Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CSS Osteoarthritis Genu
CSS Osteoarthritis Genu
Uploaded by
fatimah putri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
67 views33 pagesThe document discusses the anatomy, epidemiology, etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. It describes the knee joint as involving three bones and three articular surfaces. Risk factors for osteoarthritis include age, genetics, injury, weight, and previous joint surgery. Symptoms include pain with movement and crepitus, joint swelling, and deformities like valgus or varus. Treatment focuses on reducing pain and inflammation through medications like acetaminophen, NSAIDs, and corticosteroid injections, as well as non-pharmacologic options like physical therapy.
Original Description:
Original Title
CSS Osteoarthritis genu
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the anatomy, epidemiology, etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. It describes the knee joint as involving three bones and three articular surfaces. Risk factors for osteoarthritis include age, genetics, injury, weight, and previous joint surgery. Symptoms include pain with movement and crepitus, joint swelling, and deformities like valgus or varus. Treatment focuses on reducing pain and inflammation through medications like acetaminophen, NSAIDs, and corticosteroid injections, as well as non-pharmacologic options like physical therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
67 views33 pagesCSS Osteoarthritis Genu
CSS Osteoarthritis Genu
Uploaded by
fatimah putriThe document discusses the anatomy, epidemiology, etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. It describes the knee joint as involving three bones and three articular surfaces. Risk factors for osteoarthritis include age, genetics, injury, weight, and previous joint surgery. Symptoms include pain with movement and crepitus, joint swelling, and deformities like valgus or varus. Treatment focuses on reducing pain and inflammation through medications like acetaminophen, NSAIDs, and corticosteroid injections, as well as non-pharmacologic options like physical therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 33
CSS Osteoarthritis genu
Oleh kelompok 18b
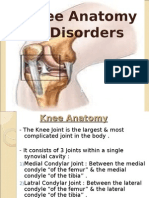
Anatomi lutut
• Lutut adalah sendi engsel
melibatkan tiga tulang: tulang
femur, tibia, dan patella, dengan
tiga permukaan artikular, dua di
antara tulang femur dan tibia dan
satu antara tulang femur dan
patela.
Anatomi lutut
Anatomi lutut
• Sendi
Anatomi Lutut
• Otot
The quadriceps femoris extends
the knee, covering the anterior,
medial, and lateral aspects of the
thigh
The hamstring muscles lie on the
posterior aspect of the thigh and
flex the knee.
Anatomi Lutut
• Struktur tambahan
Meniscus dan ligament
menisci and two important pairs
of ligaments, the collaterals and
the cruciates, are crucial to
stability of the knee.
The medial and lateral menisci
cushion the action of the femur on
the tibia.
Anatomi Lutut
• Struktur tambahan
Medial collateral ligament (MCL)
broad, flat ligament connecting
the medial femoral epicondyle to
the medial condyle of the tibia.
The medial portion of the MCL
also attaches to the medial
meniscus
Anatomi Lutut
• Struktur tambahan
The lateral collateral ligament
(LCL) connects the lateral femoral
epicondyle and the head of the
fibula.
The MCL and LCL provide medial
and lateral stability to the knee
joint.
Anatomi Lutut
• Struktur tambahan
ACL
The ACL crosses obliquely from the anterior
medial tibia to the lateral femoral condyle,
preventing the tibia from sliding forward on the
femur.
PCL
The (PCL) crosses from the posterior tibia and
lateral meniscus to the medial femoral condyle,
preventing the tibia from slipping backward on
the femur. Although the ACL and PCL lie within
the knee joint so are not palpable, they are
nonetheless crucial to the anteroposterior
stability of the knee
Anatomi Lutut
• Struktur tambahan
Bursae
Several bursae lie near the knee.
The prepatellar bursa lies between the
patella and the overlying skin.
The anserine bursa lies 1 to 2 cm below
the knee joint on the medial surface,
proximal and medial to the attachments
of the medial hamstring muscles on the
proximal tibia. It cannot be palpated
due to these overlying tendons.
Osteoarthritis
Definisi
• OA is a disease that involves degeneration in
various structures of the joint, including
cartilage, bone, synovium, muscles, and
ligaments. This can result in stiffness, loss of
mobility, swelling and pain.
• In contrast to RA, OA is primarily a
noninflammatory disorder, but inflammation
eventually occurs and is progressive.
Epidemiologi
• The prevalence of OA increases sharply for women after age 40 years
and after age 50 for men.
• OA of the hand is more prevalent in women, whereas men are slightly
more likely to have hip OA.
• Genetics is likely to contribute to the development of primary OA.
Inhibited bone abnormalities or inherited traits (e.g., dysplasia,
malalignment) that subject the joint to unusual stress increase the
likelihood of its development
Etiologi &Faktor risiko
• No single known cause of OA exists.
• Factors that might contribute to a diagnosis of OA include genetic
disposition, age, injury, weight, stress on the joint, and previous
surgery involving the joint.
• Age is the most commonly identified risk factor for OA of all joints.
Manisfestasi klinik
OA genu :
Nyeri gerak dan krepitus positif
Efusi sendi
Adanya kista popliteal
Instabilitas dan perubahan gaya berjalan
Deformitas valgus atau varus
Diagnosis
Terapi
• Goals of OA therapy are to decrease pain, increase function in
activities of daily living (ADL) and mobility, prevent and correct
deformity, and slow disease progression
Medikasi
• The first line of pharmacotherapy is
acetaminophen or NSAID
• In patients for whom NSAIDs are
contraindicated, or when combined
acetaminophen and NSAID therapy is
ineffective, tramadol can be started or a low-
dose opioid and titrated as needed and
tolerated.
• NSAIDs and opioids are mutually dose-sparing,
and combining low doses of a drug from each
class provides synergistic analgesia while
limiting toxicities
Medikasi
• Additional therapies might include the external application of local
anesthetics and topical NSAIDs as a patch or gel over the painful join
• Injections of corticosteroids into the knee joint (intraarticular [IA])
might relieve inflammation and reduce pain and disability.
Non Medikasi
• Nonpharmacologic treatment recommendations by the Osteoarthritis
Research Society include thermal modalities, acupuncture, and
transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
Musculoskeletal
provocative manuvers
You might also like
- Ergonomics in Dentistry: By, DR - Rakesh R Nair P.G Student Cons & Endo KVG Dental CollegeDocument94 pagesErgonomics in Dentistry: By, DR - Rakesh R Nair P.G Student Cons & Endo KVG Dental Collegenur awanisNo ratings yet
- TMJ Article - FullDocument11 pagesTMJ Article - FullBivian Alexandro CastilloNo ratings yet
- Activity DesignDocument2 pagesActivity Designsanie50% (2)
- Lect 6Document37 pagesLect 6eslambasuony98No ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis ImagingDocument16 pagesOsteoarthritis ImagingAgus TriwiNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument23 pagesOsteoarthritisGoutham VGouthamNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis NotesDocument11 pagesOsteoarthritis Notesjesmitha2740No ratings yet
- MS 36Document7 pagesMS 36jefrocNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Dr. C. C. VisserDocument85 pagesOsteoarthritis: Dr. C. C. VisserAhmad Fathira FitraNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Disorders 21 Dec. 2021Document61 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders 21 Dec. 2021sofiamansoorNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Joint DiseaseDocument5 pagesDegenerative Joint DiseaseskittypieNo ratings yet
- OSTEOARTHRITITSDocument25 pagesOSTEOARTHRITITSAnu Magar100% (1)
- Group 3 Fact Sheet Degenerative Joint Disease OsteoarthritisDocument6 pagesGroup 3 Fact Sheet Degenerative Joint Disease OsteoarthritisJoe Aire SalvediaNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Dr. Angelo Smith M.D WHPLDocument51 pagesOsteoarthritis: Dr. Angelo Smith M.D WHPLChuks LeviNo ratings yet
- Rol - PDF Final.Document17 pagesRol - PDF Final.Muskan khaziNo ratings yet
- Lumber SpondylosisDocument25 pagesLumber SpondylosisYusrah SaniNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Joint DiseasesDocument30 pagesDegenerative Joint DiseasesBahaa ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Introduction OADocument3 pagesIntroduction OAMae UsquisaNo ratings yet
- Oa KneeDocument17 pagesOa KneeChitra ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Keogh Osteoarthritis PresentationDocument40 pagesKeogh Osteoarthritis PresentationTirtahadi ChandraNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Prepared by Dr/Mohammed AlshehariDocument17 pagesOsteoarthritis: Prepared by Dr/Mohammed AlsheharimosaNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis 191016103144Document49 pagesOsteoarthritis 191016103144dr.abouzaid098No ratings yet
- Lecture 13 Bone, Joint, Tendon, and Soft Tissue Injury in Lower Limb (Knee)Document143 pagesLecture 13 Bone, Joint, Tendon, and Soft Tissue Injury in Lower Limb (Knee)Wilson HalimNo ratings yet
- RHEUMA OsteoarthritisDocument4 pagesRHEUMA OsteoarthritisHajime NakaegawaNo ratings yet
- Knee PainDocument10 pagesKnee Painhis.thunder122100% (2)
- Lecture 11aDocument33 pagesLecture 11amukhtarjaballaNo ratings yet
- A. Pusey Murray (MRS) RN, Cert Psych Nursing & Nursing Admin, BSC (Hons), MPH, Dip. Ed. PHD (C)Document31 pagesA. Pusey Murray (MRS) RN, Cert Psych Nursing & Nursing Admin, BSC (Hons), MPH, Dip. Ed. PHD (C)okaciaNo ratings yet
- Typical Clinical Symptoms Are Pain, Particularly After ProlongedDocument12 pagesTypical Clinical Symptoms Are Pain, Particularly After Prolongedifa afifahNo ratings yet
- Total Knee Replacement: The Path ToDocument6 pagesTotal Knee Replacement: The Path ToMoses DhinakarNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology: Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis: Dr. Meg-Angela Christi AmoresDocument25 pagesRheumatology: Osteoarthritis Rheumatoid Arthritis: Dr. Meg-Angela Christi AmoresNinaNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument45 pagesOsteoarthritisMar ClrNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: Ferdinand Robert JKKM CPT KPMDocument40 pagesOsteoarthritis: Ferdinand Robert JKKM CPT KPMFerdinand RobertNo ratings yet
- 68 DISEASES 2nd Semsester 3rd Year 1 PDFDocument117 pages68 DISEASES 2nd Semsester 3rd Year 1 PDFJimlord GarciaNo ratings yet
- Knee Injuries: DR - Sindhu Meena MEM Resident MMHRCDocument30 pagesKnee Injuries: DR - Sindhu Meena MEM Resident MMHRCP Vinod KumarNo ratings yet
- OsteoarthritisDocument2 pagesOsteoarthritisDwipratiwi 2003No ratings yet
- Arthritis (Cabansag, Ma. Flor-And-Cabansag, Joyce)Document38 pagesArthritis (Cabansag, Ma. Flor-And-Cabansag, Joyce)Carlojay IniegoNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis and GoutDocument69 pagesOsteoarthritis and Goutadamu mohammadNo ratings yet
- OA Presentation Parth SinghDocument20 pagesOA Presentation Parth Singhparthsingh4211No ratings yet
- Occlusal SplintsDocument101 pagesOcclusal SplintszpatelcapetownNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11aDocument40 pagesLecture 11aElliya Rosyida67% (3)
- OSTEOARTHRITISDocument11 pagesOSTEOARTHRITISDila MananNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis of The KneeDocument8 pagesOsteoarthritis of The Kneeas3syamut649250% (2)
- Gon ArthrosisDocument1 pageGon ArthrosisGabrielė TrumpickaitėNo ratings yet
- Gon ArthrosisDocument1 pageGon ArthrosisHossam EltayebNo ratings yet
- V.Lokeesan, BSN T.Assistant Lecturer FHCS, EuslDocument39 pagesV.Lokeesan, BSN T.Assistant Lecturer FHCS, EuslMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis: (Degenerative Arthritis/osteoarthrosis/hypertrophic Arthritis)Document64 pagesOsteoarthritis: (Degenerative Arthritis/osteoarthrosis/hypertrophic Arthritis)Linda SugiartoNo ratings yet
- OSTEOARTHRITISDocument61 pagesOSTEOARTHRITISARYAN THAPANo ratings yet
- 3 LWG Knee Pain Part 1Document1 page3 LWG Knee Pain Part 1Woo Guan LeeNo ratings yet
- 485-Article Text-605-1-10-20161227 PDFDocument10 pages485-Article Text-605-1-10-20161227 PDFJeg1No ratings yet
- Inflammatory Joint Diseases Handout-Admission ExamDocument11 pagesInflammatory Joint Diseases Handout-Admission ExamNona NadimNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Joint Disease: BY: DR Mehrunnisa Umar Assisstant Professor Department of MedicineDocument27 pagesDegenerative Joint Disease: BY: DR Mehrunnisa Umar Assisstant Professor Department of MedicinedrusmanjamilhcmdNo ratings yet
- Knee OsteoarthritisDocument22 pagesKnee OsteoarthritisHK FreeNo ratings yet
- 7 - Knee Joint - D3Document28 pages7 - Knee Joint - D3aslooclt100% (1)
- Medscape Knee OCDDocument16 pagesMedscape Knee OCDDita Ambarsari SyafruddinNo ratings yet
- Inservice For LoyolaDocument13 pagesInservice For Loyolaapi-659939847No ratings yet
- Ra and Osteoarthritis R IfDocument43 pagesRa and Osteoarthritis R IfsnfhanNo ratings yet
- Myositis OssificansDocument20 pagesMyositis OssificanssarathNo ratings yet
- 2 2-ArthritidesDocument76 pages2 2-ArthritidesAvinash KaushikNo ratings yet
- Arthritis Group 7 (FINAL)Document58 pagesArthritis Group 7 (FINAL)Roxanne Olnosen SimonNo ratings yet
- Common Rheumatologic Disease (Reichel's)Document9 pagesCommon Rheumatologic Disease (Reichel's)AhmedNo ratings yet
- Di Indo Cuma DuaDocument2 pagesDi Indo Cuma Duafatimah putriNo ratings yet
- Clinical Science Session CT Scan Anatomi Kepala Normal: Preceptor: Dyana Eka Hadiati, DR., SP - RadDocument25 pagesClinical Science Session CT Scan Anatomi Kepala Normal: Preceptor: Dyana Eka Hadiati, DR., SP - Radfatimah putriNo ratings yet
- Patgen - Patfis Case 7Document1 pagePatgen - Patfis Case 7fatimah putriNo ratings yet
- Toorthj 8 185Document10 pagesToorthj 8 185fatimah putriNo ratings yet
- Cara Mengukur Tekanan IntrakompartemenDocument2 pagesCara Mengukur Tekanan Intrakompartemenfatimah putriNo ratings yet
- Dermatovenereological ExamDocument3 pagesDermatovenereological ExamArya MaheswaraNo ratings yet
- Compartment SyndromeDocument14 pagesCompartment Syndromefatimah putriNo ratings yet
- CSS Perawatan LukaDocument19 pagesCSS Perawatan Lukafatimah putriNo ratings yet
- Guide BLS + SkenarioDocument4 pagesGuide BLS + Skenariofatimah putriNo ratings yet
- What Is AsbestosDocument73 pagesWhat Is Asbestosfatimah putriNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Lumbal: Basic ScienceDocument17 pagesAnatomi Lumbal: Basic Sciencefatimah putriNo ratings yet
- Barytes SDS 12 04INT19 03Document5 pagesBarytes SDS 12 04INT19 03Shola EshoNo ratings yet
- A-Life Kasih FamiliDocument2 pagesA-Life Kasih FamiliZaiham ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Fts 5 PDFDocument46 pagesFts 5 PDFRifqi MuslimNo ratings yet
- Symposium NRDocument4 pagesSymposium NRJodi CagampangNo ratings yet
- Gmail - FWD - Ielts For Ukvi Test Notification - 20th August 2022Document3 pagesGmail - FWD - Ielts For Ukvi Test Notification - 20th August 2022Damilola oladayoNo ratings yet
- Certified HVAC Designer (CHD) : Candidate GuidebookDocument20 pagesCertified HVAC Designer (CHD) : Candidate GuidebookObi-Wan KenobiNo ratings yet
- 55 Selection of Appropriate Internal Process Challenge Devices PCDsDocument4 pages55 Selection of Appropriate Internal Process Challenge Devices PCDsRakeshNo ratings yet
- Gurley, Bill J, - Clinically Relevant Herb Mineral Vitamin IntrxnDocument9 pagesGurley, Bill J, - Clinically Relevant Herb Mineral Vitamin IntrxnMSKCNo ratings yet
- 16 MLT PDFDocument148 pages16 MLT PDFTanveer100% (1)
- JHS - Syllabus AFA-7 (Crop Prod) - 1920-EricoDocument2 pagesJHS - Syllabus AFA-7 (Crop Prod) - 1920-EricoEdwin SorianoNo ratings yet
- Smart VillageDocument24 pagesSmart VillageDhruv100% (1)
- HPD Marmoleum Ohmex (Exp. 2022.01.09)Document10 pagesHPD Marmoleum Ohmex (Exp. 2022.01.09)Marco RaptusNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Safety Law enDocument40 pagesBiotechnology Safety Law enSunnyNo ratings yet
- SerratiaDocument26 pagesSerratiaduverney.gaviriaNo ratings yet
- Assessment ToolsDocument4 pagesAssessment ToolsDovi Lucero ArtecheNo ratings yet
- Abdominal TuberculosisDocument9 pagesAbdominal TuberculosisImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Mobility, Stability and MovementDocument62 pagesMobility, Stability and MovementYuldashNo ratings yet
- OT 535 Documentation & ReimbursementDocument27 pagesOT 535 Documentation & ReimbursementJoanna RiveraNo ratings yet
- MSDS WD 40-AerosolDocument5 pagesMSDS WD 40-AerosolYogiNo ratings yet
- Birth Asphyxia: Prof RL Mbise PCH, ImtuDocument38 pagesBirth Asphyxia: Prof RL Mbise PCH, ImtuCharles FrankNo ratings yet
- A Clinical Guide To Orthodontics - J. Sandy (2004) WW PDFDocument77 pagesA Clinical Guide To Orthodontics - J. Sandy (2004) WW PDFAntonela CeremușNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic&Pharmacodynamics Mivacurium in Young Adult and Elderly PatientDocument8 pagesPharmacokinetic&Pharmacodynamics Mivacurium in Young Adult and Elderly PatientIndah PrihandiniNo ratings yet
- Thyroid - History Taking: 1. Patient DetailsDocument5 pagesThyroid - History Taking: 1. Patient DetailsNellayappan SivasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Approved InstDocument368 pagesApproved InstSatish VermaNo ratings yet
- Spiritual Struggle Healing Spirit Fall 2008 PDFDocument4 pagesSpiritual Struggle Healing Spirit Fall 2008 PDFphone growthNo ratings yet
- Health Economic GrowthDocument25 pagesHealth Economic GrowthCarmen Ulloa MéndezNo ratings yet
- QuestionnareDocument7 pagesQuestionnareJehannaMarEnggingAbdurahmanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Digestive System - 2020-21Document9 pagesWorksheet - Digestive System - 2020-21riddhiNo ratings yet
- 3 - Updated Undertaking For EmployerDocument1 page3 - Updated Undertaking For EmployerRamnuj Orecul SoralcNo ratings yet