Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation 7 CB
Presentation 7 CB
Uploaded by
sweta choudhary0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views11 pagesCollective bargaining is a process of negotiation between employee representatives, usually trade unions, and employers to determine terms of employment such as wages, benefits, and working conditions. It aims to maintain good relations between management and workers and resolve disputes through formal discussions and agreements that are flexible, dynamic, and continuous over time. The agreements reached through collective bargaining cover various employment issues and seek to protect worker interests through representation.
Original Description:
Original Title
presentation 7 CB
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCollective bargaining is a process of negotiation between employee representatives, usually trade unions, and employers to determine terms of employment such as wages, benefits, and working conditions. It aims to maintain good relations between management and workers and resolve disputes through formal discussions and agreements that are flexible, dynamic, and continuous over time. The agreements reached through collective bargaining cover various employment issues and seek to protect worker interests through representation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views11 pagesPresentation 7 CB
Presentation 7 CB
Uploaded by
sweta choudharyCollective bargaining is a process of negotiation between employee representatives, usually trade unions, and employers to determine terms of employment such as wages, benefits, and working conditions. It aims to maintain good relations between management and workers and resolve disputes through formal discussions and agreements that are flexible, dynamic, and continuous over time. The agreements reached through collective bargaining cover various employment issues and seek to protect worker interests through representation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 11
Collective bargaining
o This term is coined by famous authors Sydney and
Beatrice Webb which is concerned with the relations
between trade unions & management.
o It is an on going process of negotiation between
representatives of workers and employers to establish
the conditions of employment.
o The collectively determined agreement may cover not
only wages but hiring practices, layoffs, promotions,
job functions, working conditions and hours, worker
discipline and termination, and benefit programs.
Definition
All negotiations which take place between an
employer, a group of employers or one or more
employers' organisations, on the one hand, and
one or more workers' organisations, on the other,
for:
(a) determining working conditions and terms of
employment; and/or
(b) regulating relations between employers and
workers; and/or
(c) regulating relations between employers or their
organisations and a workers' organisation or
workers' organisations.”
Characteristics
Collective: Collective bargaining is a two way
group process where the employers representative
and employees representatives sit together to
negotiate terms of employment.
Strength: Both the parties in collective
bargaining are strong and equal.
Voluntary: Both parties come to the negotiation
table voluntarily in order to go in particular
negotiation. It is based on discussion, mutual trust
and understanding.
…
Formal: It is a formal process in which certain employment
related issues are to be regulated at National, organization
and workplace levels.
Flexible: It is a flexible and continuous process and not
fixed or static.
Improvement: It is a method to improve the employer-
employees relation in organization and resolve management
and employees conflicts.
Representation: Collective bargaining is between the
representatives of employees and management. The
management does not directly deal with employees. It carries
negotiations with the representatives/executives of unions
and association.
Dynamic: Collective bargaining is dynamic, that
go on changing over a period and grows and
expand the way of agreement, the way of
implementation and way of discussion.
Continuous: Collective bargaining is continuous
and begins with agreement, the implementation of
agreement and further negotiations.
Bipartite Process: Because the employee and
employers representatives negotiate directly face
to face across the table.
OBJECTIVES
To maintain cordial relations between management
& the workers
To settle disputes/conflicts relating to working
conditions & wages
To protect interest of workers through collective
action.
To ensure participation of Trade Unions
To resolve the differences between workers and
management.
Principles of CB
Principles for Trade Unions-:
a) They should have open mind on various issues.
b) There should not be any room for confusion &
misunderstanding.
c) Trade Unions should fully support management.
d) Strike calls should be the last resort.
Principles for Management-:
a) Mgt.should give proper recoginition to trade unions.
b) Rules governing labour should be periodically examined.
c) All the clauses of agreements should be accepted in true
spirit.
Types of collective bargaining
1. Conjunctive or Distributive Bargaining:
Both the parties viz. The employee and the employer
try to maximize their respective gains.
It is based on the principle, “my gain is your loss, and
your gain is my loss” i.e. one party wins over the other.
The economic issues such as wages, bonus, other
benefits are discussed.
Here the employee wishes to have an increased wage
or bonus for his work done, whereas the employer
wishes to increase the workload and reduce the wages.
2. Co-operative or Integrative Bargaining:
Both the employee and the employer sit together and
try to resolve the problems of their common interest
and reach to an amicable solution.
In the case of economic crisis, such as recession, which
is beyond the control of either party, may enter into a
mutual agreement with respect to the working terms.
For example, the workers may agree for the low wages
or the management may agree to adopt the modernized
methods, so as to have an increased production.
Process of CB
Preparing for negotiations: Careful and advance preparations for
employees and employers are necessary because of the complexity
of the issues and broad range of topics discussed during
negotiations.
Identifying the bargaining issues: The major issues discussed in
CB fall under the following four categories:
a. Wage related issues
b. Supplementary economic benefits
c. Institutional issues
d. Administrative issues
Negotiation: This phase begins with each side presenting initial
demands. Negotiation goes on until final agreement is reached.
4. Reaching the agreement: After the initial agreement is
made, both the parties come to a conclusion.
Ratifying the agreement: In this stage union- negotiating
team explains and puts the agreement to the union
members for a vote. If voted, this agreement is formalised
into a contract.
Administration of the agreement: The agreement must
be implemented according to the letter and spirit of the
provisions of the agreement.
You might also like
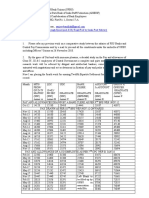
- CoSHH Blank Risk Assessment TemplateDocument5 pagesCoSHH Blank Risk Assessment Templatepablapurubi03No ratings yet
- Corporate Finance for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #1From EverandCorporate Finance for CFA level 1: CFA level 1, #1Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Successful Negotiation: Communicating effectively to reach the best solutionsFrom EverandSuccessful Negotiation: Communicating effectively to reach the best solutionsNo ratings yet
- Labor Law and Legislation Final Quiz 1Document10 pagesLabor Law and Legislation Final Quiz 1shaneNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining: Content of SeminarDocument12 pagesCollective Bargaining: Content of SeminarRhea MalikNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining: Content of SeminarDocument12 pagesCollective Bargaining: Content of SeminarRhea MalikNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument28 pagesCollective Bargaining46 Kajal PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- CollectivebargainingDocument18 pagesCollectivebargainingKinjal VasavaNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument24 pagesCollective BargainingPavithra0% (1)
- Collective Bargaining: Introduction/ DefinitionDocument6 pagesCollective Bargaining: Introduction/ DefinitionYash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 (Sir Note)Document39 pagesUnit-3 (Sir Note)ShiwaniNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument11 pagesCollective BargainingDelphy Varghese100% (2)
- Class Presentation ON Collective Bargaining: PresenterDocument27 pagesClass Presentation ON Collective Bargaining: PresenterEugene PilotonNo ratings yet
- Employee/Labor Management Relations: Emily A. Sumalinog MPA StudentDocument41 pagesEmployee/Labor Management Relations: Emily A. Sumalinog MPA StudentklipordNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining For NursingDocument21 pagesCollective Bargaining For NursingPrasann RoyNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument72 pagesCollective Bargaininggoldfish8100% (1)
- IRL Collective BargainingDocument16 pagesIRL Collective BargainingPavithra SNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining Faculty GP Capt (DR.) RM SaxenaDocument19 pagesCollective Bargaining Faculty GP Capt (DR.) RM SaxenaSkill Cube Private LimitedNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument13 pagesCollective BargainingGraceNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument35 pagesCollective BargainingSanjana Ganesh100% (1)
- Maniba Bhula Nursing College: Sub: Advance Nursing Practice Topic: Individual and Collective BargainingDocument10 pagesManiba Bhula Nursing College: Sub: Advance Nursing Practice Topic: Individual and Collective BargainingRinal BaradNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument9 pagesCollective BargainingDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining: HR Labor Relations ManagerDocument4 pagesCollective Bargaining: HR Labor Relations ManagerTrina McdanielNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument15 pagesCollective Bargainingjeena joyNo ratings yet
- Professional EthicsDocument16 pagesProfessional Ethicshemarajasekar46No ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining: Concept, Functions and Position in IndiaDocument22 pagesCollective Bargaining: Concept, Functions and Position in Indiashamini6No ratings yet
- Main Features of Collective Bargaining:: 1. It Is A Group ActionDocument3 pagesMain Features of Collective Bargaining:: 1. It Is A Group ActionPrateek VermaNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument12 pagesCollective BargainingsreekalaNo ratings yet
- BT17EEE037Document15 pagesBT17EEE037Nitin AryaNo ratings yet
- Types of Pay StructureDocument6 pagesTypes of Pay StructurerishabhNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 IRDocument66 pagesUnit 2 IRpreeti20.officeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Collective Bargaining 1Document11 pagesChapter 10 Collective Bargaining 1Jyothy ShajiNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining DefinitionDocument19 pagesCollective Bargaining Definitionprasanna murthyNo ratings yet
- Industrial RelationDocument39 pagesIndustrial RelationMidhat firdousNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument25 pagesCollective BargainingDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining AssignmentDocument7 pagesCollective Bargaining AssignmentPrashant ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining: Prepared By: Asst. Prof. Charmi LiyaDocument21 pagesCollective Bargaining: Prepared By: Asst. Prof. Charmi LiyaMakwana RahuLNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument5 pagesCollective BargainingPREJA PATELNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument22 pagesCase Studyneetisom89% (9)
- Submitted To:-Submitted By: - Prof. Shashi Sharma Loveleen Kaur ROLL NO. 6335Document32 pagesSubmitted To:-Submitted By: - Prof. Shashi Sharma Loveleen Kaur ROLL NO. 6335Loveleen JhiountNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument12 pagesCollective BargainingCoolsun SunnyNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument29 pagesCollective Bargainingmayu27bhaduriNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining AgentsDocument6 pagesCollective Bargaining AgentsGhulam Mustafa GMNo ratings yet
- ERLL UNIT 2 (Complete)Document27 pagesERLL UNIT 2 (Complete)ritisha khatriNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Management UNIT 28Document13 pagesHuman Resources Management UNIT 28tjnihalNo ratings yet
- Collective BargainingDocument10 pagesCollective BargainingDurga Prasad Dash100% (3)
- 1Q) Characteristics of Collective Bargaining: NegotiationsDocument11 pages1Q) Characteristics of Collective Bargaining: NegotiationsMurali ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter: 03. Collective Bargaining: Industrial RelationsDocument5 pagesChapter: 03. Collective Bargaining: Industrial RelationsEthan CoenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19Document31 pagesLecture 19Software EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Session 7 Grievance Management and Collective BargainingDocument25 pagesSession 7 Grievance Management and Collective BargainingShreya Binu SathyanNo ratings yet
- HR402 Aritra Majumder 26300922019Document26 pagesHR402 Aritra Majumder 26300922019aritramajumder3000No ratings yet
- 4 - Collective-BargainingDocument19 pages4 - Collective-BargainingNasim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sony GeorgeDocument119 pagesSony GeorgeKishan PatelNo ratings yet
- What Is Collective Bargaining? - Definition, Process & QuizDocument7 pagesWhat Is Collective Bargaining? - Definition, Process & QuizNøthîñgLîfèNo ratings yet
- Industrial Relations ModifiedDocument16 pagesIndustrial Relations ModifiedsomechnitjNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining: Alternative Dispute ResolutionDocument4 pagesCollective Bargaining: Alternative Dispute ResolutionIndresh SinghNo ratings yet
- Collective Bargaining & Negotiation: Khushdeep Class Mba (F) Roll No 36Document32 pagesCollective Bargaining & Negotiation: Khushdeep Class Mba (F) Roll No 36Mukul BabbarNo ratings yet
- GRIEVANCE PROCEDURE and Collective BargainingDocument18 pagesGRIEVANCE PROCEDURE and Collective BargainingShalu PalNo ratings yet
- Macdo PresentationDocument45 pagesMacdo PresentationLyra Mae De BotonNo ratings yet
- Refer Books, Elaborate The Points: Collective BargainingDocument4 pagesRefer Books, Elaborate The Points: Collective Bargainingjitukhandelwal6No ratings yet
- LISONDRA Vs WIZARD MANPOWER - RFA Form 1Document1 pageLISONDRA Vs WIZARD MANPOWER - RFA Form 1Tricia DC PalileoNo ratings yet
- Central Pay Comm Vs PSU Bank PayDocument8 pagesCentral Pay Comm Vs PSU Bank PayRaghunatahNo ratings yet
- Printable Employee Attendance SheetDocument2 pagesPrintable Employee Attendance Sheetjojofuellas22No ratings yet
- Hre NotesDocument3 pagesHre NotesMaureen Joy Esguerra ZamudioNo ratings yet
- MR-ISP-006 Hazard Identification - RISK ASSESSMENT & RISKDocument8 pagesMR-ISP-006 Hazard Identification - RISK ASSESSMENT & RISKsufyan shahidNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document2 pagesBook 1Rey Marion CabagNo ratings yet
- Labour Law ProjectDocument9 pagesLabour Law Projectisha agrawalNo ratings yet
- Ppe Training Record: Department Occupation Type of Ppe Make/Model Name InitialsDocument3 pagesPpe Training Record: Department Occupation Type of Ppe Make/Model Name Initialsvlad100% (1)
- Case: Manila Hotel Employees Association v. Manila Hotel Corp. GR No. 1154591Document5 pagesCase: Manila Hotel Employees Association v. Manila Hotel Corp. GR No. 1154591Michael Ang SauzaNo ratings yet
- Labor Law Review - 1st Sem, AY 2020-21 (First Half - As of 13 July 2020) - 1 PDFDocument12 pagesLabor Law Review - 1st Sem, AY 2020-21 (First Half - As of 13 July 2020) - 1 PDFStephany PolinarNo ratings yet
- JSA Unstuffing Air Charge Intake...Document5 pagesJSA Unstuffing Air Charge Intake...warryNo ratings yet
- 286 - International Container Terminal, Inc. Vs NLRCDocument3 pages286 - International Container Terminal, Inc. Vs NLRCManz Edam C. JoverNo ratings yet
- MR Muhammad Rafeek Offer Letter DomDocument2 pagesMR Muhammad Rafeek Offer Letter Domhzaib768No ratings yet
- Instructor Manual (5G-Small Cell Deployment Training)Document258 pagesInstructor Manual (5G-Small Cell Deployment Training)elmoustaphaelNo ratings yet
- Tabangao Shell Refinery Employees Association v. Pilipinas ShellDocument17 pagesTabangao Shell Refinery Employees Association v. Pilipinas ShellJohn FerarenNo ratings yet
- GR 96078Document2 pagesGR 96078glennNo ratings yet
- Preventing Slips Trips and FallsDocument26 pagesPreventing Slips Trips and Fallstelteguh01No ratings yet
- SOP-24 Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesSOP-24 Risk AssessmentCahya SemestaNo ratings yet
- Tos and Summative TestDocument5 pagesTos and Summative TestRomel Garcia100% (1)
- Parties in This CaseDocument1 pageParties in This CaselexxNo ratings yet
- TBT-Scaffolding Safety1Document2 pagesTBT-Scaffolding Safety1Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- SDS - Maxiclean MP1 - REV05.08.04.2022 1Document13 pagesSDS - Maxiclean MP1 - REV05.08.04.2022 1Muhamad Gaddafi SamsudinNo ratings yet
- Confined Space Entry PermitDocument2 pagesConfined Space Entry Permitreda mesbahNo ratings yet
- Dr. Shakuntala Misra National Rehabilitation UniversityDocument14 pagesDr. Shakuntala Misra National Rehabilitation Universityshubham0% (1)
- Midterm Output Reaction PaperDocument3 pagesMidterm Output Reaction PaperTitong CherazelNo ratings yet
- Salary Slip (Indra)Document3 pagesSalary Slip (Indra)Ali MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Surat Izin Kerja AmanDocument1 pageSurat Izin Kerja AmanNUNIK CELLNo ratings yet
- Worker Exposure To Silica During Countertop Manufacturing, Finishing and InstallationDocument8 pagesWorker Exposure To Silica During Countertop Manufacturing, Finishing and InstallationShahid BhattiNo ratings yet