Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 viewsBooks of Accounts: Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.D
Books of Accounts: Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.D
Uploaded by
DodgeSanchezThe document discusses various accounting journals and ledgers used to record financial transactions. It describes general and special journals like the cash receipts journal, cash disbursements journal, sales journal, and purchase journal. It also discusses the general ledger and subsidiary ledger, with the general ledger serving as the central record of accounts and controlling account that summarizes subsidiary ledgers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Online Poker Starting Guide (Frank Miller) PDFDocument39 pagesThe Online Poker Starting Guide (Frank Miller) PDFDe_VinciNo ratings yet
- Bike Lane CaseDocument3 pagesBike Lane CaseDodgeSanchezNo ratings yet
- 8 Accounting Books Journal and LedgersDocument17 pages8 Accounting Books Journal and LedgersJc Coronacion100% (3)
- Furnace PDFDocument9 pagesFurnace PDFBilalNo ratings yet
- Books of AccountsDocument44 pagesBooks of AccountsChristine Mae BurgosNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 WK 2 Session 2 Journals and LedgersDocument43 pagesFabm1 WK 2 Session 2 Journals and LedgersDomingo Princess JoyNo ratings yet
- Books of AccountsDocument32 pagesBooks of AccountsMichael AngeloNo ratings yet
- AccountantsDocument15 pagesAccountantsJenny EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Book of Accounts WD ActivityDocument3 pagesBook of Accounts WD ActivityChristopher SelebioNo ratings yet
- Book of AccountsDocument8 pagesBook of AccountsJenny SaynoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 9 Books of AccountsDocument7 pagesLESSON 9 Books of AccountsUnamadable UnleomarableNo ratings yet
- Books of AccountsDocument31 pagesBooks of AccountsFerly Mae ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Special Journals Lecture No. 6Document25 pagesSpecial Journals Lecture No. 6Yuu100% (1)
- Module 7Document8 pagesModule 7Charissa Jamis ChingwaNo ratings yet
- Books of Accounts: A. JournalDocument3 pagesBooks of Accounts: A. JournalMylen Noel Elgincolin ManlapazNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9-Books of AccountsDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 9-Books of AccountsRichael Ann Delubio ZapantaNo ratings yet
- Accou Levele III 4-8Document31 pagesAccou Levele III 4-8embaendo27uNo ratings yet
- Accounting Books - Journal, Ledger and Trial BalanceDocument35 pagesAccounting Books - Journal, Ledger and Trial BalanceGhie Ragat100% (3)
- Books of AccountsDocument36 pagesBooks of AccountsLevi CorralNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Books of Accounts (Autosaved)Document22 pagesChapter 8. Books of Accounts (Autosaved)Ana BretañaNo ratings yet
- The Accounting SystemDocument6 pagesThe Accounting SystemSebastian FeuersteinNo ratings yet
- 4TH Reviewer (Fabm)Document13 pages4TH Reviewer (Fabm)Jihane TanogNo ratings yet
- Paete Science and Business College, Inc.: Course Code Course DescriptionDocument7 pagesPaete Science and Business College, Inc.: Course Code Course DescriptionRDC Clothing AvenueNo ratings yet
- Special JournalsDocument14 pagesSpecial JournalsCriziel Ann LealNo ratings yet
- Special JournalsDocument15 pagesSpecial JournalsJan Allyson BiagNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Journal Ledger and Trial BalanceDocument40 pagesPowerpoint Journal Ledger and Trial BalanceChris Iero-Way100% (1)
- Submitted By: Submitted To: TopicDocument4 pagesSubmitted By: Submitted To: TopicNavsNo ratings yet
- Simple Book KeepingDocument57 pagesSimple Book KeepinglagunzadjidNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Financial Accounting ConceptsDocument40 pagesCH-2 Financial Accounting Conceptsnemik007No ratings yet
- InventoryDocument9 pagesInventorychippNo ratings yet
- Recording of Transactions I Class 11 NotesDocument23 pagesRecording of Transactions I Class 11 NotesAshna vargheseNo ratings yet
- 09 12 Fabm1 Content1Document23 pages09 12 Fabm1 Content1Vicky Ann SoriaNo ratings yet
- The Accounting CycleDocument17 pagesThe Accounting Cycleyuvita prasadNo ratings yet
- FABM1 Quarter 1 Week 5Document27 pagesFABM1 Quarter 1 Week 5FERNANDO TAMZ2003No ratings yet
- JournalDocument9 pagesJournalchippNo ratings yet
- Source: 1. Sales JournalDocument3 pagesSource: 1. Sales JournalDonita SotolomboNo ratings yet
- SLK Fabm1 Week 6Document8 pagesSLK Fabm1 Week 6Mylene SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Books of Original EntriesDocument21 pagesBooks of Original EntriesMohamed Adil GibreelNo ratings yet
- Account ReportDocument23 pagesAccount ReportAzrahNo ratings yet
- FABM Q3 L5. SLEM 5 - W5 - 2S - Q3 - Books of AccountsDocument14 pagesFABM Q3 L5. SLEM 5 - W5 - 2S - Q3 - Books of AccountsSophia MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1 Module 9 - The Books of Accounts - Journals Part 1Document19 pagesAccounting 1 Module 9 - The Books of Accounts - Journals Part 1Blanche MargateNo ratings yet
- Auditing Report Final AnishDocument30 pagesAuditing Report Final AnishA. SheikNo ratings yet
- 2 - Account - IBBIDocument33 pages2 - Account - IBBIRajwinder Singh Bansal100% (1)
- Chapter IVDocument13 pagesChapter IVMariel OroNo ratings yet
- Subsidiary BooksDocument15 pagesSubsidiary BooksJohnPrajwalMendoncaNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 Handout 7 Chapter 7Document6 pagesFABM 1 Handout 7 Chapter 7christiancayago676No ratings yet
- Review of The Accounting ProcessDocument18 pagesReview of The Accounting ProcessRoyceNo ratings yet
- Types of Major Accounts: Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management 1Document5 pagesTypes of Major Accounts: Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management 1Vanessa Lou TorejasNo ratings yet
- Accountancy/Books of Prime Entry: Sales Day BookDocument5 pagesAccountancy/Books of Prime Entry: Sales Day BookKhulekani KumaloNo ratings yet
- Books of Original EntriesDocument27 pagesBooks of Original EntriesfunnkyarulNo ratings yet
- Summarized Accounts O Level NotesDocument17 pagesSummarized Accounts O Level NotesClaudius MuzimbaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Book of AccountsDocument5 pagesTopic 1 Book of AccountsRey ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Financial StatementsDocument60 pagesLec 3 Financial StatementsAyanChatterjee100% (1)
- What Is A Journal Entry in AccountingDocument20 pagesWhat Is A Journal Entry in AccountingIc Abacan100% (1)
- Chapter 6Document57 pagesChapter 6api-358995037100% (1)
- Metalanguage: BIG PICTURE IN FOCUS: SLO (7) Record The Transactions Using Special JournalsDocument13 pagesMetalanguage: BIG PICTURE IN FOCUS: SLO (7) Record The Transactions Using Special JournalsAllan LopezNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 Subsidiary BooksDocument10 pagesCh-4 Subsidiary BooksRujhan KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Types of Subsidiary Books Usually Maintained by A Firm?Document11 pagesWhat Are The Different Types of Subsidiary Books Usually Maintained by A Firm?sweet19girlNo ratings yet
- Module 3 CFAS PDFDocument7 pagesModule 3 CFAS PDFErmelyn GayoNo ratings yet
- SECRET SAUCE-WITH FORMATS - Aslevel - 2023Document81 pagesSECRET SAUCE-WITH FORMATS - Aslevel - 2023Anayah KhanNo ratings yet
- Subsidiary BooksDocument7 pagesSubsidiary BooksRajaRajeswari.LNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping And Accountancy Made Simple: For Owner Managed Businesses, Students And Young EntrepreneursFrom EverandBookkeeping And Accountancy Made Simple: For Owner Managed Businesses, Students And Young EntrepreneursNo ratings yet
- Benguet Pines and Alnus Trees CaseDocument3 pagesBenguet Pines and Alnus Trees CaseDodgeSanchezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Applied EconomicsDocument21 pagesLesson 2 - Applied EconomicsDodgeSanchezNo ratings yet
- The Accounting Cycle - Service Business: Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.DDocument41 pagesThe Accounting Cycle - Service Business: Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.DDodgeSanchezNo ratings yet
- Sulpicio Carvajal Vs CADocument3 pagesSulpicio Carvajal Vs CADodgeSanchezNo ratings yet
- Alyssa Locken Resume Jan 2021Document3 pagesAlyssa Locken Resume Jan 2021api-544203584No ratings yet
- Oim552-Lean Manufacturing Question BankDocument6 pagesOim552-Lean Manufacturing Question BankRaagul SNo ratings yet
- Nanomaterials HomeworkDocument5 pagesNanomaterials Homeworkafefiebfr100% (1)
- Boyle's Law Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageBoyle's Law Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Perske CRP Revision7Document14 pagesPerske CRP Revision7Greg ThomsonNo ratings yet
- IK Safety Morning TalkDocument4 pagesIK Safety Morning TalkYayanPristiadyfbqueeaslieeArekMoxerNo ratings yet
- Payslip Apr2020Document1 pagePayslip Apr2020Pinki Mitra DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Health Information SystemDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Health Information SystemAirishNo ratings yet
- Scott Cooley Lyric and Chord Songbook Volume OneDocument272 pagesScott Cooley Lyric and Chord Songbook Volume OneScott CooleyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Fabrication of Steel Girders For Field EngineersDocument55 pagesGuidelines For Fabrication of Steel Girders For Field EngineersradhakrishnangNo ratings yet
- Palma Review of Dependency Theory World Development 1978Document44 pagesPalma Review of Dependency Theory World Development 1978Juan Hermidas100% (1)
- "The Difference Between Horizontal and Vertical Organizations Is That VerticalDocument2 pages"The Difference Between Horizontal and Vertical Organizations Is That VerticalMARY ATHENA GUNDANNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument22 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and ArchitectureJannat HappyNo ratings yet
- FLIX Ticket 1069511041 PDFDocument2 pagesFLIX Ticket 1069511041 PDFAngela RedeiNo ratings yet
- International CompensationDocument39 pagesInternational CompensationyogaknNo ratings yet
- PMC Composites:,, Are Generally SmallDocument13 pagesPMC Composites:,, Are Generally SmallharnoorNo ratings yet
- FIRST SUMMATIVE TEST IN MEDIA First QuarterDocument2 pagesFIRST SUMMATIVE TEST IN MEDIA First QuarterRhaieyee ElNo ratings yet
- RFS UD Series DipoleDocument2 pagesRFS UD Series DipoleBryan PittmanNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of AlgorithmsDocument15 pagesAnalysis and Design of AlgorithmsShivani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Soc4396.501.11s Taught by Malinda Hicks (Meh033000)Document11 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Soc4396.501.11s Taught by Malinda Hicks (Meh033000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Boq of Dire Dawa Project Final Price AdjustedDocument67 pagesBoq of Dire Dawa Project Final Price Adjustedbings1997 BiniamNo ratings yet
- 5000 PDFDocument36 pages5000 PDFMohamed RashedNo ratings yet
- Automatic WateringDocument2 pagesAutomatic WateringkkaunNo ratings yet
- Job Knowledge 65Document5 pagesJob Knowledge 65Mehmet SoysalNo ratings yet
- Residence Time DistributionDocument13 pagesResidence Time DistributionWillykateKairuNo ratings yet
- D FM Cost User GuideDocument135 pagesD FM Cost User GuideUdaya RangaNaikNo ratings yet
- HLS PON FR12 TheNewConflictMgmt 102021 EdsDocument10 pagesHLS PON FR12 TheNewConflictMgmt 102021 Edskarishma PradhanNo ratings yet
Books of Accounts: Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.D
Books of Accounts: Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.D
Uploaded by
DodgeSanchez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views44 pagesThe document discusses various accounting journals and ledgers used to record financial transactions. It describes general and special journals like the cash receipts journal, cash disbursements journal, sales journal, and purchase journal. It also discusses the general ledger and subsidiary ledger, with the general ledger serving as the central record of accounts and controlling account that summarizes subsidiary ledgers.
Original Description:
Original Title
Books of Accounts
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various accounting journals and ledgers used to record financial transactions. It describes general and special journals like the cash receipts journal, cash disbursements journal, sales journal, and purchase journal. It also discusses the general ledger and subsidiary ledger, with the general ledger serving as the central record of accounts and controlling account that summarizes subsidiary ledgers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views44 pagesBooks of Accounts: Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.D
Books of Accounts: Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.D
Uploaded by
DodgeSanchezThe document discusses various accounting journals and ledgers used to record financial transactions. It describes general and special journals like the cash receipts journal, cash disbursements journal, sales journal, and purchase journal. It also discusses the general ledger and subsidiary ledger, with the general ledger serving as the central record of accounts and controlling account that summarizes subsidiary ledgers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 44
Books of Accounts
Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.D.
What is accounting
It is the process of identifying, recording, and
communicating economic events of an organization to
interested users.
What are the components of accounting
Identifying, recording, and communicating economic
events
JOURNAL
What is a Journal?
It is a record of financial transactions in order by date.
Traditionally, a journal has been defined as the book of
original entry. For each transaction the journal shows
the debit and credit effects on specific accounts.
What are the two types of Journal?
General journal and Special journal
What is A General Journal?
The general journal is the most basic journal. Typically, a
general journal has spaces for dates, account titles and
explanations, references, and two amount columns.
The journal makes several significant contributions to the
recording process:
• It discloses in one place the complete effects of a
transaction.
• It provides a chronological record of transactions.
• It helps to prevent or locate errors because the debit and
credit amounts for each entry can be easily compared.
What is A General Journal?
The Journalizing Process
Entering transaction data in the journal is known as
journalizing. Companies make separate journal entries for
each transaction. A complete entry consists of:
• The date of the transaction which is entered in the Date
column.
• The debit account title (that is, the account to be debited)
which is entered first at the extreme left margin of the column
headed “Account Titles and Explanation,” and the amount of
the debit is recorded in the Debit column.
The Journalizing Process
• The credit account title (that is, the account to be credited)
which is indented and entered on the next line in the column
headed “Account Titles and Explanation,” and the amount of
the credit is recorded in the Credit column.
• A brief explanation of the transaction which appears on the
line below the credit account title. A space is left between
journal entries. The blank space separates individual journal
entries and makes the entire journal easier to read.
The Journalizing Process
• The column titled Ref. (which stands for Reference)which is
left blank when the journal entry is made. This column is used
later when the journal entries are transferred to the ledger
accounts.
The Journalizing Process
September 1, 2015 Mr. Ken Yubemayn invested PHP500,000 in a
restaurant business by opening an account with Banco Wey Klero.
September 5, 2015 purchased kitchen appliances from James
Spaydir for his business amounting to PHP100,000 on account
supported by a note.
September 6, 2015 started his operations a made a sales for that
day amounting to PHP20,000.
September 7, 2015, Ken Yubemayn purchased a motorcycle costing
PHP80,000 for his business. He pays PHP30,000 cash and agrees to pay
the remaining PHP50,000 on account.
Answer on the board
Some entries involve only two accounts, one debit and one
credit. An entry like these is considered a simple entry. Some
transactions, however, require more than two accounts in
journalizing. An entry that requires three or more accounts is
a compound entry.
What is A Special Journal?
A special journal (also known as a specialized journal) is useful
in a manual accounting or bookkeeping system to reduce the
tedious task of recording both the debit and credit general
ledger account names and amounts in a general journal.
What is A Special Journal?
Some businesses encounter voluminous quantities of similar
and recurring transactions which may create congestion if
these transactions are recorded repeatedly in a single day or a
month in the general journal.
Take the case of our example above, if Ken Yubemayn will
record the sales per day using the Official Receipt or Cash
Sales Invoice issued, it would be unnecessary and impractical
to credit “sales” account repeatedly. In order to facilitate
efficient and practical recording of similar and recurring
transactions, a special journal is used.
What are the commonly used special
journals?
1. Cash Receipts Journal
2. Cash Disbursements Journal
3. Sales Journal (Sales on Account Journal)
4. Purchase Journal (Purchase on Account Journal)
What is a Cash Receipts Journal?
It is used to record transaction involving receipt or collection
of cash.
Cash Receipts Journal
• The date of the transaction is entered in the date column.
• A brief explanation of the transaction is entered in the
description column.
• The column titled Ref. (which stands for Reference) which is
left blank when the journal entry is made. This column is used
later when the journal entries are transferred to the ledger
accounts.
• The Debit Cash column represents the amount of cash
received for a particular transaction.
Cash Receipts Journal
• Major categories of receipts, such as cash sales and
collection of accounts receivable are provided with separate
columns. These transactions are frequent and repetitive items,
therefore a separate column is provided.
• The column sundry is used for various miscellaneous and
less regular items, such as capital investment, receipt of loan
proceeds, among others.
What is the source document for this journal?
The source document for this journal is the Official Receipts or
Cash Receipts issued by the business.
What is a Cash Disbursements Journal?
It is the opposite of the cash receipts journal. It is the journal
where all cash payments are recorded.
Cash Disbursements Journal
• The date of the transaction is entered in the date column.
• A brief explanation of the transaction is entered in the
description column.
• The column titled Ref. (which stands for Reference) which is
left blank when the journal entry is made. This column is used
later when the journal entries are transferred to the ledger
accounts.
Cash Disbursements Journal
• The Check or Voucher number represents the identifying
number of the check issued for the related cash payment.
Most of the time, a check or cash voucher accompanies the
disbursement. The voucher number may be used as the
alternative for this column.
• The Debit Cash column represents the amount of cash
received for a particular transaction.
• Major categories of receipts, such cash sales and collection
of accounts receivable are provided with separate columns.
These transactions are frequent and repetitive items,
therefore a separate column is provided.
Cash Disbursements Journal
• The column sundry is used for various miscellaneous and
less regular items, such as capital investment, receipt of loan
proceeds, among others.
What is the source document for this journal?
The source documents used to update this journal are the
Check Voucher or Cash Voucher, Cash Receipts or Official
Receipts from suppliers or vendors.
What is a Sales Journal?
The Sales Journal or Sales on Account Journal is used in
recording several sales transactions on account.
Sales Journal (Sales on Account Journal)
• The date of the transaction is entered in the date column.
• A brief explanation of the transaction is entered in the
description column or the name of the customer.
• The column titled Ref. (which stands for Reference) which is
left blank when the journal entry is made. This column is used
later when the journal entries are transferred to the ledger
accounts.
• The Charge Invoice Number or Sales Invoice Number
represents the identifying number of the source document
issued to the customer when the sale was made.
Sales Journal (Sales on Account Journal)
• The Debit Accounts Receivable column represents the
amount of the sale transactions indicated in the charge
invoice.
• The Credit Sales column represents the amount of the sale
transactions indicated in the charge invoice.
What is the source document for this journal?
The source document for this journal is the Charge Invoice
issued by the business.
What is a Purchase Journal?
The Purchase journal or the Purchases on Account Journal is
used to record recurring transactions of purchases on account.
Purchase Journal (Purchase on Account
Journal)
• The date of the transaction is entered in the date column.
• A brief explanation of the transaction is entered in the
description column or the name of the supplier.
• The column titled Ref. (which stands for Reference) which is
left blank when the journal entry is made. This column is used
later when the journal entries are transferred to the ledger
accounts.
Purchase Journal (Purchase on Account
Journal)
• The Charge Invoice Number or Sales Invoice Number
represents the identifying number of the source document
issued by the supplier when the items, goods or merchandise
were delivered to the company when the purchase was made.
• The Debit Purchases column represents the amount of the
goods purchases as indicated in the charge invoice from the
supplier
• The Credit Accounts Payable column represents the amount
of the goods or items purchased on credit from the supplier.
The amount is indicated in the charge invoice issued by the
supplier.
What is the source document for this journal?
The source document for this journal is the Charge Invoice
from the supplier or vendor.
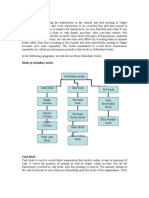
ledger
What is a Ledger?
The ledger refers to the accounting book in which the
accounts and their related amounts as recorded in the
journal are posted periodically. The ledger is also called
the ‘book of final entry’ because all the balances in the
ledger are used in the preparation of financial
statements. This is also referred to as the T-Account
because the basic form of a ledger is like the letter ‘T’.
What are the two kinds of ledger?
General ledger and Subsidiary ledger
What is a General Ledger?
The general ledger (commonly referred by accounting
professionals as GL) is a grouping of all accounts used
in the preparation of financial statements.
The GL is a controlling account because it summarizes
all the activities that have taken place as recorded in its
subsidiary ledger.
What is a General Ledger?
General Ledger
• The account portion refers to the account title for example:
cash, accounts receivable.
• The account number is an assigned number for each account
title to facilitate ease in recording and cross-referencing.
• The Date column identifies when the transaction happened.
• The item represents the source journal and the nature of the
transactions
General Ledger
• The Reference identifies the page number of the general our
special journal from which the information was taken.
• The Debit and Credit columns are used in recording the amount
of transactions from the general journal or special journal.
• The Balance Column represents the running balance of the
Account after considering the debit and credit amounts. If the
running balance amount is positive, the account has a debit
balance whereas if it has a negative running balance, the
accounts has a credit balance.
What is a Subsidiary Ledger?
A subsidiary ledger is a group of like accounts that
contains the independent data of a specific general
ledger. A subsidiary ledger is created or maintained if
individualized data is needed for a specific general
ledger account.
An example of a subsidiary ledger is the individual
record of various payables to suppliers. The total
amount of these subsidiary ledgers should equal the
balance in the Accounts Payable general ledger.
What is a Subsidiary Ledger?
Subsidiary Ledger
• The upper portion indicates the name and address of the
vendor or supplier.
• The vendor number is an assigned number for each vendor
as reference in keeping the records of a supplier.
• The Date column identifies when the transaction happened.
• The description column describes the nature of transaction.
• The Reference identifies the page number of the general our
special journal from which the information was taken.
Subsidiary Ledger
• The Debit and Credit columns reflect the various effects of
every transaction to the record of the supplier or vendor.
• The Balance column provides the running balance of every
supplier.
recap
You might also like
- The Online Poker Starting Guide (Frank Miller) PDFDocument39 pagesThe Online Poker Starting Guide (Frank Miller) PDFDe_VinciNo ratings yet
- Bike Lane CaseDocument3 pagesBike Lane CaseDodgeSanchezNo ratings yet
- 8 Accounting Books Journal and LedgersDocument17 pages8 Accounting Books Journal and LedgersJc Coronacion100% (3)
- Furnace PDFDocument9 pagesFurnace PDFBilalNo ratings yet
- Books of AccountsDocument44 pagesBooks of AccountsChristine Mae BurgosNo ratings yet
- Fabm1 WK 2 Session 2 Journals and LedgersDocument43 pagesFabm1 WK 2 Session 2 Journals and LedgersDomingo Princess JoyNo ratings yet
- Books of AccountsDocument32 pagesBooks of AccountsMichael AngeloNo ratings yet
- AccountantsDocument15 pagesAccountantsJenny EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Book of Accounts WD ActivityDocument3 pagesBook of Accounts WD ActivityChristopher SelebioNo ratings yet
- Book of AccountsDocument8 pagesBook of AccountsJenny SaynoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 9 Books of AccountsDocument7 pagesLESSON 9 Books of AccountsUnamadable UnleomarableNo ratings yet
- Books of AccountsDocument31 pagesBooks of AccountsFerly Mae ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Special Journals Lecture No. 6Document25 pagesSpecial Journals Lecture No. 6Yuu100% (1)
- Module 7Document8 pagesModule 7Charissa Jamis ChingwaNo ratings yet
- Books of Accounts: A. JournalDocument3 pagesBooks of Accounts: A. JournalMylen Noel Elgincolin ManlapazNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9-Books of AccountsDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 9-Books of AccountsRichael Ann Delubio ZapantaNo ratings yet
- Accou Levele III 4-8Document31 pagesAccou Levele III 4-8embaendo27uNo ratings yet
- Accounting Books - Journal, Ledger and Trial BalanceDocument35 pagesAccounting Books - Journal, Ledger and Trial BalanceGhie Ragat100% (3)
- Books of AccountsDocument36 pagesBooks of AccountsLevi CorralNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Books of Accounts (Autosaved)Document22 pagesChapter 8. Books of Accounts (Autosaved)Ana BretañaNo ratings yet
- The Accounting SystemDocument6 pagesThe Accounting SystemSebastian FeuersteinNo ratings yet
- 4TH Reviewer (Fabm)Document13 pages4TH Reviewer (Fabm)Jihane TanogNo ratings yet
- Paete Science and Business College, Inc.: Course Code Course DescriptionDocument7 pagesPaete Science and Business College, Inc.: Course Code Course DescriptionRDC Clothing AvenueNo ratings yet
- Special JournalsDocument14 pagesSpecial JournalsCriziel Ann LealNo ratings yet
- Special JournalsDocument15 pagesSpecial JournalsJan Allyson BiagNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Journal Ledger and Trial BalanceDocument40 pagesPowerpoint Journal Ledger and Trial BalanceChris Iero-Way100% (1)
- Submitted By: Submitted To: TopicDocument4 pagesSubmitted By: Submitted To: TopicNavsNo ratings yet
- Simple Book KeepingDocument57 pagesSimple Book KeepinglagunzadjidNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Financial Accounting ConceptsDocument40 pagesCH-2 Financial Accounting Conceptsnemik007No ratings yet
- InventoryDocument9 pagesInventorychippNo ratings yet
- Recording of Transactions I Class 11 NotesDocument23 pagesRecording of Transactions I Class 11 NotesAshna vargheseNo ratings yet
- 09 12 Fabm1 Content1Document23 pages09 12 Fabm1 Content1Vicky Ann SoriaNo ratings yet
- The Accounting CycleDocument17 pagesThe Accounting Cycleyuvita prasadNo ratings yet
- FABM1 Quarter 1 Week 5Document27 pagesFABM1 Quarter 1 Week 5FERNANDO TAMZ2003No ratings yet
- JournalDocument9 pagesJournalchippNo ratings yet
- Source: 1. Sales JournalDocument3 pagesSource: 1. Sales JournalDonita SotolomboNo ratings yet
- SLK Fabm1 Week 6Document8 pagesSLK Fabm1 Week 6Mylene SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Books of Original EntriesDocument21 pagesBooks of Original EntriesMohamed Adil GibreelNo ratings yet
- Account ReportDocument23 pagesAccount ReportAzrahNo ratings yet
- FABM Q3 L5. SLEM 5 - W5 - 2S - Q3 - Books of AccountsDocument14 pagesFABM Q3 L5. SLEM 5 - W5 - 2S - Q3 - Books of AccountsSophia MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1 Module 9 - The Books of Accounts - Journals Part 1Document19 pagesAccounting 1 Module 9 - The Books of Accounts - Journals Part 1Blanche MargateNo ratings yet
- Auditing Report Final AnishDocument30 pagesAuditing Report Final AnishA. SheikNo ratings yet
- 2 - Account - IBBIDocument33 pages2 - Account - IBBIRajwinder Singh Bansal100% (1)
- Chapter IVDocument13 pagesChapter IVMariel OroNo ratings yet
- Subsidiary BooksDocument15 pagesSubsidiary BooksJohnPrajwalMendoncaNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 Handout 7 Chapter 7Document6 pagesFABM 1 Handout 7 Chapter 7christiancayago676No ratings yet
- Review of The Accounting ProcessDocument18 pagesReview of The Accounting ProcessRoyceNo ratings yet
- Types of Major Accounts: Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management 1Document5 pagesTypes of Major Accounts: Fundamentals of Accountancy, Business, and Management 1Vanessa Lou TorejasNo ratings yet
- Accountancy/Books of Prime Entry: Sales Day BookDocument5 pagesAccountancy/Books of Prime Entry: Sales Day BookKhulekani KumaloNo ratings yet
- Books of Original EntriesDocument27 pagesBooks of Original EntriesfunnkyarulNo ratings yet
- Summarized Accounts O Level NotesDocument17 pagesSummarized Accounts O Level NotesClaudius MuzimbaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Book of AccountsDocument5 pagesTopic 1 Book of AccountsRey ViloriaNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Financial StatementsDocument60 pagesLec 3 Financial StatementsAyanChatterjee100% (1)
- What Is A Journal Entry in AccountingDocument20 pagesWhat Is A Journal Entry in AccountingIc Abacan100% (1)
- Chapter 6Document57 pagesChapter 6api-358995037100% (1)
- Metalanguage: BIG PICTURE IN FOCUS: SLO (7) Record The Transactions Using Special JournalsDocument13 pagesMetalanguage: BIG PICTURE IN FOCUS: SLO (7) Record The Transactions Using Special JournalsAllan LopezNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 Subsidiary BooksDocument10 pagesCh-4 Subsidiary BooksRujhan KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Types of Subsidiary Books Usually Maintained by A Firm?Document11 pagesWhat Are The Different Types of Subsidiary Books Usually Maintained by A Firm?sweet19girlNo ratings yet
- Module 3 CFAS PDFDocument7 pagesModule 3 CFAS PDFErmelyn GayoNo ratings yet
- SECRET SAUCE-WITH FORMATS - Aslevel - 2023Document81 pagesSECRET SAUCE-WITH FORMATS - Aslevel - 2023Anayah KhanNo ratings yet
- Subsidiary BooksDocument7 pagesSubsidiary BooksRajaRajeswari.LNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping And Accountancy Made Simple: For Owner Managed Businesses, Students And Young EntrepreneursFrom EverandBookkeeping And Accountancy Made Simple: For Owner Managed Businesses, Students And Young EntrepreneursNo ratings yet
- Benguet Pines and Alnus Trees CaseDocument3 pagesBenguet Pines and Alnus Trees CaseDodgeSanchezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Applied EconomicsDocument21 pagesLesson 2 - Applied EconomicsDodgeSanchezNo ratings yet
- The Accounting Cycle - Service Business: Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.DDocument41 pagesThe Accounting Cycle - Service Business: Rodmarc P. Sanchez, J.DDodgeSanchezNo ratings yet
- Sulpicio Carvajal Vs CADocument3 pagesSulpicio Carvajal Vs CADodgeSanchezNo ratings yet
- Alyssa Locken Resume Jan 2021Document3 pagesAlyssa Locken Resume Jan 2021api-544203584No ratings yet
- Oim552-Lean Manufacturing Question BankDocument6 pagesOim552-Lean Manufacturing Question BankRaagul SNo ratings yet
- Nanomaterials HomeworkDocument5 pagesNanomaterials Homeworkafefiebfr100% (1)
- Boyle's Law Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageBoyle's Law Problems and SolutionsBasic PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Perske CRP Revision7Document14 pagesPerske CRP Revision7Greg ThomsonNo ratings yet
- IK Safety Morning TalkDocument4 pagesIK Safety Morning TalkYayanPristiadyfbqueeaslieeArekMoxerNo ratings yet
- Payslip Apr2020Document1 pagePayslip Apr2020Pinki Mitra DasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Health Information SystemDocument36 pagesChapter 5 Health Information SystemAirishNo ratings yet
- Scott Cooley Lyric and Chord Songbook Volume OneDocument272 pagesScott Cooley Lyric and Chord Songbook Volume OneScott CooleyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Fabrication of Steel Girders For Field EngineersDocument55 pagesGuidelines For Fabrication of Steel Girders For Field EngineersradhakrishnangNo ratings yet
- Palma Review of Dependency Theory World Development 1978Document44 pagesPalma Review of Dependency Theory World Development 1978Juan Hermidas100% (1)
- "The Difference Between Horizontal and Vertical Organizations Is That VerticalDocument2 pages"The Difference Between Horizontal and Vertical Organizations Is That VerticalMARY ATHENA GUNDANNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Computer Organization and ArchitectureDocument22 pagesWilliam Stallings Computer Organization and ArchitectureJannat HappyNo ratings yet
- FLIX Ticket 1069511041 PDFDocument2 pagesFLIX Ticket 1069511041 PDFAngela RedeiNo ratings yet
- International CompensationDocument39 pagesInternational CompensationyogaknNo ratings yet
- PMC Composites:,, Are Generally SmallDocument13 pagesPMC Composites:,, Are Generally SmallharnoorNo ratings yet
- FIRST SUMMATIVE TEST IN MEDIA First QuarterDocument2 pagesFIRST SUMMATIVE TEST IN MEDIA First QuarterRhaieyee ElNo ratings yet
- RFS UD Series DipoleDocument2 pagesRFS UD Series DipoleBryan PittmanNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of AlgorithmsDocument15 pagesAnalysis and Design of AlgorithmsShivani SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Soc4396.501.11s Taught by Malinda Hicks (Meh033000)Document11 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For Soc4396.501.11s Taught by Malinda Hicks (Meh033000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupNo ratings yet
- Boq of Dire Dawa Project Final Price AdjustedDocument67 pagesBoq of Dire Dawa Project Final Price Adjustedbings1997 BiniamNo ratings yet
- 5000 PDFDocument36 pages5000 PDFMohamed RashedNo ratings yet
- Automatic WateringDocument2 pagesAutomatic WateringkkaunNo ratings yet
- Job Knowledge 65Document5 pagesJob Knowledge 65Mehmet SoysalNo ratings yet
- Residence Time DistributionDocument13 pagesResidence Time DistributionWillykateKairuNo ratings yet
- D FM Cost User GuideDocument135 pagesD FM Cost User GuideUdaya RangaNaikNo ratings yet
- HLS PON FR12 TheNewConflictMgmt 102021 EdsDocument10 pagesHLS PON FR12 TheNewConflictMgmt 102021 Edskarishma PradhanNo ratings yet