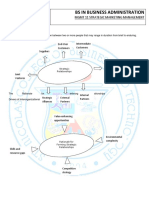
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ch12 Evaluation Control
ch12 Evaluation Control
Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- AT&T's Talent OverhaulDocument9 pagesAT&T's Talent OverhaulDivyaNo ratings yet
- Group4 - PBM - Sec CDocument13 pagesGroup4 - PBM - Sec Ckiran venugopalNo ratings yet
- BSBHRM614 AT2 Updated Human Resources Strategic PlanDocument3 pagesBSBHRM614 AT2 Updated Human Resources Strategic PlantamaraNo ratings yet
- Barney Smca6 PPT 06Document20 pagesBarney Smca6 PPT 06HagarMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Hill and Jones Chapter 12 SlidesDocument31 pagesHill and Jones Chapter 12 SlidesC Sandeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document33 pagesModule 1Wejdan Alghamdi100% (1)
- David - Sm14 Inppt04Document50 pagesDavid - Sm14 Inppt04Glorden Mae Ibañez SalandananNo ratings yet
- Strategy Formulation: Functional Strategy and Strategic ChoiceDocument36 pagesStrategy Formulation: Functional Strategy and Strategic ChoiceStuti SinghalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Evaluation and ControlDocument22 pagesStrategic Evaluation and ControlroshiramNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management and Business Policy 15e: Strategy Implementation: Global StrategyDocument27 pagesStrategic Management and Business Policy 15e: Strategy Implementation: Global StrategyAnnisa Dewi0% (2)
- Wheelan 14e ch01Document41 pagesWheelan 14e ch01mostafaragab1983No ratings yet
- Strategic Management and Business Policy 15e: Strategy Implementation: Staffing and DirectingDocument29 pagesStrategic Management and Business Policy 15e: Strategy Implementation: Staffing and DirectingJacklineNo ratings yet
- ch7 Corporate StrategyDocument36 pagesch7 Corporate StrategyYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- ch5 Internal AnalysisDocument45 pagesch5 Internal AnalysisYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel Latif100% (1)
- Building An Organization Capable of Good Strategy Execution: People, Capabilities, and StructureDocument47 pagesBuilding An Organization Capable of Good Strategy Execution: People, Capabilities, and StructureMI chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document26 pagesChapter 4raghooosh yNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Strategic ManagementDocument4 pagesThe Nature of Strategic Managementscribd uploaderNo ratings yet
- SM - Unit 15 - PPTDocument18 pagesSM - Unit 15 - PPTBrian BoydNo ratings yet
- Week7 SM Chapter05 Product DifferentiationDocument23 pagesWeek7 SM Chapter05 Product DifferentiationMin Soo JohNo ratings yet
- 09 - Strategy Review, Evaluation and ControlDocument32 pages09 - Strategy Review, Evaluation and ControlIm NayeonNo ratings yet
- Wheelen 14e ch01Document40 pagesWheelen 14e ch01franky sunaryo100% (1)
- 5david - sm16 - ppt04Document60 pages5david - sm16 - ppt04Emad EisaNo ratings yet
- The Role and Environment of Managerial FinanceDocument37 pagesThe Role and Environment of Managerial FinanceMATHILDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document34 pagesChapter 8Tayba AwanNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance Chapter 10 Michael A. Hitt R. Duane Ireland Robert E. HoskissonDocument18 pagesCorporate Governance Chapter 10 Michael A. Hitt R. Duane Ireland Robert E. HoskissonROger Rabit100% (1)
- IE MatrixDocument5 pagesIE MatrixShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- Lec11 Controlling Activities and Operations Ver2Document43 pagesLec11 Controlling Activities and Operations Ver2Darren KhewNo ratings yet
- Leadership and EthicsDocument22 pagesLeadership and EthicsmathanNo ratings yet
- CH2 ... Introduction To Financial Statement AnalysisDocument96 pagesCH2 ... Introduction To Financial Statement AnalysisMariam AlraeesiNo ratings yet
- IB - Hills - Chapter 09Document18 pagesIB - Hills - Chapter 09Nahid Tasneem TasneemNo ratings yet
- Ch1 SMDocument24 pagesCh1 SMAbdiaziz Mohamed OmarNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 5 Management StrategicDocument33 pagesPertemuan Ke 5 Management StrategicErica SPNo ratings yet
- DBA (2nd Year - 1st Semester - Summer Course) Subject: Instructor: Date: AssignmentDocument43 pagesDBA (2nd Year - 1st Semester - Summer Course) Subject: Instructor: Date: AssignmentOla AtefNo ratings yet
- David sm13 PPT 07Document32 pagesDavid sm13 PPT 07Ahmed YousufzaiNo ratings yet
- LESSON 7 Strategic RelationshipsDocument7 pagesLESSON 7 Strategic RelationshipsKrisel IbanezNo ratings yet
- Hitt13e PPT Ch11Document67 pagesHitt13e PPT Ch11Nirvana ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Leadership Being An Effective Project ManagerDocument14 pages10 - Leadership Being An Effective Project ManagerAamir ChohanNo ratings yet
- Bovee Bct13 Inppt 14Document32 pagesBovee Bct13 Inppt 14Shuhada ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Final Presentation-4Document31 pagesChapter 8 Final Presentation-4api-269676361No ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument34 pagesStrategic ManagementDewi PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Wheelen smbp12 PPT 12Document19 pagesWheelen smbp12 PPT 12nabilredascribdNo ratings yet
- მე 5Document26 pagesმე 5Ni Ni Bobokhidze100% (1)
- Social Responsibility and Ethics in Strategic ManagementDocument29 pagesSocial Responsibility and Ethics in Strategic ManagementSanthiya Mogen100% (1)
- Strategic Management CH 08Document13 pagesStrategic Management CH 08Khadra NuurNo ratings yet
- The Internal Assessment: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 10 Edition Fred DavidDocument88 pagesThe Internal Assessment: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 10 Edition Fred DavidMaharani KumalasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1Bảo QuốcNo ratings yet
- ch9 RevisedDocument11 pagesch9 Revisedshaikha alneyadiNo ratings yet
- Branches of Business ManagementDocument3 pagesBranches of Business ManagementHerbert RulononaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.5 (BP)Document2 pagesAssignment No.5 (BP)Bernadette AnicetoNo ratings yet
- David sm13 PPT 09Document24 pagesDavid sm13 PPT 09Alejandro Perez SantanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?Document30 pagesChapter 5: The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?yrkprasadNo ratings yet
- Strategy Execution: Chapter TenDocument38 pagesStrategy Execution: Chapter TenChristy Machaalany100% (1)
- Chapter-3: The Roots of Competitive AdvantagesDocument14 pagesChapter-3: The Roots of Competitive AdvantagesSakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Strategic Entrepreneurship: Fourth Edition © 2007 Philip A WickhamDocument14 pagesStrategic Entrepreneurship: Fourth Edition © 2007 Philip A WickhamerikloevgrenNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument17 pagesStrategic ManagementKECEBONG ALBINONo ratings yet
- Leadership 2013Document32 pagesLeadership 2013Soumi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Best Practices Award For Improving Corruption in Public Sector AgenciesDocument7 pagesManagement Accounting Best Practices Award For Improving Corruption in Public Sector AgenciesESTERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document49 pagesChapter 5Dos patrickNo ratings yet
- IPSAS Explained: A Summary of International Public Sector Accounting StandardsFrom EverandIPSAS Explained: A Summary of International Public Sector Accounting StandardsNo ratings yet
- Wheelen - Chapter 12 - Execution - ControlDocument39 pagesWheelen - Chapter 12 - Execution - ControlpoisonboxNo ratings yet
- W14-15 BSCDocument41 pagesW14-15 BSCTalha GillNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document36 pagesCH 1apip ajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: The Organization and Structure of Banking and The Financial-Services IndustryDocument16 pagesChapter Three: The Organization and Structure of Banking and The Financial-Services IndustryYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1Youssef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Ad AnalysisDocument21 pagesAd AnalysisYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: The Financial Statements of Banks and Their Principal CompetitorsDocument58 pagesChapter Five: The Financial Statements of Banks and Their Principal CompetitorsYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: Measuring & Evaluating The Performance of Banks & Their Principal CompetitorsDocument10 pagesChapter Six: Measuring & Evaluating The Performance of Banks & Their Principal CompetitorsYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- ch5 Internal AnalysisDocument45 pagesch5 Internal AnalysisYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel Latif100% (1)
- ch7 Corporate StrategyDocument36 pagesch7 Corporate StrategyYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Speech Analysis Outline: I. Basic InfoDocument2 pagesSpeech Analysis Outline: I. Basic InfoYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- ch8 Functional StrategyDocument22 pagesch8 Functional StrategyYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Quiz CorporateDocument4 pagesQuiz CorporateYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Final Revision Before MidtermDocument6 pagesFinal Revision Before MidtermYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 International FinanceDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 International FinanceYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Company Portrait Gea Westfalia Separator 9997 5856 100 PDFDocument60 pagesCompany Portrait Gea Westfalia Separator 9997 5856 100 PDFbanerjeeamlanNo ratings yet
- U.S. Department of Energy (Doe) : Final Closeout Technical ReportDocument84 pagesU.S. Department of Energy (Doe) : Final Closeout Technical ReportZEUS ARMYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 QsDocument7 pagesTutorial 9 QsDylan Rabin PereiraNo ratings yet
- Government of Andhra PradeshDocument1 pageGovernment of Andhra PradeshD V BHASKARNo ratings yet
- BLUEPRINT - Jack and Michelle BoschDocument19 pagesBLUEPRINT - Jack and Michelle BoschHaziqNo ratings yet
- Gartner Reprint Video PlatformDocument28 pagesGartner Reprint Video PlatformFranc DolencNo ratings yet
- MGT7103 Group 4 - Maxis - Presentation 3Document41 pagesMGT7103 Group 4 - Maxis - Presentation 3hpone.mbaNo ratings yet
- To Study The Effectiveness of Talent Management Strategies On Employees Retention in IT SectorDocument8 pagesTo Study The Effectiveness of Talent Management Strategies On Employees Retention in IT SectorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Aregash Final Thesis 2018Document89 pagesAregash Final Thesis 2018Aregash MandieNo ratings yet
- The Audit ProcessDocument39 pagesThe Audit ProcessMarcos ViníciusNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance (Fm304)Document17 pagesCorporate Finance (Fm304)Sailashree ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Knowledge Management Chap#1Document12 pagesIntroduction To Knowledge Management Chap#1raja farhanNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Human Resource in Vietnam: Necessity and Research ProposalDocument15 pagesSustainable Human Resource in Vietnam: Necessity and Research ProposalHạnh NguyênNo ratings yet
- LAS EPP or TLEDocument2 pagesLAS EPP or TLEAntonio TagordaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), Fifth EditionDocument2 pagesA Guide To The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), Fifth EditionPriya JuligantiNo ratings yet
- Edutopia STW Financial Lit Ariel Lessonplan RememberingDocument3 pagesEdutopia STW Financial Lit Ariel Lessonplan Rememberingjohnmauro alapagNo ratings yet
- Beige Clean Lines Marketing Executive Resume 1Document2 pagesBeige Clean Lines Marketing Executive Resume 1Ivie Mae Lorenzo BienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MarketingDocument27 pagesChapter 1 MarketingAfsar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bills of LadingDocument27 pagesBills of LadingAkanshaNo ratings yet
- Astm D 660 - 93 (2019)Document9 pagesAstm D 660 - 93 (2019)Sur VaniNo ratings yet
- Machinery's - Reference - Series - No - 140 SafeguardsDocument61 pagesMachinery's - Reference - Series - No - 140 SafeguardsJohnNo ratings yet
- ObliconDocument22 pagesObliconNoel Christopher G. BellezaNo ratings yet
- W6 Lesson 5 Transaction Cycle, Business Processes and Its Associated Controls - Part II - ModuleDocument13 pagesW6 Lesson 5 Transaction Cycle, Business Processes and Its Associated Controls - Part II - ModuleBellaNo ratings yet
- Your Results For: "Multiple Choice Questions"Document21 pagesYour Results For: "Multiple Choice Questions"Jearick Reario AtazanNo ratings yet
- Assigment 1 - Q1024153 - GABRIEL RIOSDocument6 pagesAssigment 1 - Q1024153 - GABRIEL RIOSGabriel Rios LopezNo ratings yet
- Iec 61131-8 PDFDocument4 pagesIec 61131-8 PDFAndres GomezNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 1-2 Workbook-Bsbcrt512-Bsb50420-Cycle A-Edu Nomad-V1.0 2023Document17 pagesAssessment Task 1-2 Workbook-Bsbcrt512-Bsb50420-Cycle A-Edu Nomad-V1.0 2023Sujal KutalNo ratings yet
ch12 Evaluation Control
ch12 Evaluation Control
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ch12 Evaluation Control
ch12 Evaluation Control
Copyright:
Available Formats
Strategic Management and
Business Policy 15e, Global Edition
Chapter 12
Evaluation and
Control
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
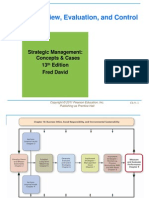
Figure 12-1: Evaluation and Control Process
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-2
Measuring Performance
• Performance
– end result of an activity
• One of the obstacles to effective control is
the difficulty in developing appropriate measures
of important activities and outputs.
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-3
Types of Controls (1 of 2)
• Output controls
– specify what is to be accomplished by focusing on the
end result through the use of objectives
• Behavior controls
– specify how something is done through policies, rules,
standard operating procedures and orders from
supervisors
• Input controls
– emphasize resources, as knowledge, skills, abilities
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-4
Activity-based Costing
• Activity-based costing
– allocates indirect and direct costs to individual
product lines based on value-added activities
going into that product
• Allows accountants to charge costs more
accurately since it allocates overhead more
precisely.
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-5
Balanced Scorecard (1 of 3)
• Balanced scorecard
– combines financial measures that tell results of
actions already taken with operational
measures on customer satisfaction, internal
processes, and corporation’s innovation and
improvement activities—the drivers of future
financial performance
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-6
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
7
Balanced Scorecard (2 of 3)
In the balanced scorecard, management develops
goals or objectives in each of four areas:
1. Financial: How do we appear to shareholders?
2. Customer: How do customers view us?
3. Internal business perspective: What must we
excel at?
4. Innovation and learning: Can we continue to
improve and create value?
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-8
Balanced Scorecard (3 of 3)
• Key performance measures
– measures that are essential for achieving a
desired strategic option
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-9
Using Benchmarking To Evaluate
Performance
• Benchmarking
– the continual process of measuring products,
services and practices against the toughest
competitors or those companies recognized as
industry leaders
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-10
Benchmarking
1. Identify area or process to be examined
2. Find behavioral and output measures
3. Select accessible set of competitors of best
practices
4. Calculate differences among company’s
performance measurements and competitors;
determine why differences exist
5. Develop tactical programs for closing
performance gaps
6. Implement the programs and compare the results
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-11
Problems in Measuring Performance
• Lack of quantifiable objectives or performance
standards
• Inability to use information systems to provide
timely and valid information
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-12
Short-Term Orientation
Long-term evaluations may not be conducted
because executives:
• Don’t realize their importance.
• Believe that short-term considerations are more
important than long-term considerations.
• Aren’t personally evaluated on a long-term basis.
• Don’t have the time to make a long-term analysis.
Copyright © 2018 Pearson Education, Ltd. All Rights Reserved..
12-13
You might also like
- AT&T's Talent OverhaulDocument9 pagesAT&T's Talent OverhaulDivyaNo ratings yet
- Group4 - PBM - Sec CDocument13 pagesGroup4 - PBM - Sec Ckiran venugopalNo ratings yet
- BSBHRM614 AT2 Updated Human Resources Strategic PlanDocument3 pagesBSBHRM614 AT2 Updated Human Resources Strategic PlantamaraNo ratings yet
- Barney Smca6 PPT 06Document20 pagesBarney Smca6 PPT 06HagarMahmoudNo ratings yet
- Hill and Jones Chapter 12 SlidesDocument31 pagesHill and Jones Chapter 12 SlidesC Sandeep ReddyNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document33 pagesModule 1Wejdan Alghamdi100% (1)
- David - Sm14 Inppt04Document50 pagesDavid - Sm14 Inppt04Glorden Mae Ibañez SalandananNo ratings yet
- Strategy Formulation: Functional Strategy and Strategic ChoiceDocument36 pagesStrategy Formulation: Functional Strategy and Strategic ChoiceStuti SinghalNo ratings yet
- Strategic Evaluation and ControlDocument22 pagesStrategic Evaluation and ControlroshiramNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management and Business Policy 15e: Strategy Implementation: Global StrategyDocument27 pagesStrategic Management and Business Policy 15e: Strategy Implementation: Global StrategyAnnisa Dewi0% (2)
- Wheelan 14e ch01Document41 pagesWheelan 14e ch01mostafaragab1983No ratings yet
- Strategic Management and Business Policy 15e: Strategy Implementation: Staffing and DirectingDocument29 pagesStrategic Management and Business Policy 15e: Strategy Implementation: Staffing and DirectingJacklineNo ratings yet
- ch7 Corporate StrategyDocument36 pagesch7 Corporate StrategyYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- ch5 Internal AnalysisDocument45 pagesch5 Internal AnalysisYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel Latif100% (1)
- Building An Organization Capable of Good Strategy Execution: People, Capabilities, and StructureDocument47 pagesBuilding An Organization Capable of Good Strategy Execution: People, Capabilities, and StructureMI chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document26 pagesChapter 4raghooosh yNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Strategic ManagementDocument4 pagesThe Nature of Strategic Managementscribd uploaderNo ratings yet
- SM - Unit 15 - PPTDocument18 pagesSM - Unit 15 - PPTBrian BoydNo ratings yet
- Week7 SM Chapter05 Product DifferentiationDocument23 pagesWeek7 SM Chapter05 Product DifferentiationMin Soo JohNo ratings yet
- 09 - Strategy Review, Evaluation and ControlDocument32 pages09 - Strategy Review, Evaluation and ControlIm NayeonNo ratings yet
- Wheelen 14e ch01Document40 pagesWheelen 14e ch01franky sunaryo100% (1)
- 5david - sm16 - ppt04Document60 pages5david - sm16 - ppt04Emad EisaNo ratings yet
- The Role and Environment of Managerial FinanceDocument37 pagesThe Role and Environment of Managerial FinanceMATHILDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document34 pagesChapter 8Tayba AwanNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance Chapter 10 Michael A. Hitt R. Duane Ireland Robert E. HoskissonDocument18 pagesCorporate Governance Chapter 10 Michael A. Hitt R. Duane Ireland Robert E. HoskissonROger Rabit100% (1)
- IE MatrixDocument5 pagesIE MatrixShereen AlobinayNo ratings yet
- Lec11 Controlling Activities and Operations Ver2Document43 pagesLec11 Controlling Activities and Operations Ver2Darren KhewNo ratings yet
- Leadership and EthicsDocument22 pagesLeadership and EthicsmathanNo ratings yet
- CH2 ... Introduction To Financial Statement AnalysisDocument96 pagesCH2 ... Introduction To Financial Statement AnalysisMariam AlraeesiNo ratings yet
- IB - Hills - Chapter 09Document18 pagesIB - Hills - Chapter 09Nahid Tasneem TasneemNo ratings yet
- Ch1 SMDocument24 pagesCh1 SMAbdiaziz Mohamed OmarNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke 5 Management StrategicDocument33 pagesPertemuan Ke 5 Management StrategicErica SPNo ratings yet
- DBA (2nd Year - 1st Semester - Summer Course) Subject: Instructor: Date: AssignmentDocument43 pagesDBA (2nd Year - 1st Semester - Summer Course) Subject: Instructor: Date: AssignmentOla AtefNo ratings yet
- David sm13 PPT 07Document32 pagesDavid sm13 PPT 07Ahmed YousufzaiNo ratings yet
- LESSON 7 Strategic RelationshipsDocument7 pagesLESSON 7 Strategic RelationshipsKrisel IbanezNo ratings yet
- Hitt13e PPT Ch11Document67 pagesHitt13e PPT Ch11Nirvana ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Leadership Being An Effective Project ManagerDocument14 pages10 - Leadership Being An Effective Project ManagerAamir ChohanNo ratings yet
- Bovee Bct13 Inppt 14Document32 pagesBovee Bct13 Inppt 14Shuhada ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Final Presentation-4Document31 pagesChapter 8 Final Presentation-4api-269676361No ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument34 pagesStrategic ManagementDewi PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Wheelen smbp12 PPT 12Document19 pagesWheelen smbp12 PPT 12nabilredascribdNo ratings yet
- მე 5Document26 pagesმე 5Ni Ni Bobokhidze100% (1)
- Social Responsibility and Ethics in Strategic ManagementDocument29 pagesSocial Responsibility and Ethics in Strategic ManagementSanthiya Mogen100% (1)
- Strategic Management CH 08Document13 pagesStrategic Management CH 08Khadra NuurNo ratings yet
- The Internal Assessment: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 10 Edition Fred DavidDocument88 pagesThe Internal Assessment: Strategic Management: Concepts & Cases 10 Edition Fred DavidMaharani KumalasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1Bảo QuốcNo ratings yet
- ch9 RevisedDocument11 pagesch9 Revisedshaikha alneyadiNo ratings yet
- Branches of Business ManagementDocument3 pagesBranches of Business ManagementHerbert RulononaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.5 (BP)Document2 pagesAssignment No.5 (BP)Bernadette AnicetoNo ratings yet
- David sm13 PPT 09Document24 pagesDavid sm13 PPT 09Alejandro Perez SantanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?Document30 pagesChapter 5: The Five Generic Competitive Strategies: Which One To Employ?yrkprasadNo ratings yet
- Strategy Execution: Chapter TenDocument38 pagesStrategy Execution: Chapter TenChristy Machaalany100% (1)
- Chapter-3: The Roots of Competitive AdvantagesDocument14 pagesChapter-3: The Roots of Competitive AdvantagesSakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Strategic Entrepreneurship: Fourth Edition © 2007 Philip A WickhamDocument14 pagesStrategic Entrepreneurship: Fourth Edition © 2007 Philip A WickhamerikloevgrenNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument17 pagesStrategic ManagementKECEBONG ALBINONo ratings yet
- Leadership 2013Document32 pagesLeadership 2013Soumi SinhaNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Best Practices Award For Improving Corruption in Public Sector AgenciesDocument7 pagesManagement Accounting Best Practices Award For Improving Corruption in Public Sector AgenciesESTERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document49 pagesChapter 5Dos patrickNo ratings yet
- IPSAS Explained: A Summary of International Public Sector Accounting StandardsFrom EverandIPSAS Explained: A Summary of International Public Sector Accounting StandardsNo ratings yet
- Wheelen - Chapter 12 - Execution - ControlDocument39 pagesWheelen - Chapter 12 - Execution - ControlpoisonboxNo ratings yet
- W14-15 BSCDocument41 pagesW14-15 BSCTalha GillNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document36 pagesCH 1apip ajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: The Organization and Structure of Banking and The Financial-Services IndustryDocument16 pagesChapter Three: The Organization and Structure of Banking and The Financial-Services IndustryYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1Youssef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Ad AnalysisDocument21 pagesAd AnalysisYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five: The Financial Statements of Banks and Their Principal CompetitorsDocument58 pagesChapter Five: The Financial Statements of Banks and Their Principal CompetitorsYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: Measuring & Evaluating The Performance of Banks & Their Principal CompetitorsDocument10 pagesChapter Six: Measuring & Evaluating The Performance of Banks & Their Principal CompetitorsYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- ch5 Internal AnalysisDocument45 pagesch5 Internal AnalysisYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel Latif100% (1)
- ch7 Corporate StrategyDocument36 pagesch7 Corporate StrategyYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Speech Analysis Outline: I. Basic InfoDocument2 pagesSpeech Analysis Outline: I. Basic InfoYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- ch8 Functional StrategyDocument22 pagesch8 Functional StrategyYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Quiz CorporateDocument4 pagesQuiz CorporateYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Final Revision Before MidtermDocument6 pagesFinal Revision Before MidtermYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 International FinanceDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 International FinanceYoussef Youssef Ahmed Abdelmeguid Abdel LatifNo ratings yet
- Company Portrait Gea Westfalia Separator 9997 5856 100 PDFDocument60 pagesCompany Portrait Gea Westfalia Separator 9997 5856 100 PDFbanerjeeamlanNo ratings yet
- U.S. Department of Energy (Doe) : Final Closeout Technical ReportDocument84 pagesU.S. Department of Energy (Doe) : Final Closeout Technical ReportZEUS ARMYNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 QsDocument7 pagesTutorial 9 QsDylan Rabin PereiraNo ratings yet
- Government of Andhra PradeshDocument1 pageGovernment of Andhra PradeshD V BHASKARNo ratings yet
- BLUEPRINT - Jack and Michelle BoschDocument19 pagesBLUEPRINT - Jack and Michelle BoschHaziqNo ratings yet
- Gartner Reprint Video PlatformDocument28 pagesGartner Reprint Video PlatformFranc DolencNo ratings yet
- MGT7103 Group 4 - Maxis - Presentation 3Document41 pagesMGT7103 Group 4 - Maxis - Presentation 3hpone.mbaNo ratings yet
- To Study The Effectiveness of Talent Management Strategies On Employees Retention in IT SectorDocument8 pagesTo Study The Effectiveness of Talent Management Strategies On Employees Retention in IT SectorInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Aregash Final Thesis 2018Document89 pagesAregash Final Thesis 2018Aregash MandieNo ratings yet
- The Audit ProcessDocument39 pagesThe Audit ProcessMarcos ViníciusNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance (Fm304)Document17 pagesCorporate Finance (Fm304)Sailashree ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Knowledge Management Chap#1Document12 pagesIntroduction To Knowledge Management Chap#1raja farhanNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Human Resource in Vietnam: Necessity and Research ProposalDocument15 pagesSustainable Human Resource in Vietnam: Necessity and Research ProposalHạnh NguyênNo ratings yet
- LAS EPP or TLEDocument2 pagesLAS EPP or TLEAntonio TagordaNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), Fifth EditionDocument2 pagesA Guide To The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), Fifth EditionPriya JuligantiNo ratings yet
- Edutopia STW Financial Lit Ariel Lessonplan RememberingDocument3 pagesEdutopia STW Financial Lit Ariel Lessonplan Rememberingjohnmauro alapagNo ratings yet
- Beige Clean Lines Marketing Executive Resume 1Document2 pagesBeige Clean Lines Marketing Executive Resume 1Ivie Mae Lorenzo BienNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MarketingDocument27 pagesChapter 1 MarketingAfsar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Bills of LadingDocument27 pagesBills of LadingAkanshaNo ratings yet
- Astm D 660 - 93 (2019)Document9 pagesAstm D 660 - 93 (2019)Sur VaniNo ratings yet
- Machinery's - Reference - Series - No - 140 SafeguardsDocument61 pagesMachinery's - Reference - Series - No - 140 SafeguardsJohnNo ratings yet
- ObliconDocument22 pagesObliconNoel Christopher G. BellezaNo ratings yet
- W6 Lesson 5 Transaction Cycle, Business Processes and Its Associated Controls - Part II - ModuleDocument13 pagesW6 Lesson 5 Transaction Cycle, Business Processes and Its Associated Controls - Part II - ModuleBellaNo ratings yet
- Your Results For: "Multiple Choice Questions"Document21 pagesYour Results For: "Multiple Choice Questions"Jearick Reario AtazanNo ratings yet
- Assigment 1 - Q1024153 - GABRIEL RIOSDocument6 pagesAssigment 1 - Q1024153 - GABRIEL RIOSGabriel Rios LopezNo ratings yet
- Iec 61131-8 PDFDocument4 pagesIec 61131-8 PDFAndres GomezNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 1-2 Workbook-Bsbcrt512-Bsb50420-Cycle A-Edu Nomad-V1.0 2023Document17 pagesAssessment Task 1-2 Workbook-Bsbcrt512-Bsb50420-Cycle A-Edu Nomad-V1.0 2023Sujal KutalNo ratings yet