Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Preference Shares
Types of Preference Shares
Uploaded by
Manigandan SrinivasaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Preference Shares
Types of Preference Shares
Uploaded by
Manigandan SrinivasaCopyright:
Available Formats
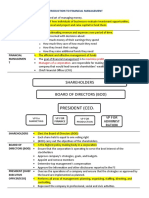
WHAT IS FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT? WHAT IS RETAINED EARNINGS? DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TRANSACTION AND SPECULATIVE MOTIVE?
Financial management refers to acquisition of funds and effective utilization of funds. Portion of profit which is not distributed in the form of dividends In transaction motive money is used for day-to-day transaction whereas in
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT SOURCES OF FUNDS? Readily available funds speculative motive money is hold to take advantage of unexpected
Term loans opportunities.
Used for emergency purpose
Equity shares WHAT IS CASH BUDGET?
Preference shares WHAT ARE THE OBJECTIVES OF FM? Estimation of cash inflow and outflow of a business over a specifies period
Debentures To ensure adequate and regular supply of funds of time. it can be weekly monthly or annually.
Retained Earnings Proper estimation of financial requirements DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DEBENTURES AND BONDS
WHAT IS EQUITY CAPITAL? Securing future by ensuring high return on investment Bonds are financial instruments showing indebtedness of issuing body
Also known as owner’s capital and they are the true owners of the company Profit maximization towards its holders. They are generally secured by collaterals and have low
They have voting rights Wealth maximization interest rates. Issued by government agencies financial institutions.
Have preemptive rights and have no tax benefit WHAT IS WEALTH MAXIMISATION? Whereas debentures are debt instruments used to raise long term
WHAT ARE PREEMPTIVE RIGHTS? One of the main objectives of FM is to maximize the SH’s wealth to achieve finance. They generally have high interest rates and can be both secured
It allows the existing shareholder of a company to avoid involuntary dilution of optimal capital structure (mix of debt and equity which maximizes company’s and unsecured. Issues by companies.
ownership by purchasing new shares before the public. market value and minimizes the cost of capital) and utilization of funds. DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DIVIDEND AND INTEREST
WHAT IS PREFERENCE SHARE CAPITAL? WHAT ARE ITS TYPES? Long term focus and this is less prone to manipulation. Interest is the charge against the money lent to the borrower.
Dividends are fixed as well as their payments are mandatory and the PS holders does It is based on generation of cash flow not on accounting profits A dividend is the percentage of profit distributed. Interest is paid to the
not have voting rights WHAT IS PROFIT MAXIMISATION? lenders/creditors/debenture holders. A dividend is paid to the preferred
Raised through PS It’s a traditional approach and is one of the important objectives of FM shareholders and equity shareholders.
Hybrid form of financing in which it has the certain characteristics of both equity Concerned with the determination of price and output level that returns DIFFERENCE BETWEEN OL AND CL
shares and debentures maximum profit. Operating leverage shows the effect of change in sales revenue on EBIT
Types of preference shares It implies that every decision which we take in the company gives profit. and financial leverage shows the effect of change in EBIT on
Convertible PS – converted into ES HOW TO CALCULATE % CHANGE IN EPS EPS. ... Combined leverage shows the effect of change in sales revenue on
Non-Convertible PS – %change in EPS = (NEW EPS – OLD EPS) /OLD EPS EPS of a company. Combined leverage is calculated as the multiplication
Participating PS - pay both preferred dividends and additional dividends to the SH of Operating leverage and Financial Leverage.
Non-Participating PS HOW TO CALCULATE % CHANGE IN EBIT DIFFERENCE BETWEEN OL AND FL
Cumulative PS %change in EBIT = (New EBIT – Old EBIT) /Old EBIT OL is the firms ability to use fixed cost to generate more returns whereas
Non-Cumulative PS OPERATING PROFIT also called as EBIT FL is the firm’s ability to use capital structure to earn better returns and to
WHAT ARE DEBENTURES? WHAT ARE ITS FEATURES AND TYPES? WHAT IS THE FORMULA FOR ROI? reduce tax
Borrowed capital from the public and the payment of interest is compulsory. ROI (Return on investment) = (Operating profit or EBIT/Total investment) X100 DIFFERENCE BETWEEN EPS AND DIVIDENDS
There is tax benefit associated with the payment of interest Total investment = Equity capital + Debt capital Both reflections of the company’s profitability. . Earnings per share is a
Does not result in dilution of control WHAT IS ASSET TURNOVER RATIO? gauge of how profitable a company is per share of its stock. Dividends per
Types of debentures is the ratio between the value of a company’s sales or revenues and the value of share, on the other hand, measures the portion of a company's earnings
Redeemable its assets. It is an indicator of the efficiency with which a company is deploying its that is paid out to shareholders.
Non-Redeemable assets to produce the revenue. HOW CAN YOU SAY COMPANY IS HAVING FAVOURABLE LEVERAGE?
Secured ATR = Sale/Total assets When ROI is greater than Cost of capital
Unsecured Total assets = total liabilities DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FINANCE AND ACCOUNTING
Convertible Total liabilities = Equity capital + Debt capital Accounting focuses on the day-to-day flow of money in and out of a
Non-convertible HOW TO FIND company or institution. It is responsible for preparing the financial
Leverages and types-it is the employment of fixed funds or borrowed funds to % Of VARIABLE COST = (variable /sales) X100 statement and is backward looking, whereas finance is a broader term for
generate greater profit. Operating leverage-measures percentage change in EBIT for a EBIT = Invested capital X ROI the management of assets and liabilities and the planning of future
given percentage change in sales.(contribution/EBIT) Financial leverage-measures WHAT IS SPECULATIVE MOTIVE? growth. It is responsible for preparing analyzing the financial statement
percentage change in EPS for a given percentage change in EBIT.(EBIT/EBT) Combined Hold cash to take advantage of unexpected opportunities. and is forward looking.
leverage-measures percentage change in EPS for a given percentage change in sales WHAT IS BUDGET DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TRANSACTION AND PRECAUTIONARY MOTIVE
(OL*FL). Estimating the future cash flow. In case of transaction motive, money is held for ordinary transactions,
WHAT ARE THE FUNCTIONS OF FM? WHAT ARE TYPES OF MOTIVES while under precautionary motive, cash is kept to meet
Estimating the amount of capital required for different needs. Transaction Motive unforeseen transactions. ... In general, the cash balances held
Managing the inflow and outflow of cash Precautionary motive for transaction and precautionary motives are directly dependent on the
Effectively utilizing the funds needed Speculative motive level of income.
Procurement of funds WHY IS CASH BUDGET PREPARED? WHAT ARE ITS MOTIVES? ROI = (EBIT/TOTAL INVESTMENT)*100
DEBENTIURES CAN BE DILUTED WHY? Cash budget is prepared to show all the planned monthly cash inflow and any EBT = EBIT – INTEREST
It cannot be diluted because debenture holders does not have any voting rights. planned cash outflow. This helps the business in taking better decisions. EBIT = CAPITAL INVESTED * ROI
WHAT IS TERM LOAN? Transaction motive TOTAL INVESTMENT = EQUITY CAPTIAL + DEBT CAPITAL
Money borrowed from the financial institutions Speculative motive
Precautionary motive ( to keep extra cash in case of unforeseen situations.)
You might also like
- Dentist Chart of AccountDocument4 pagesDentist Chart of AccountrajawhbNo ratings yet
- Data Domain Operating System Command Reference Guide, 5.7Document392 pagesData Domain Operating System Command Reference Guide, 5.7FatihNo ratings yet
- Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives, 8th Edition, 1Document25 pagesOptions, Futures, and Other Derivatives, 8th Edition, 1Anissa Nurlia KusumaningtyasNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Intro To Bus FinDocument38 pagesWeek 2 - Intro To Bus FinKim Patrick VictoriaNo ratings yet
- SCF PPT 1Document22 pagesSCF PPT 1Tanisha DoshiNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document20 pagesCH 6Gizaw BelayNo ratings yet
- CityU - Chapter 1 Intro To CF - STDDocument34 pagesCityU - Chapter 1 Intro To CF - STDNguyễn Đăng HiếuNo ratings yet
- Business Finance - INTRODUCTION-TO-FINANCIAL-MANAGEMENTDocument4 pagesBusiness Finance - INTRODUCTION-TO-FINANCIAL-MANAGEMENTArtemis LyNo ratings yet
- 4 Leverage in Cap StruDocument30 pages4 Leverage in Cap StruTatunNo ratings yet
- Slide 1Document24 pagesSlide 1Akash SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - LeverageDocument4 pagesChapter 5 - LeverageSteffany RoqueNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure and LeverageDocument19 pagesCapital Structure and Leverageemon hossainNo ratings yet
- Q.1. (E) Comparison ChartDocument19 pagesQ.1. (E) Comparison Chartshiv mehraNo ratings yet
- FM 3-4Document13 pagesFM 3-4shaik.712239No ratings yet
- Long Term Source FinalDocument43 pagesLong Term Source Finalsuparshva99iimNo ratings yet
- FM Unit 3Document20 pagesFM Unit 3chandru R (RE)No ratings yet
- Financial Filings and Annual Reports: Separating The Wheat From The ChaffDocument10 pagesFinancial Filings and Annual Reports: Separating The Wheat From The ChaffsuksesNo ratings yet
- FM Module 1Document362 pagesFM Module 1Ankita DebtaNo ratings yet
- Ringkasan Manajemen KeuanganDocument68 pagesRingkasan Manajemen KeuanganMira Alya SafiraNo ratings yet
- Finman ReviewerDocument6 pagesFinman ReviewerAlyssa ArenilloNo ratings yet
- FM Ii Handout-2Document85 pagesFM Ii Handout-2Fãhâd Õró ÂhmédNo ratings yet
- FM 1 Bba ViDocument52 pagesFM 1 Bba Vikhalil shaikhNo ratings yet
- Week 15 Risk ManagementDocument22 pagesWeek 15 Risk ManagementRay MundNo ratings yet
- Dav KPDocument14 pagesDav KPAcma Renu SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Scope and Objectives of Financial ManagementDocument23 pagesScope and Objectives of Financial ManagementAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- LeveragesDocument25 pagesLeveragesDilip YadavNo ratings yet
- Meaning Leverage: AccordingDocument5 pagesMeaning Leverage: AccordingSneha SenNo ratings yet
- 2380 BeerelDocument6 pages2380 BeerelWendy SequeirosNo ratings yet
- Financial MGT NotesDocument42 pagesFinancial MGT Notes匿匿No ratings yet
- LeverageDocument7 pagesLeverageChiranjeev RoutrayNo ratings yet
- Corpuz, Aily Bsbafm2 2 - ReviewquestionsDocument5 pagesCorpuz, Aily Bsbafm2 2 - ReviewquestionsAily CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance: Suresh HerurDocument49 pagesCorporate Finance: Suresh Herurlove_abhi_n_22No ratings yet
- Intoduction To Business Finance Lectue 1Document25 pagesIntoduction To Business Finance Lectue 1ummisaharanNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure - MAINDocument69 pagesCapital Structure - MAINSHASHANK TOMER 21211781No ratings yet
- 7 Important Financial Ratios To Know When Analyzing A Stock _ BankrateDocument8 pages7 Important Financial Ratios To Know When Analyzing A Stock _ BankrateAnkur ParshavNo ratings yet
- FRA DossierDocument94 pagesFRA DossierRNo ratings yet
- FM TheoryDocument23 pagesFM TheoryBhavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chpater-1 1.review of Literature Management:: - HenryfayolDocument49 pagesChpater-1 1.review of Literature Management:: - Henryfayolshaik karishmaNo ratings yet
- Socf With IllustrationDocument10 pagesSocf With IllustrationamirahNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance 2Document6 pagesCorporate Finance 2Zahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance 18MBA-201 (Semester - 2nd) : Presented byDocument17 pagesCorporate Finance 18MBA-201 (Semester - 2nd) : Presented bySahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Amity University Kolkata: Fundamentals of Financial ManagementDocument16 pagesAmity University Kolkata: Fundamentals of Financial ManagementSupratim RoychowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Equity Securities Market Final05272023Document39 pagesEquity Securities Market Final05272023Bea Bianca MadlaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology:: The Objectives For Which Study Has Been Undertaken AreDocument13 pagesResearch Methodology:: The Objectives For Which Study Has Been Undertaken Arearpita64No ratings yet
- Assignment Financial Institutes and Markets 24 11 2018Document7 pagesAssignment Financial Institutes and Markets 24 11 2018devang asherNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance BasicsDocument27 pagesCorporate Finance BasicsAhimbisibwe BenyaNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument11 pagesFinancial ManagementManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Dividend PolicyDocument9 pagesDividend PolicyrutujachoudeNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Bs 12Document15 pagesFinancial Management Bs 12Lavanya TyagiNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument9 pagesReviewerAngel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument34 pagesFinancial ManagementNuky Presiari DjajalaksanaNo ratings yet
- FM - 1Document15 pagesFM - 1akesingsNo ratings yet
- FM Chap1Document36 pagesFM Chap1Muntaha HaseenNo ratings yet
- Final Decision: Leverage - Nugraha WDocument14 pagesFinal Decision: Leverage - Nugraha WNugraha WijayantoNo ratings yet
- 0.3-Financial Statement AnalysisDocument26 pages0.3-Financial Statement AnalysisMatsuno ChifuyuNo ratings yet
- CF TheoryDocument7 pagesCF Theorybackup.harshilchoudharyNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance B40.2302 Lecture Notes: Packet 1: Aswath DamodaranDocument332 pagesCorporate Finance B40.2302 Lecture Notes: Packet 1: Aswath Damodaranset_hitNo ratings yet
- FM Cia 2120883 2120889 2120845Document18 pagesFM Cia 2120883 2120889 2120845GourishNo ratings yet
- Dividend Decision NotesDocument6 pagesDividend Decision NotesSavya SachiNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance in 30 Minutes: A Guide For Family Business Directors and ShareholdersDocument14 pagesCorporate Finance in 30 Minutes: A Guide For Family Business Directors and ShareholdersRohan S. PatilNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance - EliteDocument16 pagesCorporate Finance - EliteSrashti BrizawarNo ratings yet
- Free Cash Flow To Equity Discount ModelsDocument2 pagesFree Cash Flow To Equity Discount ModelsDavid Ignacio Berastain HurtadoNo ratings yet
- The Six Things of Culture: Membership Groups-The Head or Leader of The Group As Also The KeyDocument5 pagesThe Six Things of Culture: Membership Groups-The Head or Leader of The Group As Also The KeyManigandan SrinivasaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Brand Image, Brand Trust and Advertisement On Consumer Loyalty & Consumer Buying BehaviorDocument24 pagesImpact of Brand Image, Brand Trust and Advertisement On Consumer Loyalty & Consumer Buying BehaviorManigandan SrinivasaNo ratings yet
- The Taj'S People Philosophy and Star System: Presented byDocument20 pagesThe Taj'S People Philosophy and Star System: Presented byManigandan SrinivasaNo ratings yet
- Kushal Kala: Treasuring, Managing and Rewarding People Towards BettermentDocument9 pagesKushal Kala: Treasuring, Managing and Rewarding People Towards BettermentManigandan SrinivasaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Fundamentals: The Accounting Equation and The Double-Entry SystemDocument70 pagesAccounting Fundamentals: The Accounting Equation and The Double-Entry SystemAllana Mier100% (1)
- USCG Public Affairs ManualDocument192 pagesUSCG Public Affairs Manualcgreport100% (1)
- Corporate Legal Managing Counsel in Dallas TX Resume Alan WinnDocument3 pagesCorporate Legal Managing Counsel in Dallas TX Resume Alan WinnAlanWinnNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Philippine Public Procurement System - Volume IIIDocument31 pagesAssessment of The Philippine Public Procurement System - Volume IIIAlodia RiveraNo ratings yet
- Cabanatuan City: Coach ChaperonDocument38 pagesCabanatuan City: Coach ChaperonJayjay RonielNo ratings yet
- Crash Report 85853814 - Marco Island Police DepartmentDocument4 pagesCrash Report 85853814 - Marco Island Police DepartmentOmar Rodriguez OrtizNo ratings yet
- Computation FY 18-19 PDFDocument6 pagesComputation FY 18-19 PDFRuch JainNo ratings yet
- Dow CorningDocument3 pagesDow CorningRatih AriyaniNo ratings yet
- Immigration Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesImmigration Lesson PlanRaluca MihalacheNo ratings yet
- S.R. Bommai v. Union of India: CritiqueDocument4 pagesS.R. Bommai v. Union of India: Critiqueanon_913299743No ratings yet
- Legal Forms Letter Request For Lumpsum SupportDocument1 pageLegal Forms Letter Request For Lumpsum SupportIris Pauline TaganasNo ratings yet
- Student's HandbookDocument15 pagesStudent's HandbookMi Co100% (1)
- 77d8135f PDFDocument12 pages77d8135f PDFKhgdueve BuatsaihaNo ratings yet
- HDPE KT10000 HD Ép Dow Mfi 8Document3 pagesHDPE KT10000 HD Ép Dow Mfi 8Vishal RawlaniNo ratings yet
- Securities and Exchange Commission v. Heinen Et Al - Document No. 23Document3 pagesSecurities and Exchange Commission v. Heinen Et Al - Document No. 23Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Salary Slip (00890429 February, 2019)Document1 pageSalary Slip (00890429 February, 2019)shah fahadNo ratings yet
- Hanbali Sufi HistoryDocument10 pagesHanbali Sufi HistoryDawudIsrael1100% (1)
- Where To Buy Brother Products - Brother IndiaDocument3 pagesWhere To Buy Brother Products - Brother IndiaPradeep DeepuNo ratings yet
- University of Calcutta: B.A. LL.B. (Hons.)Document3 pagesUniversity of Calcutta: B.A. LL.B. (Hons.)Shivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Professional Issues in Social MediaDocument6 pagesProfessional Issues in Social Mediaxcloin GasmaskNo ratings yet
- Essay Fintech Vs Traditional Tech - Angela Putri KeziaDocument4 pagesEssay Fintech Vs Traditional Tech - Angela Putri KeziaAngela KeziaNo ratings yet
- Dow Jones V Contessa BourbonDocument11 pagesDow Jones V Contessa BourbonFindLawNo ratings yet
- Action Plan (Neap PDP)Document2 pagesAction Plan (Neap PDP)RACHEL ABE100% (1)
- Plaintiff Elizabeth Kogucki Brief in Support of Complaint For Administrative ReviewDocument16 pagesPlaintiff Elizabeth Kogucki Brief in Support of Complaint For Administrative ReviewGregory J. Bueche100% (1)
- N-10012-4-OPM-1501-0 Operation and Maintenance Manual Evaporation Section PDFDocument149 pagesN-10012-4-OPM-1501-0 Operation and Maintenance Manual Evaporation Section PDFmario feuilladeNo ratings yet
- Advanced Ledger Entry Service in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 For Public SectorDocument15 pagesAdvanced Ledger Entry Service in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 For Public SectorIbrahim Khaleel0% (1)
- Bar 2021 - Data Privacy ActDocument7 pagesBar 2021 - Data Privacy Act김비앙카No ratings yet