Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Memory and Brain: The Physical Aspects of Memory
Memory and Brain: The Physical Aspects of Memory
Uploaded by
Anis Nabilla Md Wazilah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
439 views12 pagesThe document discusses how memories are formed and stored in the brain. It explains that memories involve physical changes in the brain called engrams that occur in specific areas when memories are consolidated. The hippocampus is identified as responsible for forming new long-term memories, as damage to it causes anterograde amnesia where new memories cannot be stored. Retrograde amnesia involves the loss of past memories, while infantile amnesia is the inability to recall events before age 2-3. Alzheimer's disease and other disorders can impair memory areas of the brain.
Original Description:
Original Title
present psycho
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses how memories are formed and stored in the brain. It explains that memories involve physical changes in the brain called engrams that occur in specific areas when memories are consolidated. The hippocampus is identified as responsible for forming new long-term memories, as damage to it causes anterograde amnesia where new memories cannot be stored. Retrograde amnesia involves the loss of past memories, while infantile amnesia is the inability to recall events before age 2-3. Alzheimer's disease and other disorders can impair memory areas of the brain.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
439 views12 pagesMemory and Brain: The Physical Aspects of Memory
Memory and Brain: The Physical Aspects of Memory
Uploaded by
Anis Nabilla Md WazilahThe document discusses how memories are formed and stored in the brain. It explains that memories involve physical changes in the brain called engrams that occur in specific areas when memories are consolidated. The hippocampus is identified as responsible for forming new long-term memories, as damage to it causes anterograde amnesia where new memories cannot be stored. Retrograde amnesia involves the loss of past memories, while infantile amnesia is the inability to recall events before age 2-3. Alzheimer's disease and other disorders can impair memory areas of the brain.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Memory And Brain : The Physical
Aspects of Memory
BY FARAH HAZWANIE SUHAIMI
NUR ASMA LAILI SHAHABUDIN
AIDI AMIZUL RASIDI
6.1 How and where are memories
formed in the brain
The physical change that takes place in the
brain when a memory is full called the
engram.
Proved that specific areas of the brain may be
the place in which engrams are formed and
these areas are different for different types of
memory.
Neural Activity and Structure in Memory
Formation
Several studies offered evidence that the engram
is not simply one physical change but many.
These change that take place as an engram is
forming called consilidation.
Consolidation- consists of the physical changes in
neutrons that take place during the formation of
the memory.
Although people learn quickly, the memory of
what has been learned take some time to be form
quickly.
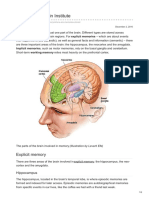
The Hippocampus and Memory
A part of limbic system, it was identified as the
part of the brain that is responsible for the
formation of new long-term memories.
As with most amnesiacs of type (refer with
H.M’s case although was quite severe), his
procedural memory was still intact.
Appears to be responsible for the storage of
new long-term memories. If it is removed, the
ability to store anything new is completely lost.
When Memory Fails:
Organic Amnesia
Retrograde Amnesia- loss of memory
from the pain of some injury or
trauma backwards, or loss of memory
for the past.
6.12 What is Alzheimer’s disease?
Two forms of severe loss of memory
disorders caused by problems in the
functioning of the memory areas of the
brain.
These problems is called brain injuries
which can cause trauma and alcoholism
(Korsakoff Syndrome).
For example- You are working on your
computer, trying to finish a history paper that
is due tomorrow. Your computer saves the
document every 10 minutes, then the power
goes out. When the power comes back on,
you find that while all the files you had
already saved to your disk are still intact.
All memories that were in the process of
being stored but not yet permanent are lost.
One of the therapies for severe
despression:-
ECT (Electroconvulsive therapy)- *refer chptr 15
Can disrupt consolidation and cause
retrograde amnesia.
Consists of applying an electric shock to one
or both side of the head.
The result is rapid improvement in mood-
(most effective) but not respond to
medication.
Anterograde Amnesia
Memory for anything new become impossible
although old memories may still be
retrievable.
People with this kind of amnesia have
difficulty remembering anything new.
They also most often seen in people with
senile dementia- the primary symptoms such
as severe forgetfulness, mental confusion and
mood swings.
For example- You can read data that already
in hard drive but you can’t store any new info.
As long as are looking at the data in
computer, you can access it but as soon as
you close the window, the info is lost then it
was never transfer to hard drive because the
hard drive has become defective.
Meaning that your long-term memory
physically weak.
Infantile Amnesia
Most people cannot remember events
that occurred before age 2-3.
It is most likely due to the implicit
nature of infant memory.
Autobiographical Memory
The memory for events and facts related
to one’s personal life story.
Also gives credit to the social relationships
that small children have with others. (by
Katherine Nelson, 1993)
You might also like
- Wodarg Yeadon EMA Petition Pfizer Trial FINAL 01DEC2020 en Unsigned With ExhibitsDocument43 pagesWodarg Yeadon EMA Petition Pfizer Trial FINAL 01DEC2020 en Unsigned With ExhibitsZerohedge Janitor96% (52)
- Suicide and Self-HarmDocument14 pagesSuicide and Self-HarmbraispmNo ratings yet
- John Medina - Brain Rules PDFDocument11 pagesJohn Medina - Brain Rules PDFDiego Cunha100% (2)
- Brain Plasticity Essay KATTYDocument5 pagesBrain Plasticity Essay KATTYKatty SorrosaNo ratings yet
- Attachment, Anxiety, and Agoraphobia PDFDocument17 pagesAttachment, Anxiety, and Agoraphobia PDFkatiaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Submitted To: Submitted By: Ms Kamini Manisha Joshi Asst. Prof. Acn Msc. Nursing 1 SemesterDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan: Submitted To: Submitted By: Ms Kamini Manisha Joshi Asst. Prof. Acn Msc. Nursing 1 SemesterDIMPYNo ratings yet
- Amnesia: There Are Two Main Types of AmnesiaDocument2 pagesAmnesia: There Are Two Main Types of AmnesiaRussell OdangoNo ratings yet
- Bio Psych Chapter 8 - Learning, Memory, and IntelligenceDocument6 pagesBio Psych Chapter 8 - Learning, Memory, and Intelligenceyzabel.biancaNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocument29 pagesBiology Investigatory ProjectBalaji K100% (1)
- NeurobiologyDocument7 pagesNeurobiologykaisNo ratings yet
- Memory Human BrainDocument40 pagesMemory Human Brainismannaba7No ratings yet
- Sedatives Hypnotic DrugsDocument3 pagesSedatives Hypnotic DrugsBernardete Freitas BarrosNo ratings yet
- Mem 2Document12 pagesMem 2Shyamol BoseNo ratings yet
- Brain Memory and AmnesiaDocument14 pagesBrain Memory and AmnesiacristinarosuNo ratings yet
- 9 Memory FactsDocument10 pages9 Memory Factsfarosol670No ratings yet
- AP Psych Study Guide - CognitionDocument12 pagesAP Psych Study Guide - CognitionMike Kang HkNo ratings yet
- 9 Memory FactsDocument10 pages9 Memory Factsfarosol670No ratings yet
- Psychology Paper 3Document4 pagesPsychology Paper 3api-663730856No ratings yet
- Involvement of brain in memoryDocument5 pagesInvolvement of brain in memoryalishbaiqbal816No ratings yet
- Learning and MemoryDocument7 pagesLearning and MemoryJacob RosasNo ratings yet
- Language, Learning, and MemoryDocument78 pagesLanguage, Learning, and MemoryRonalyn A.No ratings yet
- Extra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 PurposeDocument35 pagesExtra Class This Sat: Time: 9am-12pm Venue: CG04 Purposelengers poworNo ratings yet
- Amnesia: Amnesia Is The General Term For A Condition in Which Memory (Either StoredDocument6 pagesAmnesia: Amnesia Is The General Term For A Condition in Which Memory (Either StoredputrianabrsitompulNo ratings yet
- Amnesia ExplanationDocument2 pagesAmnesia ExplanationMuslim NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Queensland Brain InstituteDocument3 pagesQueensland Brain InstituteInês Sousa0% (1)
- Cause & Effect ViviDocument3 pagesCause & Effect ViviFiqhi WulandariNo ratings yet
- Brain RulesDocument13 pagesBrain RulesKeith ParkerNo ratings yet
- Think Faster, Remember MoreDocument3 pagesThink Faster, Remember MoreKalajanNo ratings yet
- Memory and LearningDocument11 pagesMemory and LearningNeus Sangrós VidalNo ratings yet
- Cogniiii Chap 6Document5 pagesCogniiii Chap 6Khayla AcramanNo ratings yet
- Brain Rules: 12 Principles For Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home and SchoolDocument13 pagesBrain Rules: 12 Principles For Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home and SchoolSandwacsNo ratings yet
- PDF 20230517 183009 0000Document67 pagesPDF 20230517 183009 0000Wac TheNo ratings yet
- 2 8 LearningDocument9 pages2 8 LearningTőkés BernadettNo ratings yet
- GlossaryDocument5 pagesGlossaryTinx LenaNo ratings yet
- FORGETTINGDocument4 pagesFORGETTINGMeetali SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Biological Approach To BehaviourDocument27 pagesUnit 2 - Biological Approach To BehaviourMyra Jain100% (1)
- Boost Your Brain Power: Learn Better, Smarter, and Faster - Scientifically Proven Guides to Sharpen Your Focus and Retrain Your BrainFrom EverandBoost Your Brain Power: Learn Better, Smarter, and Faster - Scientifically Proven Guides to Sharpen Your Focus and Retrain Your BrainNo ratings yet
- AmnesiaDocument4 pagesAmnesiaapi-351680270No ratings yet
- He Did Not Only Lose The Ability To Form New MemoriesDocument1 pageHe Did Not Only Lose The Ability To Form New MemoriesAnastasiya KravchenkoNo ratings yet
- Memory Loss (Amnesia), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMemory Loss (Amnesia), A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document3 pagesChapter 8sebastianramirez01217No ratings yet
- MCI V.S. Alzheimer DSM-5 All About Amnesia: Occur Together DifficultyDocument4 pagesMCI V.S. Alzheimer DSM-5 All About Amnesia: Occur Together DifficultyFizal gunawanNo ratings yet
- Anterograde AmnesiaDocument16 pagesAnterograde AmnesiacristinekeithescobarNo ratings yet
- OpenStax Psychology2e LN08Document6 pagesOpenStax Psychology2e LN08Shehib GulaimidNo ratings yet
- A. What Is Amnesia?Document7 pagesA. What Is Amnesia?byun syahiraNo ratings yet
- Brain Rules Chapter SummariesDocument13 pagesBrain Rules Chapter SummariesPear Press93% (15)
- U 5 GiangDocument3 pagesU 5 Gianglaicanhlam1999No ratings yet
- MEMORY Presentation - Introduction To PsychologyDocument32 pagesMEMORY Presentation - Introduction To PsychologyBrittany OliphantNo ratings yet
- Memory and The BrainDocument13 pagesMemory and The BrainWenderson Morais100% (1)
- HippocampusDocument3 pagesHippocampusapi-507287383No ratings yet
- "Debunking Myths and Misconceptions: The Truth about the Brain and Memory"From Everand"Debunking Myths and Misconceptions: The Truth about the Brain and Memory"No ratings yet
- AmnesiaDocument2 pagesAmnesiakaren andrea garcia gonzalezNo ratings yet
- How Memories Form and How We Lose ThemDocument2 pagesHow Memories Form and How We Lose ThemGuilhermeCorrêaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PDFDocument13 pagesUnit 3 PDFKamal Kishor PantNo ratings yet
- 8 Science-Based ToolsDocument1 page8 Science-Based ToolsKrutarth PatelNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Learning and Unlimited Memory Techniques and Strategies: Real Coaching from a Real Expert. Tips & Tricks for Students and AdultsFrom EverandAccelerated Learning and Unlimited Memory Techniques and Strategies: Real Coaching from a Real Expert. Tips & Tricks for Students and AdultsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Memoria 10 Lucruri InteresanteDocument10 pagesMemoria 10 Lucruri InteresanteAlina NeagoeNo ratings yet
- Ap PsychDocument41 pagesAp PsychSherelle HiggsNo ratings yet
- Into Three Stages: We Have 7 Different Types of MemoryDocument10 pagesInto Three Stages: We Have 7 Different Types of MemoryНастя СеменчукNo ratings yet
- On MemoryDocument15 pagesOn MemoryM3 09 DHARSANA KARTHIKNo ratings yet
- Memory DysfunctionDocument8 pagesMemory DysfunctionAdamarloNo ratings yet
- Brain: Amnesia Dementia Delirium Anxiety Disorders Mood Disorders Psychotic DisordersDocument13 pagesBrain: Amnesia Dementia Delirium Anxiety Disorders Mood Disorders Psychotic Disordersmadiha ahmed khanNo ratings yet
- Dementia and The BrainDocument20 pagesDementia and The BrainLiviaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Primary HPV Testing For Cervical Cancer Screening in MalaysiaDocument38 pagesGuidelines For Primary HPV Testing For Cervical Cancer Screening in MalaysiadrnahafizahNo ratings yet
- Recalls 1 CompilationDocument180 pagesRecalls 1 CompilationReka LambinoNo ratings yet
- (Formerly Known As Max Bupa Health Insurance Co. LTD.) : Health Assurance UIN: IRDAI/HLT/MBHI/P-H/V.II/175/2016-17Document53 pages(Formerly Known As Max Bupa Health Insurance Co. LTD.) : Health Assurance UIN: IRDAI/HLT/MBHI/P-H/V.II/175/2016-17kamakshi0735No ratings yet
- Maternal Respiratory Sars-Cov-2 Infection in Pregnancy Is Associated With A Robust Inflammatory Response at The Maternal-Fetal InterfaceDocument31 pagesMaternal Respiratory Sars-Cov-2 Infection in Pregnancy Is Associated With A Robust Inflammatory Response at The Maternal-Fetal InterfaceAllan Depieri CataneoNo ratings yet
- Colegio de Dagupan: College of NursingDocument38 pagesColegio de Dagupan: College of NursingA'Lester Medina100% (4)
- Lynn Kern KoegelDocument13 pagesLynn Kern Koegelapi-500451341No ratings yet
- Walking Dead Cheat Sheet V1Document2 pagesWalking Dead Cheat Sheet V1Zgorzel McKrackenNo ratings yet
- Caesarean Delivery During Second Stage of Labor - A Study of Fetomaternal Outcome in A Tertiary Care HospitalDocument4 pagesCaesarean Delivery During Second Stage of Labor - A Study of Fetomaternal Outcome in A Tertiary Care HospitalIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Physical Characteristics: C. PlateletsDocument6 pagesPhysical Characteristics: C. PlateletsGwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- CHN 2Document14 pagesCHN 2Aira PayadNo ratings yet
- Selulitis DGN Ulkus VarikosumDocument1 pageSelulitis DGN Ulkus VarikosumdeaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis InhibitorsDocument33 pagesProtein Synthesis InhibitorssaifNo ratings yet
- Final Online Exam Guideline CBTDocument105 pagesFinal Online Exam Guideline CBTfaisalaminwani121No ratings yet
- Neuromuscular DiseasesDocument205 pagesNeuromuscular DiseasesvivicouNo ratings yet
- Barangay Health Emergency Response Teams (BHERTs)Document26 pagesBarangay Health Emergency Response Teams (BHERTs)Barangay Mintal100% (3)
- Measuring Psychological Distress 5Document32 pagesMeasuring Psychological Distress 5api-548101002No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan On Mapeh 8Document7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan On Mapeh 8JamesNo ratings yet
- Purposes of The Nursing ProcessDocument11 pagesPurposes of The Nursing ProcessNica NixNo ratings yet
- Abdulmoshin 2000 WordsDocument13 pagesAbdulmoshin 2000 WordsRizwan KazmiNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Pressure UlcersDocument15 pagesPrevention of Pressure UlcersGabriel Urrea Botero100% (1)
- The Event 201: October 2019Document5 pagesThe Event 201: October 2019Allen BurroughsNo ratings yet
- 1st Assessment Health 6 3rd QuarterDocument2 pages1st Assessment Health 6 3rd QuarterJesusa Franco DizonNo ratings yet
- BUCK VS. BELL, 274 U.S. 200 FactsDocument51 pagesBUCK VS. BELL, 274 U.S. 200 FactsJessie Daven Adrian GallardoNo ratings yet
- Word Jurnal THT Odontogenik 1Document20 pagesWord Jurnal THT Odontogenik 1RayNo ratings yet
- Ph.D. Program in Drug Discovery and Development Industry: Journal Papers Published by Our TeachersDocument25 pagesPh.D. Program in Drug Discovery and Development Industry: Journal Papers Published by Our Teachers陳筱婷No ratings yet
- AMBOSS Ear QuestionsDocument10 pagesAMBOSS Ear QuestionsSahil DnkNo ratings yet