Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 viewsEnv Laws1
Env Laws1
Uploaded by
Mounika ReddyThis document outlines several key environmental laws and compliance requirements in India, including the Water Act, Air Act, and Environment Protection Act. It discusses the agencies that enforce these laws, such as State Pollution Control Boards. It also provides details on ambient air quality standards, hazardous waste management rules, and other regulatory information industry must adhere to.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- National Ambient Air Quality StandardsDocument1 pageNational Ambient Air Quality StandardsrajanarsuNo ratings yet
- Final ROE For NB Centennial Well Water RightDocument51 pagesFinal ROE For NB Centennial Well Water RightAaron KunklerNo ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagram of Bar SoapDocument9 pagesProcess Flow Diagram of Bar SoapAndrea Cabungcal0% (1)
- Pulp and Paper Industry PresentationDocument21 pagesPulp and Paper Industry PresentationRichard Obinna100% (1)
- Alcosan Wet Weather PlanDocument16 pagesAlcosan Wet Weather Planapi-282530339No ratings yet
- ESSA - 2005 - Stimulus MagazineDocument21 pagesESSA - 2005 - Stimulus MagazineDog DogNo ratings yet
- 2 Noise Standards 1666147628370Document2 pages2 Noise Standards 1666147628370shefani pon singhNo ratings yet
- Standards For Coal MinesDocument3 pagesStandards For Coal MinesRifaiNo ratings yet
- Sindh Ambient Air Quality Standards FormattedDocument1 pageSindh Ambient Air Quality Standards FormattedSaad QudratNo ratings yet
- Environmental Standards National Ambient Air Quality StandardsDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Standards National Ambient Air Quality StandardsThambidurai KNo ratings yet
- 6.pollution Standards For Coal MinesDocument4 pages6.pollution Standards For Coal MinesSuryaKanthNo ratings yet
- Sindh Environmental Quality Ambient Text FormDocument1 pageSindh Environmental Quality Ambient Text FormSaad QudratNo ratings yet
- 11 - Environmental Quality Standard 1Document27 pages11 - Environmental Quality Standard 1Durgesh Kumar NatNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentalstandardsDocument15 pagesEnvironmentalstandardsTeam Labs LaboratoryNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument54 pagesAir PollutionShivam SonkarNo ratings yet
- Ambient AQSDocument2 pagesAmbient AQSDiya lizbeth joseNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Extra Reading Material eDocument8 pagesAir Pollution Extra Reading Material epubgsuhanigNo ratings yet
- Environmental StandardsDocument7 pagesEnvironmental StandardsDuraiMuruganNo ratings yet
- ES 200 - S2 - Air - L2 - 7 Oct 2021Document37 pagesES 200 - S2 - Air - L2 - 7 Oct 2021vishal kumarNo ratings yet
- 27 1458110426 NewItem 196 NAAQMS Volume-I-1 PDFDocument1 page27 1458110426 NewItem 196 NAAQMS Volume-I-1 PDFAkhand AkhandNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document4 pagesLecture 15Neekita NeetuNo ratings yet
- Air Polltution (Compatibility Mode)Document37 pagesAir Polltution (Compatibility Mode)Bikash chapagainNo ratings yet
- AIR POLLUTION AND CONTROL - Lecture 1Document8 pagesAIR POLLUTION AND CONTROL - Lecture 1Dhiraj YNo ratings yet
- Naaqs 2009Document2 pagesNaaqs 2009sreenNo ratings yet
- Pollution Monitoring: Annexure-6Document5 pagesPollution Monitoring: Annexure-6Nisanth ThulasidasNo ratings yet
- Annexure I: National Ambient Air Quality Standards - NewDocument5 pagesAnnexure I: National Ambient Air Quality Standards - NewKrishna SrikanthNo ratings yet
- AmbientDocument1 pageAmbientSilambarasan ThirugnanamNo ratings yet
- Ambient Air Quality and Emission Standards Aesthetic Value and VisibilityDocument11 pagesAmbient Air Quality and Emission Standards Aesthetic Value and VisibilityantonyNo ratings yet
- National Ambient Air Quality StandardsDocument6 pagesNational Ambient Air Quality StandardsDebasmita Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Delhi Planning-DataDocument9 pagesDelhi Planning-DataNrjNo ratings yet
- Current and Future Standards & Guidelines For Oil & Gas Sector in India and Status of Its ImplementationDocument64 pagesCurrent and Future Standards & Guidelines For Oil & Gas Sector in India and Status of Its ImplementationVaishnavi JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Zypher PM10 & PM2.5Document3 pagesZypher PM10 & PM2.5Kunal KumarNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Air Quality: 3.9.1 Approach To AnalysisDocument36 pages3.9 Air Quality: 3.9.1 Approach To AnalysisSelyun E OnnajNo ratings yet
- Saxenaand Sonwani 2019 Criteria Air Pollutants Chemistry SourcesDocument43 pagesSaxenaand Sonwani 2019 Criteria Air Pollutants Chemistry Sourcesrafifikri07.rfNo ratings yet
- Air Quality N Water Quality StandardsDocument12 pagesAir Quality N Water Quality StandardsTvisha KhatriNo ratings yet
- Air EmissionDocument11 pagesAir EmissionBenson Harison MajabeNo ratings yet
- Modern Ultra-Supercritical Boiler and Emission Control TechnologiesDocument18 pagesModern Ultra-Supercritical Boiler and Emission Control TechnologiesAnonymous KzJcjGCJbNo ratings yet
- Design Inputs QTY Unit: CalculationDocument7 pagesDesign Inputs QTY Unit: CalculationHemant Kale100% (1)
- Share: Ambient Air Quality Standards in IndiaDocument4 pagesShare: Ambient Air Quality Standards in IndiaDanish HassanNo ratings yet
- Zephyr Specifications Nov 2019Document1 pageZephyr Specifications Nov 2019Sommi MNo ratings yet
- Criteria Pollutants - Normal Furnace Configuration - at 3.84 Am /sDocument1 pageCriteria Pollutants - Normal Furnace Configuration - at 3.84 Am /sRufus D SNo ratings yet
- Clean Air Reg 2014Document14 pagesClean Air Reg 2014ima PetronNo ratings yet
- Air Monitoring (Skiving Belt Cutting Genset)Document13 pagesAir Monitoring (Skiving Belt Cutting Genset)mdarsalankhan.hseNo ratings yet
- Air Ambient Minimum Threshold of South Sumatera ProvinceDocument1 pageAir Ambient Minimum Threshold of South Sumatera ProvincepramadhonyNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Ambient Air Pollution PDFDocument83 pagesGuideline For Ambient Air Pollution PDFtsrinivasan5083No ratings yet
- Air Pollution and Gaussian Plume ModelDocument71 pagesAir Pollution and Gaussian Plume ModelanuNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution and Control: Chapter 2 Air Quality Management SystemDocument10 pagesAir Pollution and Control: Chapter 2 Air Quality Management SystemKaye DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Air Quality StandardDocument10 pagesAir Quality Standardसुनिल बाबु खत्रीNo ratings yet
- CTO Rohini 2023Document6 pagesCTO Rohini 2023environment NK AreaNo ratings yet
- Ghana - Accra Urban Transport Project-ESIA Summary-11 2015Document35 pagesGhana - Accra Urban Transport Project-ESIA Summary-11 2015Sergio CunhaNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter 7-1 - 7-4 PDFDocument51 pages2 Chapter 7-1 - 7-4 PDFJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Laborator 7.8 ICADocument21 pagesLaborator 7.8 ICACristina JianuNo ratings yet
- Topa CTO 2018Document5 pagesTopa CTO 2018nikhil ranjanNo ratings yet
- QCVN 05-2009 BTNMT National Technical Regulation On Ambient AirqualityDocument7 pagesQCVN 05-2009 BTNMT National Technical Regulation On Ambient AirqualityTUONG VU TANNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Control Methods & Energy EfficiencyDocument14 pagesAir Pollution Control Methods & Energy Efficiencyjoy chNo ratings yet
- D) Hydrogen - P. BrewerDocument15 pagesD) Hydrogen - P. BrewerPaloma MartinezNo ratings yet
- Raw-Gas Monitoring For Scrubber Optimizing: Continuous Emissions Monitoring and Process ControlDocument4 pagesRaw-Gas Monitoring For Scrubber Optimizing: Continuous Emissions Monitoring and Process ControlHoang Chau TrungNo ratings yet
- Air Quality StandardsDocument2 pagesAir Quality StandardsJanmejaya BarikNo ratings yet
- LN - 11 - 61 - Air Pollution MeasurmentDocument24 pagesLN - 11 - 61 - Air Pollution MeasurmentKzenetteNo ratings yet
- Performance Monitoring (PM) & Compliance Monitoring (CM) : Malaysia (DOE)Document12 pagesPerformance Monitoring (PM) & Compliance Monitoring (CM) : Malaysia (DOE)nor afiqahNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Monitoring: Envirotech Instruments Pvt. LTDDocument29 pagesAir Pollution Monitoring: Envirotech Instruments Pvt. LTDECRDNo ratings yet
- Summer Training On Ambient Air QualityDocument15 pagesSummer Training On Ambient Air Qualityakshat srivastavaNo ratings yet
- 1.03 MLD Sbr-Process DesignDocument4 pages1.03 MLD Sbr-Process DesignHemant KaleNo ratings yet
- Air Quality GuidelinesDocument1 pageAir Quality GuidelinesyascheNo ratings yet
- Waste MGMTDocument84 pagesWaste MGMTMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Technology ManagementDocument61 pagesTechnology ManagementMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- WaterFootprint Presentation LatestDocument74 pagesWaterFootprint Presentation LatestMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Framework The Natural StepDocument126 pagesSustainable Development Framework The Natural StepMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- We Humanity, Have Finally Done It: Disturbed The Environment On A Global ScaleDocument68 pagesWe Humanity, Have Finally Done It: Disturbed The Environment On A Global ScaleMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Analysis/assessment (LCA)Document85 pagesLife Cycle Analysis/assessment (LCA)Mounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- GRI Nov 2018Document199 pagesGRI Nov 2018Mounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- CSR Basics1Document42 pagesCSR Basics1Mounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Topsis: Technique For Order of Preference by Similarity To Ideal SolutionDocument18 pagesTopsis: Technique For Order of Preference by Similarity To Ideal SolutionMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Make vs. BuyDocument29 pagesMake vs. BuyMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Layout MethodsDocument25 pagesLayout MethodsMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- MSDS Lube Oils 2012Document6 pagesMSDS Lube Oils 2012Fifi UmmahNo ratings yet
- Marine ProblemsDocument4 pagesMarine ProblemsPhilip Bustos100% (1)
- Aquatic EcosytemDocument13 pagesAquatic EcosytemAllen GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Bacteriological and Residual Chlorine TestingDocument24 pagesBacteriological and Residual Chlorine TestingunnipraNo ratings yet
- New Technologies Oil Gas Industry PDFDocument235 pagesNew Technologies Oil Gas Industry PDFKhang TrầnNo ratings yet
- 4-Sewer AppurtenancesDocument11 pages4-Sewer AppurtenancesMuhammad AmirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - CE 433-1Document16 pagesLecture 5 - CE 433-1Khalid Bin OmarNo ratings yet
- Improper Waste Disposal.: Environmental IssuesDocument4 pagesImproper Waste Disposal.: Environmental IssuesAyeth MedinaNo ratings yet
- Waste Savi Datasheets RTV en 0516 EditDocument2 pagesWaste Savi Datasheets RTV en 0516 Editjhuerta888No ratings yet
- Hydrometallurgical Process: Analysis of Free, Total & WAD Cyanide in Gold Leach Slurry & WastewaterDocument1 pageHydrometallurgical Process: Analysis of Free, Total & WAD Cyanide in Gold Leach Slurry & WastewaterJUNIORNo ratings yet
- Reverse Osmosis Design With Hydranautics Design Software For Industrial Waste Water ReuseDocument10 pagesReverse Osmosis Design With Hydranautics Design Software For Industrial Waste Water ReuseMario Antonio Araya MorosoNo ratings yet
- Fyp Presentation 18 MayDocument23 pagesFyp Presentation 18 MayJohnNo ratings yet
- Five Year Development Plan (2003-2008)Document190 pagesFive Year Development Plan (2003-2008)Saurav SenNo ratings yet
- Precase Concrete Pipes (Mac, 16)Document4 pagesPrecase Concrete Pipes (Mac, 16)KpChuaNo ratings yet
- Report 166Document1 pageReport 166GalileoNewtonAristideNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Q1 Week 9Document22 pagesEarth and Life Science Q1 Week 9Tabada NickyNo ratings yet
- XII Environment Education Project & Assignments 2023-24Document2 pagesXII Environment Education Project & Assignments 2023-24salonirayakarNo ratings yet
- Water PollutionDocument24 pagesWater PollutionMstJahanaraKhanamNo ratings yet
- Plumbing and Related Basic TermsDocument14 pagesPlumbing and Related Basic TermsHusnik Maulidya Tungga DewiNo ratings yet
- MS-0041015 - Test Request Form (Wastewater Testing) - V2.1 (003) Sudah DiisiDocument1 pageMS-0041015 - Test Request Form (Wastewater Testing) - V2.1 (003) Sudah DiisiLIRIS BT RAWINo ratings yet
- Nippon Paint CWTDocument6 pagesNippon Paint CWThpsNo ratings yet
- Fateh Sagar LakeDocument8 pagesFateh Sagar LakeMadan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Systems 1996Document599 pagesWater Supply Systems 1996edianiNo ratings yet
- LANDFILLDocument37 pagesLANDFILLdevash100% (1)
- Minister of Environment Degree No. 111 2003Document10 pagesMinister of Environment Degree No. 111 20038berry8No ratings yet
Env Laws1
Env Laws1
Uploaded by
Mounika Reddy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views19 pagesThis document outlines several key environmental laws and compliance requirements in India, including the Water Act, Air Act, and Environment Protection Act. It discusses the agencies that enforce these laws, such as State Pollution Control Boards. It also provides details on ambient air quality standards, hazardous waste management rules, and other regulatory information industry must adhere to.
Original Description:
Original Title
env laws1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines several key environmental laws and compliance requirements in India, including the Water Act, Air Act, and Environment Protection Act. It discusses the agencies that enforce these laws, such as State Pollution Control Boards. It also provides details on ambient air quality standards, hazardous waste management rules, and other regulatory information industry must adhere to.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views19 pagesEnv Laws1
Env Laws1
Uploaded by
Mounika ReddyThis document outlines several key environmental laws and compliance requirements in India, including the Water Act, Air Act, and Environment Protection Act. It discusses the agencies that enforce these laws, such as State Pollution Control Boards. It also provides details on ambient air quality standards, hazardous waste management rules, and other regulatory information industry must adhere to.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
Environmental laws
Environmental Legislation in India
• The Water (Prevention and control of Pollution) Act 1974
• The Water (Prevention and control of Pollution) Cess Act 1977
• The Air (Prevention and control of Pollution) Act 1981
• Hazardous waste
• Manufacture, storage, import of hazardous chemicals
• The Environment (Protection) Act 1986
• The Environment (Protection) Rules 1986
• The Public Liabilities Insurance Act –1991
• National Tribunal Act - 1995
• Biomedical
• Ozone depleting substances
• Noise
• Fines, penalties
Enforcing Agencies
• State Pollution Control Boards for states
• Central pollution Control Board for Union
Territories
• The Green Tribunal
1.Compliance Requirements - Water Act and
Rules
• Submit information of liquid effluent such
as quantity, quality, treatment method and
disposal
• Obtain consent to operate. Renew the
consent periodically at the frequency as
mentioned in the consent.
• Consent specifies location specific
standards – comply with it
Compliance Requirements - Water Rules
• Records to be maintained meticulously.
• Conduct analysis of samples drawn from
treated and untreated water and submit
report to SPCB
2. Compliance Requirements - Air Act and Rules
• Submit information of various emissions such as
quantity, quality and control method
• Obtain air consent and adhere to conditions
stipulated
• Periodically collect samples from all stacks, vents
and exhaust of critical operations and submit report
to SPCB
• Insist on Pollution Under Control (PUC) certificate
for all the vehicles entering the premises.
• PUC to be maintained for all the in house vehicles
including Diesel operated Fork Lifts even though
they may be used only within the factory premises.
Air Rules
• Provides National Ambient Air Quality Standards
• Specifies permissible levels for industrial , residential
and sensitive areas
• Annual average – minimum 104 measurements taken
twice a week 24 hours or 8 hourly at equal intervals
• The limits may exceed standards only 2% of the time
but not on two consecutive days
Air Pollutants in Schedule
• Sulfur dioxide
• Oxides of nitrogen
• Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM)
• Respirable SPM
• Carbon monoxide
• Lead
• Ammonia
3. Environmental Protection Act (EPA) -
Rules
• Submit Enviro. Statement in Form 5 every year by
organisations requiring consent to operate.
• Schedule I – Industry specific limits
• Schedule III – Ambient Air Quality standards for noise
• Schedule IV – Motor vehicle Emission limit
• Schedule V – furnishing of information to Authorities and
Agencies in certain cases
• Schedule VI – General Standards for Discharge of
Environmental Pollutants
• Schedule VII – National Ambient Air Quality Standards
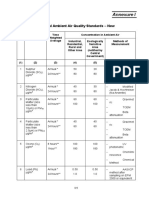
NATIONAL AMBIENT AIR QUALITY STANDARDS (NAAQS)
Air
Concentration in Ambient Method of Measurement
Time Weighted
Average Industrial Residential, Sensitive
Pollutant Area Rural and Area
other Areas
Sulphur Dioxide Annual Average* 80 µg/m3 60 µg/m3 15 µg/m3 1. Improved West and Gaeke Method
(SO2) 2. Ultraviolet Fluorescence
24 Hours 120 80 µg/m3 30 µg/m3
Average** µg/m3
Oxides of Nitrogen Annual Average* 80 µg/m3 60 µg/m3 15 µg/m3 1. Jacob & Hochheiser modified (NaOH-
as NO2 NaAsO2) Method
24 Hours 120 80 µg/m3 30 µg/m3 2. Gas Phase Chemiluminiscence
Average** µg/m3
Suspended Annual Average* 360 140 µg/m3 70 µg/m3 High Volume Sampling (Average flow
Particulate µg/m3 rate not less than 1.1m3/minute)
Matter (SPM) 24 Hours 500 200 µg/m3 100 µg/m3
Average** µg/m3
Respirable Annual Average* 120 60 µg/m3 50 µg/m3
Particulate Matter µg/m3 Respirable Particulate Matter Sampler
(Size less than 24 Hours 150 100 µg/m3 75 µg/m3
10µm) (RPM) Average** µg/m3
Lead (Pb) Annual Average* 1.0 µg/m3 0.75 µg/m3 0.50 µg/m3 AAS Method after sampling using EPM
2000
24 Hour 1.5 µg/m3 1.0 µg/m3 0.75 µg/m3 or equivalent filter paper
Average**
Carbon Monoxide 8 Hours 5.0 mg/m3 2.0 mg/m3 1.0 mg/m3
(CO) Average** Non dispersive Infrared Spectroscopy
1 Hour Average 10.0mg/m 4.0 mg/m3 2.0 mg/m3
3
Ammonia (NH3) Annual Average* 0.1 mg/m3 -
24 Hour 0.4 mg/m3
Average**
* Annual Arithmetic mean of minimum 104 measurements in a year twice a week 24 hourly at uniform interval.
** 24 hourly/8 hourly values should be met 98% of the time in a year. However, 2% of the time, it may exceed but not on two consecutive days.
NOTE
1. National Ambient Air Quality Standard : The levels of air quality necessary with an adequate margin of safety, to protect the public health, vegetation and property.
2. Whenever and wherever two consecutive values exceed the limit specified above for the respective category, it would be considered adequate reason to institute regular/continuous monitoring and further investigations.
3. The State Government / State Board shall notify the sensitive and other areas in the respective states within a period of six months from the date of notification of National Ambient Air Quality Standards.
4. Hazardous Materials (Management, Handling
and Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2008
• Provide training to personnel handling hazardous waste
and ensure use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
• Identify and address Emergency situations for spillages &
accidents etc.
• Hazardous waste to be sold only to registered / licensed
parties
• Design, setup, operate and closure of landfill for disposal
of hazardous wastes as per the guidelines & approval of
SPCB.
• In case of disposal at an approved outside landfill,
packaging, labeling and transportation has to be handled
as per Motor Vehicles Act & other guidelines specified by
government.
4. Hazardous Materials (Management, Handling
and Transboundary Movement) Rules, 2008
• Containers of hazardous waste to be marked with labels in
prescribed format.
• Hazardous waste Manifest needs to be filled up for any
movement of hazardous wastes to disposal facility.
• Obtain No Objection Certificate from SPCB for inter and
intra-state transportation of hazardous waste, in addition
to providing transport Emergency card (TREM) to the
transporter.
• In case of any accident, clean up shall be carried out.
5. Manufacture, Storage ,Import of Hazardous
Chemicals Rules 1989 Amend 2000
• This Rule has been enacted to prevent industrial accidents
leading to environmental pollution.
• Check for applicability from the list of chemicals (684
chemicals, flammable and toxic).
• MSDS to be available for all the chemicals including
proprietary ones.
• Any major accident to be reported to SPCB.
• Onsite Emergency plan to be made and periodic mock
drills to be conducted to ensure compliance.
• Safety audit to be done by an external party and report to
be submitted
6. Bio- Medical Waste- Handling & Management Rules
• Segregation of infectious waste
• Waste containers to be color coded and labeled as
specified
• Infectious waste to be disinfected using Autoclave before
transported to an approved disposal facility.
7. Ozone Depleting Substances Rules 2000
• Compulsory to register with MOEF
• Restriction on production levels as per "base level" and reductions
specified.
• Ban on creating new capacity or expansion of capacity
• Export restricted to countries who are signatory to Montreal Protocol
• Quantity produced in excess of maximum allowable consumption for the
respective years, if any, to be for export purposes only.
• Use of halon is prohibited
• Use of CFC is prohibited after 1 st January, 2003
7. ODS Rules
• Declaration, in prescribed format, to the seller, at the
time of purchase of ODS
• Exporters & Importers need to register with designated
authorities.
• No sales to persons/organizations which have not
intimated the Government of India about use of ODS
based equipment, including compressors without license.
7. India’s Proposed Phase-out dates for ODS in the Rules
Name of Activity Phase-out
S.No. Date
1 Manufacture of aerosol products excluding Metered Dose Jan. 1, 2003
Inhalers (MDI)
2 Manufacture of foam products (including domestic Jan. 1, 2003
refrigerators)
3 Manufacture of Mobile Air-conditioners (MAC’S) Jan. 1, 2003
4 Manufacture of other refrigeration &. Air-conditioning Jan. 1, 2003
products.
5 Manufacture of products based on other ODS Jan. 1, 2010
6 Manufacture of Metered Dose Inhalers (MDI) Jan. 1, 2010
7 Use of methyl bromide except Quarantine and Preshipment Jan. 1, 2015
8 Manufacture of products based on HCFC Jan. 1, 2040
8. Noise
Ambient Air Quality Standards in respect of Noise
Area Code Category of Area/Zone Limits in dB(A) Leq
Area Code Category of Area/Zone Limits in dB(A) Leq *
Day Time NightTime
(A) Industrial area 75 70
(B) Commercial area 65 55
(C) Residential area 55 45
(D) Silence Zone 50 40
Leq - cont
Note
1. Day time shall mean from 6.00 a.m. to 10.00 p.m.
2. Night time shall mean from 10.00 p.m. to 6.00 a.m.
3. Silence zone is defined as an area comprising not less than 100 metres
around hospitals, educational institutions and courts. The silence zones
are zones which are declared as such by the competent authority.
9. Fine, Penalties for violation of EPA
• Imprisonment up to 5 years
• Fine up to Rs. 1,00,000
• Or both
• Additional Rs. 5,000 per day till compliance
You might also like
- National Ambient Air Quality StandardsDocument1 pageNational Ambient Air Quality StandardsrajanarsuNo ratings yet
- Final ROE For NB Centennial Well Water RightDocument51 pagesFinal ROE For NB Centennial Well Water RightAaron KunklerNo ratings yet
- Process Flow Diagram of Bar SoapDocument9 pagesProcess Flow Diagram of Bar SoapAndrea Cabungcal0% (1)
- Pulp and Paper Industry PresentationDocument21 pagesPulp and Paper Industry PresentationRichard Obinna100% (1)
- Alcosan Wet Weather PlanDocument16 pagesAlcosan Wet Weather Planapi-282530339No ratings yet
- ESSA - 2005 - Stimulus MagazineDocument21 pagesESSA - 2005 - Stimulus MagazineDog DogNo ratings yet
- 2 Noise Standards 1666147628370Document2 pages2 Noise Standards 1666147628370shefani pon singhNo ratings yet
- Standards For Coal MinesDocument3 pagesStandards For Coal MinesRifaiNo ratings yet
- Sindh Ambient Air Quality Standards FormattedDocument1 pageSindh Ambient Air Quality Standards FormattedSaad QudratNo ratings yet
- Environmental Standards National Ambient Air Quality StandardsDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Standards National Ambient Air Quality StandardsThambidurai KNo ratings yet
- 6.pollution Standards For Coal MinesDocument4 pages6.pollution Standards For Coal MinesSuryaKanthNo ratings yet
- Sindh Environmental Quality Ambient Text FormDocument1 pageSindh Environmental Quality Ambient Text FormSaad QudratNo ratings yet
- 11 - Environmental Quality Standard 1Document27 pages11 - Environmental Quality Standard 1Durgesh Kumar NatNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentalstandardsDocument15 pagesEnvironmentalstandardsTeam Labs LaboratoryNo ratings yet
- Air PollutionDocument54 pagesAir PollutionShivam SonkarNo ratings yet
- Ambient AQSDocument2 pagesAmbient AQSDiya lizbeth joseNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Extra Reading Material eDocument8 pagesAir Pollution Extra Reading Material epubgsuhanigNo ratings yet
- Environmental StandardsDocument7 pagesEnvironmental StandardsDuraiMuruganNo ratings yet
- ES 200 - S2 - Air - L2 - 7 Oct 2021Document37 pagesES 200 - S2 - Air - L2 - 7 Oct 2021vishal kumarNo ratings yet
- 27 1458110426 NewItem 196 NAAQMS Volume-I-1 PDFDocument1 page27 1458110426 NewItem 196 NAAQMS Volume-I-1 PDFAkhand AkhandNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document4 pagesLecture 15Neekita NeetuNo ratings yet
- Air Polltution (Compatibility Mode)Document37 pagesAir Polltution (Compatibility Mode)Bikash chapagainNo ratings yet
- AIR POLLUTION AND CONTROL - Lecture 1Document8 pagesAIR POLLUTION AND CONTROL - Lecture 1Dhiraj YNo ratings yet
- Naaqs 2009Document2 pagesNaaqs 2009sreenNo ratings yet
- Pollution Monitoring: Annexure-6Document5 pagesPollution Monitoring: Annexure-6Nisanth ThulasidasNo ratings yet
- Annexure I: National Ambient Air Quality Standards - NewDocument5 pagesAnnexure I: National Ambient Air Quality Standards - NewKrishna SrikanthNo ratings yet
- AmbientDocument1 pageAmbientSilambarasan ThirugnanamNo ratings yet
- Ambient Air Quality and Emission Standards Aesthetic Value and VisibilityDocument11 pagesAmbient Air Quality and Emission Standards Aesthetic Value and VisibilityantonyNo ratings yet
- National Ambient Air Quality StandardsDocument6 pagesNational Ambient Air Quality StandardsDebasmita Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Delhi Planning-DataDocument9 pagesDelhi Planning-DataNrjNo ratings yet
- Current and Future Standards & Guidelines For Oil & Gas Sector in India and Status of Its ImplementationDocument64 pagesCurrent and Future Standards & Guidelines For Oil & Gas Sector in India and Status of Its ImplementationVaishnavi JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Zypher PM10 & PM2.5Document3 pagesZypher PM10 & PM2.5Kunal KumarNo ratings yet
- 3.9 Air Quality: 3.9.1 Approach To AnalysisDocument36 pages3.9 Air Quality: 3.9.1 Approach To AnalysisSelyun E OnnajNo ratings yet
- Saxenaand Sonwani 2019 Criteria Air Pollutants Chemistry SourcesDocument43 pagesSaxenaand Sonwani 2019 Criteria Air Pollutants Chemistry Sourcesrafifikri07.rfNo ratings yet
- Air Quality N Water Quality StandardsDocument12 pagesAir Quality N Water Quality StandardsTvisha KhatriNo ratings yet
- Air EmissionDocument11 pagesAir EmissionBenson Harison MajabeNo ratings yet
- Modern Ultra-Supercritical Boiler and Emission Control TechnologiesDocument18 pagesModern Ultra-Supercritical Boiler and Emission Control TechnologiesAnonymous KzJcjGCJbNo ratings yet
- Design Inputs QTY Unit: CalculationDocument7 pagesDesign Inputs QTY Unit: CalculationHemant Kale100% (1)
- Share: Ambient Air Quality Standards in IndiaDocument4 pagesShare: Ambient Air Quality Standards in IndiaDanish HassanNo ratings yet
- Zephyr Specifications Nov 2019Document1 pageZephyr Specifications Nov 2019Sommi MNo ratings yet
- Criteria Pollutants - Normal Furnace Configuration - at 3.84 Am /sDocument1 pageCriteria Pollutants - Normal Furnace Configuration - at 3.84 Am /sRufus D SNo ratings yet
- Clean Air Reg 2014Document14 pagesClean Air Reg 2014ima PetronNo ratings yet
- Air Monitoring (Skiving Belt Cutting Genset)Document13 pagesAir Monitoring (Skiving Belt Cutting Genset)mdarsalankhan.hseNo ratings yet
- Air Ambient Minimum Threshold of South Sumatera ProvinceDocument1 pageAir Ambient Minimum Threshold of South Sumatera ProvincepramadhonyNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Ambient Air Pollution PDFDocument83 pagesGuideline For Ambient Air Pollution PDFtsrinivasan5083No ratings yet
- Air Pollution and Gaussian Plume ModelDocument71 pagesAir Pollution and Gaussian Plume ModelanuNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution and Control: Chapter 2 Air Quality Management SystemDocument10 pagesAir Pollution and Control: Chapter 2 Air Quality Management SystemKaye DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Air Quality StandardDocument10 pagesAir Quality Standardसुनिल बाबु खत्रीNo ratings yet
- CTO Rohini 2023Document6 pagesCTO Rohini 2023environment NK AreaNo ratings yet
- Ghana - Accra Urban Transport Project-ESIA Summary-11 2015Document35 pagesGhana - Accra Urban Transport Project-ESIA Summary-11 2015Sergio CunhaNo ratings yet
- 2 Chapter 7-1 - 7-4 PDFDocument51 pages2 Chapter 7-1 - 7-4 PDFJinyoung ChoiNo ratings yet
- Laborator 7.8 ICADocument21 pagesLaborator 7.8 ICACristina JianuNo ratings yet
- Topa CTO 2018Document5 pagesTopa CTO 2018nikhil ranjanNo ratings yet
- QCVN 05-2009 BTNMT National Technical Regulation On Ambient AirqualityDocument7 pagesQCVN 05-2009 BTNMT National Technical Regulation On Ambient AirqualityTUONG VU TANNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Control Methods & Energy EfficiencyDocument14 pagesAir Pollution Control Methods & Energy Efficiencyjoy chNo ratings yet
- D) Hydrogen - P. BrewerDocument15 pagesD) Hydrogen - P. BrewerPaloma MartinezNo ratings yet
- Raw-Gas Monitoring For Scrubber Optimizing: Continuous Emissions Monitoring and Process ControlDocument4 pagesRaw-Gas Monitoring For Scrubber Optimizing: Continuous Emissions Monitoring and Process ControlHoang Chau TrungNo ratings yet
- Air Quality StandardsDocument2 pagesAir Quality StandardsJanmejaya BarikNo ratings yet
- LN - 11 - 61 - Air Pollution MeasurmentDocument24 pagesLN - 11 - 61 - Air Pollution MeasurmentKzenetteNo ratings yet
- Performance Monitoring (PM) & Compliance Monitoring (CM) : Malaysia (DOE)Document12 pagesPerformance Monitoring (PM) & Compliance Monitoring (CM) : Malaysia (DOE)nor afiqahNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Monitoring: Envirotech Instruments Pvt. LTDDocument29 pagesAir Pollution Monitoring: Envirotech Instruments Pvt. LTDECRDNo ratings yet
- Summer Training On Ambient Air QualityDocument15 pagesSummer Training On Ambient Air Qualityakshat srivastavaNo ratings yet
- 1.03 MLD Sbr-Process DesignDocument4 pages1.03 MLD Sbr-Process DesignHemant KaleNo ratings yet
- Air Quality GuidelinesDocument1 pageAir Quality GuidelinesyascheNo ratings yet
- Waste MGMTDocument84 pagesWaste MGMTMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Technology ManagementDocument61 pagesTechnology ManagementMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- WaterFootprint Presentation LatestDocument74 pagesWaterFootprint Presentation LatestMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Framework The Natural StepDocument126 pagesSustainable Development Framework The Natural StepMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- We Humanity, Have Finally Done It: Disturbed The Environment On A Global ScaleDocument68 pagesWe Humanity, Have Finally Done It: Disturbed The Environment On A Global ScaleMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle Analysis/assessment (LCA)Document85 pagesLife Cycle Analysis/assessment (LCA)Mounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- GRI Nov 2018Document199 pagesGRI Nov 2018Mounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- CSR Basics1Document42 pagesCSR Basics1Mounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Topsis: Technique For Order of Preference by Similarity To Ideal SolutionDocument18 pagesTopsis: Technique For Order of Preference by Similarity To Ideal SolutionMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Make vs. BuyDocument29 pagesMake vs. BuyMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Layout MethodsDocument25 pagesLayout MethodsMounika ReddyNo ratings yet
- MSDS Lube Oils 2012Document6 pagesMSDS Lube Oils 2012Fifi UmmahNo ratings yet
- Marine ProblemsDocument4 pagesMarine ProblemsPhilip Bustos100% (1)
- Aquatic EcosytemDocument13 pagesAquatic EcosytemAllen GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Bacteriological and Residual Chlorine TestingDocument24 pagesBacteriological and Residual Chlorine TestingunnipraNo ratings yet
- New Technologies Oil Gas Industry PDFDocument235 pagesNew Technologies Oil Gas Industry PDFKhang TrầnNo ratings yet
- 4-Sewer AppurtenancesDocument11 pages4-Sewer AppurtenancesMuhammad AmirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - CE 433-1Document16 pagesLecture 5 - CE 433-1Khalid Bin OmarNo ratings yet
- Improper Waste Disposal.: Environmental IssuesDocument4 pagesImproper Waste Disposal.: Environmental IssuesAyeth MedinaNo ratings yet
- Waste Savi Datasheets RTV en 0516 EditDocument2 pagesWaste Savi Datasheets RTV en 0516 Editjhuerta888No ratings yet
- Hydrometallurgical Process: Analysis of Free, Total & WAD Cyanide in Gold Leach Slurry & WastewaterDocument1 pageHydrometallurgical Process: Analysis of Free, Total & WAD Cyanide in Gold Leach Slurry & WastewaterJUNIORNo ratings yet
- Reverse Osmosis Design With Hydranautics Design Software For Industrial Waste Water ReuseDocument10 pagesReverse Osmosis Design With Hydranautics Design Software For Industrial Waste Water ReuseMario Antonio Araya MorosoNo ratings yet
- Fyp Presentation 18 MayDocument23 pagesFyp Presentation 18 MayJohnNo ratings yet
- Five Year Development Plan (2003-2008)Document190 pagesFive Year Development Plan (2003-2008)Saurav SenNo ratings yet
- Precase Concrete Pipes (Mac, 16)Document4 pagesPrecase Concrete Pipes (Mac, 16)KpChuaNo ratings yet
- Report 166Document1 pageReport 166GalileoNewtonAristideNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Q1 Week 9Document22 pagesEarth and Life Science Q1 Week 9Tabada NickyNo ratings yet
- XII Environment Education Project & Assignments 2023-24Document2 pagesXII Environment Education Project & Assignments 2023-24salonirayakarNo ratings yet
- Water PollutionDocument24 pagesWater PollutionMstJahanaraKhanamNo ratings yet
- Plumbing and Related Basic TermsDocument14 pagesPlumbing and Related Basic TermsHusnik Maulidya Tungga DewiNo ratings yet
- MS-0041015 - Test Request Form (Wastewater Testing) - V2.1 (003) Sudah DiisiDocument1 pageMS-0041015 - Test Request Form (Wastewater Testing) - V2.1 (003) Sudah DiisiLIRIS BT RAWINo ratings yet
- Nippon Paint CWTDocument6 pagesNippon Paint CWThpsNo ratings yet
- Fateh Sagar LakeDocument8 pagesFateh Sagar LakeMadan ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Systems 1996Document599 pagesWater Supply Systems 1996edianiNo ratings yet
- LANDFILLDocument37 pagesLANDFILLdevash100% (1)
- Minister of Environment Degree No. 111 2003Document10 pagesMinister of Environment Degree No. 111 20038berry8No ratings yet