Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neonatal Sepsis
Neonatal Sepsis
Uploaded by
Aisyah ShawtyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 8464 B 1H QP CombinedScienceTrilogy G 16may23 AMDocument32 pages8464 B 1H QP CombinedScienceTrilogy G 16may23 AMMatt A100% (3)
- ANAK (Full Permission)Document167 pagesANAK (Full Permission)anggyNo ratings yet
- 17 Jan - Paediatrics (DR Ashutosh) DAMS DVT 2022Document60 pages17 Jan - Paediatrics (DR Ashutosh) DAMS DVT 2022Lutfi HakimNo ratings yet
- (PESERTA) PEDIATRI 2 - MANTAP Februari 2017 PDFDocument157 pages(PESERTA) PEDIATRI 2 - MANTAP Februari 2017 PDFmarcelinaNo ratings yet
- Pediatri 2Document165 pagesPediatri 2YUYUM100% (2)
- Neonatal SepsisDocument7 pagesNeonatal SepsisTadesse MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Cmca Assignment #3Document3 pagesCmca Assignment #3Ayanami PascuaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric GastroenteritisDocument6 pagesPaediatric GastroenteritisANKITA RCHAWLANo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument20 pagesNeonatal SepsisNilanduniNo ratings yet
- Common Problems: in Newborn InfantDocument94 pagesCommon Problems: in Newborn InfantAhmad JustNo ratings yet
- Sepsis PowerPointDocument49 pagesSepsis PowerPointWonyenghitari GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Transient Tachypneu of The Newborn: Supervisor: Dr. Nazardi Oyong Sp. ADocument57 pagesTransient Tachypneu of The Newborn: Supervisor: Dr. Nazardi Oyong Sp. AWella FadillahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress in NewbornDocument54 pagesRespiratory Distress in NewbornAgi Azhari SandiniNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis: Definition & IncidenceDocument8 pagesNeonatal Sepsis: Definition & IncidenceahmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture On High Risk NewbornDocument51 pagesLecture On High Risk NewbornBilly RayNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress in Newborn: Presented By: Dr. Walaa MousaDocument74 pagesRespiratory Distress in Newborn: Presented By: Dr. Walaa MousasalamredNo ratings yet
- Management of Neonatal Sepsis: Niki Kosmetatos, MD Anthony Piazza, MD J. Devn Cornish, MDDocument30 pagesManagement of Neonatal Sepsis: Niki Kosmetatos, MD Anthony Piazza, MD J. Devn Cornish, MDiniidzniNo ratings yet
- Danger Signs in NewbornDocument8 pagesDanger Signs in NewbornPrabhu MagudeeswaranNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Respiratory Dist.7476158.PowerpointDocument21 pagesNeonatal Respiratory Dist.7476158.PowerpointtyapalupiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress in Newborn FinalDocument22 pagesRespiratory Distress in Newborn FinalajayganeshjNo ratings yet
- Kejang Demam Sederhana Ec - FaringitisDocument30 pagesKejang Demam Sederhana Ec - FaringitisPramita RukmanaNo ratings yet
- Danger Signs in Newborn DR Varsha Atul ShahDocument22 pagesDanger Signs in Newborn DR Varsha Atul ShahRSU ALFUADI BINJAINo ratings yet
- Management of Neonatal SepsisDocument30 pagesManagement of Neonatal SepsisRam krishnaNo ratings yet
- PPT HMDDocument60 pagesPPT HMDadityaNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care LectureDocument65 pagesNewborn Care LectureNichole daFonsecaNo ratings yet
- The Normal Newborn: Assessment and CareDocument71 pagesThe Normal Newborn: Assessment and CareElla Maica RacmanNo ratings yet
- Common Neonatal Disorders 5Document28 pagesCommon Neonatal Disorders 5Laishram Deeva ChanuNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Notes - Moodle/Text: Paediatric Emergencies (Textbook Ch.5)Document6 pagesPaediatric Notes - Moodle/Text: Paediatric Emergencies (Textbook Ch.5)Jana AldourNo ratings yet
- PCAP Report - Mark ReyesDocument53 pagesPCAP Report - Mark ReyesMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- PCAP Report - Mark ReyesDocument53 pagesPCAP Report - Mark ReyesMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Mahasiswan UPH, Neonatal SepsisDocument39 pagesKuliah Mahasiswan UPH, Neonatal Sepsiswilliam atmadjiNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Neonates in AnimalsDocument35 pagesDiseases of Neonates in AnimalshansmeetNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis-1Document35 pagesNeonatal Sepsis-1Mutai KiprotichNo ratings yet
- Common Newborn Problems (2) C1Document39 pagesCommon Newborn Problems (2) C1ZmNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.docx SemiDocument7 pagesLesson 3.docx SemiKc-Ann GalaponNo ratings yet
- Birthasphyxia 160328161503Document20 pagesBirthasphyxia 160328161503Noto SusantoNo ratings yet
- Neo Sepsis NCPDocument15 pagesNeo Sepsis NCPmelodia gandezaNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic Management of Paediatric Emergencies Corrected 3Document51 pagesAnaesthetic Management of Paediatric Emergencies Corrected 3oriaboseNo ratings yet
- Endorsement Pedia GCGMHDocument29 pagesEndorsement Pedia GCGMHFhaiiee SalapudinNo ratings yet
- PCAP Report - Mark ReyesDocument53 pagesPCAP Report - Mark ReyesMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reproductive PaedDocument150 pagesReproductive PaedThimira WaidyasekaraNo ratings yet
- High Risk Newborn: Dr. H. Usha RaniDocument28 pagesHigh Risk Newborn: Dr. H. Usha RaniNaresh GadaganiNo ratings yet
- Transient Tachypneica of NewbornDocument20 pagesTransient Tachypneica of Newbornasraf amirullahNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Complications: Donald G. Camatura, RNDocument96 pagesPostpartum Complications: Donald G. Camatura, RNDonald Garcesa Camatura100% (4)
- Pneumonia DR M ManiDocument69 pagesPneumonia DR M ManimaniNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis RabDocument25 pagesNeonatal Sepsis RabIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Budharapu RahulDocument15 pagesBudharapu RahulROXTA RAHULNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument7 pagesNeonatal Sepsispaningbatan.kristine.bNo ratings yet
- Kırşehir Ahi Evran Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Enstitüsü: Neonatal Sepsis & MeningitisDocument40 pagesKırşehir Ahi Evran Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Enstitüsü: Neonatal Sepsis & MeningitisAli FalihNo ratings yet
- C. Acute Conditions of The NeonatesDocument7 pagesC. Acute Conditions of The Neonatesprincessfarah hussinNo ratings yet
- Common Neonatal Conditions - Supplementary MaterialDocument25 pagesCommon Neonatal Conditions - Supplementary MaterialayunisallehNo ratings yet
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument21 pagesBirth AsphyxiaAntonyNo ratings yet
- Cornell's Note 4Document5 pagesCornell's Note 4Angel BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Fever - MSF Medical GuidelinesDocument6 pagesFever - MSF Medical GuidelinesUmarNo ratings yet
- Amniotic FluidDocument32 pagesAmniotic FluidFahad KhanNo ratings yet
- Approach To Preterm BabyDocument28 pagesApproach To Preterm BabyMUHAMMAD DANIAL BIN HASAN FPSKNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation On Child With Neonatal SepsisDocument37 pagesClinical Presentation On Child With Neonatal SepsisSREEDEVI T SURESHNo ratings yet
- PediatricsDocument312 pagesPediatricsمحمد ابو مناضل الافينش100% (1)
- Newborn Assessment and CareDocument79 pagesNewborn Assessment and CareStephen Gabriel TitoNo ratings yet
- Approach To Neonatal JaundiceDocument73 pagesApproach To Neonatal JaundiceG Venkatesh50% (2)
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Children: Clinical Features and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument62 pagesCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia in Children: Clinical Features and Diagnosis - UpToDateYeidhy Karin Cayo CoñezNo ratings yet
- Anemias RBC Morphology Approach To DiagnosisDocument24 pagesAnemias RBC Morphology Approach To DiagnosisAyessa VillacorteNo ratings yet
- BEKAMDocument26 pagesBEKAMeko rustamajiNo ratings yet
- Maccura Laboratories New Test Slides Rene PDFDocument4 pagesMaccura Laboratories New Test Slides Rene PDFRicardo NinaNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) As Vaccine-Vectors - Creative Biolabs01Document5 pagesHerpes Simplex Virus (HSV) As Vaccine-Vectors - Creative Biolabs01Sayed Mostafa HosseiniNo ratings yet
- Enlg Argumenative Essay 1Document15 pagesEnlg Argumenative Essay 1aishazariya02No ratings yet
- 627-Texto Do Artigo-1922-1-10-20201125Document5 pages627-Texto Do Artigo-1922-1-10-20201125Daniel GuimarãesNo ratings yet
- Original Research: © 2020 International Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Science (IJNMS)Document7 pagesOriginal Research: © 2020 International Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Science (IJNMS)Morysia Masyriqol ANo ratings yet
- 2nd. AssessmentDocument61 pages2nd. AssessmentYunus ElonNo ratings yet
- Wbi15-01-Jan-2023 Scientific ArticleDocument4 pagesWbi15-01-Jan-2023 Scientific ArticleCindy TsumaNo ratings yet
- TSI ReactionsDocument6 pagesTSI ReactionsPrimavera3193No ratings yet
- Aetna Student Health: Plan Design and Benefits SummaryDocument54 pagesAetna Student Health: Plan Design and Benefits SummaryrupikaNo ratings yet
- Legal Medicine 2020 2021Document4 pagesLegal Medicine 2020 2021Zie DammiNo ratings yet
- Endodontics Key Points by DaneshDocument16 pagesEndodontics Key Points by DaneshNoor HaiderNo ratings yet
- Maribel D. Fuentes, SN Jimson Altomia, SN: Kieth Amei Falalimpa, SNDocument46 pagesMaribel D. Fuentes, SN Jimson Altomia, SN: Kieth Amei Falalimpa, SNJam CorrosNo ratings yet
- Rciu AcogDocument13 pagesRciu AcogChristian Yzaguirre AbantoNo ratings yet
- Waste ManagementDocument42 pagesWaste ManagementAbdinasir Hasan DualeNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument6 pagesPhysical AssessmentDonna Flor NabuaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6 - Mental HealthDocument9 pagesAssignment 6 - Mental HealthJoe TorresNo ratings yet
- Admin and Finance Officer MKN 0 PDFDocument2 pagesAdmin and Finance Officer MKN 0 PDFsaw thomasNo ratings yet
- Iso 13485 Iso 9001Document56 pagesIso 13485 Iso 9001Juliamm MartNo ratings yet
- 60-27 Diabetes MellitusDocument10 pages60-27 Diabetes MellitusGabriel Navarro100% (1)
- Therapy With Erythropoietin Alpha And.2Document9 pagesTherapy With Erythropoietin Alpha And.2Alvin JiwonoNo ratings yet
- Micropara LabDocument8 pagesMicropara LabFatima KateNo ratings yet
- Chain of InfectionsDocument38 pagesChain of InfectionsMa Theresa PunoNo ratings yet
- Pathogenic Yield of Genetic Testing in Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument11 pagesPathogenic Yield of Genetic Testing in Autism Spectrum DisorderRaul Morales VillegasNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 4 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 4 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Maria Karla BalamadNo ratings yet
- Genetics - HumanKaryotyping - GizmoDocument4 pagesGenetics - HumanKaryotyping - GizmoRicky DunlapNo ratings yet
Neonatal Sepsis
Neonatal Sepsis
Uploaded by
Aisyah ShawtyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Neonatal Sepsis
Neonatal Sepsis
Uploaded by
Aisyah ShawtyCopyright:
Available Formats
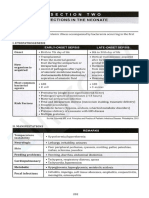
SEPSIS IN NEONATES
CLASSIFICATION
Late-onset sepsis is usually defined as
Early-onset sepsis is usually defined illness between days 4 and 30 of life
as illness during the first 3 days of life (some define it as illness between
(some define it as illness within first 7 days 7 and 30, whereas others define
days) it as illness earlier than 90-120 days of
life
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
• HISTORY
Temperature instability Tachypnea
Evidence of peripartum fetal distress
Hyperthermia / Hypothermia Diminished tone/activity
• Intrapartum fetal tachycardia
Lethargy or irritability Anorexia/poor feeding
• Apgar score of 6 or lower at 5 minutes
Apnea, bradycardia, and cyanosis in Seizure-like activity
• Meconium staining of amniotic fluid
preterm infants Vomiting
• Purulent amniotic fluid
Respiratory distress in full-term infants Diarrhea
History of maternal complications during delivery
Associated with preterm birth and small infants
Chorioamnionitis
Higher risk of infection is associated with gestational
Prolonged rupture of membranes (longer than 18 hours)
ages less than 37 weeks and neonatal weight less than
Maternal intrapartum fever
2500 g
Maternal urinary tract infection
CLINICAL MANIFESTATION
• Physical examination findings can be nonspecific, but sepsis is unlikely in healthy-looking
neonates Hemodynamic decompensation
Respiratory changes are a common presenting clinical sign
of infection Bradycardia
Dyspnea : Grunting / Flaring / Intercostal retractions Tachycardia (more than 160 beats per minute)
Tachypnea (more than 60 breaths per minute) Hypotension
Apnea Prolonged capillary refill time
Abdominal findings
Color changes:
Temperature instability Abdominal distention
Cyanosis / Jaundice / Pallor
Hypothermia (<=35) Hepatomegaly
More common in preterm infants Skin finding :
Central nervous system findings
Hyperthermia (>=38) Petechiae
Altered level of alertness
More common in term infants Periumbilical
Lethargy
Serious bacterial infection is found in 12% to erythema
Irritability
28% of febrile neonates presenting to Granulomatosis
Hypotonia/weak suck
emergency department infantiseptica
Seizures
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE
•Any neonate with signs of sepsis requires full diagnostic evaluation
• History and physical examination
• Most neonates with early-onset sepsis show abnormal clinical signs within first 24 hours after birth
•Full diagnostic evaluation for bacterial sepsis includes
• Early-onset disease (first 72 hours of life)
• CBC and blood culture
• Cerebrospinal fluid analysis and culture
• Chest radiograph if any abnormal respiratory signs are present
• Tracheal aspirate testing, if intubated
• Late-onset disease (after 72 hours of life)
• CBC and blood culture
• Cerebrospinal fluid analysis and culture
• Urinalysis with microscopy and urine culture
• Chest radiograph if any abnormal respiratory signs/symptoms are present or if reliable SaO₂ value is persistently less
than 95%
• Tracheal aspirate testing, if intubated
• Stool bacterial culture in infants with diarrhea
• Cultures from any other potential area of focus, such as pustules or purulent ocular or umbilical drainage
TREATMENT
Goals
Promptly identify infants with high likelihood of sepsis and start
antimicrobial therapy; provide supportive therapy
Any neonate with signs of sepsis requires full diagnostic evaluation, admission, antibiotic therapy, and inpatient
clinical monitoring pending culture results
Typical empiric antibiotic choice for suspected sepsis
•Early-onset neonatal sepsis
• Ampicillin and gentamicin
•Late-onset neonatal sepsis
• Ampicillin and gentamicin or cefotaxime
Supportive therapy includes:
•Administer oxygen to maintain SaO₂ between 94% and 99% and provide respiratory support
•Use fluid resuscitation and vasopressors (dopamine/debutamine) to treat poor perfusion and hypotension
•Monitor to prevent hypoglycemia, electrolyte imbalances (eg, hypocalcemia), and metabolic acidosis
•Provide antipyretic for comfort (Acetaminophen)
You might also like
- 8464 B 1H QP CombinedScienceTrilogy G 16may23 AMDocument32 pages8464 B 1H QP CombinedScienceTrilogy G 16may23 AMMatt A100% (3)
- ANAK (Full Permission)Document167 pagesANAK (Full Permission)anggyNo ratings yet
- 17 Jan - Paediatrics (DR Ashutosh) DAMS DVT 2022Document60 pages17 Jan - Paediatrics (DR Ashutosh) DAMS DVT 2022Lutfi HakimNo ratings yet
- (PESERTA) PEDIATRI 2 - MANTAP Februari 2017 PDFDocument157 pages(PESERTA) PEDIATRI 2 - MANTAP Februari 2017 PDFmarcelinaNo ratings yet
- Pediatri 2Document165 pagesPediatri 2YUYUM100% (2)
- Neonatal SepsisDocument7 pagesNeonatal SepsisTadesse MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Cmca Assignment #3Document3 pagesCmca Assignment #3Ayanami PascuaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric GastroenteritisDocument6 pagesPaediatric GastroenteritisANKITA RCHAWLANo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument20 pagesNeonatal SepsisNilanduniNo ratings yet
- Common Problems: in Newborn InfantDocument94 pagesCommon Problems: in Newborn InfantAhmad JustNo ratings yet
- Sepsis PowerPointDocument49 pagesSepsis PowerPointWonyenghitari GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Transient Tachypneu of The Newborn: Supervisor: Dr. Nazardi Oyong Sp. ADocument57 pagesTransient Tachypneu of The Newborn: Supervisor: Dr. Nazardi Oyong Sp. AWella FadillahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress in NewbornDocument54 pagesRespiratory Distress in NewbornAgi Azhari SandiniNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis: Definition & IncidenceDocument8 pagesNeonatal Sepsis: Definition & IncidenceahmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture On High Risk NewbornDocument51 pagesLecture On High Risk NewbornBilly RayNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress in Newborn: Presented By: Dr. Walaa MousaDocument74 pagesRespiratory Distress in Newborn: Presented By: Dr. Walaa MousasalamredNo ratings yet
- Management of Neonatal Sepsis: Niki Kosmetatos, MD Anthony Piazza, MD J. Devn Cornish, MDDocument30 pagesManagement of Neonatal Sepsis: Niki Kosmetatos, MD Anthony Piazza, MD J. Devn Cornish, MDiniidzniNo ratings yet
- Danger Signs in NewbornDocument8 pagesDanger Signs in NewbornPrabhu MagudeeswaranNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Respiratory Dist.7476158.PowerpointDocument21 pagesNeonatal Respiratory Dist.7476158.PowerpointtyapalupiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress in Newborn FinalDocument22 pagesRespiratory Distress in Newborn FinalajayganeshjNo ratings yet
- Kejang Demam Sederhana Ec - FaringitisDocument30 pagesKejang Demam Sederhana Ec - FaringitisPramita RukmanaNo ratings yet
- Danger Signs in Newborn DR Varsha Atul ShahDocument22 pagesDanger Signs in Newborn DR Varsha Atul ShahRSU ALFUADI BINJAINo ratings yet
- Management of Neonatal SepsisDocument30 pagesManagement of Neonatal SepsisRam krishnaNo ratings yet
- PPT HMDDocument60 pagesPPT HMDadityaNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care LectureDocument65 pagesNewborn Care LectureNichole daFonsecaNo ratings yet
- The Normal Newborn: Assessment and CareDocument71 pagesThe Normal Newborn: Assessment and CareElla Maica RacmanNo ratings yet
- Common Neonatal Disorders 5Document28 pagesCommon Neonatal Disorders 5Laishram Deeva ChanuNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Notes - Moodle/Text: Paediatric Emergencies (Textbook Ch.5)Document6 pagesPaediatric Notes - Moodle/Text: Paediatric Emergencies (Textbook Ch.5)Jana AldourNo ratings yet
- PCAP Report - Mark ReyesDocument53 pagesPCAP Report - Mark ReyesMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- PCAP Report - Mark ReyesDocument53 pagesPCAP Report - Mark ReyesMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Mahasiswan UPH, Neonatal SepsisDocument39 pagesKuliah Mahasiswan UPH, Neonatal Sepsiswilliam atmadjiNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Neonates in AnimalsDocument35 pagesDiseases of Neonates in AnimalshansmeetNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis-1Document35 pagesNeonatal Sepsis-1Mutai KiprotichNo ratings yet
- Common Newborn Problems (2) C1Document39 pagesCommon Newborn Problems (2) C1ZmNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.docx SemiDocument7 pagesLesson 3.docx SemiKc-Ann GalaponNo ratings yet
- Birthasphyxia 160328161503Document20 pagesBirthasphyxia 160328161503Noto SusantoNo ratings yet
- Neo Sepsis NCPDocument15 pagesNeo Sepsis NCPmelodia gandezaNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic Management of Paediatric Emergencies Corrected 3Document51 pagesAnaesthetic Management of Paediatric Emergencies Corrected 3oriaboseNo ratings yet
- Endorsement Pedia GCGMHDocument29 pagesEndorsement Pedia GCGMHFhaiiee SalapudinNo ratings yet
- PCAP Report - Mark ReyesDocument53 pagesPCAP Report - Mark ReyesMark ReyesNo ratings yet
- Reproductive PaedDocument150 pagesReproductive PaedThimira WaidyasekaraNo ratings yet
- High Risk Newborn: Dr. H. Usha RaniDocument28 pagesHigh Risk Newborn: Dr. H. Usha RaniNaresh GadaganiNo ratings yet
- Transient Tachypneica of NewbornDocument20 pagesTransient Tachypneica of Newbornasraf amirullahNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Complications: Donald G. Camatura, RNDocument96 pagesPostpartum Complications: Donald G. Camatura, RNDonald Garcesa Camatura100% (4)
- Pneumonia DR M ManiDocument69 pagesPneumonia DR M ManimaniNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Sepsis RabDocument25 pagesNeonatal Sepsis RabIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Budharapu RahulDocument15 pagesBudharapu RahulROXTA RAHULNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SepsisDocument7 pagesNeonatal Sepsispaningbatan.kristine.bNo ratings yet
- Kırşehir Ahi Evran Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Enstitüsü: Neonatal Sepsis & MeningitisDocument40 pagesKırşehir Ahi Evran Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Enstitüsü: Neonatal Sepsis & MeningitisAli FalihNo ratings yet
- C. Acute Conditions of The NeonatesDocument7 pagesC. Acute Conditions of The Neonatesprincessfarah hussinNo ratings yet
- Common Neonatal Conditions - Supplementary MaterialDocument25 pagesCommon Neonatal Conditions - Supplementary MaterialayunisallehNo ratings yet
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument21 pagesBirth AsphyxiaAntonyNo ratings yet
- Cornell's Note 4Document5 pagesCornell's Note 4Angel BriboneriaNo ratings yet
- Fever - MSF Medical GuidelinesDocument6 pagesFever - MSF Medical GuidelinesUmarNo ratings yet
- Amniotic FluidDocument32 pagesAmniotic FluidFahad KhanNo ratings yet
- Approach To Preterm BabyDocument28 pagesApproach To Preterm BabyMUHAMMAD DANIAL BIN HASAN FPSKNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation On Child With Neonatal SepsisDocument37 pagesClinical Presentation On Child With Neonatal SepsisSREEDEVI T SURESHNo ratings yet
- PediatricsDocument312 pagesPediatricsمحمد ابو مناضل الافينش100% (1)
- Newborn Assessment and CareDocument79 pagesNewborn Assessment and CareStephen Gabriel TitoNo ratings yet
- Approach To Neonatal JaundiceDocument73 pagesApproach To Neonatal JaundiceG Venkatesh50% (2)
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Children: Clinical Features and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument62 pagesCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia in Children: Clinical Features and Diagnosis - UpToDateYeidhy Karin Cayo CoñezNo ratings yet
- Anemias RBC Morphology Approach To DiagnosisDocument24 pagesAnemias RBC Morphology Approach To DiagnosisAyessa VillacorteNo ratings yet
- BEKAMDocument26 pagesBEKAMeko rustamajiNo ratings yet
- Maccura Laboratories New Test Slides Rene PDFDocument4 pagesMaccura Laboratories New Test Slides Rene PDFRicardo NinaNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) As Vaccine-Vectors - Creative Biolabs01Document5 pagesHerpes Simplex Virus (HSV) As Vaccine-Vectors - Creative Biolabs01Sayed Mostafa HosseiniNo ratings yet
- Enlg Argumenative Essay 1Document15 pagesEnlg Argumenative Essay 1aishazariya02No ratings yet
- 627-Texto Do Artigo-1922-1-10-20201125Document5 pages627-Texto Do Artigo-1922-1-10-20201125Daniel GuimarãesNo ratings yet
- Original Research: © 2020 International Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Science (IJNMS)Document7 pagesOriginal Research: © 2020 International Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Science (IJNMS)Morysia Masyriqol ANo ratings yet
- 2nd. AssessmentDocument61 pages2nd. AssessmentYunus ElonNo ratings yet
- Wbi15-01-Jan-2023 Scientific ArticleDocument4 pagesWbi15-01-Jan-2023 Scientific ArticleCindy TsumaNo ratings yet
- TSI ReactionsDocument6 pagesTSI ReactionsPrimavera3193No ratings yet
- Aetna Student Health: Plan Design and Benefits SummaryDocument54 pagesAetna Student Health: Plan Design and Benefits SummaryrupikaNo ratings yet
- Legal Medicine 2020 2021Document4 pagesLegal Medicine 2020 2021Zie DammiNo ratings yet
- Endodontics Key Points by DaneshDocument16 pagesEndodontics Key Points by DaneshNoor HaiderNo ratings yet
- Maribel D. Fuentes, SN Jimson Altomia, SN: Kieth Amei Falalimpa, SNDocument46 pagesMaribel D. Fuentes, SN Jimson Altomia, SN: Kieth Amei Falalimpa, SNJam CorrosNo ratings yet
- Rciu AcogDocument13 pagesRciu AcogChristian Yzaguirre AbantoNo ratings yet
- Waste ManagementDocument42 pagesWaste ManagementAbdinasir Hasan DualeNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument6 pagesPhysical AssessmentDonna Flor NabuaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6 - Mental HealthDocument9 pagesAssignment 6 - Mental HealthJoe TorresNo ratings yet
- Admin and Finance Officer MKN 0 PDFDocument2 pagesAdmin and Finance Officer MKN 0 PDFsaw thomasNo ratings yet
- Iso 13485 Iso 9001Document56 pagesIso 13485 Iso 9001Juliamm MartNo ratings yet
- 60-27 Diabetes MellitusDocument10 pages60-27 Diabetes MellitusGabriel Navarro100% (1)
- Therapy With Erythropoietin Alpha And.2Document9 pagesTherapy With Erythropoietin Alpha And.2Alvin JiwonoNo ratings yet
- Micropara LabDocument8 pagesMicropara LabFatima KateNo ratings yet
- Chain of InfectionsDocument38 pagesChain of InfectionsMa Theresa PunoNo ratings yet
- Pathogenic Yield of Genetic Testing in Autism Spectrum DisorderDocument11 pagesPathogenic Yield of Genetic Testing in Autism Spectrum DisorderRaul Morales VillegasNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 4 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 4 Activity 4 - Balamad, Maria Karla M.Maria Karla BalamadNo ratings yet
- Genetics - HumanKaryotyping - GizmoDocument4 pagesGenetics - HumanKaryotyping - GizmoRicky DunlapNo ratings yet