Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Course Name: Communication Network Course Code: ELC 452
Course Name: Communication Network Course Code: ELC 452
Uploaded by
Romany Magdy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views22 pages Wireless Access Point (WAP): It extends the coverage of
networks, and may operates as a switch, router, or bridge.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lecture 1 Introduction to communication network
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document Wireless Access Point (WAP): It extends the coverage of
networks, and may operates as a switch, router, or bridge.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views22 pagesCourse Name: Communication Network Course Code: ELC 452
Course Name: Communication Network Course Code: ELC 452
Uploaded by
Romany Magdy Wireless Access Point (WAP): It extends the coverage of
networks, and may operates as a switch, router, or bridge.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 22
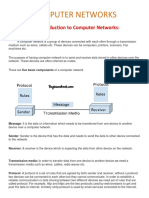
Course name: Communication Network
Course code : ELC 452
Introduction
to
Communication Networks
Evolution of Transmission Networks:
Definitions:
Broadband is used to mean any high-speed Internet
access that is faster than dial-up access over traditional
analog or ISDN PSTN services
Fixed‐telephone subscriptions: refers to the sum of
active number of analogue fixed‐ telephone lines, voice‐
over‐IP (VoIP) subscriptions, fixed wireless local loop
(WLL) subscriptions, ISDN voice‐channel equivalents and
fixed public payphones.
Mobile‐cellular telephone subscriptions: refers to the
number of subscriptions to a public mobile‐telephone
service that provide access to the PSTN using cellular
technology. It excludes subscriptions via USB modems,
radio paging, M2M and telemetry services.
Network Components:
• Terminal Devices: Telephone, computers, servers,
printers, mass storage, ….
• Nodes: switching system, signaling system, or
intermediate entities
• Links: guided and unguided media connect nodes and
terminal devices
Classifications of Communication Networks:
According to five (5) main criteria:
• Scale or Scope
• Capacity
• Performance
• Security
• Cost (installation (CapEx), operation and maintenance
(OpEX))
Network Scale or Scope:
Distance Location Network Abbreviation
<2m Interdisci Body area network BAN
plinary
<10m Room Personal area network PAN
10‐100m(1km) Building Local Area Network LAN
1‐10km City Metropolitan Area MAN
Network
100‐1000km Country Wide Area Network WAN
>1000Km - Region Region Area Network RAN
- Global Global Area Network GAN
1. A Body Area Network (BAN): also referred to as
a wireless body area network (WBAN) or a body
sensor network (BSN) or a medical body area
network (MBAN), is a wireless network of wearable
computing devices. BAN devices may be embedded
inside the body, surface-mounted , or may be carried;
in clothes pockets, by hand, or in various bags.
2. A personal area network (PAN): for interconnecting
devices centered on an individual person's
workspace. A PAN provides data transmission among
devices such as computers, smartphones, and
tablets.
3. Local Area Network (LAN):
Small & single geographical space: office, building, for a
small company or department
4. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
Network connecting multiple buildings within a limited
geographic area within boundaries of city.
5. Wide Area Network (WAN):
Typically, a WAN consists of two or more local area
networks (LANs). Computers connected to a WAN are
often connected through public networks.
6. Regional, and Global Area Network (RAN) and (GAN):
RAN covers interconnection of a group of countries,
while GAN cover the Globe. Both may rely on satellites.
Network Capacity:
The maximum Capacity of network's channel is defined by
Shannon:
C B log 2 (1 SNR ) bit / s
where B is the Bandwidth, and SNR is signal to noise ratio.
bandwidth efficiency, Spectral efficiency, or spectrum
efficiency refers to the information rate that can be
transmitted in a specific communication system.
Network performance:
Throughput, Latency, Error Rates, Resiliency,
Availability, Reliability, Serviceability
Network performance - Throughput:
The amount of data transferred from one location to
another.
A typical method of performing a measurement is to
transfer a 'large' file from one system to another system
and measure the time required to complete the transfer
or copy of the file. The throughput is then calculated by
dividing the file size by the time to get the throughput.
The results of such an exercise will often result is less
than the maximum theoretical data throughput, leading
to people believing that their communications link is not
operating correctly. In fact, there are many overheads
accounted for in throughput, in addition to some
expected latency.
Network performance - Latency:
is the term used to indicate any kind of delay that
happens in data communication over a network.
Network performance – Error Rate:
the ratio of total number of data units in error to the
total number of data units transmitted.
Resiliency: is the characteristic of being able to adapt
under stress or faults in order to avoid failure.
Network performance – Availability:
is the proportion of time a system is in a functioning
condition.
For most equipment the manufacturer will supply
information on availability expectations, often described as
Mean Time Between Failure (MTBF). The expected time to
repair each part of the network has to be estimated. This is
normally referred to as Mean Time To Repair (MTTR).
The availability for each unit MTBF
is calculated by:
availability
MTTR MTBF
To calculate the total availability of the network the
availability of all units has to be summed up !!!.
Reactive Availability: As opposed to an active
measurement of the availability, a reactive measurement
calculates the downtime using the data from; e.g. a
trouble ticket system. In a network-operations
perspective an active measurement would prove more
favorable.
Adjusted availability: Measuring the raw availability will
include also the downtime produced by planned work on
the network. These planned outages, or service
windows, are normally regulated with the customer in
the Service Level Agreement (SLA).
Network performance - Reliability:
is the measure of how long a system performs its intended
function
Notice: availability is the measure of the percentage of
time a system is operable. For example, a system may be
available 90% of the time, but reliable only 75% of the time
from a performance standpoint.
Serviceability or maintainability: is the simplicity and speed
with which a system can be repaired or maintained; if the
time to repair a failed system increases, then availability will
decrease. Serviceability includes various methods of easily
diagnosing the system when problems arise.
Security
COMmunications SECurity (COMSEC) is the prevention of
unauthorized access to telecommunication traffic. There
are several COMSEC disciplines, including:
Cryptographic: encrypts data and renders it unreadable
until the data is decrypted.
Emission: prevents the release or capture of equipment
emanations to prevent information from unauthorized
interception.
Physical security: ensures the safety of, and prevents
unauthorized access to, a network’s cryptographic
information, documents and equipment.
Transmission security: protects unauthorized access to
service interruption.
Communication Networks Nodes
The nodes may include one or more of the following:
HUB: It passes or receives
information (Data, Voice,
Video) along or "broadcast"
to every one of its ports ;
e.g. satellite HUB, and data
network HUB
Switch:
It routes an input signal to an output line as shown in
Communication Satellite network, and Data network
Bridge:
It connects (Links) two different network’s segments
together; e.g. Data networks, Satellite networks (Inter
Satellite Links (ISL)), Exchange links,… .
Router:
perform the traffic directing functions between similar
networks (terrestrial or satellite); e.g. protocol,
workstations and servers.
Gateways:
perform the traffic directing functions between
dissimilar networks (terrestrial or satellite).
Satellites constellation Network
Wireless Access Point (WAP): It extends the coverage of
networks, and may operates as a switch, router, or bridge.
You might also like
- Cmna Mini-Lab Guide (PDF) - English - 2017 06 12Document21 pagesCmna Mini-Lab Guide (PDF) - English - 2017 06 12Diego HuertasNo ratings yet
- A Summer Training Report NetworkingDocument44 pagesA Summer Training Report NetworkingMuditSinghChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Lec1+2Document29 pagesUnit-1 Lec1+2xyzNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Data Communication: Book: Data Communications and NetworkingDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Data Communication: Book: Data Communications and NetworkingSyed Nabeel AliNo ratings yet
- Network and TelecommunicationsDocument16 pagesNetwork and TelecommunicationsShunmugapriyan MuruganNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks and CommunicationsDocument60 pagesComputer Networks and CommunicationsSamuel GetachewNo ratings yet
- CNS Model Answers Unit 1Document29 pagesCNS Model Answers Unit 1asdhdahgadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Computer Networks: Evolution of Data Networks, Networks ArchitectureDocument20 pagesUnit 1: Computer Networks: Evolution of Data Networks, Networks ArchitectureVibhav MahaleNo ratings yet
- Data Communications: Communication and NetworkingDocument35 pagesData Communications: Communication and NetworkingLime EmilyNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Computer Network IDocument35 pagesLaboratory Manual: Computer Network ITedNo ratings yet
- A SCADA ComunicationsDocument27 pagesA SCADA ComunicationslasheeeenNo ratings yet
- TELECOMMUNICATIONDocument3 pagesTELECOMMUNICATIONkatya ZekoviaNo ratings yet
- Notes Mob Appl DevDocument12 pagesNotes Mob Appl DevDr Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument5 pagesNetworksShandira RoweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PDFDocument43 pagesChapter 1 PDFKavya ParasharNo ratings yet
- DATA COMMUNICATION Refers To The Exchange of Data Between A Source and A Receiver. DataDocument5 pagesDATA COMMUNICATION Refers To The Exchange of Data Between A Source and A Receiver. DataFidelis Yu RiNo ratings yet
- DCNDocument4 pagesDCNkunalNo ratings yet
- Form Four Computer NotesDocument87 pagesForm Four Computer NotesAriniitwe Davis AndersonNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and NetworkingDocument10 pagesData Communication and NetworkingAsadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Computer Network NoteDocument81 pagesComputer Network Noteupendrapaudel0No ratings yet
- Mobile ComputingDocument28 pagesMobile Computing219 DibyanshuKumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Network PracticalDocument21 pagesComputer Network PracticalPankaj DesaiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of A Network: What Is A Network?Document60 pagesFundamentals of A Network: What Is A Network?Sahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- ADocument2 pagesARachel VoonNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document6 pagesModule 2samadhiyagNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CNDocument46 pagesUnit 1 CNSulbha GathNo ratings yet
- CN Two MarksDocument4 pagesCN Two MarksSelva PalaniNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 4.1 Understand The Overview of Networking:: Characteristics of A Computer NetworkDocument14 pagesUNIT-4 4.1 Understand The Overview of Networking:: Characteristics of A Computer NetworkArunNo ratings yet
- Network 1Document14 pagesNetwork 1jhn75070No ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks, Reference ModelsDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Networks, Reference ModelsMukesh100% (2)
- PurityDocument3 pagesPurityvictoriamuiruri28No ratings yet
- Info Systems Notes 2Document22 pagesInfo Systems Notes 2michael hundiNo ratings yet
- 1.4.1.2 Physical Connection To Ieds For Substation Control and AutomationDocument5 pages1.4.1.2 Physical Connection To Ieds For Substation Control and AutomationChân Gà NướngNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 1 Stalling 8edDocument61 pagesCapitulo 1 Stalling 8edMario PachecoNo ratings yet
- CPT 1Document184 pagesCPT 1Alan VikramNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Computer Networksjoel lacayNo ratings yet
- 4 Communication NetworkDocument72 pages4 Communication Networkhsahu14No ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument21 pagesComputer NetworksJOYS NANCTNo ratings yet
- Unit 05 - Networks and The InternetDocument5 pagesUnit 05 - Networks and The Internetjulides2026No ratings yet
- What Is Meant by Telecommunication Network: Here AreDocument6 pagesWhat Is Meant by Telecommunication Network: Here AreWidimongar W. JarqueNo ratings yet
- Foc Unit 3Document42 pagesFoc Unit 3druruj jaleelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument9 pagesChapter 1 IntroductionCiifle CaddeNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Basics of NetworkingDocument32 pagesCH 1 Basics of NetworkingRanganath KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ccna Semester 1 V 3.0Document69 pagesCcna Semester 1 V 3.0roseaceNo ratings yet
- CT 4Document10 pagesCT 4mj porrasNo ratings yet
- SCT Unit-IDocument14 pagesSCT Unit-IDhanush GummidiNo ratings yet
- Nec 4106 Module 2Document24 pagesNec 4106 Module 2Jessie Rey MembreveNo ratings yet
- Define Computer NetworkDocument22 pagesDefine Computer Networkbhuvi2312No ratings yet
- Networking and InternetworkingDocument58 pagesNetworking and Internetworkingsrinivasa_ds2kNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument9 pagesUntitled Document121Anik sahaNo ratings yet
- WMN Prilim Sample Paper 1Document11 pagesWMN Prilim Sample Paper 1baxadi8221No ratings yet
- Computer Networks: Introduction To Networking Lesson 1Document48 pagesComputer Networks: Introduction To Networking Lesson 1carlonerigatusNo ratings yet
- DistributorsDocument14 pagesDistributorskatakamavinash329No ratings yet
- ITM Unit - 4Document18 pagesITM Unit - 4Naimisha 102No ratings yet
- MCA-305 Computer Networks: Data Security and IntegrityDocument14 pagesMCA-305 Computer Networks: Data Security and IntegrityAshutosh PatelNo ratings yet
- Lan Wan ManDocument40 pagesLan Wan ManmanafsulaimanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 DataDocument18 pagesChapter 5 DataAyug RaiNo ratings yet
- UNIT I NotesDocument20 pagesUNIT I Notes6041 Gowardhanan100% (1)
- 1 Computer Networks 1Document114 pages1 Computer Networks 1NishikantNo ratings yet
- CIR 209 (Lecture 6) Classification - of - Computer - NetworksDocument14 pagesCIR 209 (Lecture 6) Classification - of - Computer - Networksdancanongori9No ratings yet
- Bill Statement: News FlashDocument7 pagesBill Statement: News FlashEvelyn TayNo ratings yet
- Answer: Code Words Creates B. Invalid Codeword C. Valid Data D. Invalid DataDocument15 pagesAnswer: Code Words Creates B. Invalid Codeword C. Valid Data D. Invalid Datasan4u401No ratings yet
- 5G Mobile and Wireless Communications Technology-Cambridge University Press (2016)Document439 pages5G Mobile and Wireless Communications Technology-Cambridge University Press (2016)Dayse BandeiraNo ratings yet
- Cisco Email Security Appv 101 Product GuideDocument27 pagesCisco Email Security Appv 101 Product GuideLuis RomanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Satellite Modem (18 Kbps - 25 MBPS) Installation and Operation ManualDocument690 pagesAdvanced Satellite Modem (18 Kbps - 25 MBPS) Installation and Operation Manualosadeamos8684No ratings yet
- Dell Openmanage Network Users Guide4 en UsDocument191 pagesDell Openmanage Network Users Guide4 en Usender40No ratings yet
- Underwater Wireless CommunicationDocument16 pagesUnderwater Wireless CommunicationAchyuth JanaNo ratings yet
- Ha en Switches CiscoDocument95 pagesHa en Switches CiscoRoger VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Sat Lite Tech 103 Accessories rc3000 Antenna ControllerDocument1 pageSat Lite Tech 103 Accessories rc3000 Antenna ControllerIonionoNo ratings yet
- Category 6 U/Utp Euroclass Eca Cables: Datasheet: Gd102051V17Document3 pagesCategory 6 U/Utp Euroclass Eca Cables: Datasheet: Gd102051V17Juan R. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Pucp TeologiaDocument6 pagesPucp TeologiaAnonymous oz3YPvW9HNNo ratings yet
- 15.2.7 Packet Tracer - Logging Network Activity CiscoDocument2 pages15.2.7 Packet Tracer - Logging Network Activity CiscoHenryDíazDHNo ratings yet
- IDIRECT Technical Reference Guide PDFDocument118 pagesIDIRECT Technical Reference Guide PDFblesson123No ratings yet
- Lenovo IdeaPad S10 - QUANTA FL2 - REV 1ASec PDFDocument36 pagesLenovo IdeaPad S10 - QUANTA FL2 - REV 1ASec PDFKevin AlexanderNo ratings yet
- IMSI MSC Call Trace (Invoke Trace) : Motorola JordanDocument7 pagesIMSI MSC Call Trace (Invoke Trace) : Motorola Jordanrapture767No ratings yet
- Network Video Recorder - Quick Start Guide - V1.0.0-EngDocument33 pagesNetwork Video Recorder - Quick Start Guide - V1.0.0-EngRichard Mark FreoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SMPPDocument21 pagesIntroduction To SMPPVictor Celer100% (1)
- ElecEng4FJ4 Module03 PDFDocument22 pagesElecEng4FJ4 Module03 PDFFrew FrewNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Enterprise Networking, Security, and AutomationDocument102 pagesCCNA 3 v7.0 Final Exam Answers Full - Enterprise Networking, Security, and Automationfabrizio fioriNo ratings yet
- RPL Message DIO: Pv6 Routing Protocol For Low-Power and Lossy Networks Dodag Information ObjectDocument2 pagesRPL Message DIO: Pv6 Routing Protocol For Low-Power and Lossy Networks Dodag Information ObjectNiguss Mehari GezahegnNo ratings yet
- Cellfile2g 23 3 2017Document988 pagesCellfile2g 23 3 2017nhatnk1No ratings yet
- FNT Solution Cable Management en 05 2014Document8 pagesFNT Solution Cable Management en 05 2014Waleed Bin Abdul HafeezNo ratings yet
- WCT Lab Assignment - 1Document5 pagesWCT Lab Assignment - 1Aayush SinghNo ratings yet
- Cept Erc Rec 70-03 PDFDocument7 pagesCept Erc Rec 70-03 PDFDragan StanicNo ratings yet
- ZTE CDMA Radio Network Optimization Proposal - R1 (1) .2 - ENDocument96 pagesZTE CDMA Radio Network Optimization Proposal - R1 (1) .2 - ENDONALFYNo ratings yet
- Configuring MPLS Network With Frame RelayDocument13 pagesConfiguring MPLS Network With Frame RelayImene AsNo ratings yet
- f5 Ltmdns Operations Guide PDFDocument135 pagesf5 Ltmdns Operations Guide PDFAurelio Canales AlcayagaNo ratings yet
- E2-E3 (CM) Technical Module Handout - Dec 2009 (Upgradation Course Materials)Document128 pagesE2-E3 (CM) Technical Module Handout - Dec 2009 (Upgradation Course Materials)Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- Blackview BV9300 Rugged Phones DoC-20240116012500699Document2 pagesBlackview BV9300 Rugged Phones DoC-20240116012500699danielnews16No ratings yet