Professional Documents
Culture Documents
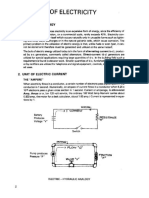
At Constant Temperature The Voltage Is Directly Proportional To The Current Flowing Through The Conductor. SI UNIT:-ohm
At Constant Temperature The Voltage Is Directly Proportional To The Current Flowing Through The Conductor. SI UNIT:-ohm
Uploaded by
Harshal GulhaneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
At Constant Temperature The Voltage Is Directly Proportional To The Current Flowing Through The Conductor. SI UNIT:-ohm
At Constant Temperature The Voltage Is Directly Proportional To The Current Flowing Through The Conductor. SI UNIT:-ohm
Uploaded by
Harshal GulhaneCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 3
At constant temperature the voltage is directly
proportional to the current flowing through the
conductor.
SI UNIT:-ohm
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter 3
Summary
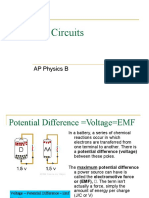
Review of V, I, and R
(V)Voltage the amount of energy per charge available to
is move electrons from one point to another in a circuit.
(I)Current the rate of charge flow and is measured in
is amperes.
(R)Resistance is the opposition to current and is measured
in ohms.
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter 3
Summary
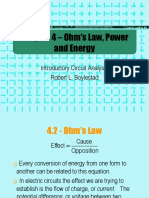
The most important fundamental law in electronics is
Ohm’s law, which relates voltage, current, and resistance.
Georg Simon Ohm (1787-1854) studied the relationship
between voltage, current, and resistance and formulated
the equation that bears his name.
V
I
R
What is the current in from a 12 V source if the
resistance is 10 ? 1.2 A
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter
Summary 3
Ohm’s law
If you need to solve for voltage, Ohm’s law is:
V IR
What is the voltage across a 680 resistor if the
current is 26.5 mA? 18 V
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter 3
Summary
Ohm’s law
V
If you need to solve for resistance, Ohm’s law is: R
I
What is the (hot)
resistance of the bulb? 132 O FF V
Hz
115 V V
m V
A Ra n g e
A u t o ra n g e 1 s
To u c h / H o ld 1 s
10 A
V
40 m A C O M
Fu se d
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter 3
Summary
A student takes data for a resistor and fits the straight
lineGraph
shown toofthe
Current versus
data. What Voltage
is the resistance and the
conductance of the resistor?
16
The slope represents the 14
conductance.
14.8 mA - 0 mA 12
G 1.48 mS
I (m A )
10.0 V - 0 V
The reciprocal of the 8
conductance is the
4
resistance:
1 1
R 676 Ω 0
0 2 4 6 8 10
G 1.48 mS
V (V )
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter 3
Summary
Graph of Current versus Voltage
Notice that the plot of 10
current versus voltage for a 8 .0
fixed resistor is a line with
a positive slope. What is
C u rren t (m A )
6 .0
the resistance indicated by
4 .0
the graph? 2.7 k
2 .0
What is its 0
conductance? 0.37 mS 0 10
V o lta g e (V )
20 30
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter 3
Summary
Graph of Current versus Resistance
10
If resistance is varied
for a constant voltage, 8.0
the current verses
Current (mA)
6.0
resistance curve plots a
hyperbola. 4.0
2.0
What is the curve for 0
a 3 V source? 0 1.0 2.0 3.0
Resistance (kW )
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter 3
Summary
Application of Ohm’s law 26.8 mA
The resistor is green-blue
brown-gold. What should the
m e te r -
D C A m
ammeter read? +
P o w e r S u p p ly
V A
+15 V
G nd 5 V 2A - + - +
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter 3
Selected Key Terms
Linear Characterized by a straight-line relationship.
Ohm’s law A law stating that current is directly
proportional to voltage and inversely
proportional to current.
Troubleshooting A systematic process of isolating, identifying,
and correcting a fault in a circuit or system.
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter 3
REPRESENTATION OF OHM’S LAW
Ammeter
Voltmeter
Resistor
cell
switch
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
Chapter 3
LIMITATION OF OHM’S LAW
1.V ceases to be proportional to I
2.The relation between V and I depends upon the sign of V
3.The relation between V and I is not unique.
Principles of Electric Circuits - Floyd © Copyright 2006 Prentice-Hall
You might also like
- 002MCQDocument15 pages002MCQAhmed FarahatNo ratings yet
- Current Voltage and ResistanceDocument31 pagesCurrent Voltage and ResistanceRa NielNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Fundamentals of Electricity I. ObjectivesDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Fundamentals of Electricity I. ObjectivesChristian Lumactod Embolode100% (1)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsFrom EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Lesson Plan Electricity and Ohms LawDocument5 pagesLesson Plan Electricity and Ohms Lawapi-30940398480% (10)
- Chapter 3Document24 pagesChapter 3Meme MNo ratings yet
- pp03Document24 pagespp03Heshalini Raja GopalNo ratings yet
- Electronics Fundamentals: Engr. Hassan Sultan Waqar Azeem Engr. Ammar HassanDocument36 pagesElectronics Fundamentals: Engr. Hassan Sultan Waqar Azeem Engr. Ammar HassanWaqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Circuits, Conventional Flow, 9 EdDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Electric Circuits, Conventional Flow, 9 EdYodel RamírezNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Circuits, Conventional Flow, 9 EdDocument24 pagesPrinciples of Electric Circuits, Conventional Flow, 9 EdjavierNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Circuit 1Document14 pagesChapter 3 Circuit 1peterNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electric Circuits, Conventional Flow, 9 EdDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Electric Circuits, Conventional Flow, 9 EdAl-hasan RayyanNo ratings yet
- 1 Sinus Bentuk GelombangDocument21 pages1 Sinus Bentuk GelombangDwi Agun WibowoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. Electric CurrentDocument44 pagesChapter 4. Electric Currentrahmah0615No ratings yet
- Unit 5: Electrical Circuits and Ohm's Law: Outline OutcomesDocument8 pagesUnit 5: Electrical Circuits and Ohm's Law: Outline Outcomesعبدالله حمدNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Electrical CircuitDocument67 pagesChapter 1-Electrical CircuitDKM 2ANo ratings yet
- OhmslawDocument17 pagesOhmslawBright OvieNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Ohms LawDocument24 pagesLecture 4 - Ohms LawRa JallowNo ratings yet
- DC CircuitsDocument59 pagesDC CircuitsAbhishek ThakkarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 10 (Autosaved)Document29 pagesCHAPTER - 10 (Autosaved)Shinn LayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Basic LawDocument115 pagesLecture 2 - Basic LawYip Tuck WaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - AC Circuits - MG HusseinDocument32 pagesChapter-2 - AC Circuits - MG Husseinضياء بن احمد الكباريNo ratings yet
- Y JL 5 Sa X8 WCML4 DJsktazDocument28 pagesY JL 5 Sa X8 WCML4 DJsktazAswini Kumar PaloNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Current and ResistanceDocument24 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Current and ResistanceCassandra Mae Bauit PascuaNo ratings yet
- Arus Dan ResistansiDocument27 pagesArus Dan ResistansiFahri AzizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27. Current and ResistanceDocument23 pagesChapter 27. Current and ResistanceKent TongloyNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL SCIENCE TERM 3 E Cape 1 - 1680Document160 pagesPHYSICAL SCIENCE TERM 3 E Cape 1 - 1680Shudufhadzo PrettyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Electricity: Cf:o - .JDocument73 pagesPrinciples of Electricity: Cf:o - .JNina GalesteNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 DC SystemDocument36 pagesChapter1 DC SystemBrian LiNo ratings yet
- DENE1113: Principle of Electrical and Electronic: Chapter 2.1: DC Circuit AnalysisDocument41 pagesDENE1113: Principle of Electrical and Electronic: Chapter 2.1: DC Circuit AnalysisNUR ASYIQIN BINTI AZAHARNo ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument24 pagesElectric CurrentGerone Tolentino AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law: Thinagariy D/o Pearanpan, Nanthini D/o Mathu, Navinaswary D/o BalakrishnanDocument5 pagesOhm'S Law: Thinagariy D/o Pearanpan, Nanthini D/o Mathu, Navinaswary D/o BalakrishnanNisha Lauren VishvanathNo ratings yet
- ρ is known as the resistivity of the material in ohm-meters. Good conductors,Document52 pagesρ is known as the resistivity of the material in ohm-meters. Good conductors,Mark BerioNo ratings yet
- Current and Resistance: By:SB Jamali Sindh Madressatul Islam University, KarachiDocument24 pagesCurrent and Resistance: By:SB Jamali Sindh Madressatul Islam University, Karachisain buxNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 1 (Final Term 2)Document31 pagesINTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 1 (Final Term 2)Abdul Halil AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 08 Corriente Electrica Dic2013Document35 pages08 Corriente Electrica Dic2013Jose Manuel BrotonsNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS NOTES 14 Class 10thDocument18 pagesPHYSICS NOTES 14 Class 10thMalikmuzamilNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit1&2Document13 pagesQuestion Bank Unit1&2Harsh AnmolNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law: University of The Immaculate Conception Bonifacio ST., Davao CityDocument5 pagesOhm'S Law: University of The Immaculate Conception Bonifacio ST., Davao CityRoselle TuraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 PhyDocument35 pagesChapter 3 Phyatintasya18No ratings yet
- Rishav Dugar 19IM3FP30: Name: Roll NumberDocument5 pagesRishav Dugar 19IM3FP30: Name: Roll NumberS VrNo ratings yet
- Beee (R 17) Short Question Bank 2017Document4 pagesBeee (R 17) Short Question Bank 2017upender raoNo ratings yet
- My ch18Document49 pagesMy ch18Hasleen BeniNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3-Ohm's Law, Energy, and PowerDocument33 pagesChapter-3-Ohm's Law, Energy, and PowershahadNo ratings yet
- Provided by Pn. Zuraidah BT Ali Mech. Eng. Dept. PUODocument53 pagesProvided by Pn. Zuraidah BT Ali Mech. Eng. Dept. PUOMuhd AkmalNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document4 pagesModule 2surajNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit I - EEC-1003 LO3 (Chapter 8) : Slides Prepared by Electric Circuit Team at Sharjah CollegesDocument39 pagesElectric Circuit I - EEC-1003 LO3 (Chapter 8) : Slides Prepared by Electric Circuit Team at Sharjah CollegesSaid Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- Circuits LabDocument5 pagesCircuits LabWyndellRioNo ratings yet
- Ac TheoryDocument61 pagesAc Theorytk techboyNo ratings yet
- Vel's University: Unit 1Document6 pagesVel's University: Unit 1Arun KumarNo ratings yet
- ElectricCircuitsActivity and LaboratoryDocument8 pagesElectricCircuitsActivity and LaboratoryalixavenicevibarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electric CircuitDocument81 pagesIntroduction To Electric Circuitkaushallyaa navindranNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuits: AP Physics BDocument24 pagesElectric Circuits: AP Physics BToto TauganNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Laws: Prepared By: Engr. Tomashita P. ArenasDocument19 pagesBasic Circuit Laws: Prepared By: Engr. Tomashita P. ArenasTomashita ArenasNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12 Electricity Annexure 1DDocument8 pagesChapter-12 Electricity Annexure 1DSuhani GosainNo ratings yet
- V, C and R: Teknik Audio VideoDocument20 pagesV, C and R: Teknik Audio VideoanisnwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27. Current and ResistanceDocument24 pagesChapter 27. Current and ResistanceRachel AustriaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic CircuitDocument8 pagesMagnetic CircuitMark Angelo M. EsclitoNo ratings yet
- PHYS 211 13ELECTRICITYCIRCUITand - OHMS LAWDocument5 pagesPHYS 211 13ELECTRICITYCIRCUITand - OHMS LAWRegina May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Basic Electro-Mechanical Engineering (EE-170) : Lecture#02Document41 pagesBasic Electro-Mechanical Engineering (EE-170) : Lecture#02Hassnain MassidNo ratings yet
- Marc Ribot & Oriol Jutglar Pràctica 1 M12Document25 pagesMarc Ribot & Oriol Jutglar Pràctica 1 M12Marc Ribot FornsNo ratings yet
- Tanishq - Ohm's LawDocument9 pagesTanishq - Ohm's LawShah Tanishq RiteshkumarNo ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Exercise 3 (2nd Sem)Document8 pagesExercise 3 (2nd Sem)Jan VegaNo ratings yet
- Example of Lab ReportDocument6 pagesExample of Lab ReportRomi Necq S. AbuelNo ratings yet
- N5 Physics All 2016 MisDocument23 pagesN5 Physics All 2016 MisPeter ZhaoNo ratings yet
- 2-week-10-LO1 and 2 Removing and Replacing Electrical UnitsDocument14 pages2-week-10-LO1 and 2 Removing and Replacing Electrical UnitsJheng Delos Reyes Pantoja100% (4)
- Sample - Physics Form 5yearly Lesson Plan 2010Document20 pagesSample - Physics Form 5yearly Lesson Plan 2010Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Test 2 PhyDocument5 pagesTest 2 PhyHassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Circuit Analysis For Complete Idiots - DAVID SMITHDocument194 pagesCircuit Analysis For Complete Idiots - DAVID SMITHDev Patel100% (1)
- MAT 1103 Tutorial 1: y y y yDocument6 pagesMAT 1103 Tutorial 1: y y y yfxgnfdggfdgbNo ratings yet
- 325C2 2005Document5 pages325C2 2005Iven GaneshaNo ratings yet
- 002-1-EE 111 Linear Circuit AnalysisDocument2 pages002-1-EE 111 Linear Circuit AnalysisBilal Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Combination CircuitsDocument6 pagesCombination CircuitsGordanPešićNo ratings yet
- Statistical Data Analysis For The Physical Sciences PDFDocument233 pagesStatistical Data Analysis For The Physical Sciences PDFCantia Dealuma100% (1)
- High Impedance Busbar Differential ProtectionDocument16 pagesHigh Impedance Busbar Differential Protectionዛላው መናNo ratings yet
- Ele 4Document10 pagesEle 4Benjamín DipNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity Lab ReportDocument6 pagesBasic Electricity Lab ReportBill Williams100% (1)
- Current Electricity Class 12Document60 pagesCurrent Electricity Class 12mukul mishraNo ratings yet
- Basic Electro-Mechanical Engineering (EE-170) : Lecture#02Document41 pagesBasic Electro-Mechanical Engineering (EE-170) : Lecture#02Hassnain MassidNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law, Power and EnergyDocument19 pagesOhm's Law, Power and Energymark saludaresNo ratings yet
- 1 Circuit TheoryDocument34 pages1 Circuit TheoryLove StrikeNo ratings yet
- Batteries: Generalized Distribution of Relaxation Times Analysis For The Characterization of Impedance SpectraDocument16 pagesBatteries: Generalized Distribution of Relaxation Times Analysis For The Characterization of Impedance SpectraMeriemNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 5Document5 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 5Technical GurujiNo ratings yet
- SERV2075 - 03/16 Module 9 - ElectronicsDocument91 pagesSERV2075 - 03/16 Module 9 - ElectronicsNovakurniawanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Lab Report TemplateDocument9 pagesEngineering Lab Report TemplateQasim KhanNo ratings yet
- EEB 231 - 2019 Lectures # 1 - 15 AugustDocument32 pagesEEB 231 - 2019 Lectures # 1 - 15 AugustLast BofeloNo ratings yet
- E109 - AgustinDocument25 pagesE109 - AgustinSeth Jarl G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- Solar Powered Cooling BoxDocument25 pagesSolar Powered Cooling BoxVaisakh RaveendranNo ratings yet