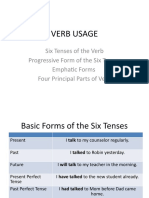
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Active Voice: Object (Recipient)
Active Voice: Object (Recipient)
Uploaded by
Andrea MendezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Active Voice: Object (Recipient)
Active Voice: Object (Recipient)
Uploaded by
Andrea MendezCopyright:
Available Formats
ACTIVE VOICE
The active voice is when the subject of a sentence performs an action on an object. In other
words, the subject does the action, and the object receives the action.
The active voice is easy to identify in writing because it follows a simple form, which is the basis of
English grammar:
Subject (doer) → Verb → Object (recipient)
The dog eats my homework.
PASSIVE VOICE
Passive voice is used when the focus is on the action. It is not important or not known who or what is performing
the action.
Subject (recipient) → Verb (verb to be + past participle) → Object (doer)
My homework is eaten by the dog
If we want to show the person or thing doing the action, we use by.
TENSES SUBJECT VERB OBJECT
Present Active: Kiara writes a letter
Simple Passive: A letter is written by Kiara
Present Active: Kiara is writting a letter
Continuous Passive: A letter is being written by Kiara
Past Simple Active: Kiara wrote a letter
Passive: A letter was written by Kiara
Past Active: Kiara was writting a letter
Continuous Passive: A letter was being written by Kiara
Present Active: Kiara has written a letter
Perfect Passive: A letter has been written by Kiara
Future Active: Kiara will write a letter
Passive: A letter will be written by Kiara
PAST SIMPLE
We use the past tense to talk about:
•something that was true for some time in the
•something that happened once in the past: past:
I met my wife in 1983. I lived abroad for ten years.
We went to Spain for our holidays. He enjoyed being a student.
They got home very late last night. She played a lot of tennis when she was
younger.
•something that happened several times in the •we often use expressions with ago with the
past: past simple:
When I was a boy, I walked a mile to school I met my wife a long time ago.
every day.
We swam a lot while we were on holiday.
They always enjoyed visiting their friends.
Affirmative
Verb to be in past
Subject + verb in past simple + C
I did my homework yesterday morning. I / he / she / it WAS
I played with my sister two hours ago. You / we / they WERE
Interrogative
Auxiliary verb (did) + Subject + Verb in infinitive + C + ?
Did you go to the party last week?
Where were you yesterday?
Who did you meet there?
Negative
Subject + Auxiliary verb (did) + NOT + Verb in infinitive + C.
She didn’t do her homework.
Thomas did not hit his brother.
Katherine didn’t play soccer when she was young.
PAST SIMPLE
• Active voice
Subject (doer) + Verb in past + Object (recipient)
A dog bite me yesterday.
The teacher corrected the mistakes two days ago.
Laura didn’t eat apples.
• Pasive voice
Subject (recipient) → Verb (verb to be in past + past participle) → Object (doer)
I was bitten by a dog yesterday
The mistakes were corrected by the teacher two days ago
Apples were not eaten by Laura
PAST CONTINOUS
We use the past continuous to talk about the past:
• for something which happened before and after another
action:
The children were doing their homework when I got home.
Compare: The children did their homework when (= after) I got • to show that something continued for some time:
home. My head was aching.
Everyone was shouting.
This use of the past continuous is very common at the beginning
of a story: • for something that happened again and again:
I was practising every day, three times a day.
The other day I was waiting for a bus when … They were meeting secretly after school.
Last week, as I was driving to work, … They were always quarrelling.
• for something that happened before and after a specific time: • with verbs which show change or growth:
It was eight o'clock. I was writing a letter. The children were growing up quickly.
Her English was improving.
Compare: At eight o'clock I wrote (= started writing) some letters. My hair was going grey.
The town was changing quickly.
• We do not normally use the past continuous with stative
verbs. We use the past simple instead:
When I got home, I really needed (NOT was needing) a shower.
Affirmative
Verb to be in past
Subject + Verb to be in past + Verb with -ing + C
I was doing my homework yesterday morning. I / he / she / it WAS
My cousins were playing with my sister two hours ago. You / we / they WERE
Interrogative
Verb to be in past + Subject + Verb with -ing + C + ?
What were you doing two hours ago?
Was she taking care of the baby?
Was he cooking?
Negative
Subject + Verb to be in past + NOT + Verb with -ing + C.
She wasn’t doing her homework.
They were not fighting.
Katherine wasn’t playing soccer.
PAST CONTINUOUS
• Active voice
Subject (doer) + Verb to be in past + verb with –ing + Object (recipient)
They were expecting a guest yesterday.
Anna was baking a cake.
My siblings were taking medicine.
• Pasive voice
Subject (recipient) → Verb (verb to be in past + being + past participle) → Object (doer)
A guest was being expected by them yesterday
A cake was being baked by Anna.
Medicine was being taken by my siblings.
You might also like
- Tiemposverbales Tabla en WordDocument4 pagesTiemposverbales Tabla en WordDesiderataNo ratings yet
- SIMPLE PAST Vs PAST CONTINUOUS AqshaDocument14 pagesSIMPLE PAST Vs PAST CONTINUOUS AqshaMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous: To Describe Parallel ActionsDocument2 pagesPast Continuous: To Describe Parallel ActionsTaty EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Past Tense + ContinuousDocument12 pagesPast Tense + ContinuousBenedictus PrabandanuNo ratings yet
- Past Simple, Past Continuous, Would, Used To and Irregular VerbsDocument24 pagesPast Simple, Past Continuous, Would, Used To and Irregular VerbsMacarenaNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument11 pagesPast ContinuousDavenia SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Vs Simple PastDocument9 pagesPast Continuous Vs Simple PastErnesto ArgüelloNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice and Present PerfectDocument23 pagesPassive Voice and Present PerfectDaniela HolguinNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice and Present PerfectDocument23 pagesPassive Voice and Present PerfectDaniela HolguinNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past Continuous Classroom Posters CLT Communicative Language Teach 74606Document9 pagesPast Simple Vs Past Continuous Classroom Posters CLT Communicative Language Teach 74606Sahra JumaberdiyevaNo ratings yet
- Past TensesDocument10 pagesPast TensesMaulidya DayangNo ratings yet
- Past TenseDocument11 pagesPast TenseRahmanda Muhammad Sukmajati2018No ratings yet
- Simple Past Vs Past Continuous. DOC 4Document7 pagesSimple Past Vs Past Continuous. DOC 4mahardhikaNo ratings yet
- Past-Simple-Vs-Past-Continuous-Classroom-Posters-Clt-Communicative-Language-Teach 74606Document9 pagesPast-Simple-Vs-Past-Continuous-Classroom-Posters-Clt-Communicative-Language-Teach 74606api-237478841No ratings yet
- Summary GrammarDocument3 pagesSummary GrammarNutchanon UdchachonNo ratings yet
- Voice Active PassiveDocument16 pagesVoice Active Passivevansh aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Handout Past TenseDocument1 pageHandout Past Tenseapi-412357828No ratings yet
- MEETING 4 1MA (For Student)Document38 pagesMEETING 4 1MA (For Student)Aufar yodha kazhimiNo ratings yet
- What Are Active and Passive Voice?Document12 pagesWhat Are Active and Passive Voice?MrNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous: I Was You Were He Was She Was It Was We Were You Were They Were Working Playing Living TalkingDocument1 pagePast Continuous: I Was You Were He Was She Was It Was We Were You Were They Were Working Playing Living TalkingTudorancea PatriciaNo ratings yet
- The Passive VoiceDocument8 pagesThe Passive VoiceMayte79100% (1)
- Repaso Grammar Vs MergedDocument15 pagesRepaso Grammar Vs MergedMelisa PerezNo ratings yet
- English GuideDocument15 pagesEnglish GuideFergie AmayaNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousDocument5 pagesPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousSorana PaleuNo ratings yet
- Past ContinuousDocument5 pagesPast Continuousqristine robaqidzeNo ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument3 pagesPassive Voicehaimar hernandez jimenezNo ratings yet
- Past Simple - Past Progressive - Present PerfectDocument9 pagesPast Simple - Past Progressive - Present PerfectAzael GaonaNo ratings yet
- Esquema Tiempos Verbales TIEMPODocument7 pagesEsquema Tiempos Verbales TIEMPOenkarniNo ratings yet
- Sesion 11Document20 pagesSesion 11Luigi RecuayNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous vs. Past Simple: Citlalli HipolitoDocument9 pagesPast Continuous vs. Past Simple: Citlalli HipolitoCitlalli MartinezNo ratings yet
- Tense Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect Continuous: Presen TDocument2 pagesTense Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect Continuous: Presen TBilal BhattiNo ratings yet
- Pasado Simple Pasado ContinuoDocument8 pagesPasado Simple Pasado ContinuoAgustin RCNo ratings yet
- Cuadro Resumen de Tiempos Verbales (2670)Document11 pagesCuadro Resumen de Tiempos Verbales (2670)Oposiciones JaénNo ratings yet
- Past Perfect Vs Past SimpleDocument24 pagesPast Perfect Vs Past Simpleaalliiccjjaa.statkiewiczNo ratings yet
- The Past Continuous and Stative VerbsDocument3 pagesThe Past Continuous and Stative VerbsclaualvarezfloripaNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument11 pagesGrammaromayma el bouzidiNo ratings yet
- English Assignment NORAIZDocument18 pagesEnglish Assignment NORAIZMuhammad YassenNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense DiaposDocument17 pagesSimple Past Tense DiaposKevin DiazNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument17 pagesTensesSara ImranNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense Form: I/ You/ We/ They He/ She/ It/ James PositiveDocument14 pagesPresent Simple Tense Form: I/ You/ We/ They He/ She/ It/ James PositiveAnitaNo ratings yet
- Past Simple Vs Past Continuous Classroom Posters CLT Communicative Language Teach - 74606Document8 pagesPast Simple Vs Past Continuous Classroom Posters CLT Communicative Language Teach - 74606Oana BondorNo ratings yet
- Grammar BookletDocument40 pagesGrammar BookletSALDAÑA NAVARRETE ANDREANo ratings yet
- Verb Tense ReviewDocument14 pagesVerb Tense ReviewJd McNo ratings yet
- English Learners All Tenses With ExamplesDocument3 pagesEnglish Learners All Tenses With ExamplesJudy Ann Jude AdornaNo ratings yet
- JFC Past-Simple-Vs-Past-ContinuousDocument22 pagesJFC Past-Simple-Vs-Past-ContinuousJhon Canizales CastroNo ratings yet
- GramarDocument24 pagesGramaraalliiccjjaa.statkiewiczNo ratings yet
- Ticket-In. Week 6. Level 5.Document2 pagesTicket-In. Week 6. Level 5.Aleja GarzoonNo ratings yet
- Verb UsageDocument21 pagesVerb UsageRaven Adrienne DimaculanganNo ratings yet
- Present PerfectDocument7 pagesPresent Perfectdonia.dodo.dsNo ratings yet
- Class 3 InglésDocument6 pagesClass 3 InglésPablo CuencaNo ratings yet
- Past Simple VS Past Progressive ExplanationDocument7 pagesPast Simple VS Past Progressive ExplanationYadira Pejerrey UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Voice:Active &passive: Week 5 Session2Document15 pagesVoice:Active &passive: Week 5 Session2Aawaiz JuttNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice and Other Grammar Topics 4Document158 pagesPassive Voice and Other Grammar Topics 4rocio silfaNo ratings yet
- Tense - : MDM Hirdyati"Document21 pagesTense - : MDM Hirdyati"Syia LoveJc100% (1)
- M7-Ugtv - PPT - Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Document25 pagesM7-Ugtv - PPT - Bahasa Inggris 1 Dan Tata Bahasa 1Aline TriciaNo ratings yet
- Past SentencesDocument15 pagesPast SentencesRatna AuliaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document118 pagesUnit 1Juan Francisco Aguilar BermeoNo ratings yet
- Active and PassiveDocument63 pagesActive and PassiveMariel MaquinianaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice in Different TensesDocument21 pagesPassive Voice in Different TensesSafira MaharaniNo ratings yet
- DebuggingYourOpenCenters 000Document162 pagesDebuggingYourOpenCenters 000phanam100% (16)
- Classroom Teacher EvaluationDocument5 pagesClassroom Teacher EvaluationPutri SudiroNo ratings yet
- The Illustrious Jade Egg EbookDocument63 pagesThe Illustrious Jade Egg EbookAndre Silva100% (3)
- Final Exam IE 7610 Fundamentals of Six Sigma: Ankur Kulkarni Access Id - fz5922Document4 pagesFinal Exam IE 7610 Fundamentals of Six Sigma: Ankur Kulkarni Access Id - fz5922Ankur KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Ucsi University Trust Education Grant 2021Document4 pagesUcsi University Trust Education Grant 2021Benz AliffNo ratings yet
- DLL Math 8-2Document2 pagesDLL Math 8-2Ai RenNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Curriculum Development ProcessDocument13 pagesOverview of The Curriculum Development ProcessAnouMalieNo ratings yet
- Implementing The Curriculum Guide: Aligned Classroom Instruction Delivery (ACID) PlanDocument19 pagesImplementing The Curriculum Guide: Aligned Classroom Instruction Delivery (ACID) Plankrisha macundanNo ratings yet
- RHEA MAE Final DemoDocument13 pagesRHEA MAE Final DemosevynNo ratings yet
- Day Number: 8 Grade Level: 4 Expected Duration: 45 Minutes ConceptsDocument12 pagesDay Number: 8 Grade Level: 4 Expected Duration: 45 Minutes Conceptsapi-313325258No ratings yet
- CNRC Exam Guide 2013Document18 pagesCNRC Exam Guide 2013StarLink1No ratings yet
- Literature Review On DaycareDocument5 pagesLiterature Review On Daycareafmzamdswsfksx100% (1)
- CAT6A Reference GuideDocument56 pagesCAT6A Reference GuideMarcilio CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Classroom Management 2020Document20 pagesClassroom Management 2020Masri'ah Binti SoekirnoNo ratings yet
- Math Gingerbread ActivityDocument3 pagesMath Gingerbread Activityapi-501803778No ratings yet
- Sample Template For Learner Activity Sheet (LAS) - English)Document2 pagesSample Template For Learner Activity Sheet (LAS) - English)Pamela Villahermosa100% (1)
- JLPT N5 Practice Test Grammar SectionDocument4 pagesJLPT N5 Practice Test Grammar SectionamIT royNo ratings yet
- Annurev Ps 32 020181 002255 PDFDocument38 pagesAnnurev Ps 32 020181 002255 PDFabderezak hassenNo ratings yet
- Serviciosdecontrol 202310314Document96 pagesServiciosdecontrol 202310314YEMER MANZANEDO AYALANo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS - M TECH Mechanical - Engineering - JNUDocument22 pagesSYLLABUS - M TECH Mechanical - Engineering - JNUVinayak GhatageNo ratings yet
- 2015 Directory of Arkansas Higher Education PersonnelDocument116 pages2015 Directory of Arkansas Higher Education PersonnelSai PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Area of CirclesDocument6 pagesArea of CirclesliahliahliahNo ratings yet
- Strixhaven Lore y RazasDocument36 pagesStrixhaven Lore y RazasÑepeco VlogsNo ratings yet
- Dental Laboratory Technology Specialist BlueprintDocument2 pagesDental Laboratory Technology Specialist BlueprintDr. Amr Khaled Al JabriNo ratings yet
- AE1 Sample Test - Test Paper SUMMER 2021 ONLINEDocument3 pagesAE1 Sample Test - Test Paper SUMMER 2021 ONLINEThu Trang VũNo ratings yet
- Presidency University KolkataDocument17 pagesPresidency University KolkataAntik MondalNo ratings yet
- (FreeCourseWeb - Com) 3030494179Document448 pages(FreeCourseWeb - Com) 3030494179Mariusz Tomasz Misiek100% (1)
- (Models and Modeling in Science Education 4) John K. Gilbert, David F. Treagust (Auth.), Prof. John K. Gilbert, Prof. David Treagust (Eds.)-Multiple Representations in Chemical Education-Springer Neth (Recovered)Document369 pages(Models and Modeling in Science Education 4) John K. Gilbert, David F. Treagust (Auth.), Prof. John K. Gilbert, Prof. David Treagust (Eds.)-Multiple Representations in Chemical Education-Springer Neth (Recovered)NestiNo ratings yet
- Walk-In-Interview For Part Time (Contractual) Teachers For The Session 2024-25Document4 pagesWalk-In-Interview For Part Time (Contractual) Teachers For The Session 2024-25ns282360No ratings yet
- Candidate Profile - Apprenticeship Training PortalDocument3 pagesCandidate Profile - Apprenticeship Training PortalTp EarningsNo ratings yet