Professional Documents
Culture Documents
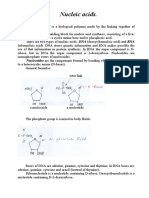
Nucleotides
Nucleotides
Uploaded by
Emm NomanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nucleotides
Nucleotides
Uploaded by
Emm NomanCopyright:
Available Formats
Peshawar Medical College
Nucleotides
Peshawar Medical College
Learning objectives
To explain what are nucleosides & nucleotides
To describe the components of nucleotides
To underline the functions of nucleotides
Peshawar Medical College
Nucleosides and nucleotides
(Components = Base + Sugar + Phosphate)
1. Bases
Nitrogenous, heterocyclic bases (purines & pyrimidines)
Numbering – in opposite direction
Single letter abbreviation (e.g. A,U)
Peshawar Medical College
Nucleosides and nucleotides
(Components = Base + Sugar + Phosphate)
Purine bases Pyrimidine bases
Peshawar Medical College
Tautomerism (keto-enol tautomerism)
amino form & oxo (keto) form
imino form & enol form
Amino & oxo (keto) forms are predominant under
physiologic conditions (suitable for base pairing)
Peshawar Medical College
Uncommon pyrimidine & purine bases
Peshawar Medical College
Components
2. Pentose sugar
Ribose De-oxy-ribose
Ribose or
de-oxy-ribose
Numbering with prime
Prefix “d” is used for
deoxy sugar
Peshawar Medical College
Components
3. Phosphate group attached to ( C5 or C3 of sugar)
through ester linkage
OH O-
- H+
HO – P = O HO – P = O
OH OH
Peshawar Medical College
Formation of Nucleotide
-N-glycosidic Phospho-ester-linkage
NB + Sugar linkage sugar–NB P –Sugar–NB
(nucleoside) PO4 Nucleotide or
Nucleoside- P
Adenine + ribose + phosphate = AMP
(Adenosine mono-phosphate)
dAMP & dGMP (DNA)
Peshawar Medical College
Syn & Anti configuration
Both “syn” and “anti” configurations occur in nucleotides
in nature but “anti” configuration predominates
(suitable for base pairing)
Peshawar Medical College
Bases, Nucleosides & Nucleotides
Base
Adenine
Guanine
Peshawar Medical College
Bases, Nucleosides & Nucleotides
Cytosine
Uracil
CH3 CH3
Thymine
Thymidine Thymidine monophosphate (TMP)
Peshawar Medical College
Polymerization of Mono-nucleotides
Mono-nucleotides are linked by 3 5 phospho-
diester bonds to form polynucleotides (having 5-end
on the left side and 3-end on right)
Written as
pG pG pA pC pT pA pA pC
Or
5 G G A C T A A C 3
Peshawar Medical College
Functions
Monomeric units or building blocks of nucleic acids
(RNA, DNA)
Energy-rich compounds (ATP, GTP)
Components of coenzymes (NAD, FAD, Co-A)
Involved in phosphate transfer reactions
(Glucose + ATP → Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP)
Peshawar Medical College
Functions
Involved in methyl transfer reactions
(S-adenosyl-methionine)
Serve as donors of sugars (UDP-Gal, UDP-GUA)
(biosynthesis of di- , oligo- , polysaccharides, GAGs)
Sulfate transfer reactions (PAPS or “active sulfate”)
(Phospho-adenosine-phospho-sulfate)
Peshawar Medical College
Functions
Serve as donors of lipids (CDP-acyl glycerol)
(lipid biosynthesis)
Inter-conversion of sugars
(UDP–Glucose UDP – Galactose)
Serve as second messengers (cAMP, cGMP)
Conjugation reaction (UDP-glucuronic acid)
Peshawar Medical College
Functions
Regulatory function
Control oxidative phosphorylation (through ADP)
ATP inhibits PFK-1 activity
As therapeutic agents (synthetic analogs)
To inhibit growth of cancer cells (Fluoro-uracil)
Treatment of gout (Allopurinol – a purine analog)
Treatment of AIDS
Suppressors of immune response during organ
transplantation
Peshawar Medical College
You might also like
- Prokaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheetDocument2 pagesProkaryote Vs Eukaryote WorksheetTaylor50% (2)
- NucleotidesDocument6 pagesNucleotidesDianne Ignacio100% (1)
- Presentacion EntenderDocument37 pagesPresentacion EntenderJuan David Marin ChiguachiNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules (Introduction, Structure and Functions) : Smita Rastogi & U. N. DwivediDocument39 pagesBiomolecules (Introduction, Structure and Functions) : Smita Rastogi & U. N. Dwivedipavan7443No ratings yet
- NucleotideDocument56 pagesNucleotideDhara NPNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Metabolism of Purines and PyrimidinesDocument11 pagesBiochemistry - Metabolism of Purines and PyrimidinesProjjal SanyalNo ratings yet
- Nucliec AcidsDocument135 pagesNucliec Acidsrmuktha6No ratings yet
- Biomedic I-Biochemistry: Department of Biochemistry. Faculty of Medicine Universitas HasanuddinDocument72 pagesBiomedic I-Biochemistry: Department of Biochemistry. Faculty of Medicine Universitas HasanuddinZafa AiharaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument55 pagesNucleic AcidsEmi gullNo ratings yet
- Molecules of HeredDocument82 pagesMolecules of HeredTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument24 pagesNucleic AcidReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of NucleoproteinsDocument71 pagesMetabolism of NucleoproteinsMi PatelNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide: Nucleotides Are Organic Molecules Consisting of A NucleosideDocument10 pagesNucleotide: Nucleotides Are Organic Molecules Consisting of A NucleosideMujahidul HasanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument30 pagesNucleic Acidjordanmusyoki19No ratings yet
- Lecture Note On BCH 202Document16 pagesLecture Note On BCH 202Muhammad LawalNo ratings yet
- Nuceic AcidsDocument124 pagesNuceic AcidsMohammed HasnatNo ratings yet
- Medical University - Plovdiv: Programme in Human Biology: 60 H. - Lecture Courses 40 H. - Practical CoursesDocument29 pagesMedical University - Plovdiv: Programme in Human Biology: 60 H. - Lecture Courses 40 H. - Practical CoursesShaima ShaheemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MBDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - MBMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- Chem & Import of Nucleotides11Document79 pagesChem & Import of Nucleotides11asaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Structure and FunctionDocument31 pagesNucleic Acid Structure and Functionsohamdasofficial02No ratings yet
- Purine Biosynthesis and RegulationDocument25 pagesPurine Biosynthesis and RegulationrivienaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesNucleic AcidAjagu ChukwuebukaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument5 pagesNucleic AcidsДмитрий МатвеевNo ratings yet
- Met Purin 28 OktDocument62 pagesMet Purin 28 OktXIID 67No ratings yet
- Metabolic Hemostasis MF PortionDocument68 pagesMetabolic Hemostasis MF PortionTsegaye HailuNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidetutbolobokNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of BiologyDocument45 pagesCentral Dogma of BiologyOdaiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument67 pagesNucleic AcidHeddy MyoiNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide BiochemDocument27 pagesNucleotide BiochemHarlyn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lec 20 Nucleotide MetabolismDocument44 pagesLec 20 Nucleotide MetabolismRamy El-HadadNo ratings yet
- Bio Lec 8 - Nucleic AcidDocument16 pagesBio Lec 8 - Nucleic AcidAbdul KabirNo ratings yet
- Study Guide T2 BioChem2Document12 pagesStudy Guide T2 BioChem2janeNo ratings yet
- Bio 99 Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesBio 99 Lecture NotesMohsin Ahmed FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Trans of Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry CH 32Document3 pagesTrans of Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry CH 32Richelle Dianne Ramos-Giang100% (1)
- Nucleotides: Synthesis And: DegradationDocument76 pagesNucleotides: Synthesis And: DegradationNike Prilil100% (1)
- 5 Nucleic AcidsDocument18 pages5 Nucleic Acidsaleyyn100% (1)
- Biochemistry of NUCLEIC ACIDDocument30 pagesBiochemistry of NUCLEIC ACIDZayan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) : Molecular BiologyDocument37 pagesPoly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) : Molecular BiologyMohammed FathyNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid 2Document3 pagesNucleic Acid 2JamiluNo ratings yet
- 2.nucleic Acids CompleteDocument91 pages2.nucleic Acids Completeazyhuang77No ratings yet
- 1 - Nucleic Acids Intro - ModuleDocument10 pages1 - Nucleic Acids Intro - ModuleMichaella CabanaNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides Chemistry and MetabolismDocument65 pagesNucleotides Chemistry and MetabolismSmiling AngelNo ratings yet
- 7 Introduction To Molecular Genetics-Part 1Document29 pages7 Introduction To Molecular Genetics-Part 1MarieFranz ChuaNo ratings yet
- Curs Nucleotide Sem 2Document58 pagesCurs Nucleotide Sem 2George PetreaNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNADocument62 pagesStructure of DNANikki SStarkNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 5Document9 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 5Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids 3Document40 pagesNucleotides and Nucleic Acids 3Alaa MohammadNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - Nucelic AcidsDocument96 pagesBiochemistry - Nucelic AcidsSandra OnceNo ratings yet
- VSU 2020 PPT Nucleic AcidDocument75 pagesVSU 2020 PPT Nucleic AcidAndreah BaylonNo ratings yet
- Nukleotida: Dr. I Dewa Ayu Susilawati, Drg. M. KesDocument33 pagesNukleotida: Dr. I Dewa Ayu Susilawati, Drg. M. KesIkatanti Ratna AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Protein and Nucleic Acid Metabolism 20182019 LectureDocument18 pagesAmino Acid Protein and Nucleic Acid Metabolism 20182019 LectureMwanja MosesNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Degra NuclotidesDocument58 pagesSynthesis and Degra Nuclotidesur.yared21No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Structure: Components of DNA and RNADocument18 pagesNucleic Acid Structure: Components of DNA and RNAShamaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of NucleotidesDocument28 pagesChemistry of Nucleotidesshadrack mungutiNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism (Unit 2)Document58 pagesMicrobial Metabolism (Unit 2)Roshini KuppiliNo ratings yet
- PUA Biochemistry II Lec 9Document5 pagesPUA Biochemistry II Lec 9CapWa7id 28No ratings yet
- NUS 123 NotesDocument14 pagesNUS 123 NotesBrevine Oduor OsoroNo ratings yet
- K Williams 1985 UP1 PNaSDocument5 pagesK Williams 1985 UP1 PNaSDolphingNo ratings yet
- Nucleosides: - Heterocyclic Nitrogen and Pentose Are Linked by N-Glycosidic BondDocument4 pagesNucleosides: - Heterocyclic Nitrogen and Pentose Are Linked by N-Glycosidic BondVitor MartinsNo ratings yet
- Key Functions:: Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument6 pagesKey Functions:: Fatty Acid SynthesisChui WaiNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Purine & PyrimidinesDocument28 pagesBiosynthesis of Purine & PyrimidinesEmm NomanNo ratings yet
- Absorption of LipidsDocument22 pagesAbsorption of LipidsEmm Noman100% (1)
- Fatty Acid OxidationDocument28 pagesFatty Acid OxidationEmm NomanNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument38 pagesFatty Acid SynthesisEmm NomanNo ratings yet
- Anatomyand Physiologyofthe Thoraciclymphatic SystemDocument15 pagesAnatomyand Physiologyofthe Thoraciclymphatic SystemLis Borda MuñozNo ratings yet
- GSSE Pathology NotesDocument120 pagesGSSE Pathology NotesEmilyNo ratings yet
- Barsanalina - Assignment For Chapter 16 Adaptive ImmunityDocument4 pagesBarsanalina - Assignment For Chapter 16 Adaptive ImmunityRalph B. BarsanalinaNo ratings yet
- The Beneficial Effects of Metformin On Cancer Prevention and Therapy: A Comprehensive Review of Recent AdvancesDocument19 pagesThe Beneficial Effects of Metformin On Cancer Prevention and Therapy: A Comprehensive Review of Recent AdvancesDeepanshu GoyalNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology Topical Question Bank - Taruvinga AdvertDocument69 pagesA Level Biology Topical Question Bank - Taruvinga Adverttanyaradzwa daison0% (1)
- Muscular - System - Lab - 2007 Goes With TourDocument22 pagesMuscular - System - Lab - 2007 Goes With TourBEA MAE VIADOYNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Reviewer 1Document18 pagesAnatomy Reviewer 1Jane EbascoNo ratings yet
- Reading Guide Honors Chapter 5 MembranesDocument2 pagesReading Guide Honors Chapter 5 MembranesAzraelNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in TLE (Wellness Massage) : Third Quarter-Week 4Document12 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in TLE (Wellness Massage) : Third Quarter-Week 4Kim Caguioa100% (3)
- WEEK 7 LAB EXERCISE - Muscular SystemDocument11 pagesWEEK 7 LAB EXERCISE - Muscular SystemMARY KATE L. CEBALLOSNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy TractsDocument7 pagesNeuroanatomy TractsLola PNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychDocument3 pagesDevelopmental PsychDOMINIQUE CALIMONNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesMale Reproductive SystemKBS100% (1)
- MINOR SURG Report SNAKE BITEDocument17 pagesMINOR SURG Report SNAKE BITENdor BariboloNo ratings yet
- Bio Investigation ProjectDocument19 pagesBio Investigation ProjectMr StarkNo ratings yet
- Neonatology: Addisu Aa (Lecturer, MSC in CM)Document35 pagesNeonatology: Addisu Aa (Lecturer, MSC in CM)Abiy AliyeNo ratings yet
- Breath SoundsDocument258 pagesBreath SoundsJose Dangali AlinaoNo ratings yet
- Hema Primary DisordersDocument13 pagesHema Primary DisordersMiki NishiharaNo ratings yet
- 19 ReproductiveDocument81 pages19 Reproductivej.a.salazar065No ratings yet
- Effect of Kundalini Yoga On Alpha MSHDocument2 pagesEffect of Kundalini Yoga On Alpha MSHUniversal Saints CommunityNo ratings yet
- Daily Test 1 - Cause and Effect, Explanation Text NAME: Nailiaveda Putri Cahyani Class: Xi Mipa 5 Date: Tuesday, 23 February 2021 A. Dialogue 1Document3 pagesDaily Test 1 - Cause and Effect, Explanation Text NAME: Nailiaveda Putri Cahyani Class: Xi Mipa 5 Date: Tuesday, 23 February 2021 A. Dialogue 1Nailia CahyaniNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis: "Descending Paralysis" (NMJ - Ai Destruction of Achr)Document39 pagesMyasthenia Gravis: "Descending Paralysis" (NMJ - Ai Destruction of Achr)Kim GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 05 - Master MyDLP Science (CH2) F1Document18 pages05 - Master MyDLP Science (CH2) F1PANG KEE TIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Echanical Sphyxia: HapterDocument16 pagesEchanical Sphyxia: HapterJRNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@s00253 019 10157 XDocument17 pages10.1007@s00253 019 10157 XRebollo Domínguez AlexisNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Practice Quiz Questions and AnswersDocument11 pagesEnzyme Practice Quiz Questions and AnswersMa Angelica Shane Navarro100% (1)
- Iron Deficiency Anemia GeneticsDocument21 pagesIron Deficiency Anemia GeneticsTammy BoudNo ratings yet
- The Ethological Approach To The Study of Human Behaviour - Zdenek KleinDocument5 pagesThe Ethological Approach To The Study of Human Behaviour - Zdenek KleinClaudio Angel RomeroNo ratings yet
- Clinical Lab Report - SampleDocument2 pagesClinical Lab Report - SampleeatpryNo ratings yet