Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classification: Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
Classification: Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
Uploaded by
S. M. Abdullah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pages1. Trichostrongylus are small, slender nematodes that infect the gastrointestinal tract of various animals.
2. They have well developed copulatory bursae and spicules, and females have double ovejectors and bluntly tapered tails.
3. Eggs are oval, elongated and pointed, measuring 85-115 um, and contain many blastomeres that allow differentiation from other parasites.
Original Description:
Nematoda
Original Title
C03
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Trichostrongylus are small, slender nematodes that infect the gastrointestinal tract of various animals.
2. They have well developed copulatory bursae and spicules, and females have double ovejectors and bluntly tapered tails.
3. Eggs are oval, elongated and pointed, measuring 85-115 um, and contain many blastomeres that allow differentiation from other parasites.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pagesClassification: Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
Classification: Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
Uploaded by
S. M. Abdullah1. Trichostrongylus are small, slender nematodes that infect the gastrointestinal tract of various animals.
2. They have well developed copulatory bursae and spicules, and females have double ovejectors and bluntly tapered tails.
3. Eggs are oval, elongated and pointed, measuring 85-115 um, and contain many blastomeres that allow differentiation from other parasites.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Classification
Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species
Animalia Nematoda Secernentea Strongylida Trichostrongylidae
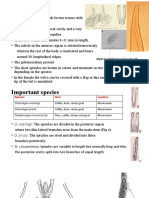
Trichostrongylus
1. T. axei
2. T. colubriformis
3. T. vitrinus
4. T. tenuis
1. Cattle, sheep, goat, deer, horse, pig Abomasum or stomach
2. Cattle, sheep, goat, camel, rabbit, pig, dog, human Duodenum, anterior small intestine
3. Sheep, goat, camel, deer, rabbit Duodenum, small intestine
4. Bird Small intestine, caeca
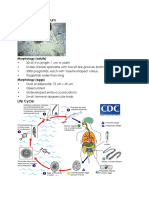
Morphology
• Adult: small, slightly reddish/brown in colour, slender and hair-like, usually less than 7.0 mm long
• No obvious buccal capsule and cephalic inflations are absent
• Well developed copulatory bursa present
• The spicules are thick and unbranched and a gubernaculum is present
• In the female, the tail is bluntly tapered and no vulval flap and the vulva opens a short distance
from the middle of the body.
• The females possess double ovejectors.
• Presence of excretory notch in the esophageal region
• Diagnosis: based on the observation of eggs in the faeces.
• The eggs are 85–115 um, oval, elongated, and pointed at one or both ends
• Contains many blastomeres
• The small poles are very similar and the side walls are parallel
[Trichostrongylus eggs must be differentiated from hookworm eggs, which are smaller and do
not have pointed ends.
Also differentiated from those of Ostertagia which have wider poles and more spherical walls]
Life cycle
Harmful effect
• Plaque of 1-2 cm in diameter in the site of infection
• increase in plasma pepsinogen level and hypoalbuminaemia
• C/S: rapid weight loss and diarrhoea
• Pathology:
• In sheep, extensive desquamation of the superficial epithelium of the mucosa.
• A mucoid hyperplasia is seen in the plaques
• Cellular infiltration of the lamina propria occurs,
• an influx of eosinophils and lymphocytes.
• Over time, infection can lead to a chronic proliferative inflammation and shallow depressed ulcers may
be present.
Treatment and control
• benzimidazoles, levamisole, an avermectin/milbemycin
• Use anthelmintics sparingly
• Use anthelmintics effectively
• Monitor for anthelmintic resistance
• Use the appropriate anthelmintic
• H
• Use effective quarantine procedures
• Use strategies to conserve susceptible worms
• Use strategies that reduce the reliance on anthelmintics
You might also like
- Ex 1-2 - Body Organization & MicroscopesDocument13 pagesEx 1-2 - Body Organization & Microscopesizabela0% (1)
- 6 Enzymes and Cellular Regulation-SDocument5 pages6 Enzymes and Cellular Regulation-Sapi-502781581No ratings yet
- Trichuris and TrichinellaDocument20 pagesTrichuris and TrichinellaDave RapaconNo ratings yet
- Medical Helminthology-CestodesDocument71 pagesMedical Helminthology-CestodesKAYISIRE EMERYNo ratings yet
- Non Soil Transmitted Helmints-1Document72 pagesNon Soil Transmitted Helmints-1Gladis Aprilla RizkiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 PDFDocument29 pagesLecture 16 PDFNa KhanNo ratings yet
- MP 11 Cestodes NewDocument46 pagesMP 11 Cestodes NewGenelyn Marquez100% (1)
- Helminth ParasitesDocument95 pagesHelminth ParasitesAngieNo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument34 pagesCestodesمصطفي خندقاويNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2.1 CestodesDocument73 pagesChapter 2.2.1 CestodesSufiyan AbduramanNo ratings yet
- Diseases Caused by TrypanosomesDocument34 pagesDiseases Caused by TrypanosomesAgochi CollinsNo ratings yet
- Outline: 1. General Characteristics of Platyhelminthes 2. Classification of Platyhelminthes 3. Cestodes 4. TrematodesDocument73 pagesOutline: 1. General Characteristics of Platyhelminthes 2. Classification of Platyhelminthes 3. Cestodes 4. TrematodesAsxe CeeNo ratings yet
- Material For Medicine pc2 StudentsDocument79 pagesMaterial For Medicine pc2 StudentskamaluNo ratings yet
- HOOKWORMSDocument47 pagesHOOKWORMSChipego ChiyaamaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Medically Significant NematodesDocument134 pagesClassification of Medically Significant Nematodesblue_blooded23100% (1)
- SK - Nematoda - 2 (Sem3)Document50 pagesSK - Nematoda - 2 (Sem3)Dianventi RiandaniNo ratings yet
- Medical Helminthology-NematodesDocument134 pagesMedical Helminthology-NematodesKAYISIRE EMERYNo ratings yet
- 12 - NematodaDocument44 pages12 - NematodaAnnisya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- 11 VPAR-55 Lec Superfamily-TrichostrongyloideaDocument39 pages11 VPAR-55 Lec Superfamily-TrichostrongyloideaLOUISE ANNE NAGALNo ratings yet
- Helminths: NematodesDocument17 pagesHelminths: NematodesNicolle PanchoNo ratings yet
- Intestinal NematodesDocument88 pagesIntestinal NematodesVincent Manganaan100% (1)
- Cestodes FinalDocument88 pagesCestodes FinalDexcel concepcionNo ratings yet
- TrichurisDocument34 pagesTrichurisayaamrsharfNo ratings yet
- Aphasmids 2Document3 pagesAphasmids 2Ivy FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Prof. DR Fahim ShaltoutDocument55 pagesProf. DR Fahim ShaltoutSumit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Taenia Solim - Taenia SaginataDocument27 pagesTaenia Solim - Taenia Saginata2253010837No ratings yet
- Taxonomic: StatusDocument14 pagesTaxonomic: StatusS. M. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document34 pagesLecture 16Nicolae ZdragusNo ratings yet
- Class Cestodes-Tape WormDocument46 pagesClass Cestodes-Tape WormRediat GossayeNo ratings yet
- Lec 2. GIT Parasitol Cestodes of SIDocument51 pagesLec 2. GIT Parasitol Cestodes of SIkareemosama9916No ratings yet
- Taenia Solium: Aritra Ghosh Roll No. 565Document15 pagesTaenia Solium: Aritra Ghosh Roll No. 565ARITRA GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Cestodes 1Document19 pagesCestodes 1ميمونه عبدالرحيم مصطفىNo ratings yet
- Cestode SDocument38 pagesCestode SJang JangNo ratings yet
- Parasit Trematode S Summer 2012Document29 pagesParasit Trematode S Summer 2012Budi AfriyansyahNo ratings yet
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument26 pagesPhylum PlatyhelminthesRen Zo ImpelidoNo ratings yet
- Ascaris, Trichuris, Oxyuris, Hookworm-2Document55 pagesAscaris, Trichuris, Oxyuris, Hookworm-2Mario EllNo ratings yet
- Unit - Three: HelminthsDocument177 pagesUnit - Three: HelminthsDembalu NuguseNo ratings yet
- 15 Theorical Entomology1Document91 pages15 Theorical Entomology1hhupNo ratings yet
- T. SaginataDocument11 pagesT. SaginataDorothyNo ratings yet
- RingwormsDocument5 pagesRingwormsCitrusNo ratings yet
- Hamster Biology HusbandryDocument39 pagesHamster Biology HusbandryKulenović Zlatan100% (1)
- Trichinella SpirDocument15 pagesTrichinella SpirBenjamin DanielNo ratings yet
- 2 NematodesDocument163 pages2 NematodesSammy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cestodes MorphDocument61 pagesCestodes MorphGilbert AggreyNo ratings yet
- Trichuris TrichiuraDocument13 pagesTrichuris TrichiuraAlvin LaurenceNo ratings yet
- Trichuriasis: Disease Type: Parasitic Disease Common Name: Causative Agent: Species of Trichuris Disease DiscriptionDocument9 pagesTrichuriasis: Disease Type: Parasitic Disease Common Name: Causative Agent: Species of Trichuris Disease DiscriptionBrijesh Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Nematodes Maricelle ManlutacDocument64 pagesIntestinal Nematodes Maricelle ManlutacGlanela ManalotoNo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument86 pagesCestodesPidchayathanakorn Paemika0% (1)
- Diphyllobothrium Latum: Morphology (Adults)Document11 pagesDiphyllobothrium Latum: Morphology (Adults)Sheana TmplNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes: Hazel Anne L. Tabo Olgga A. HaraDocument79 pagesPlatyhelminthes: Hazel Anne L. Tabo Olgga A. HaraHara OgheeNo ratings yet
- 28 Sept 16 Kuliah HelminthiasisDocument63 pages28 Sept 16 Kuliah HelminthiasisRafif AmirNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument9 pagesNematodesJessa MayNo ratings yet
- Whipworm 11 - (4) - .PDF - 2023.04.17 - 06.16.03pmDocument5 pagesWhipworm 11 - (4) - .PDF - 2023.04.17 - 06.16.03pmHussainNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة 4 مادة الطفيلياتDocument8 pagesالمحاضرة 4 مادة الطفيلياتdyabw6430No ratings yet
- Cestodes: Prepared By: Charriz A. AmoyanDocument37 pagesCestodes: Prepared By: Charriz A. AmoyanAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Lecture 2Document85 pagesParasitology Lecture 2Dr Sarah Bakhsh - Resident FCPS Community MedicineNo ratings yet
- Cestodes Lecture: Dr. Sulaiman LakohDocument53 pagesCestodes Lecture: Dr. Sulaiman LakohAbubakar JallohNo ratings yet
- Oecophorine Genera of Australia I: The Wingia Group (Lepidoptera: Oecophoridae)From EverandOecophorine Genera of Australia I: The Wingia Group (Lepidoptera: Oecophoridae)No ratings yet
- Notes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentFrom EverandNotes on Diseases of Cattle: Cause, Symptoms and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- Stomach Hair Worm Brown Stomach Worm Barber's Pole Worm: Trichostrongylus Ostertagia HaemonchusDocument11 pagesStomach Hair Worm Brown Stomach Worm Barber's Pole Worm: Trichostrongylus Ostertagia HaemonchusS. M. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Ostertagia: Elliptical, Slightly Barrel Shaped WallsDocument10 pagesOstertagia: Elliptical, Slightly Barrel Shaped WallsS. M. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Taxonomic: StatusDocument14 pagesTaxonomic: StatusS. M. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Course Learning Outcomes: The Major Learning Outcomes of This Course Are ToDocument7 pagesCourse Learning Outcomes: The Major Learning Outcomes of This Course Are ToS. M. AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Activity 2. Warning Signs That You Should Know in The LaboratoryDocument3 pagesActivity 2. Warning Signs That You Should Know in The LaboratoryMaryaa Luwizaa Allauigan0% (1)
- Diversity of Butterflies - Lepidoptera Insecta - From New Nagzira Wildlife Sanctuary Zone III in NNTR, Maharashtra, IndiaDocument6 pagesDiversity of Butterflies - Lepidoptera Insecta - From New Nagzira Wildlife Sanctuary Zone III in NNTR, Maharashtra, IndiaESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and ConservaionNo ratings yet
- Yield and Nutrient Content of Tomato As Influenced by The Application of Vermicompost and Chemical FertilizersDocument8 pagesYield and Nutrient Content of Tomato As Influenced by The Application of Vermicompost and Chemical FertilizersJingky MarzanPurisima Lumauig SallicopNo ratings yet
- Nhli Thesis PrizeDocument4 pagesNhli Thesis PrizeSomeoneToWriteMyPaperUK100% (2)
- Molecular Mechanism of High Pressure Action On LupanineDocument6 pagesMolecular Mechanism of High Pressure Action On Lupanineruty_9_3No ratings yet
- Science Y4 DLPDocument15 pagesScience Y4 DLPRina Maizura100% (1)
- Pathophysiology On Types of ShockDocument4 pagesPathophysiology On Types of ShockJessa Mae Alforque AsentistaNo ratings yet
- Bacitracin A - C66H103N17O16S - PubChemDocument28 pagesBacitracin A - C66H103N17O16S - PubChempkl cipinangcempedakNo ratings yet
- I.C. The Connections and Interactions Among Living ThingsDocument23 pagesI.C. The Connections and Interactions Among Living ThingsDarwin Nool100% (1)
- Editiorial-Board JCLBDocument1 pageEditiorial-Board JCLBMauricio MoncadaNo ratings yet
- L5 Controlling ProcessesDocument28 pagesL5 Controlling ProcessesMawadda AljawadiNo ratings yet
- Important Traits in Farm AnimalsDocument5 pagesImportant Traits in Farm Animalsrohullah1979aNo ratings yet
- Unique and Common Traits in Mycorrhizal SymbiosesDocument12 pagesUnique and Common Traits in Mycorrhizal SymbiosesThắng Trần BảoNo ratings yet
- Probni Test 1. Godina - Ina KlipaDocument4 pagesProbni Test 1. Godina - Ina KlipaMickoNo ratings yet
- Applications of BiosystematicsDocument13 pagesApplications of BiosystematicsKrizia Corrine St. PeterNo ratings yet
- PPDocument4 pagesPPrameshNo ratings yet
- Plant Coordination and ControlDocument13 pagesPlant Coordination and ControlMarilyn GumeyiNo ratings yet
- Wetland and Its ConservationDocument4 pagesWetland and Its ConservationHarish RaasuNo ratings yet
- Silver in Wound TherapyDocument28 pagesSilver in Wound TherapyGreg Wilby100% (1)
- Introduction To MorphologyDocument17 pagesIntroduction To MorphologydibabasarNo ratings yet
- Bio Paper FinalDocument8 pagesBio Paper FinalNiem PhamNo ratings yet
- CalciumsDocument5 pagesCalciums786lailaNo ratings yet
- Hipotiroidisme Pasca Radioterapi Untuk Karsinoma NasofaringDocument28 pagesHipotiroidisme Pasca Radioterapi Untuk Karsinoma NasofaringDeandles WattimuryNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway Neonatal PneumoniaDocument4 pagesClinical Pathway Neonatal PneumoniaSHAINA ALIH. JUMAANINo ratings yet
- Lipstick Mystics Guide To Time Traveling ExcerptDocument26 pagesLipstick Mystics Guide To Time Traveling ExcerptVenkatesh Kumar100% (2)
- Blood Case 6Document12 pagesBlood Case 6إنعام الحفيانNo ratings yet
- CVS AssessmentDocument119 pagesCVS AssessmentAbdurehman AyeleNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Biology Biomolecules-2Document20 pagesNEET UG Biology Biomolecules-2VyjayanthiNo ratings yet