Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsAIDA Concept: Attention-Interest-Desire-Action
AIDA Concept: Attention-Interest-Desire-Action
Uploaded by
Sumukh KThis document discusses various marketing promotion strategies and tactics. It begins by introducing the AIDA model of attention, interest, desire, and action. It then discusses promotion strategies for primary and secondary markets. The remainder of the document outlines different types of advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, public relations and provides examples and evaluation metrics for each.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 2007 Subaru Forester Service Manual PDF DownloadDocument30 pages2007 Subaru Forester Service Manual PDF Downloadsen til80% (5)
- Social Media QuestionnaireDocument7 pagesSocial Media Questionnairevivek67% (3)
- Philippine Supreme Court Jurisprudence: Home Law Firm Law Library Laws JurisprudenceDocument43 pagesPhilippine Supreme Court Jurisprudence: Home Law Firm Law Library Laws Jurisprudencemae ann rodolfoNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- IB History Guide: Causes of The Great DepressionDocument2 pagesIB History Guide: Causes of The Great DepressionKatelyn CooperNo ratings yet
- Sales Promotion and Personal SellingDocument18 pagesSales Promotion and Personal Sellingabhi02021989No ratings yet
- Asp 1Document15 pagesAsp 1balmoori.aashritha21No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Marketing (MGT-210) : Publishing As Prentice HallDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Marketing (MGT-210) : Publishing As Prentice HallMazhar IqbalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communications: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument15 pagesAn Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communications: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinRamani A RautNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Marketing (MGT-210) : Mr. Abid SaeedDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Marketing (MGT-210) : Mr. Abid SaeedArvind MallikNo ratings yet
- Promo Selling PricingDocument19 pagesPromo Selling Pricingabhi7219No ratings yet
- New Product Development Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument22 pagesNew Product Development Life-Cycle StrategiesBakhtiyar KabirNo ratings yet
- Integrated Marketing CommunicationDocument33 pagesIntegrated Marketing CommunicationAnanthu GokulNo ratings yet
- Course Note For Class 11Document45 pagesCourse Note For Class 11박서희No ratings yet
- 05 Sales DevelopmentDocument10 pages05 Sales Developmentrode1234No ratings yet
- Sales Promotion: Personal Selling AdvertisingDocument24 pagesSales Promotion: Personal Selling AdvertisingmpdharmadhikariNo ratings yet
- IMC PptsDocument270 pagesIMC Pptssamaya pypNo ratings yet
- ,promotion MixDocument22 pages,promotion MixazharmalurNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Principles of MarketingDocument16 pagesCh-1 Principles of MarketingabebeMBANo ratings yet
- Personal Sell Pt4 Sales Promo 20dec04 n24Document24 pagesPersonal Sell Pt4 Sales Promo 20dec04 n24surajit88No ratings yet
- Keller's Brand Equity ModelDocument7 pagesKeller's Brand Equity ModelVM100% (1)
- Strategic Brand Management - Keller-Chapter 5 PDFDocument35 pagesStrategic Brand Management - Keller-Chapter 5 PDFHammert Runner60% (5)
- Chapter 9 PromotionDocument35 pagesChapter 9 PromotionSandeep RajbharNo ratings yet
- Advertising and Sales Promotion StrategyDocument39 pagesAdvertising and Sales Promotion Strategyshivakumar NNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document15 pagesLecture 1Moataz ElshafieNo ratings yet
- The Role of IMC in The Marketing ProcessDocument42 pagesThe Role of IMC in The Marketing ProcessRaghav BansalNo ratings yet
- David Ogilvy Defines Brands As "The Intangible Sum of A Product's Attributes: Its NameDocument5 pagesDavid Ogilvy Defines Brands As "The Intangible Sum of A Product's Attributes: Its NameRishab GoenkaNo ratings yet
- Promo Selling PricingDocument33 pagesPromo Selling PricingRAVINDRA Pr. SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Objectives SettingDocument38 pagesObjectives SettingShipranjali PandeyNo ratings yet
- BMKT525 Case 2Document5 pagesBMKT525 Case 2Lara HarbNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix: The 7P's of MarketingDocument31 pagesMarketing Mix: The 7P's of MarketingWild RiftNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Integrating Marketing Communications To Build Brand EquityDocument19 pagesCH 6 Integrating Marketing Communications To Build Brand EquitySifat Faridi (221051043)No ratings yet
- Advertising Planning and Strategy: "How, What, Where, When, Why"Document26 pagesAdvertising Planning and Strategy: "How, What, Where, When, Why"agraaru100% (2)
- Strategic Brand ManagementDocument35 pagesStrategic Brand ManagementKrishna Chaitanya MadipalliNo ratings yet
- Keller's Brand Equity ModelDocument5 pagesKeller's Brand Equity ModelAnand Verma100% (1)
- The Strategic Integrated Marketing Communication Planning ProcessDocument10 pagesThe Strategic Integrated Marketing Communication Planning Processally brownNo ratings yet
- Slide 18-7Document27 pagesSlide 18-7Rohit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Kotler Pom CW PPT Exp Ch04Document15 pagesKotler Pom CW PPT Exp Ch04uldsNo ratings yet
- Kotler Pom18 PPT 01.ppt StsDocument44 pagesKotler Pom18 PPT 01.ppt Stskhangvhse181669No ratings yet
- Unit - 5: Unit 5: Designing The Advertising Message LH 4Document29 pagesUnit - 5: Unit 5: Designing The Advertising Message LH 4Anjana SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Retail Communication and PromotionDocument26 pagesRetail Communication and Promotionsweety100% (1)
- Bma5531 PC 1340Document6 pagesBma5531 PC 1340Rizzy PopNo ratings yet
- Week 1 ADocument29 pagesWeek 1 AHuNtEr GamerYTNo ratings yet
- Goals & Objectives of Advt.Document28 pagesGoals & Objectives of Advt.Deepa_Subraman_8745No ratings yet
- (R) Imc To Buid Brand EquityDocument30 pages(R) Imc To Buid Brand EquityAbdul SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- The Consumer Decision Process: Roger D. Blackwell, Paul W. Miniard, and James F. Engel, Consumer Behavior, Ninth EditionDocument76 pagesThe Consumer Decision Process: Roger D. Blackwell, Paul W. Miniard, and James F. Engel, Consumer Behavior, Ninth EditionMohd GhaziNo ratings yet
- B2B BrandingDocument26 pagesB2B BrandingJawad Arshed100% (1)
- Presentation Topic1 Branding and PromotionDocument35 pagesPresentation Topic1 Branding and PromotionAbhisikta ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- AdvertisingDocument15 pagesAdvertisingraveendramanipalNo ratings yet
- Promotion and Pricing Strategies: Learn Ing G OalsDocument42 pagesPromotion and Pricing Strategies: Learn Ing G OalsCristine SaludoNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Brand ManagementDocument9 pagesAssignment of Brand ManagementMuhammad Taqi AdnanNo ratings yet
- Ad BudgetDocument27 pagesAd Budgetshalu golyanNo ratings yet
- Marketing PromotionDocument7 pagesMarketing PromotionJalal HossainNo ratings yet
- MM 15 Promotion 2019 Part 1 CDocument83 pagesMM 15 Promotion 2019 Part 1 CprabigyanNo ratings yet
- Preapproach and ApproachDocument24 pagesPreapproach and ApproachAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Marketing 4Document44 pagesAdvanced Marketing 4josepadNo ratings yet
- 5.2. New Product DevDocument15 pages5.2. New Product DevJillianne JillNo ratings yet
- Development and Role of Selling in MarketingDocument19 pagesDevelopment and Role of Selling in Marketing094005135No ratings yet
- Session 6 - Products, Services and Brands - Spring 2023Document32 pagesSession 6 - Products, Services and Brands - Spring 2023Ahmed ZakyNo ratings yet
- Actionable Selling Skills - Tools and Techniques Rationale 081222day1Document40 pagesActionable Selling Skills - Tools and Techniques Rationale 081222day1Abdul MomohNo ratings yet
- Brand EquityDocument3 pagesBrand EquityDevangi MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Your Market Analysis and Marketing Plan: Presented By: Cynthia Franklin Senior Associate Director, Berkley CenterDocument24 pagesYour Market Analysis and Marketing Plan: Presented By: Cynthia Franklin Senior Associate Director, Berkley CenterVijay RandhayeNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document38 pagesCH 1snehaNo ratings yet
- Create Demand for What You Sell: The 7 High-Impact StrategiesFrom EverandCreate Demand for What You Sell: The 7 High-Impact StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Profitable Promotions : A Blueprint for Entrepreneurial Advertising SuccessFrom EverandProfitable Promotions : A Blueprint for Entrepreneurial Advertising SuccessNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet As at March 31, 2017Document4 pagesBalance Sheet As at March 31, 2017Sumukh KNo ratings yet
- Assignment Group 2Document3 pagesAssignment Group 2Sumukh KNo ratings yet
- Conducting Brand Audits: Prepared By-K Sumukh 201407029Document7 pagesConducting Brand Audits: Prepared By-K Sumukh 201407029Sumukh KNo ratings yet
- What Are Customer Touchpoints?: BackgroundDocument7 pagesWhat Are Customer Touchpoints?: BackgroundSumukh KNo ratings yet
- Formal-Relational Query Languages: Practice ExercisesDocument4 pagesFormal-Relational Query Languages: Practice ExercisesDivyanshu BoseNo ratings yet
- ALKANSYADocument2 pagesALKANSYAkhiemonsNo ratings yet
- Sanjana C Mouli CS2Document2 pagesSanjana C Mouli CS2Sanjana MouliNo ratings yet
- Immersion ReviewerDocument29 pagesImmersion ReviewerMikyla RamilNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of InfotypesDocument8 pagesEnhancement of InfotypesAshok KancharlaNo ratings yet
- DigiIvy Products US 052814Document1 pageDigiIvy Products US 052814akiridino0% (1)
- Moot Proposition-1Document6 pagesMoot Proposition-1Councellor AjayNo ratings yet
- NXMS-630 - DatasheetDocument23 pagesNXMS-630 - DatasheetAdrian HolotteNo ratings yet
- Leon Cooperman's Letter To President To ObamaDocument3 pagesLeon Cooperman's Letter To President To ObamaLuis AhumadaNo ratings yet
- MelEye - CatalogDocument4 pagesMelEye - CatalogChinmay GhoshNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps To Take Before Choosing A CareerDocument8 pages7 Steps To Take Before Choosing A CareerJade LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Duo Check Valve MaintenanceDocument2 pagesDuo Check Valve Maintenanceddoyle1351100% (1)
- Nature of Judicial ProcessDocument10 pagesNature of Judicial ProcessSandesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Sir SoreÑo BOYAN Lesson Plan For TLE 7Document2 pagesSir SoreÑo BOYAN Lesson Plan For TLE 7REYMOND SUMAYLONo ratings yet
- New Kalwa High School, Kalwa, Thane: Gopalrao Patil Shikshan Prasarak Mandal'sDocument2 pagesNew Kalwa High School, Kalwa, Thane: Gopalrao Patil Shikshan Prasarak Mandal'sNil OnlyNo ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument1 pageChecklistLarrytate15100% (2)
- Task 3 - PPT TemplateDocument2 pagesTask 3 - PPT TemplateSaloni Jain 1820343No ratings yet
- Grhoma230818252 InvDocument2 pagesGrhoma230818252 InvZaldy PutraNo ratings yet
- Handbook TNSTC CbeDocument25 pagesHandbook TNSTC CbeAnonymous SEDun6PWNo ratings yet
- Police ProjectDocument15 pagesPolice ProjectArpit SinghalNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Achieving Customer Service ExcellenceDocument19 pagesBenefits of Achieving Customer Service ExcellencemuhamadNo ratings yet
- Salaries and Wages: Prepared By: Ms. Jaeneth D. SimondoDocument47 pagesSalaries and Wages: Prepared By: Ms. Jaeneth D. SimondoJenny Stypay100% (1)
- RLE MaterialsDocument22 pagesRLE MaterialsXan LopezNo ratings yet
- Management - Organization Structures and Change - Narrative ReportDocument10 pagesManagement - Organization Structures and Change - Narrative ReportRino SangariosNo ratings yet
- Extruder Presentation 2Document63 pagesExtruder Presentation 2Dede R BakhtiyarNo ratings yet
- FOP Unit-1 Part-1 (Introduction To Computer Programming)Document34 pagesFOP Unit-1 Part-1 (Introduction To Computer Programming)Viral PanchalNo ratings yet
AIDA Concept: Attention-Interest-Desire-Action
AIDA Concept: Attention-Interest-Desire-Action
Uploaded by
Sumukh K0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views16 pagesThis document discusses various marketing promotion strategies and tactics. It begins by introducing the AIDA model of attention, interest, desire, and action. It then discusses promotion strategies for primary and secondary markets. The remainder of the document outlines different types of advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, public relations and provides examples and evaluation metrics for each.
Original Description:
Original Title
120promotion_001
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses various marketing promotion strategies and tactics. It begins by introducing the AIDA model of attention, interest, desire, and action. It then discusses promotion strategies for primary and secondary markets. The remainder of the document outlines different types of advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, public relations and provides examples and evaluation metrics for each.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views16 pagesAIDA Concept: Attention-Interest-Desire-Action
AIDA Concept: Attention-Interest-Desire-Action
Uploaded by
Sumukh KThis document discusses various marketing promotion strategies and tactics. It begins by introducing the AIDA model of attention, interest, desire, and action. It then discusses promotion strategies for primary and secondary markets. The remainder of the document outlines different types of advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, public relations and provides examples and evaluation metrics for each.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
AIDA Concept
Attention-Interest-Desire-Action
Think
Feel
Do
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 1
Promotion Strategies for Primary
and Secondary Markets
Primary market – Demand for a product
category
Pioneering Advertising
Got Milk
Social issue marketing
“Kick the Can”
Drug Free America “Talk to your kids about
drugs”
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 2
Promotion Strategies for Primary
and Secondary Markets
Secondary market – Demand for a
brand
Challenge milk
Crystal milk
Sunnyside Select milk
Energy Star Label
Get Straight Drug Program
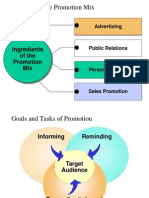
Entire Promotional Mix
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 3
Event Marketing
Effective Promotions for Events
Make media your partner
Premium item giveaways
Promote a sponsor/product
Entertainment
Cause-related promotions
Affinity-based promotions
Kids and pets never fail
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 4
Advertising
Types of Advertising
Institutional Advertising
Advocacy advertising
Comparative Advertising
Never use comparative advertising if you are
the market leader
Cooperative Advertising (vertical)
Competitive Advertising
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 5
Advertising
Advertising objectives
Awareness
Reminder to use
Change attitudes about use of the product
Change perceptions of importance of brand
attributes
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 6
Advertising
Advertising objectives
Attitude reinforcement
Product-line or corporate image building
Obtain a direct response
Process
Account sale representative
Account manager
Creative
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 7
Advertising
Process
Traffic
Media planning
Evaluation
CPM = cost of ad x 1000/circulation
Rating = program audience/total audience
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 8
Advertising
Evaluation
Reach - percentage of the target audience
that will be exposed to the message
Frequency - average number of times a
member of the target audience is exposed
to the message
Gross Rating points - reach percentage x
number of exposures
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 9
Advertising
Evaluation
Recognition tests
Recall tests
Theater tests
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 10
Sales Promotion
About 25% of each promotional dollar is
spent on sales promotion
Short-term results
Objectives
Inquiries - free gifts, mail-in coupon for
information, catalog offers, exhibits
Trial - coupons, free samples, contests,
premiums, demonstrations
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 11
Sales Promotion
Objectives
Repurchase - on-pack coupons, mail-in
rebates
Traffic building - special sales, weekly
specials, entertainment events, retailer
coupons
Increase rate of purchase - multipacks,
special price on twos
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 12
Sales Promotion
Objectives
Inventory building - return allowances,
slotting allowances
Promotional support - reusable display
cases, sales contests, merchandise
allowances
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 13
Sales Promotion
Evaluation
Redemption rates
Acquisition rates
Displacement rates
Conversion rates
Stock-up rates
Product-line effects
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 14
Personal Selling
About 50% of each promotional dollar
is spent on personal selling activities
Recruitment
Compensation
Evaluation
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 15
Public Relations
Less than 1% of each promotional dollar is
spent on public relations
Difficult to control and evaluate
Process
Set objectives
Identify target audience
Design message
Reach media that serves target audience
Write Press Release
Evaluate results
Kelley Fall 2004 Principles of Mark 16
You might also like
- 2007 Subaru Forester Service Manual PDF DownloadDocument30 pages2007 Subaru Forester Service Manual PDF Downloadsen til80% (5)
- Social Media QuestionnaireDocument7 pagesSocial Media Questionnairevivek67% (3)
- Philippine Supreme Court Jurisprudence: Home Law Firm Law Library Laws JurisprudenceDocument43 pagesPhilippine Supreme Court Jurisprudence: Home Law Firm Law Library Laws Jurisprudencemae ann rodolfoNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- IB History Guide: Causes of The Great DepressionDocument2 pagesIB History Guide: Causes of The Great DepressionKatelyn CooperNo ratings yet
- Sales Promotion and Personal SellingDocument18 pagesSales Promotion and Personal Sellingabhi02021989No ratings yet
- Asp 1Document15 pagesAsp 1balmoori.aashritha21No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Marketing (MGT-210) : Publishing As Prentice HallDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Marketing (MGT-210) : Publishing As Prentice HallMazhar IqbalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communications: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument15 pagesAn Introduction To Integrated Marketing Communications: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinRamani A RautNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Marketing (MGT-210) : Mr. Abid SaeedDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Marketing (MGT-210) : Mr. Abid SaeedArvind MallikNo ratings yet
- Promo Selling PricingDocument19 pagesPromo Selling Pricingabhi7219No ratings yet
- New Product Development Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument22 pagesNew Product Development Life-Cycle StrategiesBakhtiyar KabirNo ratings yet
- Integrated Marketing CommunicationDocument33 pagesIntegrated Marketing CommunicationAnanthu GokulNo ratings yet
- Course Note For Class 11Document45 pagesCourse Note For Class 11박서희No ratings yet
- 05 Sales DevelopmentDocument10 pages05 Sales Developmentrode1234No ratings yet
- Sales Promotion: Personal Selling AdvertisingDocument24 pagesSales Promotion: Personal Selling AdvertisingmpdharmadhikariNo ratings yet
- IMC PptsDocument270 pagesIMC Pptssamaya pypNo ratings yet
- ,promotion MixDocument22 pages,promotion MixazharmalurNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Principles of MarketingDocument16 pagesCh-1 Principles of MarketingabebeMBANo ratings yet
- Personal Sell Pt4 Sales Promo 20dec04 n24Document24 pagesPersonal Sell Pt4 Sales Promo 20dec04 n24surajit88No ratings yet
- Keller's Brand Equity ModelDocument7 pagesKeller's Brand Equity ModelVM100% (1)
- Strategic Brand Management - Keller-Chapter 5 PDFDocument35 pagesStrategic Brand Management - Keller-Chapter 5 PDFHammert Runner60% (5)
- Chapter 9 PromotionDocument35 pagesChapter 9 PromotionSandeep RajbharNo ratings yet
- Advertising and Sales Promotion StrategyDocument39 pagesAdvertising and Sales Promotion Strategyshivakumar NNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document15 pagesLecture 1Moataz ElshafieNo ratings yet
- The Role of IMC in The Marketing ProcessDocument42 pagesThe Role of IMC in The Marketing ProcessRaghav BansalNo ratings yet
- David Ogilvy Defines Brands As "The Intangible Sum of A Product's Attributes: Its NameDocument5 pagesDavid Ogilvy Defines Brands As "The Intangible Sum of A Product's Attributes: Its NameRishab GoenkaNo ratings yet
- Promo Selling PricingDocument33 pagesPromo Selling PricingRAVINDRA Pr. SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Objectives SettingDocument38 pagesObjectives SettingShipranjali PandeyNo ratings yet
- BMKT525 Case 2Document5 pagesBMKT525 Case 2Lara HarbNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix: The 7P's of MarketingDocument31 pagesMarketing Mix: The 7P's of MarketingWild RiftNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Integrating Marketing Communications To Build Brand EquityDocument19 pagesCH 6 Integrating Marketing Communications To Build Brand EquitySifat Faridi (221051043)No ratings yet
- Advertising Planning and Strategy: "How, What, Where, When, Why"Document26 pagesAdvertising Planning and Strategy: "How, What, Where, When, Why"agraaru100% (2)
- Strategic Brand ManagementDocument35 pagesStrategic Brand ManagementKrishna Chaitanya MadipalliNo ratings yet
- Keller's Brand Equity ModelDocument5 pagesKeller's Brand Equity ModelAnand Verma100% (1)
- The Strategic Integrated Marketing Communication Planning ProcessDocument10 pagesThe Strategic Integrated Marketing Communication Planning Processally brownNo ratings yet
- Slide 18-7Document27 pagesSlide 18-7Rohit JoshiNo ratings yet
- Kotler Pom CW PPT Exp Ch04Document15 pagesKotler Pom CW PPT Exp Ch04uldsNo ratings yet
- Kotler Pom18 PPT 01.ppt StsDocument44 pagesKotler Pom18 PPT 01.ppt Stskhangvhse181669No ratings yet
- Unit - 5: Unit 5: Designing The Advertising Message LH 4Document29 pagesUnit - 5: Unit 5: Designing The Advertising Message LH 4Anjana SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Retail Communication and PromotionDocument26 pagesRetail Communication and Promotionsweety100% (1)
- Bma5531 PC 1340Document6 pagesBma5531 PC 1340Rizzy PopNo ratings yet
- Week 1 ADocument29 pagesWeek 1 AHuNtEr GamerYTNo ratings yet
- Goals & Objectives of Advt.Document28 pagesGoals & Objectives of Advt.Deepa_Subraman_8745No ratings yet
- (R) Imc To Buid Brand EquityDocument30 pages(R) Imc To Buid Brand EquityAbdul SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- The Consumer Decision Process: Roger D. Blackwell, Paul W. Miniard, and James F. Engel, Consumer Behavior, Ninth EditionDocument76 pagesThe Consumer Decision Process: Roger D. Blackwell, Paul W. Miniard, and James F. Engel, Consumer Behavior, Ninth EditionMohd GhaziNo ratings yet
- B2B BrandingDocument26 pagesB2B BrandingJawad Arshed100% (1)
- Presentation Topic1 Branding and PromotionDocument35 pagesPresentation Topic1 Branding and PromotionAbhisikta ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- AdvertisingDocument15 pagesAdvertisingraveendramanipalNo ratings yet
- Promotion and Pricing Strategies: Learn Ing G OalsDocument42 pagesPromotion and Pricing Strategies: Learn Ing G OalsCristine SaludoNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Brand ManagementDocument9 pagesAssignment of Brand ManagementMuhammad Taqi AdnanNo ratings yet
- Ad BudgetDocument27 pagesAd Budgetshalu golyanNo ratings yet
- Marketing PromotionDocument7 pagesMarketing PromotionJalal HossainNo ratings yet
- MM 15 Promotion 2019 Part 1 CDocument83 pagesMM 15 Promotion 2019 Part 1 CprabigyanNo ratings yet
- Preapproach and ApproachDocument24 pagesPreapproach and ApproachAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Marketing 4Document44 pagesAdvanced Marketing 4josepadNo ratings yet
- 5.2. New Product DevDocument15 pages5.2. New Product DevJillianne JillNo ratings yet
- Development and Role of Selling in MarketingDocument19 pagesDevelopment and Role of Selling in Marketing094005135No ratings yet
- Session 6 - Products, Services and Brands - Spring 2023Document32 pagesSession 6 - Products, Services and Brands - Spring 2023Ahmed ZakyNo ratings yet
- Actionable Selling Skills - Tools and Techniques Rationale 081222day1Document40 pagesActionable Selling Skills - Tools and Techniques Rationale 081222day1Abdul MomohNo ratings yet
- Brand EquityDocument3 pagesBrand EquityDevangi MakwanaNo ratings yet
- Your Market Analysis and Marketing Plan: Presented By: Cynthia Franklin Senior Associate Director, Berkley CenterDocument24 pagesYour Market Analysis and Marketing Plan: Presented By: Cynthia Franklin Senior Associate Director, Berkley CenterVijay RandhayeNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document38 pagesCH 1snehaNo ratings yet
- Create Demand for What You Sell: The 7 High-Impact StrategiesFrom EverandCreate Demand for What You Sell: The 7 High-Impact StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Profitable Promotions : A Blueprint for Entrepreneurial Advertising SuccessFrom EverandProfitable Promotions : A Blueprint for Entrepreneurial Advertising SuccessNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet As at March 31, 2017Document4 pagesBalance Sheet As at March 31, 2017Sumukh KNo ratings yet
- Assignment Group 2Document3 pagesAssignment Group 2Sumukh KNo ratings yet
- Conducting Brand Audits: Prepared By-K Sumukh 201407029Document7 pagesConducting Brand Audits: Prepared By-K Sumukh 201407029Sumukh KNo ratings yet
- What Are Customer Touchpoints?: BackgroundDocument7 pagesWhat Are Customer Touchpoints?: BackgroundSumukh KNo ratings yet
- Formal-Relational Query Languages: Practice ExercisesDocument4 pagesFormal-Relational Query Languages: Practice ExercisesDivyanshu BoseNo ratings yet
- ALKANSYADocument2 pagesALKANSYAkhiemonsNo ratings yet
- Sanjana C Mouli CS2Document2 pagesSanjana C Mouli CS2Sanjana MouliNo ratings yet
- Immersion ReviewerDocument29 pagesImmersion ReviewerMikyla RamilNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of InfotypesDocument8 pagesEnhancement of InfotypesAshok KancharlaNo ratings yet
- DigiIvy Products US 052814Document1 pageDigiIvy Products US 052814akiridino0% (1)
- Moot Proposition-1Document6 pagesMoot Proposition-1Councellor AjayNo ratings yet
- NXMS-630 - DatasheetDocument23 pagesNXMS-630 - DatasheetAdrian HolotteNo ratings yet
- Leon Cooperman's Letter To President To ObamaDocument3 pagesLeon Cooperman's Letter To President To ObamaLuis AhumadaNo ratings yet
- MelEye - CatalogDocument4 pagesMelEye - CatalogChinmay GhoshNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps To Take Before Choosing A CareerDocument8 pages7 Steps To Take Before Choosing A CareerJade LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Duo Check Valve MaintenanceDocument2 pagesDuo Check Valve Maintenanceddoyle1351100% (1)
- Nature of Judicial ProcessDocument10 pagesNature of Judicial ProcessSandesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Sir SoreÑo BOYAN Lesson Plan For TLE 7Document2 pagesSir SoreÑo BOYAN Lesson Plan For TLE 7REYMOND SUMAYLONo ratings yet
- New Kalwa High School, Kalwa, Thane: Gopalrao Patil Shikshan Prasarak Mandal'sDocument2 pagesNew Kalwa High School, Kalwa, Thane: Gopalrao Patil Shikshan Prasarak Mandal'sNil OnlyNo ratings yet
- ChecklistDocument1 pageChecklistLarrytate15100% (2)
- Task 3 - PPT TemplateDocument2 pagesTask 3 - PPT TemplateSaloni Jain 1820343No ratings yet
- Grhoma230818252 InvDocument2 pagesGrhoma230818252 InvZaldy PutraNo ratings yet
- Handbook TNSTC CbeDocument25 pagesHandbook TNSTC CbeAnonymous SEDun6PWNo ratings yet
- Police ProjectDocument15 pagesPolice ProjectArpit SinghalNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Achieving Customer Service ExcellenceDocument19 pagesBenefits of Achieving Customer Service ExcellencemuhamadNo ratings yet
- Salaries and Wages: Prepared By: Ms. Jaeneth D. SimondoDocument47 pagesSalaries and Wages: Prepared By: Ms. Jaeneth D. SimondoJenny Stypay100% (1)
- RLE MaterialsDocument22 pagesRLE MaterialsXan LopezNo ratings yet
- Management - Organization Structures and Change - Narrative ReportDocument10 pagesManagement - Organization Structures and Change - Narrative ReportRino SangariosNo ratings yet
- Extruder Presentation 2Document63 pagesExtruder Presentation 2Dede R BakhtiyarNo ratings yet
- FOP Unit-1 Part-1 (Introduction To Computer Programming)Document34 pagesFOP Unit-1 Part-1 (Introduction To Computer Programming)Viral PanchalNo ratings yet