Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CARTILAGE
CARTILAGE
Uploaded by
Matthew Bryan Adonay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views19 pagesCartilage is a connective tissue composed of chondrocytes and an extracellular matrix. There are three main types of cartilage: hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, and fibrocartilage. Hyaline cartilage is found in joints and provides a low friction surface. It contains collagen, proteoglycans, and multiadhesive glycoproteins in its matrix. Elastic cartilage is found in the ear and contains elastin. Fibrocartilage is a combination of connective tissue and hyaline cartilage found in joints and where tendons attach to bone.
Original Description:
Original Title
CARTILAGE (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCartilage is a connective tissue composed of chondrocytes and an extracellular matrix. There are three main types of cartilage: hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, and fibrocartilage. Hyaline cartilage is found in joints and provides a low friction surface. It contains collagen, proteoglycans, and multiadhesive glycoproteins in its matrix. Elastic cartilage is found in the ear and contains elastin. Fibrocartilage is a combination of connective tissue and hyaline cartilage found in joints and where tendons attach to bone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views19 pagesCARTILAGE
CARTILAGE
Uploaded by
Matthew Bryan AdonayCartilage is a connective tissue composed of chondrocytes and an extracellular matrix. There are three main types of cartilage: hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, and fibrocartilage. Hyaline cartilage is found in joints and provides a low friction surface. It contains collagen, proteoglycans, and multiadhesive glycoproteins in its matrix. Elastic cartilage is found in the ear and contains elastin. Fibrocartilage is a combination of connective tissue and hyaline cartilage found in joints and where tendons attach to bone.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 19
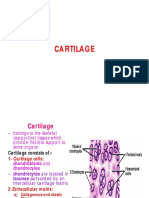
CARTILAGE
• Cartilage is a form of connective tissue
composed of cells called CHONDROCYTES
and a highly specialized extracellular matrix
• > 95% of cartilage volume consists of the
extracellular matrix which is a functional
element of the tissue
• Chondrocytes are essential participants in
producing & maintaining the matrix
• Cartilage and bones are categorized as
special types of dense regular connective
tissues
TYPES
• HYALINE
• ELASTIC
• FIBROCARTILAGE
Types
• HYALINE
– Characterized by matrix containing type II
collagen fibers, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs),
proteoglycans & multiadhesive glycoproteins
– Distinguished by homogenous amorphous
matrix
– Appears glassy in living state
– Throughout the cartilage matrix are spaces
are spaces called LACUNAE
Types
• HYALINE
– w/in the lacunae are chondrocytes
– Provides a low friction surface, participates in
lubrication in synovial joints, and distributes
applied forces to the underlying bone
3 molecules in hyaline cartilage
matrix
• Collagen molecules
• Proteoglycans
• Multiadhesive glycoproteins
Collagen Molecules
• Major matrix protein
Type II collagen Constitues the bulk of fibril
Involved in formation
Type IX Facilitates fibril interaction w/ matrix
of matrix fibrils
collagen proteoglycan molecules
Type XI Regulates the fibril size
collagen
Type X collagen Organizes collagen fibrils into a 3-
dimensional haxagonal lattice
Type VI Also found in matrix, mainly at periphery of
collagen chondrocytes where it helps attach these
cells to matrix framework
* II, VI, IX, X, XI : cartilage specific collagen
Proteoglycans
• Contains glycosaminoglycans
– Hyaluronan
– Chondrotin sulfate forms a proteoglycan
– Keratin sulfate monomer
• Most important monomer is aggrecan
Multiadhesive Glycoproteins
• Also referred to as non-collagenous &
non-proteoglycan linked glycoproteins,
influence interaction between
chondrocytes & matrix molecules & value
as markers of cartilage turnover and
degeneration
Types
• HYALINE
– Hyaline cartilage matrix is highly hydrated to
provide diffusion of small metabolites &
resilience
– H.C. provides a model for the developing
skeleton of fetus in utero
– A firmly attached connective tissue, the
perichondrium surrounds hyaline cartilage
– H.C. of articular joint surfaces do not possess
a perichondrium
Types
• ELASTIC
– Distinguished by the presence of elastin in
cartilage matrix
– Found in external ear, walls of external
acoustic meatus, the auditory (eustachian)
tube, & epiglottis of the larynx
– Matrix of elastic cartilage do not decalcify
upon aging
Types
• FIBROCARTILAGE
– Consists of chondrocytes & their matrix
material in combination w/ dense connective
tissue
– Combination of dense connective tissue &
hyaline cartilage
– No surrounding perichondrium
Types
• FIBROCARTILAGE
– Typically present in intervertebral disks,
symphysis pubis,articular disks of
sternoclavicular & temporomandibular joints,
triangular fibrocartilage of wrist, & anatomic
locations where tendons attached to bones
– Presence of fibrocartilage indicates resistance
to both compression & shearing forces
Types
• FIBROCARTILAGE
– Extracellualar matrix of fibrocartilage is
characterized by presence of both type I & II
collagen fibrils
Chondrogenesis & Cartilage Growth
• Most cartilage arise from mesenchyme
during chondrogenesis (cartilage
development)
• 2 kinds of growth:
– Appositional – process that forms new
cartilage at surface of an existing cartilage
– Interstitial – process that forms new cartilage
w/in an existing cartilage mass
Repair of Hyaline Cartilage
• H.C. has limited ability for repair
• When H.C. calcifies, it is replaced by bone
in the ff situations:
– The portion of articular cartilage that is in
contact w/ bone tissue in growing adult bones,
but not the surface portion is calcified
– Calcification always occurs in cartilage that is
about to be replaced by bone during the
growth period of individual
– H.C. in adult calcifies in time as part of aging
process
Hyaline Cartilage
Elastic Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
You might also like
- Elements of Ecology Canadian 1st Edition Smith Test Bank DownloadDocument20 pagesElements of Ecology Canadian 1st Edition Smith Test Bank DownloadLois Overy100% (23)
- Mitosis and Meiosis WorksheetDocument4 pagesMitosis and Meiosis WorksheetAutumn Jackson-ButlerNo ratings yet
- Resepiratory Quiz PDFDocument4 pagesResepiratory Quiz PDFapi-448873912No ratings yet
- Cartilage: Ethel Marie M. Mangada, RMTDocument34 pagesCartilage: Ethel Marie M. Mangada, RMTAesthetics MinNo ratings yet
- مستند PDF 3Document24 pagesمستند PDF 3alshb7 gamesNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument17 pagesCartilageasadullah2315No ratings yet
- CARTILAGEDocument16 pagesCARTILAGEelliot kafumukacheNo ratings yet
- HistoPath (Lect #4) TransDocument2 pagesHistoPath (Lect #4) TransSherlyn Giban InditaNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument26 pagesCartilageAbdi Asiis Omar MohamedNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument1 pageCartilageTarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- Bones and CartilageDocument69 pagesBones and Cartilagesjs6r8wwv9No ratings yet
- Cartilage HistologyDocument27 pagesCartilage HistologyNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Cartilage Bone (2566)Document54 pagesCartilage Bone (2566)pachara.p65No ratings yet
- DMS2 K3 (Kelas A) LECTURE CARTILAGE&BONE2020 PDFDocument67 pagesDMS2 K3 (Kelas A) LECTURE CARTILAGE&BONE2020 PDFdiqa aridaniNo ratings yet
- Cartilogo and Bone 2021Document43 pagesCartilogo and Bone 2021Mila AnriyaniNo ratings yet
- 1cartilage DR Amam PDFDocument49 pages1cartilage DR Amam PDFSarfraz Ahmad FaniNo ratings yet
- Cartilage Tissue 2022Document33 pagesCartilage Tissue 2022aws20032016No ratings yet
- Connective Tissue: Dr. Jan Tambayong, PHK Histologi FK-UPHDocument51 pagesConnective Tissue: Dr. Jan Tambayong, PHK Histologi FK-UPHJoshua ObrienNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument16 pagesCartilageClaraNo ratings yet
- CollagenDocument18 pagesCollagenROHITHNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument26 pagesCartilageMaxamed Faarax XaashiNo ratings yet
- Cartilage: Histology Dr. BernalDocument4 pagesCartilage: Histology Dr. BernalA18- Jessa Mae DayagNo ratings yet
- Cartilagedr 190528154146Document30 pagesCartilagedr 190528154146Dr.Aman SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Cartilage LectureDocument31 pagesCartilage LecturemalyaaNo ratings yet
- EDR Kartilago 2018Document20 pagesEDR Kartilago 2018Artha CimutNo ratings yet
- Histologymidterm Topics Part 1Document39 pagesHistologymidterm Topics Part 1leeshianbNo ratings yet
- Cartilage: Cartilage Is A Specialized Form of Connective Tissue Composed of Cells Called and An Extensive Composed of andDocument7 pagesCartilage: Cartilage Is A Specialized Form of Connective Tissue Composed of Cells Called and An Extensive Composed of andKamran AmeerNo ratings yet
- Cartilage& BoneDocument61 pagesCartilage& BoneNihal BilalNo ratings yet
- Cartilage and BoneDocument58 pagesCartilage and BoneGer BengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Cart IDocument2 pagesChapter 7 Cart IJan Margaret Peñafiel VillarbaNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument20 pagesCartilageDoctora NourhanNo ratings yet
- 2 Cartilage and BoneDocument51 pages2 Cartilage and BoneJulia Anne RosalemNo ratings yet
- CARTILAGEDocument24 pagesCARTILAGEEdzeal Bruan JrNo ratings yet
- Histology of Cartilage & Bone: DR Punita Manik Department of Anatomy K G Medical Univesity U P LucknowDocument61 pagesHistology of Cartilage & Bone: DR Punita Manik Department of Anatomy K G Medical Univesity U P LucknowbeylaNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Cartilage and JointsDocument52 pagesSeminar On Cartilage and Jointskoyachew abateNo ratings yet
- B.pharm-Connective Tissue & SkinDocument73 pagesB.pharm-Connective Tissue & Skin安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- Connective Tissue: Cells and Extra-Cellular MatrixDocument82 pagesConnective Tissue: Cells and Extra-Cellular Matrixeyob getachewNo ratings yet
- Cartilage: Dr. Naglaa BayomyDocument15 pagesCartilage: Dr. Naglaa BayomyAhadNo ratings yet
- Cartilage Tissue-1Document2 pagesCartilage Tissue-1Muhammet Fatih CantepeNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument41 pagesConnective TissueAstrud LabradorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Connective TissueDocument5 pagesChapter 5: Connective TissueAALIYAH REIGN MAPUSAONo ratings yet
- Condylar CartilageDocument11 pagesCondylar CartilageMahesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Biochem - EcmDocument168 pagesBiochem - EcmPrincess Jeyan PagatpatanNo ratings yet
- 7 CartilageDocument8 pages7 Cartilagegsyvj97qtdNo ratings yet
- Cartilage and Bone 2024-01Document39 pagesCartilage and Bone 2024-01jcrosa137No ratings yet
- CartilageDocument32 pagesCartilageMajd HusseinNo ratings yet
- CARTILAGEDocument2 pagesCARTILAGEvallecerajamaicaNo ratings yet
- Periodontal LigamentDocument56 pagesPeriodontal LigamentPurwana Nasir100% (2)
- Cartilage, Bone and Muscle 2021Document69 pagesCartilage, Bone and Muscle 2021PeachybalmnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 (Cartilage)Document5 pagesChapter 7 (Cartilage)Jovilyn SilongaNo ratings yet
- L10 Cartilage and BoneDocument43 pagesL10 Cartilage and BoneCarinaTingEeNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Histology of CartilageDocument6 pagesLearning Objectives Histology of CartilageRas WhoknowsmeNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument37 pagesCartilageFiraol DiribaNo ratings yet
- Periodontal LigamentDocument43 pagesPeriodontal LigamentShashi kiran0% (1)
- Chapter 6: Adipose Tissue: Two Major Types of AdiposeDocument3 pagesChapter 6: Adipose Tissue: Two Major Types of AdiposeAALIYAH REIGN MAPUSAONo ratings yet
- Histology 7Document2 pagesHistology 7amirhsheikhiNo ratings yet
- Tissues: Dr. Tanveer Ahmed Khan Lecturer RLCPDocument65 pagesTissues: Dr. Tanveer Ahmed Khan Lecturer RLCPShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument29 pagesCartilageMASHAL ABDINo ratings yet
- PDLDocument25 pagesPDLHamid AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Cartilage (Structure & Types)Document26 pagesCartilage (Structure & Types)muhammadumarnawazsattiNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2022-10-09 at 1.39.31 AMDocument29 pagesScreenshot 2022-10-09 at 1.39.31 AMSeco AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Anatomy Histology - Bone and CartilageDocument49 pages2024 - Anatomy Histology - Bone and CartilageSyakir FahmieNo ratings yet
- Organization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and NeurotransmittersDocument3 pagesOrganization, Neurons, Basic Functions of Synapses, and Neurotransmitters22 - Fernandez, Lyza Mae D.No ratings yet
- Andrology Lecture 3 Male Reprod Organs ScrotumDocument23 pagesAndrology Lecture 3 Male Reprod Organs ScrotumgnpobsNo ratings yet
- CellDocument3 pagesCellwahyu kurniawanNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY SASE REVIEW Answer KeyDocument2 pagesBIOLOGY SASE REVIEW Answer KeyTasnimah Moh. IsmaelNo ratings yet
- PhysioEx Exercise 5 Activity 4Document3 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 5 Activity 4lucisNo ratings yet
- Drug Profiling PHARMACOLOGYDocument71 pagesDrug Profiling PHARMACOLOGYJay MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal Attraction: From First Impressions To Long Term IntimacyDocument54 pagesInterpersonal Attraction: From First Impressions To Long Term IntimacyPranali Basu100% (1)
- Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Revision NotesDocument4 pagesClass 7 Science Chapter 2 Revision NotesGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Report in Gen BioDocument7 pagesReport in Gen BioJavier KennnyNo ratings yet
- Histology 3 - Cytoplasm 4 & NucleusDocument8 pagesHistology 3 - Cytoplasm 4 & NucleusShariffa KhadijaNo ratings yet
- Chem &bio 2Document3 pagesChem &bio 2Milcah TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Lung Ventilation, Natural and MechanicalDocument19 pagesLung Ventilation, Natural and MechanicalMariö OlveraNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Changes With AgingDocument8 pagesEndocrine Changes With Agingcy lifeNo ratings yet
- Thoracic: InletDocument34 pagesThoracic: Inlet19 Arya Ganesh OjhaNo ratings yet
- Animal Husbandry and Veterinary ScienceDocument8 pagesAnimal Husbandry and Veterinary ScienceflowergenNo ratings yet
- Review 3Document15 pagesReview 3YUAN YINGQINo ratings yet
- By: Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & DR - Sanaa AlshaarawiDocument24 pagesBy: Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & DR - Sanaa AlshaarawiRakesh Kumar RanjanNo ratings yet
- Implantation & Second WeekDocument18 pagesImplantation & Second WeekCabdiladif Ahmed McrfNo ratings yet
- The Claustrum Coordinates Cortical Slow-Wave Activity: ArticlesDocument27 pagesThe Claustrum Coordinates Cortical Slow-Wave Activity: ArticlescutkilerNo ratings yet
- Biology of Bone Formation, Fracture Healing, and Distraction OsteogenesisDocument10 pagesBiology of Bone Formation, Fracture Healing, and Distraction OsteogenesisenviNo ratings yet
- Pons and Midbrain Neuroanatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradeDocument47 pagesPons and Midbrain Neuroanatomy: Abbas A. A. Shawka Medical Student 2nd GradePlutokidNo ratings yet
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Document17 pagesSHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 Cell Structure and Functions 1Dette Dominic Ballano67% (3)
- Endothelial Dysfunction in Diabetic Erectile DysfunctionDocument11 pagesEndothelial Dysfunction in Diabetic Erectile DysfunctionILham SyahNo ratings yet
- M.M.: 100 Time: 3 Hours: Write Short Notes OnDocument4 pagesM.M.: 100 Time: 3 Hours: Write Short Notes OnMamta KumariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Coordination and Response NoteDocument17 pagesChapter 14 - Coordination and Response NoteShort FilmsNo ratings yet
- File 395Document381 pagesFile 395Habibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Liquichek D-Dimer Control Levels Low, 1, 2 and 3: MétodoDocument3 pagesLiquichek D-Dimer Control Levels Low, 1, 2 and 3: Métodotavogaona8979No ratings yet