Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Navjot Singh (BBA III Sem)
Navjot Singh (BBA III Sem)
Uploaded by
Ramandeep SinghOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Navjot Singh (BBA III Sem)
Navjot Singh (BBA III Sem)
Uploaded by
Ramandeep SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
Invertis University
Topic:- Basic Concept of Income
Tax
Name:- Navjot Singh
Student ID:- BB2019108
BBA (III Semester)
Content
1. What is tax?
2. Concept of Income Tax Act
3. Income Tax law in India
4. Person
5. Assessee
6. Assessment Year
7. Previous Year
8. Heads of Income
9. Tax Rates
10. Surcharge
11. Education Cess and Secondary Higher Education Cess
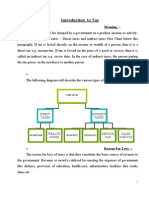
What is Tax?
Tax is the compulsory financial charge levy by
the government on income, commodity,
services, activities or transaction. The word ‘tax’
derived from the Latin word ‘Taxo’. Taxes are
the basic source of revenue for the
government, which are utilized for the welfare
of the people of the country through
government policies, provisions and practices.
Concept of Income Tax Act
“Income Tax is levied on the total income of the previous year
of every person”. To understand the basic concept .It is very
important to know the various other concepts.
In common parlance, Income is known as a regular periodic
return to a person from his activities. However, the Income
has broader classified in Income Tax law. The Income Tax Act,
even take consideration of income which has not arisen
regularly and periodically. For instance, winning from
lotteries, crossword puzzles, income from winning of shows is
also subject to tax as per income tax
Moreover, the income is defined in Section 2(24) of the Act
Income Tax law in India
The Income Tax law in India consists of the following components;
Income Tax Act, 1961: The Act contains the major provisions related to
Income Tax in India.
Income Tax Rules, 1962: Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) is the body
which looks after the administration of Direct Tax. The CBDT is empowered to
make rules for carrying out the purpose of this Act.
Finance Act: Every year Finance Minister of Government of India presents the
budget to the parliament. Once the finance bill is approved by the parliament
and get the clearance from President of India, it became the Finance Act.
Circulars and Notifications: Sometimes the provisions of an act may need
clarification and that clarification usually in a form of circulars and
notifications which has been issued by the CBDT from time to time. It
includes clarifying the doubts regarding the scope and meaning of the
provisions.
Person
Income tax is levied on the total income of the previous year of every person.
In general terms, the meaning of a person can be interpreted in a short term.
Whereas, as per Section 2 (31), Person includes:
i. an individual,
ii. a Hindu undivided family (HUF),
iii. a company,
iv. a firm,
v. an association of persons (AOP) or a body of individuals (BOI), whether
incorporated or not,
vi. a local authority, and
vii. every artificial juridical person (AJP), not falling within any of the preceding
sub-clauses.
The definition of Person starts with the word includes, therefore, the list is
inclusive, not exhaustive.
Assessee
An assessee is a taxpayer means a person who under
the income tax act is subject to pay taxes or any other
sum of money, as defined under section 2 (7) of the
Act. The expression ‘any other sum of money’ includes
other such obligations payable, for instance fine,
interest, penalty and other tax etc.
Assessment Year
“Assessment Year” means the year in which income of
the previous year of an assessee is taxed. The timed
lap of assessment year is of twelve months beginning
from the 1st April every year. The period starts from
1st April of one year and ending on 31st March of next
year. Broadly, assessment year is defined under section
2 (9) of the Act.
Previous Year
Income earned during the year is taxable in the next year.
The definition of “Previous Year” is given under section 3 of
the Act. Previous Year is the year in which income is earned.
Previous year is the financial year immediately preceding the
relevant assessment year. From 1989-90 onwards, every
taxpayer is obliged to follow financial year (i.e., April 1st of
one year to March 31st of next year) as the previous year.
For a newly set up business or profession, the first previous
year will start from the day from which that business or
profession has commenced, but the period of ending will
remains same (i.e., 31st March).
Heads of Income
As per Income tax, section 14 classifies income under
five heads:
i. Income from salaries
ii. Income from House Property
iii. Profits and gains of business and profession
iv. Capital Gains
v. Income from other sources
Tax Rates
The Income is taxed at the rates prescribed by the
relevant Finance Act. The tax levied on the basis of a
slab system where different tax rates have been
directed for the different slab. In India, there are three
categories of individual taxpayers:
i. An individual below the age of 60 years,
ii. A senior citizen above the age of 60 years, but below
the age of 80 years,
iii. A super senior citizen above 80 years of age.
The tax slab varies according to the different persons.
Surcharge
The Surcharge is commonly known as Tax on Tax. It is
an additional tax levied on the taxpayers on a special
group of people. It is an additional tax liability levied
on the person having more income than prescribed.
Education Cess and
Secondary Higher Education
Cess
The amount of income tax shall be increased by an
Education Cess on Income Tax by 2% and Secondary
and Higher Education Cess by 1% of the tax liability.
You might also like
- Tax Unit 2Document43 pagesTax Unit 2naikdibyaranjan53No ratings yet
- Income Tax Study MaterialDocument303 pagesIncome Tax Study MaterialAbith Mathew77% (217)
- Proposal Majlis Berbuka PuasaDocument4 pagesProposal Majlis Berbuka PuasaheryizwanNo ratings yet
- 4100XPB 4198 Grupo Mexico CananDocument758 pages4100XPB 4198 Grupo Mexico CananWalissonNo ratings yet
- OSTEORADIONECROSISDocument38 pagesOSTEORADIONECROSISAbel AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Retaning Wall BOQDocument5 pagesRetaning Wall BOQMuhammadWazimAkram100% (2)
- Basic-Concepts-Ita 1961Document26 pagesBasic-Concepts-Ita 1961Gurpreet Sandhu100% (1)
- Analysis of The Capital of The World by Ernest HemingwayDocument9 pagesAnalysis of The Capital of The World by Ernest HemingwayRamandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Carbon Footprint of Organic FertilizerDocument5 pagesCarbon Footprint of Organic FertilizerSteve Savage100% (6)
- Unit 1 Topic 1stDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Topic 1stAnjali. 1999No ratings yet
- UNIT-1 Basic Concepts of Income TaxDocument38 pagesUNIT-1 Basic Concepts of Income TaxGarimaNo ratings yet
- 603 - Taxation LawsDocument41 pages603 - Taxation LawsSiddhartha Singhal057No ratings yet
- III B.com. - 18UCOE2 - Dr. R Sathru Sankara VelsamyDocument132 pagesIII B.com. - 18UCOE2 - Dr. R Sathru Sankara VelsamyDebdeep C.No ratings yet
- Unit 1 ItlaDocument11 pagesUnit 1 ItlaAbdul basitNo ratings yet
- Meenu Chopra Income Tax BasicsDocument66 pagesMeenu Chopra Income Tax BasicsRvi Mahay100% (1)
- Business and Tax Laws: After Reading This Chapter, You Will Be Conversant WithDocument20 pagesBusiness and Tax Laws: After Reading This Chapter, You Will Be Conversant WithRaj MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 TaxlawDocument20 pagesChap 6 TaxlawShahzadSyedNo ratings yet
- Tax Combined NotesDocument48 pagesTax Combined NotesignatiousmugovaNo ratings yet
- Income tax(1) (1)Document4 pagesIncome tax(1) (1)littleman4050No ratings yet
- Heads of IncomeDocument26 pagesHeads of IncomeShardulWaikar100% (2)
- Introduction To Income TaxDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Income TaxmanishsinghkrNo ratings yet
- DT20MBAFM304Document12 pagesDT20MBAFM304Gagan KSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 of Introduction With Margin 1111-1-2Document33 pagesChapter 1 of Introduction With Margin 1111-1-2YogiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Tax: MeaningDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Tax: MeaningRAMNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concept of Income Tax - Law Times JournalDocument10 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concept of Income Tax - Law Times JournalYash RankaNo ratings yet
- Business Taxation Notes Income Tax NotesDocument303 pagesBusiness Taxation Notes Income Tax NotesIkra MalikNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Basic Concepts of Income TaxDocument8 pagesIntroduction and Basic Concepts of Income TaxmanjushreeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 TheoryDocument17 pagesModule 1 TheoryPremkumarNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Law and PracticeDocument11 pagesIncome Tax Law and PracticeAnsh NayyarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Income TaxDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Income Taxsipabow760No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Taxation NotesDocument74 pagesUnit 1 Taxation Notesmanishogare788No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Taxation NotesDocument74 pagesUnit 1 Taxation NotesT. P.No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ITDocument26 pagesBasic Concepts of ITAnishaAppuNo ratings yet
- Income TaxDocument100 pagesIncome TaxDr Sachin Chitnis M O UPHC AiroliNo ratings yet
- Concept and Framework of TaxationDocument16 pagesConcept and Framework of Taxationanandbm1231750No ratings yet
- Taxation UNIT 1Document16 pagesTaxation UNIT 1PARTH NAIKNo ratings yet
- Income Tax: Why Tax Is Required?Document21 pagesIncome Tax: Why Tax Is Required?Rohit DhoundiyalNo ratings yet
- 00 Income Tax Basic ConceptsDocument13 pages00 Income Tax Basic Conceptsapi-286872716No ratings yet
- Financial System ProjectDocument17 pagesFinancial System ProjectLata PardeshiNo ratings yet
- Indirect Taxes Are Levied On The Production or Consumption of Goods andDocument10 pagesIndirect Taxes Are Levied On The Production or Consumption of Goods andPARTH NAIKNo ratings yet
- Law of TaxationDocument12 pagesLaw of TaxationiemhardikNo ratings yet
- Income Tax: B C: Asic OnceptsDocument35 pagesIncome Tax: B C: Asic OnceptsAbhinandan soniNo ratings yet
- Tax ExamDocument29 pagesTax ExamAnn Olivia VallavanadanNo ratings yet
- Kishor IT-1Document22 pagesKishor IT-1Mohan SinghNo ratings yet
- SLM 19665 (F) Bba Income Tax FinalDocument363 pagesSLM 19665 (F) Bba Income Tax Finalnadeemvp111No ratings yet
- FP&TM - Unit Iii - Tax NotesDocument77 pagesFP&TM - Unit Iii - Tax NotesMansi sharmaNo ratings yet
- SeemaDocument61 pagesSeemaAkash ShewadeNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts: 1.1 What Is A Tax?Document31 pagesBasic Concepts: 1.1 What Is A Tax?sourav kumar rayNo ratings yet
- SLM-19615-B Com-INCOME TAX LAW AND ACCOUNTS - 0Document308 pagesSLM-19615-B Com-INCOME TAX LAW AND ACCOUNTS - 0Deva T NNo ratings yet
- Law of Taxation 2Document16 pagesLaw of Taxation 2iemhardikNo ratings yet
- Income Tax Short Note (R0)Document9 pagesIncome Tax Short Note (R0)Personal UseNo ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument54 pagesAccounting NotesIfLah ITooNo ratings yet
- Taxsmile Notes On Income TaxDocument46 pagesTaxsmile Notes On Income Taxaman16755747No ratings yet
- Income TaxDocument195 pagesIncome TaxAleti NithishNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of WhatDocument31 pagesBasic Concepts of WhatRajdeep KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Notes 4Document18 pagesNotes 4babuaditya1998No ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument35 pagesBasic Concepts3208 A PallaviNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Taxation NotesDocument74 pagesUnit 1 Taxation Notesstevin.john538No ratings yet
- Questions and Answers - Section A - Taxation LawDocument6 pagesQuestions and Answers - Section A - Taxation LawSuneet KapoorNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Income TaxDocument25 pagesUnit-I Income Taxprashant vaishnavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1CA Mohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- TaxDocument508 pagesTaxCherry DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- Indonesian Taxation: for Academics and Foreign Business Practitioners Doing Business in IndonesiaFrom EverandIndonesian Taxation: for Academics and Foreign Business Practitioners Doing Business in IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- 1040 Exam Prep Module III: Items Excluded from Gross IncomeFrom Everand1040 Exam Prep Module III: Items Excluded from Gross IncomeRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Forward Budgeting: A Paperless and Electronic Household Budget SystemFrom EverandForward Budgeting: A Paperless and Electronic Household Budget SystemNo ratings yet
- Consumer Satisfaction Towards Samsung TelevisionDocument9 pagesConsumer Satisfaction Towards Samsung TelevisionRamandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills & Technical Report Writing: Presented by Amritansh Mishra Assistant Professor (Invertis University)Document74 pagesCommunication Skills & Technical Report Writing: Presented by Amritansh Mishra Assistant Professor (Invertis University)Ramandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Samsung Karam PprojectDocument57 pagesSamsung Karam PprojectRamandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Diploma Mech. (Automobile)Document14 pagesDiploma Mech. (Automobile)Ramandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Railway PresentationDocument12 pagesRailway PresentationRamandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Environmental Geotechniques: Theories of Ion ExchangeDocument21 pagesEnvironmental Geotechniques: Theories of Ion ExchangeTenkurala srujanaNo ratings yet
- Obat Kausatif Infeksi: 6ggpo, 0shqwlget Grad Corporis Ult Hui Form 3DDocument5 pagesObat Kausatif Infeksi: 6ggpo, 0shqwlget Grad Corporis Ult Hui Form 3DMaulana Malik IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Activated Carbon MSDS PDFDocument6 pagesActivated Carbon MSDS PDFRIANG TRIANDONONo ratings yet
- Microbial Ecology of Sourdough Fermentations: Diverse or Uniform?Document19 pagesMicrobial Ecology of Sourdough Fermentations: Diverse or Uniform?roadrunner100% (1)
- S100X220YAJ Panduit Datasheet 5314981Document2 pagesS100X220YAJ Panduit Datasheet 5314981Ilham MaurizaNo ratings yet
- Catálogo de Referencias - Power Conversion SystemsDocument60 pagesCatálogo de Referencias - Power Conversion SystemsBENo ratings yet
- Stress and Coping Strategies Among Distance Education Students at The University of Cape Coast, GhanaDocument15 pagesStress and Coping Strategies Among Distance Education Students at The University of Cape Coast, GhanaReign EvansNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Troubleshooting For Industrial EnginesDocument25 pagesElectrical and Electronic Troubleshooting For Industrial EnginespanddyanNo ratings yet
- Bio-Organic Chem LecturesDocument205 pagesBio-Organic Chem LecturesРаони Мессиас100% (2)
- 1 Case IDC PDFDocument7 pages1 Case IDC PDFPilar Dueñas Maldonado0% (1)
- Covalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionDocument4 pagesCovalence S1301-M Epoxy Primer: DescriptionJuan Carlos Contreras CherresNo ratings yet
- Background of The StudyDocument13 pagesBackground of The Studyjeffrey rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Guide To Laboratory Establishment For Plant Nutrient AnalysisDocument1 pageGuide To Laboratory Establishment For Plant Nutrient AnalysisOsama MadanatNo ratings yet
- Model ETR-9200 Automatic Tuning Smarter Logic ControllerDocument26 pagesModel ETR-9200 Automatic Tuning Smarter Logic ControllervhelectronicaNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocument1 pageJob Hazard AnalysisZaul tatingNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - ETERSET 2960-2 - MSDSDocument5 pagesMicrosoft Word - ETERSET 2960-2 - MSDSWinsonLimHuiWahNo ratings yet
- UO Mixing Liquid PhaseDocument2 pagesUO Mixing Liquid PhaseKumara Haekal Hafidz AmrullahNo ratings yet
- Surgical Operation PDFDocument64 pagesSurgical Operation PDFshifna.latheefNo ratings yet
- PLKS321 Unit 8.9 PMDocument56 pagesPLKS321 Unit 8.9 PMmonagomolemo9No ratings yet
- TPH (Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons) : Immunoassay Method 10050Document10 pagesTPH (Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons) : Immunoassay Method 10050Cindy Valenzuela RuedaNo ratings yet
- Proforma A1: Residential/Domicile CertificateDocument6 pagesProforma A1: Residential/Domicile CertificateSamim ParvezNo ratings yet
- URL #Flushyourmeds Scott BarryDocument8 pagesURL #Flushyourmeds Scott Barryurl-flushyourmedsNo ratings yet
- Dental Implant Site Preparation - A Review: C.J.Venkatakrishnan, S.Bhuminathan and Chitraa.R.ChandranDocument4 pagesDental Implant Site Preparation - A Review: C.J.Venkatakrishnan, S.Bhuminathan and Chitraa.R.ChandranLouis HutahaeanNo ratings yet
- PintoDocument18 pagesPintosinagadianNo ratings yet
- PCB HandlingDocument8 pagesPCB HandlingscanlonlNo ratings yet