Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global Edition
Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global Edition
Uploaded by
mohd sajidCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- CHCPRP001 - Roleplay V1.2 - CDocument8 pagesCHCPRP001 - Roleplay V1.2 - CShaneNo ratings yet
- Myer Briggs Personality TypesDocument15 pagesMyer Briggs Personality TypesGauri100% (2)
- Vineland Adaptive Behavior ScalesDocument2 pagesVineland Adaptive Behavior ScalesAnonymous 1HGqtl7No ratings yet
- MBA514-Topic 7Document22 pagesMBA514-Topic 7BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth EditionDocument33 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth EditionAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Theories of MotivationDocument57 pagesTheories of Motivationyadavakshat586No ratings yet
- Chapter Three Motivation in OrganizationsDocument29 pagesChapter Three Motivation in Organizationsomayaad mohammedNo ratings yet
- Management: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument22 pagesManagement: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionAmjad J AliNo ratings yet
- Motivation MBADocument31 pagesMotivation MBAAkshitaNo ratings yet
- Management: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument33 pagesManagement: Fourteenth Edition, Global Editionbasit.sharif566No ratings yet
- Management: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument39 pagesManagement: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDarren KhewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document15 pagesChapter 3Javix ThomasNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document14 pagesCH 2juhanaNo ratings yet
- Management: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument44 pagesManagement: Fourteenth Edition, Global Editiontan lee huiNo ratings yet
- Motivation 2Document22 pagesMotivation 2Amandeep GaraiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management: Motivating and Rewarding EmployeesDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Management: Motivating and Rewarding EmployeesSandeep SonarNo ratings yet
- Ob Chapter 3Document16 pagesOb Chapter 3Nayama NayamaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Introduction To OBDocument23 pagesCH 1 Introduction To OBjuhanaNo ratings yet
- Motivation Theories Unit 3Document42 pagesMotivation Theories Unit 3Manju DoraisamiNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior, 17/e: Motivation ConceptsDocument41 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior, 17/e: Motivation ConceptsSabiha MirNo ratings yet
- Robbins Mgmt14 PPT 15Document48 pagesRobbins Mgmt14 PPT 15kenziechanz tedjalaksanaNo ratings yet
- Module I Sessions 1-3 NotesDocument36 pagesModule I Sessions 1-3 Notesjoel joyNo ratings yet
- Management Robbins 14e-Ge C09 Slides - OrganizedDocument9 pagesManagement Robbins 14e-Ge C09 Slides - Organizedtranthithuthuy.studyNo ratings yet
- Management: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument42 pagesManagement: Fourteenth Edition, Global Editionbasit.sharif566No ratings yet
- Report On Incentive SchemesDocument72 pagesReport On Incentive SchemesRafael-Cheryl Tupas-LimboNo ratings yet
- 1. 동기부여의 기본이론Document24 pages1. 동기부여의 기본이론Frank SmithNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: Esteem SADocument23 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs: Esteem SAJefferson Nolty GenoviaNo ratings yet
- Motivation at WorkDocument27 pagesMotivation at WorkPraajitNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument46 pagesMotivationShikha DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- 2023 M&C Collated Sessions Post Quiz 1Document35 pages2023 M&C Collated Sessions Post Quiz 1Siddharth PandeyNo ratings yet
- MOTIVATION Definition: Motivation Is The Set ofDocument21 pagesMOTIVATION Definition: Motivation Is The Set oflilashcoco100% (1)
- Robbins Eob15 PPT 07Document29 pagesRobbins Eob15 PPT 07thienmanvt123No ratings yet
- PO 2019 Part 1 - EDIT PDFDocument34 pagesPO 2019 Part 1 - EDIT PDFRaden AkbarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document17 pagesChapter 16Viper's CreationNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document33 pagesUnit 6rupakchamp_291587564No ratings yet
- Motivating & LeadingDocument52 pagesMotivating & LeadingABDUR REHMAN SAITNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1Muhd FiekrieNo ratings yet
- CSR of Business MOTIVATIONDocument34 pagesCSR of Business MOTIVATIONlanar78505No ratings yet
- Bigstu L16 Mot 1Document20 pagesBigstu L16 Mot 1privynoble.05No ratings yet
- MotivationDocument38 pagesMotivationNaman MittalNo ratings yet
- Managing Employee Motivation and PerformanceDocument25 pagesManaging Employee Motivation and PerformanceA. K. MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document34 pagesLecture 4IFRA KANWALNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument19 pagesMotivationNeelima Varma NadimpalliNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1570804681635Document41 pagesOrca Share Media1570804681635Rhea Mae Caramonte AmitNo ratings yet
- Importance of MotivationDocument15 pagesImportance of MotivationRam Kumar ShahNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument19 pagesMotivationKanupriyamNo ratings yet
- Industrial PsychologyDocument20 pagesIndustrial PsychologyViji VenkyNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 07 Motivating The Workforce ToSDocument51 pagesLecture - 07 Motivating The Workforce ToSCFAB K62 Kiểm toánNo ratings yet
- Motivation ProcessDocument7 pagesMotivation ProcessAmit729No ratings yet
- MotivationDocument31 pagesMotivationdeepalisharma100% (4)
- Managerial Behaviour and Effectiveness Unit 2Document29 pagesManagerial Behaviour and Effectiveness Unit 2standalonembaNo ratings yet
- Management of Human Resource: MGT 315 Bba 5 SemesterDocument42 pagesManagement of Human Resource: MGT 315 Bba 5 SemesterPrajwol ShakaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Theories of MotivationDocument48 pagesLecture 3 - Theories of MotivationPearlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document9 pagesChapter 16Arif MelsingNo ratings yet
- HRM Unit 1Document65 pagesHRM Unit 1Ankush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Griffin Chap 16Document38 pagesGriffin Chap 16Spil_vv_IJmuidenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document41 pagesChapter 5Mẫn NghiNo ratings yet
- MGMT 17Document29 pagesMGMT 17s3denhoo99No ratings yet
- Robbins Eob13ge Ppt07Document27 pagesRobbins Eob13ge Ppt07Mingxiang Wu100% (1)
- Ch05 Motivation TheoriesDocument31 pagesCh05 Motivation TheoriesgaandusinghrajNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: A Case Study of Reliance Industries Limited: Organizational BehaviourFrom EverandOrganizational Behavior: A Case Study of Reliance Industries Limited: Organizational BehaviourNo ratings yet
- List of Empanelled Corporate Hospitals Under DR YSR Aarogyasri Health Care TrustDocument34 pagesList of Empanelled Corporate Hospitals Under DR YSR Aarogyasri Health Care Trustmohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument32 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global Editionmohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Flynas en Regulations 20SEP18 v4Document1 pageFlynas en Regulations 20SEP18 v4mohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument26 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global Editionmohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Important - MOE - Sample Interview Questions 2017Document6 pagesImportant - MOE - Sample Interview Questions 2017mohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ReportDocument5 pagesDecision Making Reportmohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Bohol Island State University Bilar Campus: College of Advanced StudiesDocument2 pagesBohol Island State University Bilar Campus: College of Advanced StudiesMearie Jean Amba FaustinoNo ratings yet
- Kinesthetic LearnerDocument1 pageKinesthetic LearnerMaliheh KareshkyNo ratings yet
- Review of Patricia BennerDocument3 pagesReview of Patricia BennerZul AmitafNo ratings yet
- Emdr PromptDocument1 pageEmdr Promptalinamuha100% (4)
- Weekly Home Learning Plan For HGP 9Document2 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan For HGP 9russel silvestreNo ratings yet
- SARSing Lesson PlansDocument9 pagesSARSing Lesson PlansEmilia Gomes Barbosa Barbosa100% (1)
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form (IPCRF) For Teacher I-IIIDocument59 pagesIndividual Performance Commitment and Review Form (IPCRF) For Teacher I-IIIStephanieNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Satisfaction MCQDocument5 pagesMotivation and Satisfaction MCQkhweziNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 PE Irica Mae Gallano CiervoDocument2 pagesActivity 1 PE Irica Mae Gallano CiervoIrica Mae CiervoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Proficient Teachers Objective 1: Applied Knowledge of Content Within andDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Proficient Teachers Objective 1: Applied Knowledge of Content Within andJM RamirezNo ratings yet
- M4 - Literacy TrainingDocument5 pagesM4 - Literacy TrainingPrincess PulintanNo ratings yet
- 1 SalamaDocument2 pages1 Salamaapi-382182406No ratings yet
- Multimedia Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesMultimedia Lesson PlansheilaperezNo ratings yet
- Ob Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesOb Case AnalysisKIRAN SONYNo ratings yet
- Ncbts-Tsna Electronic Version3Document51 pagesNcbts-Tsna Electronic Version3Paulo OropesaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development 160109040133Document25 pagesCurriculum Development 160109040133میاں مبشر100% (2)
- Self Learning ModuleDocument16 pagesSelf Learning ModuleVanessa Naomi GalidoNo ratings yet
- Task 4 - Reflective EssayDocument11 pagesTask 4 - Reflective EssayKARSHININo ratings yet
- The Value of Human Resource Management For Organizational PerformanceDocument9 pagesThe Value of Human Resource Management For Organizational PerformancetanyaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Self: Less Stress, More CareDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Self: Less Stress, More CareJoseph SolivenNo ratings yet
- Modulo 3Document5 pagesModulo 3Daniel AlejandroNo ratings yet
- DLP DIASS Week B - The Discipline of CounselingDocument9 pagesDLP DIASS Week B - The Discipline of CounselingSteff SteffzkeehNo ratings yet
- Poster ML2008Document1 pagePoster ML2008dr gawdatNo ratings yet
- The Flippered Doctor Is 'IN': Autism and Therapies AvailableDocument2 pagesThe Flippered Doctor Is 'IN': Autism and Therapies Availableapi-14841216No ratings yet
- Pe 9Document3 pagesPe 9Saligan Dolf100% (1)
- LDT F2F MSEd-Program Guide Updated-08122021Document14 pagesLDT F2F MSEd-Program Guide Updated-08122021Noemi Yanet Yanqui CuevaNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in Introduction To World Religion 2nd QuarterDocument1 pagePerformance Task in Introduction To World Religion 2nd QuarterAnatta AttanaNo ratings yet
Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global Edition
Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global Edition
Uploaded by
mohd sajidOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global Edition
Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global Edition
Uploaded by
mohd sajidCopyright:
Available Formats
Essentials of Organizational Behavior
Fourteenth Edition, Global Edition
Chapter 5
Basic Motivation
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
After studying this chapter you should be
able to:
1. Describe the three key elements of motivation.
2. Compare the early theories of motivation.
3. Contrast the elements of self-determination theory and
goal-setting theory.
4. Demonstrate the differences between self-efficacy theory,
reinforcement theory, equity theory, and expectancy
theory.
5. Identify the implications of employee job engagement for
managers.
6. Describe how the contemporary theories of motivation
complement one another.
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
What Is Motivation?
• Motivation: The processes that account for an
individual’s intensity, direction, and persistence of
effort toward attaining an organizational goal
– Intensity: the amount of effort put forth to meet the goal
– Direction: efforts are channeled toward organizational
goals
– Persistence: how long the effort is maintained
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Early Theories of Motivation
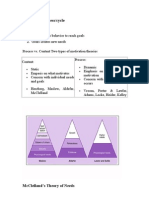
• Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory
• Herzberg’s Two-Factor (Motivation-Hygiene)
Theory
• McClellan’s Theory of Needs (Three Needs
Theory)
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Hierarchy of Needs Theory (1 of 2)
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Two-Factor Theory
Not Dissatisfied Satisfied
Quality of
•• Quality of Promotional
•• Promotional
Motivation
Motivation Factors
supervision opportunities
Factors
supervision opportunities
Hygiene Factors
Pay
•• Pay Opportunities for
•• Opportunities for
Company policies
•• Company policies personal growth
growth
personal
Physical working
•• Physical working
Hygiene
Recognition
•• Recognition
conditions
conditions
Factors
Relationships
•• Relationships Responsibility
•• Responsibility
Job security
•• Job security Achievement
•• Achievement
Dissatisfied Not Satisfied
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Hierarchy of Needs Theory (2 of 2)
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
McClelland's Theory of Needs
• Need for Achievement (nAch)
– The drive to excel
• Need for Power (nPow)
– The need to make others behave in a way they would
not have behaved otherwise
• Need for Affiliation (nAff)
– The desire for friendly and close interpersonal
relationships
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
McClelland's High Achievers
• High achievers prefer jobs with:
– Personal responsibility
– Feedback
– Intermediate degree of risk (50/50)
• High achievers are not necessarily good
managers
• High nPow and low nAff is
related to managerial success
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Contemporary Theories of Motivation
• Self-Determination Theory
• Goal-Setting Theory
– Management by Objectives
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Self-Determination Theory
• Self-determination theory: People prefer to have
control over their actions so when they feel they
are forced to do something they previously
enjoyed, motivation will decrease
– Cognitive evaluation theory: Proposes that the
introduction of extrinsic rewards for work (pay) that was
previously intrinsically rewarding tends to decrease
overall motivation
– Self-concordance: Considers how strongly people’s
reasons for pursuing goals are consistent with their
interests and core values
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Goal-Setting Theory
• Goals increase performance when goals are:
– Specific
– Difficult, but accepted by employees
– Accompanied by feedback: self-generated feedback is
best
• Contingencies in goal-setting theory
– Goal commitment: public goals better
– Task characteristics: simple and familiar is better
– National culture: Western culture suits best
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Management by Objectives
• Management by objectives (MBO): Converts
overall organizational objectives into specific
objectives for work units and individuals
• Common ingredients:
– Goal specificity
– Explicit time period
– Performance feedback
– Participation in decision making
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Cascading of Objectives
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Other Contemporary Theories of
Motivation
• Self-Efficacy Theory
• Reinforcement Theory
• Equity Theory
– Organizational Justice
• Expectancy Theory
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Self-Efficacy Theory (1 of 2)
• Self-efficacy theory: An individual’s belief that he
or she is capable of performing a task
– Also known as social cognitive theory or social learning
theory
• Self-efficacy increased by:
1. Enactive mastery: gain experience
2. Vicarious modeling: see someone else do the task
3. Verbal persuasion: someone convinces you that you
have the skills
4. Arousal: get energized
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Self-Efficacy Theory (2 of 2)
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Reinforcement Theory
• Reinforcement theory: Behavior is a function of
consequences
– Operant conditioning theory
Behaviorism
– Social- learning theory and reinforcement
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Equity Theory (1 of 2)
• Equity theory: Employees weigh what they put
into a job situation (input) against what they get
from it (outcome)
– They compare their input-outcome ratio with the input-
outcome ratio of relevant others
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Equity Theory (2 of 2)
• Equity theory suggests employees who perceive
inequity will make one of six choices:
1. Change inputs
2. Change outcomes
3. Distort perceptions of self
4. Distort perceptions of others
5. Choose a different referent
6. Leave the field
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Model of Organizational Justice
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Expectancy Theory (1 of 2)
• Three key relationships:
1. Effort-performance: perceived probability that
exerting effort leads to successful performance
2. Performance-reward: the belief that successful
performance leads to desired outcome
3. Rewards-personal goals: the attractiveness of
organizational outcome (reward) to the individual
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Expectancy Theory (2 of 2)
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Job Engagement
• Job Engagement: The investment of an
employee’s physical, cognitive, and emotional
energies into job performance
• Organizations where employees are highly
engaged have:
– Higher levels of productivity
– Fewer safety incidents
– Lower turnover
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Integrating Theories
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
Implications for Managers
• Make sure extrinsic rewards for employees are not viewed as
coercive, but instead provide information about competence and
relatedness.
• Consider goal-setting theory. Clear and difficult goals often lead
to higher levels of employee productivity.
• Consider reinforcement theory regarding quality and quantity of
work, persistence of effort, absenteeism, and accident rates.
• Consult equity theory to help understand productivity,
satisfaction, absence, and turnover variables.
• Expectancy theory offers a powerful explanation of performance
variables such as employee productivity, absenteeism, and
turnover.
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
You might also like
- CHCPRP001 - Roleplay V1.2 - CDocument8 pagesCHCPRP001 - Roleplay V1.2 - CShaneNo ratings yet
- Myer Briggs Personality TypesDocument15 pagesMyer Briggs Personality TypesGauri100% (2)
- Vineland Adaptive Behavior ScalesDocument2 pagesVineland Adaptive Behavior ScalesAnonymous 1HGqtl7No ratings yet
- MBA514-Topic 7Document22 pagesMBA514-Topic 7BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth EditionDocument33 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth EditionAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Theories of MotivationDocument57 pagesTheories of Motivationyadavakshat586No ratings yet
- Chapter Three Motivation in OrganizationsDocument29 pagesChapter Three Motivation in Organizationsomayaad mohammedNo ratings yet
- Management: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument22 pagesManagement: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionAmjad J AliNo ratings yet
- Motivation MBADocument31 pagesMotivation MBAAkshitaNo ratings yet
- Management: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument33 pagesManagement: Fourteenth Edition, Global Editionbasit.sharif566No ratings yet
- Management: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument39 pagesManagement: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDarren KhewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document15 pagesChapter 3Javix ThomasNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document14 pagesCH 2juhanaNo ratings yet
- Management: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument44 pagesManagement: Fourteenth Edition, Global Editiontan lee huiNo ratings yet
- Motivation 2Document22 pagesMotivation 2Amandeep GaraiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management: Motivating and Rewarding EmployeesDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Management: Motivating and Rewarding EmployeesSandeep SonarNo ratings yet
- Ob Chapter 3Document16 pagesOb Chapter 3Nayama NayamaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Introduction To OBDocument23 pagesCH 1 Introduction To OBjuhanaNo ratings yet
- Motivation Theories Unit 3Document42 pagesMotivation Theories Unit 3Manju DoraisamiNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior, 17/e: Motivation ConceptsDocument41 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior, 17/e: Motivation ConceptsSabiha MirNo ratings yet
- Robbins Mgmt14 PPT 15Document48 pagesRobbins Mgmt14 PPT 15kenziechanz tedjalaksanaNo ratings yet
- Module I Sessions 1-3 NotesDocument36 pagesModule I Sessions 1-3 Notesjoel joyNo ratings yet
- Management Robbins 14e-Ge C09 Slides - OrganizedDocument9 pagesManagement Robbins 14e-Ge C09 Slides - Organizedtranthithuthuy.studyNo ratings yet
- Management: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument42 pagesManagement: Fourteenth Edition, Global Editionbasit.sharif566No ratings yet
- Report On Incentive SchemesDocument72 pagesReport On Incentive SchemesRafael-Cheryl Tupas-LimboNo ratings yet
- 1. 동기부여의 기본이론Document24 pages1. 동기부여의 기본이론Frank SmithNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: Esteem SADocument23 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs: Esteem SAJefferson Nolty GenoviaNo ratings yet
- Motivation at WorkDocument27 pagesMotivation at WorkPraajitNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument46 pagesMotivationShikha DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- 2023 M&C Collated Sessions Post Quiz 1Document35 pages2023 M&C Collated Sessions Post Quiz 1Siddharth PandeyNo ratings yet
- MOTIVATION Definition: Motivation Is The Set ofDocument21 pagesMOTIVATION Definition: Motivation Is The Set oflilashcoco100% (1)
- Robbins Eob15 PPT 07Document29 pagesRobbins Eob15 PPT 07thienmanvt123No ratings yet
- PO 2019 Part 1 - EDIT PDFDocument34 pagesPO 2019 Part 1 - EDIT PDFRaden AkbarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document17 pagesChapter 16Viper's CreationNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document33 pagesUnit 6rupakchamp_291587564No ratings yet
- Motivating & LeadingDocument52 pagesMotivating & LeadingABDUR REHMAN SAITNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1Muhd FiekrieNo ratings yet
- CSR of Business MOTIVATIONDocument34 pagesCSR of Business MOTIVATIONlanar78505No ratings yet
- Bigstu L16 Mot 1Document20 pagesBigstu L16 Mot 1privynoble.05No ratings yet
- MotivationDocument38 pagesMotivationNaman MittalNo ratings yet
- Managing Employee Motivation and PerformanceDocument25 pagesManaging Employee Motivation and PerformanceA. K. MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document34 pagesLecture 4IFRA KANWALNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument19 pagesMotivationNeelima Varma NadimpalliNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1570804681635Document41 pagesOrca Share Media1570804681635Rhea Mae Caramonte AmitNo ratings yet
- Importance of MotivationDocument15 pagesImportance of MotivationRam Kumar ShahNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument19 pagesMotivationKanupriyamNo ratings yet
- Industrial PsychologyDocument20 pagesIndustrial PsychologyViji VenkyNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 07 Motivating The Workforce ToSDocument51 pagesLecture - 07 Motivating The Workforce ToSCFAB K62 Kiểm toánNo ratings yet
- Motivation ProcessDocument7 pagesMotivation ProcessAmit729No ratings yet
- MotivationDocument31 pagesMotivationdeepalisharma100% (4)
- Managerial Behaviour and Effectiveness Unit 2Document29 pagesManagerial Behaviour and Effectiveness Unit 2standalonembaNo ratings yet
- Management of Human Resource: MGT 315 Bba 5 SemesterDocument42 pagesManagement of Human Resource: MGT 315 Bba 5 SemesterPrajwol ShakaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Theories of MotivationDocument48 pagesLecture 3 - Theories of MotivationPearlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document9 pagesChapter 16Arif MelsingNo ratings yet
- HRM Unit 1Document65 pagesHRM Unit 1Ankush ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Griffin Chap 16Document38 pagesGriffin Chap 16Spil_vv_IJmuidenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document41 pagesChapter 5Mẫn NghiNo ratings yet
- MGMT 17Document29 pagesMGMT 17s3denhoo99No ratings yet
- Robbins Eob13ge Ppt07Document27 pagesRobbins Eob13ge Ppt07Mingxiang Wu100% (1)
- Ch05 Motivation TheoriesDocument31 pagesCh05 Motivation TheoriesgaandusinghrajNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: A Case Study of Reliance Industries Limited: Organizational BehaviourFrom EverandOrganizational Behavior: A Case Study of Reliance Industries Limited: Organizational BehaviourNo ratings yet
- List of Empanelled Corporate Hospitals Under DR YSR Aarogyasri Health Care TrustDocument34 pagesList of Empanelled Corporate Hospitals Under DR YSR Aarogyasri Health Care Trustmohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument32 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global Editionmohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Flynas en Regulations 20SEP18 v4Document1 pageFlynas en Regulations 20SEP18 v4mohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global EditionDocument26 pagesEssentials of Organizational Behavior: Fourteenth Edition, Global Editionmohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Important - MOE - Sample Interview Questions 2017Document6 pagesImportant - MOE - Sample Interview Questions 2017mohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Decision Making ReportDocument5 pagesDecision Making Reportmohd sajidNo ratings yet
- Bohol Island State University Bilar Campus: College of Advanced StudiesDocument2 pagesBohol Island State University Bilar Campus: College of Advanced StudiesMearie Jean Amba FaustinoNo ratings yet
- Kinesthetic LearnerDocument1 pageKinesthetic LearnerMaliheh KareshkyNo ratings yet
- Review of Patricia BennerDocument3 pagesReview of Patricia BennerZul AmitafNo ratings yet
- Emdr PromptDocument1 pageEmdr Promptalinamuha100% (4)
- Weekly Home Learning Plan For HGP 9Document2 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan For HGP 9russel silvestreNo ratings yet
- SARSing Lesson PlansDocument9 pagesSARSing Lesson PlansEmilia Gomes Barbosa Barbosa100% (1)
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form (IPCRF) For Teacher I-IIIDocument59 pagesIndividual Performance Commitment and Review Form (IPCRF) For Teacher I-IIIStephanieNo ratings yet
- Motivation and Satisfaction MCQDocument5 pagesMotivation and Satisfaction MCQkhweziNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 PE Irica Mae Gallano CiervoDocument2 pagesActivity 1 PE Irica Mae Gallano CiervoIrica Mae CiervoNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Proficient Teachers Objective 1: Applied Knowledge of Content Within andDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education: Proficient Teachers Objective 1: Applied Knowledge of Content Within andJM RamirezNo ratings yet
- M4 - Literacy TrainingDocument5 pagesM4 - Literacy TrainingPrincess PulintanNo ratings yet
- 1 SalamaDocument2 pages1 Salamaapi-382182406No ratings yet
- Multimedia Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesMultimedia Lesson PlansheilaperezNo ratings yet
- Ob Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesOb Case AnalysisKIRAN SONYNo ratings yet
- Ncbts-Tsna Electronic Version3Document51 pagesNcbts-Tsna Electronic Version3Paulo OropesaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development 160109040133Document25 pagesCurriculum Development 160109040133میاں مبشر100% (2)
- Self Learning ModuleDocument16 pagesSelf Learning ModuleVanessa Naomi GalidoNo ratings yet
- Task 4 - Reflective EssayDocument11 pagesTask 4 - Reflective EssayKARSHININo ratings yet
- The Value of Human Resource Management For Organizational PerformanceDocument9 pagesThe Value of Human Resource Management For Organizational PerformancetanyaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Self: Less Stress, More CareDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Self: Less Stress, More CareJoseph SolivenNo ratings yet
- Modulo 3Document5 pagesModulo 3Daniel AlejandroNo ratings yet
- DLP DIASS Week B - The Discipline of CounselingDocument9 pagesDLP DIASS Week B - The Discipline of CounselingSteff SteffzkeehNo ratings yet
- Poster ML2008Document1 pagePoster ML2008dr gawdatNo ratings yet
- The Flippered Doctor Is 'IN': Autism and Therapies AvailableDocument2 pagesThe Flippered Doctor Is 'IN': Autism and Therapies Availableapi-14841216No ratings yet
- Pe 9Document3 pagesPe 9Saligan Dolf100% (1)
- LDT F2F MSEd-Program Guide Updated-08122021Document14 pagesLDT F2F MSEd-Program Guide Updated-08122021Noemi Yanet Yanqui CuevaNo ratings yet
- Performance Task in Introduction To World Religion 2nd QuarterDocument1 pagePerformance Task in Introduction To World Religion 2nd QuarterAnatta AttanaNo ratings yet