Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kuliah 3: Sejarah Pertanian
Kuliah 3: Sejarah Pertanian
Uploaded by
Rizka Pratiwi IbrahimCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Principles of Crop ProductionDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Crop ProductionLenny Fe Repe Largo100% (1)
- Maca Lepidium Meyenii Materia Medica HerbsDocument9 pagesMaca Lepidium Meyenii Materia Medica HerbsAlejandra GuerreroNo ratings yet
- The PotatoDocument36 pagesThe PotatoMarcela ZRNo ratings yet
- Handouts CS10 Chapter 1Document11 pagesHandouts CS10 Chapter 1Daisy MoralaNo ratings yet
- Handouts CS10 Chapter 1Document12 pagesHandouts CS10 Chapter 1Jimhar A. AmarilloNo ratings yet
- The Origin of AgricultureDocument1 pageThe Origin of AgricultureMahantNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Evolution of AgricultureDocument398 pagesUnit 1 The Evolution of AgricultureSachin SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Crop Science 1 REVISED 030721Document101 pagesCrop Science 1 REVISED 030721joann jacobNo ratings yet
- CashewDocument7 pagesCashewHoàng Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- PrehistoryDocument12 pagesPrehistoryQais Bani HaniNo ratings yet
- AmaranthDocument38 pagesAmaranthRoberto MarchesiniNo ratings yet
- Commodity Fact Sheet: © California Rice CommissionDocument2 pagesCommodity Fact Sheet: © California Rice CommissionHero DiasNo ratings yet
- Loredo, Jessa Mae D. - Agricultural ArtsDocument11 pagesLoredo, Jessa Mae D. - Agricultural ArtsJessa Mae LoredoNo ratings yet
- Overview On Millets (Nutri Cereals) : January 2015Document6 pagesOverview On Millets (Nutri Cereals) : January 2015kartik100% (1)
- Saldivar 2016Document6 pagesSaldivar 2016maymaycute1510No ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument8 pagesChapter TwoidrisshehuinuwaNo ratings yet
- Intro To AgricultureDocument23 pagesIntro To AgricultureJireh Mae ArrozNo ratings yet
- Development of AgricultureDocument18 pagesDevelopment of AgricultureFriences Joyce Dela Cerna100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document49 pagesChapter 1jhasminsingcay0No ratings yet
- Agri-Fisheries ModuleDocument11 pagesAgri-Fisheries ModuleJamil OrenciadaNo ratings yet
- Achira Canna Edulis PDFDocument9 pagesAchira Canna Edulis PDFLidiaPariNo ratings yet
- Handouts CS10 Chapter 2Document7 pagesHandouts CS10 Chapter 2Jimhar A. AmarilloNo ratings yet
- Maiz y ArrozDocument9 pagesMaiz y ArrozJaider Santiago PastranaNo ratings yet
- Grain InformationDocument44 pagesGrain InformationSanju ShettigarNo ratings yet
- From Ancient Grains To Modern Solutions: A History of Millets and Their Significance in Agriculture and Food SecurityDocument7 pagesFrom Ancient Grains To Modern Solutions: A History of Millets and Their Significance in Agriculture and Food SecurityTRIPTI PANDEYNo ratings yet
- BIO2 - PERFORMANCE TAST - Document - 2021-2022 - ROQUEDocument8 pagesBIO2 - PERFORMANCE TAST - Document - 2021-2022 - ROQUEdjisthecoolNo ratings yet
- Maize in Human NutritionDocument112 pagesMaize in Human NutritionwinstonNo ratings yet
- TKSDG 6a RiceDocument24 pagesTKSDG 6a RiceGilang Satya ArdhanaNo ratings yet
- Belda & Oreste Genbio2Document6 pagesBelda & Oreste Genbio2Ana Rafaela BeldaNo ratings yet
- P. Sativum Is An Annual Plant, With A Life Cycle of One Year. It Is A CoolDocument13 pagesP. Sativum Is An Annual Plant, With A Life Cycle of One Year. It Is A Coolenzo abrahamNo ratings yet
- Corn CobDocument63 pagesCorn CobbongNo ratings yet
- Wheat: of Usefulness, and What Origin of Modern Wheat?Document10 pagesWheat: of Usefulness, and What Origin of Modern Wheat?Dan BolserNo ratings yet
- Handouts CS10 Chapter 2Document7 pagesHandouts CS10 Chapter 2Daisy MoralaNo ratings yet
- Maize: Maize Maize (/meɪzDocument18 pagesMaize: Maize Maize (/meɪzNirmal BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Informative FinalDocument7 pagesInformative FinalJefry GhazalehNo ratings yet
- Final Module Unit 1Document12 pagesFinal Module Unit 1Edd Benedict B. DensingNo ratings yet
- Carney 2001 - African Rice in The Columbian ExchangeDocument21 pagesCarney 2001 - African Rice in The Columbian ExchangeParisTiembiNo ratings yet
- Draft Genoma AmarantoDocument18 pagesDraft Genoma AmarantoPablo VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Potential of Underutilized Crops To Introduce The Nutritional Diversity and Achieve Zero HungerDocument7 pagesPotential of Underutilized Crops To Introduce The Nutritional Diversity and Achieve Zero HungerEfosa OdiaNo ratings yet
- Compendium of Transgenic Crop PlantsDocument2,273 pagesCompendium of Transgenic Crop PlantsFlavius BeleanNo ratings yet
- World CivilizationsDocument15 pagesWorld CivilizationsRicamae BalmesNo ratings yet
- Agri Science Form 4 Term 1 2020-2021 Handout 1Document15 pagesAgri Science Form 4 Term 1 2020-2021 Handout 1Ishmael Samuel 4Y ABCCNo ratings yet
- CornDocument2 pagesCorngnbeccariaNo ratings yet
- CornDocument4 pagesCorngtlsgalaxyNo ratings yet
- Grain Other Than WheatDocument2 pagesGrain Other Than WheatMike GiannoutsosNo ratings yet
- Crop ClassificationDocument13 pagesCrop ClassificationSofia JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Cousin 1997Document20 pagesCousin 1997Vero CastroNo ratings yet
- The Development of AgricultureDocument11 pagesThe Development of AgricultureJudith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Renato'S Integrated FarmDocument4 pagesRenato'S Integrated FarmDare QuimadaNo ratings yet
- Microfiche Reference Library: 4 Project of Volunteers in AsiaDocument36 pagesMicrofiche Reference Library: 4 Project of Volunteers in AsiaPat BomilleNo ratings yet
- Basics of Agriculture - LECTURE NOTESDocument8 pagesBasics of Agriculture - LECTURE NOTESSathish Kumar100% (1)
- Ale Crop Science Lecture Topics - Ustp Claveria. FinalDocument107 pagesAle Crop Science Lecture Topics - Ustp Claveria. FinalLambaco Earl Adam100% (3)
- Chapter II 2Document72 pagesChapter II 2Jehu100% (2)
- Cassava FeedDocument56 pagesCassava FeedAbigail Kaunda Sovi100% (3)
- Chapter 2 Agri-Crop ProductionDocument64 pagesChapter 2 Agri-Crop ProductionJayvee RetadaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Crop Production 2021Document37 pagesLecture 1 Crop Production 2021Wolie GebreegziherNo ratings yet
- Overview of AgricultureDocument17 pagesOverview of AgricultureJosephine TeroNo ratings yet
- Overview of AgricultureDocument5 pagesOverview of AgricultureJosephine TeroNo ratings yet
- Agroforestry As A Means of Alleviating Poverty in Sri LankaDocument7 pagesAgroforestry As A Means of Alleviating Poverty in Sri LankaArjuna SeneviratneNo ratings yet
- Danh Sách ImporterDocument9 pagesDanh Sách Importerbobnguyen.tinimexNo ratings yet
- Ordering at The RestaurantDocument4 pagesOrdering at The RestaurantANGELA ANDREANo ratings yet
- Application of Hydrocolloids in The Beverage Industry - Dedi FardiazDocument35 pagesApplication of Hydrocolloids in The Beverage Industry - Dedi FardiazbanakhoiriNo ratings yet
- 1.01Y - FooSaf V FooSan PDFDocument15 pages1.01Y - FooSaf V FooSan PDFJunei DyosaNo ratings yet
- Meat ProcessingDocument9 pagesMeat ProcessingJoseph Allan DocotNo ratings yet
- Agricultural MarketngDocument6 pagesAgricultural MarketngJane CANo ratings yet
- Keynote Address National Urban Peri Urban Agriculture Program Responses Prospects AmidstDocument18 pagesKeynote Address National Urban Peri Urban Agriculture Program Responses Prospects AmidstJezell De Torres-dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Food Preservation Epp ReviewerDocument6 pagesFood Preservation Epp ReviewerElaine FajanilanNo ratings yet
- Rabbit From Farm To TableDocument3 pagesRabbit From Farm To Tablekarthik kumar100% (1)
- Year Author Solution TS, % N K Shear Rate R2 T, C Y0 or CommentsDocument2 pagesYear Author Solution TS, % N K Shear Rate R2 T, C Y0 or CommentsДмитрий ГрадовNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Building and StructureDocument5 pagesAgricultural Building and StructureNick ivan Alvares100% (1)
- Storage Temperatures and Procedures PPT LESSONDocument15 pagesStorage Temperatures and Procedures PPT LESSONkathryn sorianoNo ratings yet
- ICAR-Directorate of Poultry Research, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad - 500 030 IndiaDocument81 pagesICAR-Directorate of Poultry Research, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad - 500 030 IndiareinpolyNo ratings yet
- A Review On Status and Determinants of Household Food Security in EthiopiaDocument12 pagesA Review On Status and Determinants of Household Food Security in EthiopiaTeshome Betru Tadesse100% (1)
- Test - CME 3 Lesson 10Document3 pagesTest - CME 3 Lesson 10Siew UngNo ratings yet
- 22-06-2024 PIcklistDocument17 pages22-06-2024 PIcklistdeepak.yadavNo ratings yet
- Maggi FinalDocument10 pagesMaggi FinalDeepak Singh NegiNo ratings yet
- SECOND PERIODICAL TEST in EPP VIDocument29 pagesSECOND PERIODICAL TEST in EPP VIMelliones JR DonatoNo ratings yet
- Preliminary 2019 Gulfood Usa Pavilion Exhibitor ListDocument25 pagesPreliminary 2019 Gulfood Usa Pavilion Exhibitor ListThebagabeachresort ResortNo ratings yet
- Competitive Analysis MatrizDocument6 pagesCompetitive Analysis Matrizannieriaz100% (2)
- Belgian Meat SuppliersDocument60 pagesBelgian Meat SuppliersValeria DumitrescuNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document23 pagesModule 2Byrhon AtigaNo ratings yet
- Strayer APWH CH 2Document27 pagesStrayer APWH CH 2Albert AnNo ratings yet
- 1 TDocument1,309 pages1 TAmlan BiswalNo ratings yet
- Food RiddlesDocument18 pagesFood Riddlesriza.prastantiNo ratings yet
- List of Low Glycemic FoodsDocument3 pagesList of Low Glycemic FoodsMaureen Gabrielle ColinaresNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Survey Results and InterpretationDocument6 pagesConsolidated Survey Results and InterpretationjustineNo ratings yet
- Analytical ExpositionDocument6 pagesAnalytical ExpositionHelmi GunawanNo ratings yet
- Agriculture SectorDocument16 pagesAgriculture SectorDrbake accountNo ratings yet
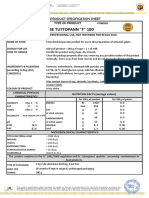
- Base Tuttopann "F" 100: Code 02113 Name Type of ProductDocument2 pagesBase Tuttopann "F" 100: Code 02113 Name Type of ProductPedro barriaNo ratings yet
Kuliah 3: Sejarah Pertanian
Kuliah 3: Sejarah Pertanian
Uploaded by
Rizka Pratiwi IbrahimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kuliah 3: Sejarah Pertanian
Kuliah 3: Sejarah Pertanian
Uploaded by
Rizka Pratiwi IbrahimCopyright:
Available Formats
Kuliah 3: Sejarah Pertanian
IPB 107; 2(2-0)
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 1
SEJARAH PERTANIAN
TIK :
Setelah mengikuti kuliah ini, anda akan
dapat menjelaskan sejarah pertanian.
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 2
Sejarah pertanian
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 3
Sejarah pertanian
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 4
Sejarah Pertanian
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 5
History of Agriculture
Hunter-Gatherers
Neolithic Revolution
Domestication of Plants and Animals
Diffusion of Agriculture
Agricultural Industrialization
The “Green Revolution”
Modern Agribusiness
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 6
Pemburu dan Pengumpul
Hingga 11,000 SM,
disemua benua sebagai
pemburu dan
pengumpul
11,000 SM -1500 AD
perbedaan
perkembangan antar
benua
The spread of humans around the world.
How do we know? Archaeology
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 7
Hunter-Gatherers
Humanity’s only “economic” activity for at
least 90% of our existence.
Low population densities.
Wide variety of natural foodstuffs eaten.
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 8
Asal muasal Pangan
Area Domesticated Domesticated
Date Plants Animals
S.W. Asia Wheat, Pea, Sheep, Goat
8,500 B.C. Olive
China Rice, Millet Pig, Silkworm
7,500 B.C.
Mesoamerica Corn,Beans Turkey
3500 B.C. Squash
A question mark indicates this Andes, Potato Llama
may be an origin or Amazonia Manioc Guinea pig
influenced by the spread of 3500 B.C.
food production. Eastern United Sunflower, None
States Goosefoot
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 9
2500 B.C.
Dibudidayakan
Liar sudah berkurang
Perkembangan teknologi
pengumpulan, pengolahan
dan penyimpanan
Pertambahan penduduk dan
produksi pangan
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 10
Tumbuhan utama zaman Purba
Area Cereals & Grasses Pulses Fiber Roots & Tubers Melons
Fertile emmer and einkorn pea, lentil, chickpea flax ------ muskmelon
Crescent wheat, barley
China Foxtail millet, broom soybean, adzuki hemp ------ ------
corn millet, rice bean, mung bean
Meso- corn pole bean, scarlet cotton, jicama squashes
america runner bean yucca
Andes quinoa lima bean, pole bean cotton manioc, sweet potato, squashes
Amazonia potato, oca
West Africa Sorghum, millet, African cowpea, ground nut cotton African yams watermelon,
rice bottle gourd
India ------ Hyacinth bean, gram cotton, ------ cucumber
bean flax
Ethiopia finger millet ------ (coffee) ------ ------ ------
E. United maygrass, barley, ------ ------ Jerusalem artichoke squash
States knotweed, goosefoot
New Guinea sugar cane ------ ------ yams, taro ------
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 11
Fertile Crescent
Civilization; cities, writing,
empires, and agriculture.
Mediterranean climate.
Easily domesticated
plants.
Most of the plants
pollinate themselves.
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 12
Mediterranean Climate
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 13
Mediterranean Agriculture
Where: areas surrounding the
Mediterranean, California, Oregon,
Chile, South Africa, Australia
Climate has summer dry season.
Landscape is mountainous.
crops: olives, grapes, nuts, fruits and
vegetables; winter wheat
California: high quality land is being
lost to suburbanization; initially offset
by irrigation
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 14
Potato, native of Peru
Native to the Andes of Peru, the
potato plant is now cultivated
throughout the temperate regions
of the world. It is grown for
human consumption and for its
starch.
Other uses or connections
manufacture alcohol
Adhesives
Underground, safe food for
warring factions
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 15
Sugarcane, native to Polynesia
The common sugarcane is
extensively cultivated in
tropical and subtropical
countries throughout the world
for the sugar contained within
its many-jointed stems.
Sugarcane grows to about 8 to
20 feet high and has stems 1 to
2 inches thick.
Other uses or connections
rum
slavery
food additive
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 16
Cotton, native to Asia
Cotton, natural vegetable fiber of
great economic importance as a
raw material for cloth. Its
widespread use is largely due to
the ease with which its fibers are
spun into yarns and it comfort.
Other uses or connections
textile
seed oil
papermaking
slavery
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 17
Tea, native to East Asia
Tea, is brewed from the dried
leaves of this plant and has been
drunk in China for centuries. It
was first brought to Europe by the
Dutch in the early 17th century
AD. England became the only
European country of tea drinkers
rather than coffee drinkers.
Other uses or connections
Creation of cups with handles
China, Hong Kong, and India
become part of the British
empire
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 18
Mengadakan ekosistem buatan yang
bertugas menyediakan bahan makanan
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 19
Biji-bijian dan bertanam; berburu dan
beternak; mencari ikan dan budidaya;
mengolah tanah dan menyimpan; pasar
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 20
Pertanian Menetap
Ekosistem mantap, stabilitas tanah,
pasokan hara, sawah
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 21
budidaya ikan
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 22
sayuran
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 23
usaha budidaya jamur
12/04/21 Kuliah III, Pengantar Ilmu Pertanian 24
You might also like
- Principles of Crop ProductionDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Crop ProductionLenny Fe Repe Largo100% (1)
- Maca Lepidium Meyenii Materia Medica HerbsDocument9 pagesMaca Lepidium Meyenii Materia Medica HerbsAlejandra GuerreroNo ratings yet
- The PotatoDocument36 pagesThe PotatoMarcela ZRNo ratings yet
- Handouts CS10 Chapter 1Document11 pagesHandouts CS10 Chapter 1Daisy MoralaNo ratings yet
- Handouts CS10 Chapter 1Document12 pagesHandouts CS10 Chapter 1Jimhar A. AmarilloNo ratings yet
- The Origin of AgricultureDocument1 pageThe Origin of AgricultureMahantNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Evolution of AgricultureDocument398 pagesUnit 1 The Evolution of AgricultureSachin SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Crop Science 1 REVISED 030721Document101 pagesCrop Science 1 REVISED 030721joann jacobNo ratings yet
- CashewDocument7 pagesCashewHoàng Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- PrehistoryDocument12 pagesPrehistoryQais Bani HaniNo ratings yet
- AmaranthDocument38 pagesAmaranthRoberto MarchesiniNo ratings yet
- Commodity Fact Sheet: © California Rice CommissionDocument2 pagesCommodity Fact Sheet: © California Rice CommissionHero DiasNo ratings yet
- Loredo, Jessa Mae D. - Agricultural ArtsDocument11 pagesLoredo, Jessa Mae D. - Agricultural ArtsJessa Mae LoredoNo ratings yet
- Overview On Millets (Nutri Cereals) : January 2015Document6 pagesOverview On Millets (Nutri Cereals) : January 2015kartik100% (1)
- Saldivar 2016Document6 pagesSaldivar 2016maymaycute1510No ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument8 pagesChapter TwoidrisshehuinuwaNo ratings yet
- Intro To AgricultureDocument23 pagesIntro To AgricultureJireh Mae ArrozNo ratings yet
- Development of AgricultureDocument18 pagesDevelopment of AgricultureFriences Joyce Dela Cerna100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document49 pagesChapter 1jhasminsingcay0No ratings yet
- Agri-Fisheries ModuleDocument11 pagesAgri-Fisheries ModuleJamil OrenciadaNo ratings yet
- Achira Canna Edulis PDFDocument9 pagesAchira Canna Edulis PDFLidiaPariNo ratings yet
- Handouts CS10 Chapter 2Document7 pagesHandouts CS10 Chapter 2Jimhar A. AmarilloNo ratings yet
- Maiz y ArrozDocument9 pagesMaiz y ArrozJaider Santiago PastranaNo ratings yet
- Grain InformationDocument44 pagesGrain InformationSanju ShettigarNo ratings yet
- From Ancient Grains To Modern Solutions: A History of Millets and Their Significance in Agriculture and Food SecurityDocument7 pagesFrom Ancient Grains To Modern Solutions: A History of Millets and Their Significance in Agriculture and Food SecurityTRIPTI PANDEYNo ratings yet
- BIO2 - PERFORMANCE TAST - Document - 2021-2022 - ROQUEDocument8 pagesBIO2 - PERFORMANCE TAST - Document - 2021-2022 - ROQUEdjisthecoolNo ratings yet
- Maize in Human NutritionDocument112 pagesMaize in Human NutritionwinstonNo ratings yet
- TKSDG 6a RiceDocument24 pagesTKSDG 6a RiceGilang Satya ArdhanaNo ratings yet
- Belda & Oreste Genbio2Document6 pagesBelda & Oreste Genbio2Ana Rafaela BeldaNo ratings yet
- P. Sativum Is An Annual Plant, With A Life Cycle of One Year. It Is A CoolDocument13 pagesP. Sativum Is An Annual Plant, With A Life Cycle of One Year. It Is A Coolenzo abrahamNo ratings yet
- Corn CobDocument63 pagesCorn CobbongNo ratings yet
- Wheat: of Usefulness, and What Origin of Modern Wheat?Document10 pagesWheat: of Usefulness, and What Origin of Modern Wheat?Dan BolserNo ratings yet
- Handouts CS10 Chapter 2Document7 pagesHandouts CS10 Chapter 2Daisy MoralaNo ratings yet
- Maize: Maize Maize (/meɪzDocument18 pagesMaize: Maize Maize (/meɪzNirmal BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Informative FinalDocument7 pagesInformative FinalJefry GhazalehNo ratings yet
- Final Module Unit 1Document12 pagesFinal Module Unit 1Edd Benedict B. DensingNo ratings yet
- Carney 2001 - African Rice in The Columbian ExchangeDocument21 pagesCarney 2001 - African Rice in The Columbian ExchangeParisTiembiNo ratings yet
- Draft Genoma AmarantoDocument18 pagesDraft Genoma AmarantoPablo VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Potential of Underutilized Crops To Introduce The Nutritional Diversity and Achieve Zero HungerDocument7 pagesPotential of Underutilized Crops To Introduce The Nutritional Diversity and Achieve Zero HungerEfosa OdiaNo ratings yet
- Compendium of Transgenic Crop PlantsDocument2,273 pagesCompendium of Transgenic Crop PlantsFlavius BeleanNo ratings yet
- World CivilizationsDocument15 pagesWorld CivilizationsRicamae BalmesNo ratings yet
- Agri Science Form 4 Term 1 2020-2021 Handout 1Document15 pagesAgri Science Form 4 Term 1 2020-2021 Handout 1Ishmael Samuel 4Y ABCCNo ratings yet
- CornDocument2 pagesCorngnbeccariaNo ratings yet
- CornDocument4 pagesCorngtlsgalaxyNo ratings yet
- Grain Other Than WheatDocument2 pagesGrain Other Than WheatMike GiannoutsosNo ratings yet
- Crop ClassificationDocument13 pagesCrop ClassificationSofia JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Cousin 1997Document20 pagesCousin 1997Vero CastroNo ratings yet
- The Development of AgricultureDocument11 pagesThe Development of AgricultureJudith RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Renato'S Integrated FarmDocument4 pagesRenato'S Integrated FarmDare QuimadaNo ratings yet
- Microfiche Reference Library: 4 Project of Volunteers in AsiaDocument36 pagesMicrofiche Reference Library: 4 Project of Volunteers in AsiaPat BomilleNo ratings yet
- Basics of Agriculture - LECTURE NOTESDocument8 pagesBasics of Agriculture - LECTURE NOTESSathish Kumar100% (1)
- Ale Crop Science Lecture Topics - Ustp Claveria. FinalDocument107 pagesAle Crop Science Lecture Topics - Ustp Claveria. FinalLambaco Earl Adam100% (3)
- Chapter II 2Document72 pagesChapter II 2Jehu100% (2)
- Cassava FeedDocument56 pagesCassava FeedAbigail Kaunda Sovi100% (3)
- Chapter 2 Agri-Crop ProductionDocument64 pagesChapter 2 Agri-Crop ProductionJayvee RetadaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Crop Production 2021Document37 pagesLecture 1 Crop Production 2021Wolie GebreegziherNo ratings yet
- Overview of AgricultureDocument17 pagesOverview of AgricultureJosephine TeroNo ratings yet
- Overview of AgricultureDocument5 pagesOverview of AgricultureJosephine TeroNo ratings yet
- Agroforestry As A Means of Alleviating Poverty in Sri LankaDocument7 pagesAgroforestry As A Means of Alleviating Poverty in Sri LankaArjuna SeneviratneNo ratings yet
- Danh Sách ImporterDocument9 pagesDanh Sách Importerbobnguyen.tinimexNo ratings yet
- Ordering at The RestaurantDocument4 pagesOrdering at The RestaurantANGELA ANDREANo ratings yet
- Application of Hydrocolloids in The Beverage Industry - Dedi FardiazDocument35 pagesApplication of Hydrocolloids in The Beverage Industry - Dedi FardiazbanakhoiriNo ratings yet
- 1.01Y - FooSaf V FooSan PDFDocument15 pages1.01Y - FooSaf V FooSan PDFJunei DyosaNo ratings yet
- Meat ProcessingDocument9 pagesMeat ProcessingJoseph Allan DocotNo ratings yet
- Agricultural MarketngDocument6 pagesAgricultural MarketngJane CANo ratings yet
- Keynote Address National Urban Peri Urban Agriculture Program Responses Prospects AmidstDocument18 pagesKeynote Address National Urban Peri Urban Agriculture Program Responses Prospects AmidstJezell De Torres-dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Food Preservation Epp ReviewerDocument6 pagesFood Preservation Epp ReviewerElaine FajanilanNo ratings yet
- Rabbit From Farm To TableDocument3 pagesRabbit From Farm To Tablekarthik kumar100% (1)
- Year Author Solution TS, % N K Shear Rate R2 T, C Y0 or CommentsDocument2 pagesYear Author Solution TS, % N K Shear Rate R2 T, C Y0 or CommentsДмитрий ГрадовNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Building and StructureDocument5 pagesAgricultural Building and StructureNick ivan Alvares100% (1)
- Storage Temperatures and Procedures PPT LESSONDocument15 pagesStorage Temperatures and Procedures PPT LESSONkathryn sorianoNo ratings yet
- ICAR-Directorate of Poultry Research, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad - 500 030 IndiaDocument81 pagesICAR-Directorate of Poultry Research, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad - 500 030 IndiareinpolyNo ratings yet
- A Review On Status and Determinants of Household Food Security in EthiopiaDocument12 pagesA Review On Status and Determinants of Household Food Security in EthiopiaTeshome Betru Tadesse100% (1)
- Test - CME 3 Lesson 10Document3 pagesTest - CME 3 Lesson 10Siew UngNo ratings yet
- 22-06-2024 PIcklistDocument17 pages22-06-2024 PIcklistdeepak.yadavNo ratings yet
- Maggi FinalDocument10 pagesMaggi FinalDeepak Singh NegiNo ratings yet
- SECOND PERIODICAL TEST in EPP VIDocument29 pagesSECOND PERIODICAL TEST in EPP VIMelliones JR DonatoNo ratings yet
- Preliminary 2019 Gulfood Usa Pavilion Exhibitor ListDocument25 pagesPreliminary 2019 Gulfood Usa Pavilion Exhibitor ListThebagabeachresort ResortNo ratings yet
- Competitive Analysis MatrizDocument6 pagesCompetitive Analysis Matrizannieriaz100% (2)
- Belgian Meat SuppliersDocument60 pagesBelgian Meat SuppliersValeria DumitrescuNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document23 pagesModule 2Byrhon AtigaNo ratings yet
- Strayer APWH CH 2Document27 pagesStrayer APWH CH 2Albert AnNo ratings yet
- 1 TDocument1,309 pages1 TAmlan BiswalNo ratings yet
- Food RiddlesDocument18 pagesFood Riddlesriza.prastantiNo ratings yet
- List of Low Glycemic FoodsDocument3 pagesList of Low Glycemic FoodsMaureen Gabrielle ColinaresNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Survey Results and InterpretationDocument6 pagesConsolidated Survey Results and InterpretationjustineNo ratings yet
- Analytical ExpositionDocument6 pagesAnalytical ExpositionHelmi GunawanNo ratings yet
- Agriculture SectorDocument16 pagesAgriculture SectorDrbake accountNo ratings yet
- Base Tuttopann "F" 100: Code 02113 Name Type of ProductDocument2 pagesBase Tuttopann "F" 100: Code 02113 Name Type of ProductPedro barriaNo ratings yet