 pagesConfiguring Connections: Simatic NetMazarel AurelNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Communication Protocol PDFDocument2 pagesEthernet Communication Protocol PDFDanielaNo ratings yet
- Network Overview: Simatic S7Document16 pagesNetwork Overview: Simatic S7EduardoNo ratings yet
- CT1e 02 Standardization BodiesDocument9 pagesCT1e 02 Standardization BodiesAmir ShahaniNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between Ethernet Types?Document4 pagesWhat's The Difference Between Ethernet Types?leonardo_melo_costaNo ratings yet
- The Design of Industrial Ethernet Adapter Based On Ethernet/IPDocument4 pagesThe Design of Industrial Ethernet Adapter Based On Ethernet/IPSherlock HolmesNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument64 pagesTCP IpMohamed ShabanaNo ratings yet
- RTA - EtherNet - IP and TCP - IP - Real Time Automation, IncDocument8 pagesRTA - EtherNet - IP and TCP - IP - Real Time Automation, InczeinNo ratings yet
- Netsim: Model - Predict - Validate Network Simulation/Emulation PlatformDocument12 pagesNetsim: Model - Predict - Validate Network Simulation/Emulation PlatformChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- WK6 Lecture PTC Model PDFDocument19 pagesWK6 Lecture PTC Model PDFStephen AdingoNo ratings yet
- EtherNet IP Industrial ProtocolDocument10 pagesEtherNet IP Industrial Protocolamhosny64No ratings yet
- Communication Protocols PDFDocument14 pagesCommunication Protocols PDFChethan SNo ratings yet
- ALNET II On Ethernet Tcp/Ip: Woodhead WoodheadDocument50 pagesALNET II On Ethernet Tcp/Ip: Woodhead WoodheadThiago Barroso PeixotoNo ratings yet
- AdvComNwLectureSlideTCP-IP and ApplicationDocument99 pagesAdvComNwLectureSlideTCP-IP and ApplicationTesfaye GunnersNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Ip Protocol PDFDocument2 pagesEthernet Ip Protocol PDFMichaelNo ratings yet
- Ethernet/IP: IT Infrastructure SolutionsDocument3 pagesEthernet/IP: IT Infrastructure SolutionsJOSE LUISNo ratings yet
- Types of Network/Project: Simatic NetDocument9 pagesTypes of Network/Project: Simatic NetMazarel AurelNo ratings yet
- The Design and Implementation of Network Data Link Layer Based On Embedded TCP/IP Protocol StackDocument4 pagesThe Design and Implementation of Network Data Link Layer Based On Embedded TCP/IP Protocol StackkrishnamoorthyeceNo ratings yet
- Ethernet 8051Document4 pagesEthernet 8051So Was RedNo ratings yet
- Writing Client/Server Programs in C Using Sockets (A Tutorial) Session 5958 Greg Granger Grgran at Sas SAS/C & C++ Support Institute Cary, NCDocument31 pagesWriting Client/Server Programs in C Using Sockets (A Tutorial) Session 5958 Greg Granger Grgran at Sas SAS/C & C++ Support Institute Cary, NCSudha PatelNo ratings yet
- HW FunctionalityDocument35 pagesHW FunctionalityBeto MurguiaNo ratings yet
- Protocol & Data Trasfer: Internet of ThingsDocument26 pagesProtocol & Data Trasfer: Internet of ThingsSyifa KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- IK-TIAPN 01E Communication With SIMATICDocument18 pagesIK-TIAPN 01E Communication With SIMATICenrique laicaNo ratings yet
- Extension: Introduction To The Internet ProtocolDocument6 pagesExtension: Introduction To The Internet ProtocolAnGel MEndozaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - 4) TCPIP Basis ISSUE1.00Document29 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - 4) TCPIP Basis ISSUE1.00Randy DookheranNo ratings yet
- E-Mail Support Maintenance Functions Via The Web Remote Operation Via The WebDocument21 pagesE-Mail Support Maintenance Functions Via The Web Remote Operation Via The WebEngenheiro AmoedoNo ratings yet
- AZ120 Industrial Network ProtocolsDocument34 pagesAZ120 Industrial Network ProtocolsBahaa bunniNo ratings yet
- IMS Basic Concepts and Network Structure-20091029-A-1.0Document106 pagesIMS Basic Concepts and Network Structure-20091029-A-1.0Ahmed Gad100% (1)
- SICAM A8000 CP-8050: Hardware Based Application Layer FirewallDocument2 pagesSICAM A8000 CP-8050: Hardware Based Application Layer FirewallDenis100% (1)
- HuaweiDocument120 pagesHuaweiMini KaurNo ratings yet
- Ethernet: Introduction To NetworksDocument62 pagesEthernet: Introduction To NetworksAdie Madi AsmadiNo ratings yet
- Ethernet Protocol PDFDocument2 pagesEthernet Protocol PDFBrittany0% (1)
- L2 - INP-Ethernet-Based Industrial Protocols 2Document30 pagesL2 - INP-Ethernet-Based Industrial Protocols 2nounkhayNo ratings yet
- ITN InstructorPPT Chapter 5 CiscoDocument67 pagesITN InstructorPPT Chapter 5 Ciscohendrian15No ratings yet
- System and Network Administration Network EssentialsDocument45 pagesSystem and Network Administration Network EssentialsArsalan JahaniNo ratings yet
- ITN InstructorPPT Chapter5Document67 pagesITN InstructorPPT Chapter5JeremySumilhigNo ratings yet
- IoT - Module 4Document18 pagesIoT - Module 4bhargaviNo ratings yet
- A Case Study: Innovations in TDM/ATM To IP ArchitectureDocument12 pagesA Case Study: Innovations in TDM/ATM To IP ArchitectureEdwin IromaNo ratings yet
- Siemens Simatic TIA Portal v18.0 Free Download - FileCRDocument4 pagesSiemens Simatic TIA Portal v18.0 Free Download - FileCRManuel Antonio CostaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4.1: Tcp/Ip and UrlDocument7 pagesChapter - 4.1: Tcp/Ip and UrlNandgulabDeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Certification Exam Objectives: N10-005: Domain % of ExaminationDocument23 pagesCertification Exam Objectives: N10-005: Domain % of Examinationdyake04No ratings yet
- FINS Omron On TCP/IP: Headquarters SubsidiariesDocument11 pagesFINS Omron On TCP/IP: Headquarters SubsidiariesDaniel Sapiain CaroNo ratings yet
- Building Automation: Communication systems with EIB/KNX, LON and BACnetFrom EverandBuilding Automation: Communication systems with EIB/KNX, LON and BACnetNo ratings yet
- Manual FB45 PDFDocument168 pagesManual FB45 PDFLuis Miguel Lancho CastilloNo ratings yet
- Manual ASM456 PDFDocument60 pagesManual ASM456 PDFLuis Miguel Lancho CastilloNo ratings yet
- Manual ASM456 PDFDocument60 pagesManual ASM456 PDFLuis Miguel Lancho CastilloNo ratings yet
- BT200 V2 eDocument31 pagesBT200 V2 eFernando DallaquaNo ratings yet
- DCDIAGDocument6 pagesDCDIAGAmardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Ntag213 215 216Document60 pagesNtag213 215 216edgardoboieroNo ratings yet
- Types of Internet Connections - Internet BasicsDocument3 pagesTypes of Internet Connections - Internet Basicsskr channelNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument4 pagesDatasheet PDFruffles1986No ratings yet
- Cisco Catalyst 4500-X Series Fixed 10 Gigabit Ethernet Aggregation Switch Data SheetDocument12 pagesCisco Catalyst 4500-X Series Fixed 10 Gigabit Ethernet Aggregation Switch Data SheetJoannaNo ratings yet
- L Use Only - Do Not Share: Junos Layer 3 VpnsDocument294 pagesL Use Only - Do Not Share: Junos Layer 3 VpnsNikolay IvanovNo ratings yet
- PM5560 PM5563 PublicFirmwareRevisionHistory v2.1.0 PDFDocument3 pagesPM5560 PM5563 PublicFirmwareRevisionHistory v2.1.0 PDFfelipeasmullerNo ratings yet
- Cisco Touch 10 Room Control Button HelpDocument4 pagesCisco Touch 10 Room Control Button Helpmmousa12501No ratings yet
- Trabajo Definición de Términos Par TrenzadoDocument3 pagesTrabajo Definición de Términos Par TrenzadoAndrei Dumitru ApostolacheNo ratings yet
- FaxFinder Admin GuideDocument151 pagesFaxFinder Admin GuidemexicalidudeNo ratings yet
- MC 12 PDFDocument5 pagesMC 12 PDFtobi10No ratings yet
- International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) Version 2 PDFDocument2 pagesInternational Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) Version 2 PDFgonzalo_barrioNo ratings yet
- JD740A User Manual R09.0 (241-320)Document80 pagesJD740A User Manual R09.0 (241-320)halfonsoNo ratings yet
- Multipath and Receiver Models For Assessing The VOR Bearing ErrorDocument146 pagesMultipath and Receiver Models For Assessing The VOR Bearing ErrorYuranan LimpananvadeeNo ratings yet
- Ericsson Review Vol 53 1976 2 PDFDocument60 pagesEricsson Review Vol 53 1976 2 PDFgbaetaNo ratings yet
- DaikinBuildingsAirconditioningControlSystem-721 Part1 - tcm135-98478Document139 pagesDaikinBuildingsAirconditioningControlSystem-721 Part1 - tcm135-98478atameteNo ratings yet
- Data Aquisition PDFDocument28 pagesData Aquisition PDFyaregal limenihNo ratings yet
- Cisco Packet Tracer 53Document3 pagesCisco Packet Tracer 53Abdul MaatNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Internet of Things IoT BasDocument5 pagesComparative Analysis of Internet of Things IoT BasPavan VNo ratings yet
- AP-500 Install Guide enDocument15 pagesAP-500 Install Guide enMaruf isla fudinNo ratings yet
- Re - 1983-10Document196 pagesRe - 1983-10Anonymous kdqf49qbNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1389128618308739 Main PDFDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S1389128618308739 Main PDFArunNo ratings yet
- Mobile Payments Systems GuidelinesDocument20 pagesMobile Payments Systems Guidelinesmohammad zameenNo ratings yet
- Course Name P-0: Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without PermissionDocument26 pagesCourse Name P-0: Confidential Information of Huawei. No Spreading Without PermissionHazem MaherNo ratings yet
- GSM Timers 160705062521 PDFDocument26 pagesGSM Timers 160705062521 PDFCuongDolaNo ratings yet
- ISP Busniess PlanDocument65 pagesISP Busniess PlanRaheel ZararNo ratings yet
- Technology Enabled Solutions To Grow Your Business: Abuja: 5th Floor, IGI HouseDocument17 pagesTechnology Enabled Solutions To Grow Your Business: Abuja: 5th Floor, IGI HouseOyaje IdokoNo ratings yet
- A Combined Antijamming and Antispoofing Algorithm For GPS ArraysDocument10 pagesA Combined Antijamming and Antispoofing Algorithm For GPS ArraysMojtaba KhakiNo ratings yet
- Network Management (SNMP) : Raj Jain The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@cse - Ohio-State - EduDocument17 pagesNetwork Management (SNMP) : Raj Jain The Ohio State University Columbus, OH 43210 Jain@cse - Ohio-State - EduChandani ShahNo ratings yet
- CV Yoyok Dwi Parindra 2016 LTEDocument5 pagesCV Yoyok Dwi Parindra 2016 LTEYoyok Dwi ParindraNo ratings yet