Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reproductive System
Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Md AsifulOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reproductive System
Reproductive System
Uploaded by
Md AsifulCopyright:
Available Formats
Reproductive system
Medical Services Department 1
Introduction
Reproductive system is made up of several organs. It is
divided into two parts:
• Male reproductive system- testis, prostate, penis etc.
• Female reproductive system- ovary, uterus, fallopian
tube, vagina
Function: it’s main function is reproduction (প্রজনন).
Medical Services Department 2
Male reproductive system
Parts of male reproductive system
External parts:
Penis (পেনিস)
Scrotum (ইস্ক্রটাম): which includes
testis (টেস্টিস) and epididymis and
the part of vas deferens
Spermatic cord
Internal parts:
Seminal vesicle (সেমিনাল
ভেসিক্যাল)
Vas deferens (ভাস ডিফারেন্স)
Prostate (প্রোস্টেট)
Ejaculatory ducts (ইজাকুলেটরি ডাক্ট)
Medical Services Department 3
Scrotum
The scrotum is a cutaneous bag containing testis,
epididymis, the part of spermatic cords
Function:
• It regulates the temperature of testis
Medical Services Department 4
Testis
The testis are pair of mixed gland which is suspended within the
scrotum and is surrounded by the testicular capsule which is
composed of three layers:
Tunica vaginalis (outer layer)
Tunica albuginea (middle layer)
Tunica vasculosa (innermost layer)
The hormones of mature testis:
Testosterone
Estrogen (small amount)
Inhibin
Sperm (স্পার্ম): It is the male reproductive cell which comes from
testis
Medical Services Department 5
Prostate
The prostate is an accessory exocrine gland of male reproductive
system. The secretions of this gland add bulk to the seminal fluid
along with those of seminal vesicles and the bulbourethral glands
Function: Produces seminal fluid.
Medical Services Department 6
Common diseases male reproductive system
• Orchitis (অরকাইটিস): Inflammation of testis
• Prostatitis (প্রস্টাটাইটিস): Inflammation of prostate
• BPH (Benign prostatic hyperplasia) / BEP (Benign
enlargement of prostate): Enlargement of prostate usually
after 50 years.
Medical Services Department
7
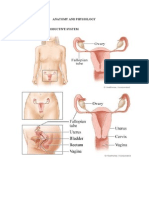
Female reproductive system
Parts of female reproductive system
Primary sex organ:
• Ovary (ওভারি)
Secondary sex organ:
• Fallopian Tube (ফেলোপিয়ান টিউব)
• Uterus (ইউটেরাস)
• Vagina (ভ্যাজাইনা)
Medical Services Department 8
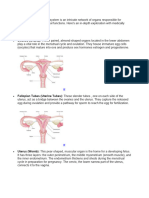
Ovary
The ovaries (ডিম্বাশয়) are pair of mixed gland which are part of
female reproductive system.
• Number: 2 (1 on each side)
• Ovary produce and discharge an ovum in each month.
(During a lifetime a woman release 400 to 500 fully matured
ovum for fertilization)
Function :
a) Produce ovum (Ovum is the female reproductive cell which
comes from ovary)
b) Produce hormone
- Estrogen (ইস্ট্রোজেন)
- Progesterone (প্রজেস্টেরন)
Medical Services Department 9
Fallopian tube/uterine tube
The fallopian tube transports ovum from ovary to uterus.
Number: 2 (each side of uterus)
• It has two opening- One opening opens in the uterine cavity
and the other opening opens in the abdominal cavity
Function: It is the main site of Fertilization. (mainly in ampulla)
Medical Services Department 10
Uterus
The uterus is a major female
reproductive organ
It has three parts :
1. Fundus (ফান্ডাস)
2. Body (বডি)
3. Cervix (সারভিক্স)
Note: Normal size of uterus is 8 to 10
cm. The uterus expands up to 20 times
to its normal size during pregnancy
Medical Services Department 11
Layers of uterus
Three basic layers:
– Perimetrium (পেরিমেট্রিয়াম): Outer layer
– Myometrium (মায়োমেট্রিয়াম): Middle layer
– Endometrium (এন্ডোমেট্রিয়াম): Inner layer
Medical Services Department 12
Menstruation
Menstruation (মেন্সট্রুয়েসন) is the periodic (নির্দিষ্ট সময় অন্তর-অন্তর
ঘটে এমন) discharge of damaged endometrial tissue, unfertilized
ovum and blood through the vagina.
Menarche (মেনারকি): Initiation of menstruation. It begins at the
age of 9 to 13 years of age.
Menopause (মেনোপজ): Stop of menstruation. It occurs between
45 to 55 years of age.
Medical Services Department 13
Menstrual cycle (MC)
• The regular cyclic changes of the uterus regarded as periodic
preparation for implantation and pregnancy is known as
menstrual cycle.
• Duration of the MC : Normally 28 days
Range 21-35 days
• Normal estimated blood loss during MC :
Approximately 20-80 ml
• Duration of mensuration: 3 to 5 days
• Menstruation does not occur in pregnancy
Medical Services Department 14
Menstrual cycle (MC)
Menstrual Cycle can be divided as:
Ovarian cycle (in the ovary)
Follicular phase
Ovulation
Luteal phase
Uterine cycle (in the uterus)
Proliferative phase
Secretory phase
Menstruation
Medical Services Department 15
Ovarian cycle
Hypothalamus begins to secrete gonadotropins- releasing
hormone(GnRH)
Which stimulates secretion of LH and FSH from pituitary
LH causes secretion of estrogen and progesterone from
ovary and FSH stimulates development of follicles in the
ovary(folliculogenesis)
Although many follicles are recruited for development in
early folliculogenesis, a leading follicle is selected for
development into a mature graafian follicle
Medical Services Department 16
Around day 14, LH surge (mid cycle peak of LH secretion by
high estrogen levels) stimulates ovulation from the ovary
After ovulation, remaining part of rupture graafian follicle is
called corpus luteum.corpus luteum secrets progesterone
Estrogen initially and then progesterone cause uterine
endometrial proliferation in preparation for possible
implantation
If implantation does not occur corpus luteum regress and
progesterone level falls. So that the endometrium is shed and
menustration occurs.
Medical Services Department 17
Uterine cycle
Menstruation (1 to 4 day)
Hormonal support of endometrium withdrawn (no estrogen or
progesterone)
Constriction of uterine artery which supplies stratum
functionale (endometrium)
Stratum functionale becomes ischemic
Uterine artery become necrotic and then rupture
This blood from rupture blood vessels, damaged tissue of
endometrium comes through vagina and that is menstruation
Medical Services Department 18
Cont..
Proliferative phase/ estrogen phase (5- 14 day)
(Under the influence of estrogen secreted from ovary,
following changes occur in the endometrium of uterus)
The endometrial surface re-epithelized
The gland increase in number and become large
The blood vessels become large and tortuous
Endometrium become 3-4 mm thick
Medical Services Department 19
Cont..
Secretory phase/Progesterone phase (15-28 day)
(Under the influence of progesterone secreted from corpus
luteum following changes)
Glands increase more in number and secretory character
appear in them
Blood vessels become large and highly tortuous
Increase fat deposition
Endometrium becomes 5-6 mm thick
Medical Services Department 20
Menstrual cycle
Medical Services Department 21
Some disorders of menstruation
Dysmenorrhea (ডিসমেনোরিয়া): Pain during
menstruation.
Amenorrhea (এমিনোরিয়া): Absence of menstruation.
Menorrhagia (মেনোরেজিয়া): Heavy and prolonged
bleeding during menstrual period.
Medical Services Department 22
Pregnancy
Definition: Carrying a developing embryo or fetus within the
uterus is called pregnancy.
Pregnancy lasts for about nine months, measured from the
date of the woman's last menstrual period (LMP).
• Pregnancy is divided into three trimester (ট্রাইমেস্টার):
1. First trimester (1 to 3 month)
2. Second trimester (4 to 6 month)
3. Third trimester (7 to 9 month)
Medical Services Department 23
Some important point about pregnancy
Ovulation (অভুলেশন) : Discharging of matured ovum from
ovary to fallopian tube is called ovulation. Ovulation occurs
usually on the 14th day of menstrual cycle.
Fertilization (ফারটিলাইজেশন) /conception: It is the process
where an ovum and sperm is fused to form an embryo.
Implantation is the very early stage of pregnancy in which
the conceptus adheres to the posterior wall of the uterus.
Embryo (এমব্রায়ো): First eighth week of development after
fertilization, the product of conception is called embryo.
Fetus (ফিটাস) : After eighth week of development till
delivery, the product of conception is called fetus.
Medical Services Department 24
Placenta (প্লাসেন্টা)
Placenta is a temporary organ that
develops in the uterus during
pregnancy, consisting of a fetal part
(chorion) and a maternal part
(decidua basalis).
Function:
• It provides nutrition and oxygen to the
baby from mother
• Removes waste products from the baby
• It produces hCG (Human chorionic
gonadotropin) hormone
Medical Services Department 25
Umbilical cord (আম্বিলিকাল কর্ড)
The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta through
which the fetal blood flows to and from the placenta.
• Our ACI has Hexicord preparation to prevent infection of the
umbilical cord.
Medical Services Department 26
Pregnancy Disorder
Pre-eclampsia (প্রি-একলাম্পসিয়া): Hypertension (BP- 140/90 mm
Hg) and proteinuria after the 20th week of pregnancy in a
previously normotensive and non protienuric woman
Eclampsia (একলাম্পসিয়া): Pre eclampsia when complicated with
convulsions (খিঁচুনি) during pregnancy is called eclampsia
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM): First appearance of
diabetes during pregnancy is called Gestational diabetes mellitus
(GDM). Baby with GDM mother may have diabetes after birth
IUGR: Intrauterine Growth Retardation
Medical Services Department 27
Abortion (অ্যাবোরশন)
Abortion is the expulsion or extraction from its mother
of an embryo or fetus before the age of viability
(before 28th week of pregnancy).
• Threatened Abortion: Discontinuation of
pregnancy occurs in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy
is called threatened abortion.
• Habitual abortion: Discontinuation of pregnancy
occurs three or more consecutive (পর পর) times is
called habitual abortion
Medical Services Department 28
Common female reproductive system diseases
• Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS) (প্রি-মেন্সট্রুয়াল সিনড্রম)
• Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB) (ডিসফাংশনাল ইউটেরাইন ব্লিডিং)
• Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) (পেলভিক ইনফ্লামেটরি ডিজিজ)
• Endometriosis (এনডোমেট্রিওসিস)
• Adenomyosis (এডিনোমায়োসিস)
• Fibroid uterus (ফাইব্রোয়েড ইউটেরাস)
• Ectopic pregnancy (এ ক টপিক প্রে গ ন্ যা
ন্
সি)
• Mastitis (ম্যাসটাইটিস)
• Climacteric syndrome (ক্লাইমেকট্রিক সিনড্রম)
• Molar pregnancy (মোলার প্রেগনেন্সি)
• Utero vaginal prolapse (ইউটেরো ভ্যাজাইনাল প্রোল্যাপস)
• Vaginal discharge(ভ্যাজাইনাল ডিসচার্জ)
Medical Services Department 29
Pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS)
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) is a set of specific physical and
psychological features that may occur in luteal phase of menstrual
cycle.
Clinical features
Physical features Psychological features
• Fatigue (ক্লান্তি) • Anger and irritability
• Bloating (পেট ফুলে যাওয়া) • Anxiety (উদ্বেগ)
• Weight gain • Tension (দুশ্চিন্তা)
• Breast tenderness • Depression (বিষন্নতা)
• Acne (ব্রণ) • Crying
• Sleep disturbances • Mood change
Medical Services Department 30
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding (DUB)
• Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB) is irregular
uterine bleeding that occurs in the absence of pelvic
pathology, general medical disease, or pregnancy.
• It is usually due to hormonal imbalance mainly
reduced levels of progesterone.
• The bleeding may be excessively heavy or light and
may be prolonged, frequent or random.
Medical Services Department 31
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is infection or inflammation
of female reproductive organ (ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus)
It includes:
• Oophoritis (ওফোরাইটিস) : Inflammation of ovaries
• Salpingitis (সালপিনজাইটিস): Inflammation of fallopian
tubes
• Endometritis (এন্ডোমেট্রাইটিস): Inflammation of uterus
• Cervicitis (সারভিসাইটিস): Inflammation of cervix
Medical Services Department 32
Endometriosis
Presence of endometrial (uterine) tissue outside the uterus.
Common sites:
• Ovary (commonest site)
• Pelvic peritonium
• Fallopian tubes
• Uterine ligaments such as the broad or round ligament
• Intestine
Medical Services Department 33
Ectopic pregnancy
It is a condition where pregnancy (implantation) occurs
outside the uterus.
Common site:
Almost all ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian
tube.
Medical Services Department 34
Mastitis
Inflammation of breast is called Mastitis.
Clinical features
• Breast pain
• Breast swelling
• Pain or a burning sensation continuously or while
breast-feeding
• Skin redness over the breast
• Fever
Medical Services Department 35
Climacteric syndrome
• Climacteric syndrome is the most common symptom of
menopausal women which occur between pre-menopause,
peri-menopause and early postmenopausal.
• Clinical feature: Menstrual irregularity, hot flushes (হঠাৎ গ রম
লাগা, ঘেমে মুখ লাল হয়ে যাওয়া), increased weight, painful
breasts,, dyspareunia (বেদনাদায়ক যৌন মিলন) increased or
decreased libido (যৌন কার্যকলাপ করার জন্য ইচ্ছা), atrophy of
skin, MI, strokes, osteoporosis, endometrial and breast cancer,
hypertension.
Medical Services Department 36
Medical Services Department 37
You might also like
- Ganapati UpanishadDocument4 pagesGanapati UpanishadNeha SharmaNo ratings yet
- MPSFPRG Unit3Document14 pagesMPSFPRG Unit3Haruna Gibril BenduNo ratings yet
- Objectives: at The End of This Session The Students Will Be Able ToDocument33 pagesObjectives: at The End of This Session The Students Will Be Able ToPeachy HeartsNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Bleeding During PregnancyDocument67 pagesVaginal Bleeding During PregnancyLunaLureNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemAhmie MarcosNo ratings yet
- ANATOMI - Chapter25ReproFemaleMariebDocument30 pagesANATOMI - Chapter25ReproFemaleMariebAdhi TjahyadiNo ratings yet
- HSP2 Topic 4 Part 4 (Menstrual Disorders)Document60 pagesHSP2 Topic 4 Part 4 (Menstrual Disorders)gilliansong17No ratings yet
- Gyne All in OneDocument119 pagesGyne All in Onetkimbini95No ratings yet
- Powerpoint Case Study of MiscarriageDocument25 pagesPowerpoint Case Study of MiscarriageAngel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Repro. - NursingDocument79 pagesRepro. - NursingARAK Aldarwish100% (1)
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument38 pagesFemale Reproductive SystemnasyitahnorzlanNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle:: MenarcheDocument21 pagesMenstrual Cycle:: MenarcheAlpesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Dekey Biology ProjectDocument12 pagesDekey Biology ProjecttseringchondenmakhamNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument5 pagesHuman ReproductionKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument33 pagesReproductive Systemjheannegabriellea.ylaganNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child (Family Concepts)Document22 pagesMaternal and Child (Family Concepts)Lenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- Physiology 2024Document12 pagesPhysiology 2024Tawshiq HassanNo ratings yet
- MCN Nursing 1Document107 pagesMCN Nursing 1Fau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- Carroll Chapter 05.female AnatomyDocument50 pagesCarroll Chapter 05.female AnatomySitaramNo ratings yet
- GyneDocument4 pagesGynemughaltalha01249212015No ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument16 pagesSexual Reproductionprince matamboNo ratings yet
- Physiology of MenstruationDocument52 pagesPhysiology of Menstruationmahirad001100% (2)
- REPRODUCTION_NOTES_2_092948Document11 pagesREPRODUCTION_NOTES_2_092948nkondeprince77No ratings yet
- Peralta Robles, Nicole Palomino Ruiz, Jorge Montero Túpac, Alejandra Tataje, José Yanamango Salazar, Juan LuisDocument26 pagesPeralta Robles, Nicole Palomino Ruiz, Jorge Montero Túpac, Alejandra Tataje, José Yanamango Salazar, Juan LuisAlfredo Zavaleta GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Handout MCNDocument124 pagesHandout MCNcarol_gigliotti24No ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyBurni GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Production of Germ Cell Spermatozoa From The Testis During Coitus Production of Male Sex Hormone Testosterone From The TestisDocument3 pagesProduction of Germ Cell Spermatozoa From The Testis During Coitus Production of Male Sex Hormone Testosterone From The Testisamelia niitaNo ratings yet
- Normal Menstrual CycleDocument6 pagesNormal Menstrual CycleTeef SumayaNo ratings yet
- FemrepnotesDocument38 pagesFemrepnotesLibi FarrellNo ratings yet
- UNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Document12 pagesUNIT 11 (Reproductive System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Female Repro System Must Produce Gametes AND Maintain Developing EmbryoDocument27 pagesFemale Repro System Must Produce Gametes AND Maintain Developing EmbryoAbhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle 1Document16 pagesMenstrual Cycle 1CoxnxkNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION ONG EditedDocument21 pagesCASE PRESENTATION ONG EditedMary Mathel Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument9 pagesFemale Reproductive Systembyata pausanosNo ratings yet
- Kub Gyne Anemia PDFDocument117 pagesKub Gyne Anemia PDFWaterfall ShapelessNo ratings yet
- Intro To Pregnancy LVL 1Document34 pagesIntro To Pregnancy LVL 1Helene NketchouaNo ratings yet
- Obstetrical NursingDocument36 pagesObstetrical NursingFreeNursingNotes100% (7)
- ANATOMY: Introduction To EmbryologyDocument22 pagesANATOMY: Introduction To EmbryologyNur Liyana MohamadNo ratings yet
- 4 - Menstrual and Ovarian Cycles-Dr - GosaiDocument22 pages4 - Menstrual and Ovarian Cycles-Dr - GosaiDr.B.B.GosaiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Reproductive SystemDocument48 pagesStructure and Function of The Reproductive SystemJohnryl FranciscoNo ratings yet
- CP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Document11 pagesCP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument8 pagesMenstrual CycleAlloiBialba100% (1)
- MENSTRUATION: Monthly Discharge of Blood From The Uterus Occurring Form Puberty To MenopauseDocument18 pagesMENSTRUATION: Monthly Discharge of Blood From The Uterus Occurring Form Puberty To Menopauselyka resurreccionNo ratings yet
- Gynecological Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument39 pagesGynecological Anatomy & Physiologynursereview100% (3)
- Case StudyDocument23 pagesCase StudyLucero HyacinthNo ratings yet
- Modul Hormon Reproduksi Dan Kontrasepsi WanitaDocument46 pagesModul Hormon Reproduksi Dan Kontrasepsi Wanitahendra2darmawanNo ratings yet
- The Phases of Menstrual CycleDocument5 pagesThe Phases of Menstrual CycleKristine AlejandroNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument7 pagesREVIEWERKhaskie Geneva DumaguinNo ratings yet
- The Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Ovarian TumorDocument25 pagesThe Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Malignant Ovarian TumorShanon LimNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Female Reproductive System 01092010Document57 pagesPhysiology of Female Reproductive System 01092010Azry MustapaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: Dr. Dicky Moch. Rizal, Mkes, Spand Bag. Ilmu Faal, FK UgmDocument94 pagesReproductive System: Dr. Dicky Moch. Rizal, Mkes, Spand Bag. Ilmu Faal, FK UgmNi Made Dwiki AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cyst FinalDocument26 pagesOvarian Cyst FinalReicy Aquino SacularNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PathophysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PathophysiologyRaymond EscuzarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology OvaryDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology OvaryFretchell Aripal MontesNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic ApprDocument33 pagesDiagnostic ApprNicole ArandingNo ratings yet
- FEMALE and MALE REPRUDUCTION SYSTEMDocument23 pagesFEMALE and MALE REPRUDUCTION SYSTEMHalseyNo ratings yet
- Gynaecology TextbookDocument35 pagesGynaecology Textbooktkimbini95No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandFemale Reproductive System, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- SKB Stainless Steel Mills LTD.: Cookware Price ListDocument4 pagesSKB Stainless Steel Mills LTD.: Cookware Price ListMd Asiful100% (2)
- 251pran Confectionery Catalogue-Compressed 1Document84 pages251pran Confectionery Catalogue-Compressed 1Md Asiful100% (1)
- 156pran Snacks Catalogue-CompressedDocument12 pages156pran Snacks Catalogue-CompressedMd AsifulNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System: Medical Services Department 1Document26 pagesEndocrine System: Medical Services Department 1Md AsifulNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System/ Renal System: Medical Services Department 1Document28 pagesThe Urinary System/ Renal System: Medical Services Department 1Md AsifulNo ratings yet
- Basic Pathology: Medical Services Department 1Document10 pagesBasic Pathology: Medical Services Department 1Md AsifulNo ratings yet
- Transport Management PlanDocument13 pagesTransport Management Planprmrao100% (3)
- Tips and Tricks Motivation LetterDocument5 pagesTips and Tricks Motivation LetterTousif RahmanNo ratings yet
- FM and TMDocument445 pagesFM and TMKrishna Singh100% (1)
- CDU BIOCHEMISTRY Structure of Triacylglycerols WorksheetDocument2 pagesCDU BIOCHEMISTRY Structure of Triacylglycerols WorksheetKrisha Mae VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology and Public Health: Burton's Microbiology For The Health SciencesDocument33 pagesEpidemiology and Public Health: Burton's Microbiology For The Health SciencesMarlop Casicas100% (1)
- GEV Organic ProductsDocument4 pagesGEV Organic ProductssubhashNo ratings yet
- Sds File-16179386Document7 pagesSds File-16179386omar silimNo ratings yet
- Underwriting Training - CollateralDocument60 pagesUnderwriting Training - CollateralHimani SachdevNo ratings yet
- CMC Development Project Management in Boston MA Resume Gary LavineDocument4 pagesCMC Development Project Management in Boston MA Resume Gary LavineGaryLavine2No ratings yet
- All Rights Reserved. Kim Seng Technical School, 1979Document164 pagesAll Rights Reserved. Kim Seng Technical School, 1979lengyianchua206No ratings yet
- Spectrophotometer UseDocument4 pagesSpectrophotometer UseEsperanza Fernández MuñozNo ratings yet
- Mind Over MatterDocument3 pagesMind Over MatterCharles LeRoyNo ratings yet
- B2 Listening 11Document1 pageB2 Listening 11Juan MiguelNo ratings yet
- GMW8 2019 03 (Hot Dip Zinc Coating Sheet Steel)Document8 pagesGMW8 2019 03 (Hot Dip Zinc Coating Sheet Steel)dpfloresNo ratings yet
- Bagi 'INS 2004-2010-Ins99.pdf'Document11 pagesBagi 'INS 2004-2010-Ins99.pdf'Syarifuddin RahmanNo ratings yet
- Mode Emploi Yamaha Cs2xDocument78 pagesMode Emploi Yamaha Cs2xHauserNo ratings yet
- The Welding Journal 1958 7Document150 pagesThe Welding Journal 1958 7AlexeyNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Toad DissectionDocument5 pagesLab Manual Toad DissectionDegorio, Jay Anthony G. 11 - QuartzNo ratings yet
- Christian SongsDocument12 pagesChristian Songsmarie crisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Abbreviations - Flash CardsDocument78 pagesNursing Abbreviations - Flash Cardsɹǝʍdןnos100% (4)
- Win LandDocument20 pagesWin LandaowsNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment TemplateDocument7 pagesRisk Assessment TemplateMihiretu MelkamuNo ratings yet
- Yes and AmenDocument2 pagesYes and AmenBernNo ratings yet
- DermatomycosesDocument2 pagesDermatomycosesRay CullenNo ratings yet
- Lichtenberg Figures - Lightning As ArtDocument14 pagesLichtenberg Figures - Lightning As ArtSyncOrSwimNo ratings yet
- DJ X11Document113 pagesDJ X11AbrahamNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument2 pagesCalculussagarNo ratings yet
- Sis - SSM Price List Yarn For The Month of Feb 2024 Upto 15.02.2024Document1 pageSis - SSM Price List Yarn For The Month of Feb 2024 Upto 15.02.2024GOWRIJEYASHANKAR S KNo ratings yet
- r05310404 Digital CommunicationsDocument7 pagesr05310404 Digital CommunicationsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet