Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 viewsJames A. Senn's Information Technology, 3 Edition: Enterprise Databases and Data Warehouses
James A. Senn's Information Technology, 3 Edition: Enterprise Databases and Data Warehouses
Uploaded by
Aayush ManubanshIdentify the reasons organizations choose to share databases and the functions of a database management system. Explain the difference between relational and object-oriented databases and their uses in business. Describe the differences between schemas, views, and indexes.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Delphi Legacy Projects - Strategies and Survival GuideDocument484 pagesDelphi Legacy Projects - Strategies and Survival GuideAndry100% (3)
- Computing Concepts With Java Essentials: Advanced Placement Computer Science Study GuideDocument10 pagesComputing Concepts With Java Essentials: Advanced Placement Computer Science Study GuideDoIT ChuruNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - The Database Environment and Development ProcessDocument14 pagesChapter I - The Database Environment and Development ProcessHarris Harijono50% (2)
- Lecture 3 - DatabasesDocument59 pagesLecture 3 - DatabasesmwanwajoelNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementDocument43 pagesFoundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementArbab AshrafNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management Systems: Unit 3Document57 pagesIntroduction To Database Management Systems: Unit 3Charlie Thomas VictorNo ratings yet
- Design Database Main Module Simplified TvetDocument238 pagesDesign Database Main Module Simplified Tvetmohammed ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Database Approach To Data ManagementDocument50 pagesThe Database Approach To Data Managementtampoo67% (6)
- Introd BmsDocument20 pagesIntrod BmsMohitul ShafirNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument70 pagesDBMSGitte DnyaneshwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Lecture 1Document54 pagesChapter 1 - Lecture 1Aliyan AmanNo ratings yet
- File Systems and DatabasesDocument54 pagesFile Systems and Databasesobiwan xeonNo ratings yet
- 1.database IntroDocument28 pages1.database IntroAjiSetiajiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Databases Transparencies: © Pearson Education Limited, 2004 1Document22 pagesIntroduction To Databases Transparencies: © Pearson Education Limited, 2004 1ArbabAmjadNo ratings yet
- Managing Data ResourcesDocument51 pagesManaging Data ResourcesDebabrata PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document43 pagesChapter 11Anonymous 3BpcKiFBUNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Management Systems: UNIT-1Document120 pagesRelational Database Management Systems: UNIT-1Srinivas KanakalaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Database - 2021 T1Document33 pagesWeek 3 - Database - 2021 T1Odria ArshianaNo ratings yet
- Managing Data ResourcesDocument50 pagesManaging Data Resourcesmicroman_123No ratings yet
- Rdbms (Unit 1)Document13 pagesRdbms (Unit 1)hari karanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Database NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Database NotesDibyeshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Databases: © Pearson Education Limited, 2004 1Document22 pagesIntroduction To Databases: © Pearson Education Limited, 2004 1hardeepcharmingNo ratings yet
- Principles of Information Systems Eighth Edition: Organizing Data and InformationDocument60 pagesPrinciples of Information Systems Eighth Edition: Organizing Data and InformationHope..!No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Information: Systems, Sixth EditionDocument56 pagesFundamentals of Information: Systems, Sixth EditionVengie BragaNo ratings yet
- 05 DatabaseDocument29 pages05 DatabaseShivangi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Database Management System: Unit-I The Database Environment: Basic Concepts and Definitions: Data, Information, MetadataDocument70 pagesDatabase Management System: Unit-I The Database Environment: Basic Concepts and Definitions: Data, Information, MetadataDeekonda AshwiniNo ratings yet
- DBMS MaterialDocument70 pagesDBMS MaterialMitesh PujaraNo ratings yet
- MIS: Database, Lecture-1Document81 pagesMIS: Database, Lecture-1Sunjida EnamNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Files Vs DatabasesDocument36 pagesWeek 4 Files Vs Databaseskobamelo LetowaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Database Systems Lect 1Document14 pagesFundamentals of Database Systems Lect 1YabNo ratings yet
- DBMS (Part 1)Document57 pagesDBMS (Part 1)Harsh WaghelaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementDocument36 pagesFoundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementTanvi MittalNo ratings yet
- Managing Data ResourcesDocument47 pagesManaging Data ResourcesErnst OtienoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Database SystemDocument94 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To Database SystemNabil Syahmi100% (3)
- ME DBMS Unit1 FinalDocument139 pagesME DBMS Unit1 FinalSendurusrinivas NadarNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 IDBDocument21 pagesLecture03 IDBhudaiNo ratings yet
- Dbms NotesDocument20 pagesDbms NotesSangeeta PalNo ratings yet
- 8 9dayDocument23 pages8 9dayGuess WhoNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis15 PPT Ch06Document40 pagesLaudon Mis15 PPT Ch06Amar NsouliNo ratings yet
- DBMS ConceptsDocument38 pagesDBMS ConceptsRahul RaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DatabaseDocument61 pagesIntroduction To DatabasezainabNo ratings yet
- INT 306 Database Management SystemDocument43 pagesINT 306 Database Management SystemAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Oracle ch1Document88 pagesOracle ch1Jenner Patrick Lopes BrasilNo ratings yet
- Database Management: Dr. Md. Rakibul Hoque University of DhakaDocument57 pagesDatabase Management: Dr. Md. Rakibul Hoque University of DhakaShahriar HaqueNo ratings yet
- Sistem Informasi AkuntansiDocument40 pagesSistem Informasi AkuntansiAngga SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Database Systems: Module TitleDocument17 pagesAdvanced Database Systems: Module TitleMclab MedcollegeNo ratings yet
- Database Design and ManagementDocument45 pagesDatabase Design and ManagementJeneath TahilNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Database ConceptsDocument64 pages7.1 Database ConceptsTawanda MahereNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4 Databse Basics - For JCOsDocument35 pagesLecture-4 Databse Basics - For JCOscbhavelianNo ratings yet
- Module 16 Introduction To Database Management SystemDocument32 pagesModule 16 Introduction To Database Management SystemMadaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Database Design Process PDFDocument19 pagesLecture 6 - Database Design Process PDFChia Wei HanNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 08: Class: BBA 5 Credit HoursDocument49 pagesLecture # 08: Class: BBA 5 Credit HoursMuiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- BRT Chapter 1Document49 pagesBRT Chapter 1yonasante2121No ratings yet
- Data Base EnggDocument116 pagesData Base EnggPendem Sai SrujanNo ratings yet
- PPT ch05Document60 pagesPPT ch05Felicia Lee Li ErnNo ratings yet
- 279 - DBMS Complete1Document121 pages279 - DBMS Complete1Pratiksha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- 1st Chap Data ModelsDocument47 pages1st Chap Data ModelsGuru DarshanNo ratings yet
- Databases: System Concepts, Designs, Management, and ImplementationFrom EverandDatabases: System Concepts, Designs, Management, and ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Analytics: Techniques to Analyze and Visualize Streaming DataFrom EverandReal-Time Analytics: Techniques to Analyze and Visualize Streaming DataNo ratings yet
- THE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)From EverandTHE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)No ratings yet
- 10 Things A Real Man Does When He's in A Relationship PDFDocument12 pages10 Things A Real Man Does When He's in A Relationship PDFAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- 14 App - Sci - Computer ApplicationDocument8 pages14 App - Sci - Computer ApplicationAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- User Manual Enrollment StationDocument20 pagesUser Manual Enrollment StationAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- ESD Best PracticesDocument23 pagesESD Best PracticesAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Excel WorksheetDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Office Excel WorksheetAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Rsa Softtoken InstructionsDocument7 pagesRsa Softtoken InstructionsAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Bells and WhistesDocument1 pageBells and WhistesAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Topic Name Roll No. (B2804) Sig1 Sig2Document1 pageSr. No. Topic Name Roll No. (B2804) Sig1 Sig2Aayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Video Compression: Principles, Practice, and Standards: SumberDocument41 pagesVideo Compression: Principles, Practice, and Standards: SumberAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Chandra Prakash Assistant Professor LPUDocument65 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Chandra Prakash Assistant Professor LPUAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Home Work 1 Part ADocument1 pageHome Work 1 Part AAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Question 6.16 Page 186: ( ( ( Employee) ) - X - ( ( Works - On) ) - X - ( ( Project) ) )Document8 pagesQuestion 6.16 Page 186: ( ( ( Employee) ) - X - ( ( Works - On) ) - X - ( ( Project) ) )Aayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Srs ProjectDocument40 pagesSrs ProjectFATIMA NASIR AWANNo ratings yet
- ClassXI CS SampleQuestionPaperDocument9 pagesClassXI CS SampleQuestionPaperAnimesh SirNo ratings yet
- Conditional State NotesDocument12 pagesConditional State NotesSamrudh MysoreNo ratings yet
- Software Requirements Specification FOR: Book Shop Automation SoftwareDocument17 pagesSoftware Requirements Specification FOR: Book Shop Automation SoftwareGowtham SaiNo ratings yet
- SPL 161 Assignment 1 - Cybersecurity Simulation: 1 Before You StartDocument6 pagesSPL 161 Assignment 1 - Cybersecurity Simulation: 1 Before You StartMizie TarmizieNo ratings yet
- System Programming NotesDocument63 pagesSystem Programming NotesSAM CYRILNo ratings yet
- Vmware Site Recovery Manager DatasheetDocument3 pagesVmware Site Recovery Manager Datasheetmani224537No ratings yet
- The Art of Agile MarketingDocument32 pagesThe Art of Agile MarketingKatherine CastroNo ratings yet
- Assignment 0 OOPDocument11 pagesAssignment 0 OOPHUZAIFA SAEEDNo ratings yet
- 00877a - DeviceNet™ Group 2 Slave Firmware For PIC18 With CANDocument34 pages00877a - DeviceNet™ Group 2 Slave Firmware For PIC18 With CANFernando PeixeiroNo ratings yet
- PHP Answer 1Document5 pagesPHP Answer 1Dhiraj ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 360 Peoplesoft Interview QuestionsDocument10 pages360 Peoplesoft Interview QuestionsRaghu Nandepu100% (1)
- Unit 5 Procedures & Functions: Stored ProcedureDocument6 pagesUnit 5 Procedures & Functions: Stored ProcedureishuNo ratings yet
- 3.BADI Implementation For Transaction FB60Document12 pages3.BADI Implementation For Transaction FB60kiranmeesalaNo ratings yet
- 4 Reverse Engineer's Blog (KDSBest)Document5 pages4 Reverse Engineer's Blog (KDSBest)Mohammad Mohsen AmiriNo ratings yet
- Semantic HTML Use CasesDocument9 pagesSemantic HTML Use CasesHruday charanNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Programming (C++) Topic:-InheritanceDocument14 pagesObject-Oriented Programming (C++) Topic:-InheritanceMitul Kuvadiya 58No ratings yet
- AL 2012 Sample Questions ATM v1.3 QuestionsDocument41 pagesAL 2012 Sample Questions ATM v1.3 QuestionsPraful KaulNo ratings yet
- Sorting and Reversing A Linked ListDocument4 pagesSorting and Reversing A Linked ListhasibujtabaNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Force Com Enterprise Architecture 2Nd Edition Andrew Fawcett Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument38 pages(Download PDF) Force Com Enterprise Architecture 2Nd Edition Andrew Fawcett Online Ebook All Chapter PDFhelen.white772100% (11)
- Scratch Programming and Digital Literacy - WorksheetDocument5 pagesScratch Programming and Digital Literacy - WorksheetSamiNo ratings yet
- Name Synopsis: Italic TextDocument10 pagesName Synopsis: Italic TextbubbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Overview of Operating System (8 M)Document20 pagesChapter 1 Overview of Operating System (8 M)Abhi RajNo ratings yet
- Amazon SrsDocument45 pagesAmazon SrsLalam CharanNo ratings yet
- 8Th Sem Internship Report Final BSC CSITDocument20 pages8Th Sem Internship Report Final BSC CSITVishal PurkutiNo ratings yet
- Software Validation and Verification PlanDocument4 pagesSoftware Validation and Verification PlanDaniel AdesegunNo ratings yet
- Mike Driscoll - Python Interviews - Discussions With Python Experts (2018, Packt Publishing)Document367 pagesMike Driscoll - Python Interviews - Discussions With Python Experts (2018, Packt Publishing)FelipNo ratings yet
- PDF Table ExtractorDocument17 pagesPDF Table ExtractorJaneNo ratings yet
James A. Senn's Information Technology, 3 Edition: Enterprise Databases and Data Warehouses
James A. Senn's Information Technology, 3 Edition: Enterprise Databases and Data Warehouses
Uploaded by
Aayush Manubansh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views38 pagesIdentify the reasons organizations choose to share databases and the functions of a database management system. Explain the difference between relational and object-oriented databases and their uses in business. Describe the differences between schemas, views, and indexes.
Original Description:
Original Title
ch07_Senn3e
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIdentify the reasons organizations choose to share databases and the functions of a database management system. Explain the difference between relational and object-oriented databases and their uses in business. Describe the differences between schemas, views, and indexes.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views38 pagesJames A. Senn's Information Technology, 3 Edition: Enterprise Databases and Data Warehouses
James A. Senn's Information Technology, 3 Edition: Enterprise Databases and Data Warehouses
Uploaded by
Aayush ManubanshIdentify the reasons organizations choose to share databases and the functions of a database management system. Explain the difference between relational and object-oriented databases and their uses in business. Describe the differences between schemas, views, and indexes.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 38
James A.
Senn’s
Information Technology, 3rd Edition
Chapter 7
Enterprise Databases and
Data Warehouses
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 1
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Objectives
• Identify the reasons organizations choose to
share databases and the functions of a
database management system.
• Explain the difference between relational and
object-oriented databases and their uses in
business.
• Describe the differences between schemas,
views, and indexes.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 2
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Objectives (Continued)
• Discuss the benefits of client/server
computing.
• Differentiate between shared and distributed
databases.
• Explain why enterprises establish data
warehouses and how they differ from data
marts and enterprise databases.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 3
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Objectives (Continued)
• Distinguish between a database administrator
and a system programmer.
• Discuss database administration procedures
and concurrency procedures and explain why
these are an essential part of a shared
database system.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 4
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
The Principles of Data Sharing
Definition
• Database: A collection of data and information
describing items of interest to an organization.
• Entity: A person, place, thing, event or
condition about which data and information
are collected.
• Enterprise Database: A collection of data
designed to be shared by many users within an
organization.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 5
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
The Principles of Data Sharing
Definition (Continued)
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 6
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
The Principles of Data Sharing
Database Management Systems
• Database Management Systems (DBMS): A program that
makes it possible for users to manage the data in a
database in order to increase accessibility and
productivity.
• The Functions of Database Management:
– Integrating Databases
– Reducing Redundancy
– Sharing Information
– Maintaining Integrity
– Enabling Database Evolution
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 7
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
The Principles of Data Sharing
Database Management Systems (Continued)
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 8
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
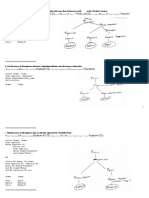
Enterprise Database Structures
Enterprise Data Model
• Enterprise Data Model/Entity Relationship: A
graphical representation of the items (the
entities) of interest about which data is
captured and stored in the database.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 9
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Enterprise Database Structures
Enterprise Data Model (Continued)
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 10
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Enterprise Database Structures
Schema
• Schema: The structure of a database.
• Schema for Relational Database
– Relational Database: A database in which
the data are structured in a table format
consisting of rows and columns.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 11
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Enterprise Database Structures
Schema (Continued)
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 12
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Enterprise Database Structures
Schema (Continued)
• Schema for Object-Oriented Database
– Object-oriented Database: A database that
stores data and information about objects.
– Object: A component that contains data
about itself and how it is to be processed.
– Action/Method: An instruction that tells a
database how to process an object to
produce specific information.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 13
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Enterprise Database Structures
Schema (Continued)
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 14
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Enterprise Database Structures
Views
• View: A subset of one or more databases,
created either by extracting copies of records
from a database or by merging copies of
records from multiple databases.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 15
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Enterprise Database Structures
Views (Continued)
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 16
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Enterprise Database Structures
Indexes
• Index: A data file that contains identifying
information about each record and its location
in storage.
• Record Key: In a database, a designated field
used to distinguish one record from another.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 17
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Enterprise Database Structures
Indexes (Continued)
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 18
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Client/Server Computing
Definition
• File Server: A computer containing files that
are available to all users interconnected on a
local area network.
• Client/Server Computing: A type of computing
in which all data and information retrieval
requests and responses pass over a network.
Much of the processing is performed on the
server and the results of the processing are
transmitted to the client.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 19
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Client/Server Computing
Definition (Continued)
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 20
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Client/Server Computing
Definition
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 21
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Client/Server Computing
Definition (Continued)
• Client: In client-server computing, a desktop
workstation.
• Server: A computer that hosts a network and
provides the resources that are shared on the
network.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 22
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Client/Server Computing
The Benefits of Client/Server Computing
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 23
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Databases on the Internet
Definition
• Web-based Integration: Makes data from
enterprise databases available to users
connecting through the Internet (including
enterprise intranets and extranets).
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 24
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Databases on the Internet
Definition (Continued)
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 25
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Distributed Databases
Definition
• Shared Database: A database shared among
many users and applications.
• Distributed Database: A database that resides
in more than one system in a distributed
network. Each component of the database can
be retrieved from any node in the network.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 26
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Distributed Databases
Partitioning and Replication
• Partitioning: A method of database distribution
in which different portions of the database
reside at different nodes in the network.
• Replication: A method of database distribution
in which one database contains data that are
included in another database.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 27
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Distributed Databases
Distribution Strategies
• Geographic Distribution Strategy: A database
distribution strategy in which the database is
located in a region where the data and
information are used most frequently.
• Functional Distribution Strategy: A database
distribution strategy in which the database is
distributed according to business functions.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 28
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Distributed Databases
Designed a Distributed Database
• Database Directory: The component of a shared
database that keeps track of data and information.
• Other Design Factors
– Storage Costs
– Processing Costs
– Communication Costs
– Retrieval and Processing
– Reliability
– Frequency of Updates and Queries
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 29
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Distributed Databases
Designed a Distributed Database
(Continued)
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 30
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Data Warehouses and OLAP
Definition
• Online Analytical Processing (OLAP):
Database processing that selectively extracts
data from different points of view.
• Data Warehouse: A large data store, designed
from inquiries, that combines details of both
current and historical operations, usually
drawn from a number of sources.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 31
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Data Warehouses and OLAP
Comparison of Enterprise Databases
and Data Warehouses
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 32
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Data Warehouses and OLAP
Data Warehouse
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 33
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Data Warehouses and OLAP
Definition
• Data Mining: Uses software designed to detect
information hidden in the data.
• Data Marts: Processed to focus on a specific
area of activities or isolated scientific or
commercial processes.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 34
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
People
Definition
• Database Administrator (DBA): The IT
professional responsible for managing all the
activities and procedures related to an
organization’s database.
• Systems Programmer
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 35
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Procedures
Database Administration Procedures
• Database Administration Procedures: The
procedures associated with managing a
database.
– Database Planning
– Database Design
– Database Creation
– Database Maintenance
– Analysis of Usage
– Creation and Monitoring of Security
Procedures
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 36
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Procedures
Concurrency Procedures
• Concurrent Data Sharing: A database
procedure that allows several users to access
the database simultaneously.
• Nonconcurrent Data Sharing: A database
procedure that allows individuals to access a
database only when no other person or
application is processing the data.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 37
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
Procedures
Concurrency Procedures (Continued)
• Record Locking: A concurrency procedure that
prohibits another user from accessing or
altering a records that is in use.
• File Locking: Used in systems that store
unstructured information and have file-level
sharing.
• Deadlock: A situation in which each user of a
database is waiting for the others to unlock a
record.
Senn, Information Technology, 3rd Edition 38
© 2004 Pearson Prentice Hall
You might also like
- Delphi Legacy Projects - Strategies and Survival GuideDocument484 pagesDelphi Legacy Projects - Strategies and Survival GuideAndry100% (3)
- Computing Concepts With Java Essentials: Advanced Placement Computer Science Study GuideDocument10 pagesComputing Concepts With Java Essentials: Advanced Placement Computer Science Study GuideDoIT ChuruNo ratings yet
- Chapter I - The Database Environment and Development ProcessDocument14 pagesChapter I - The Database Environment and Development ProcessHarris Harijono50% (2)
- Lecture 3 - DatabasesDocument59 pagesLecture 3 - DatabasesmwanwajoelNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementDocument43 pagesFoundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementArbab AshrafNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Database Management Systems: Unit 3Document57 pagesIntroduction To Database Management Systems: Unit 3Charlie Thomas VictorNo ratings yet
- Design Database Main Module Simplified TvetDocument238 pagesDesign Database Main Module Simplified Tvetmohammed ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Database Approach To Data ManagementDocument50 pagesThe Database Approach To Data Managementtampoo67% (6)
- Introd BmsDocument20 pagesIntrod BmsMohitul ShafirNo ratings yet
- DBMSDocument70 pagesDBMSGitte DnyaneshwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Lecture 1Document54 pagesChapter 1 - Lecture 1Aliyan AmanNo ratings yet
- File Systems and DatabasesDocument54 pagesFile Systems and Databasesobiwan xeonNo ratings yet
- 1.database IntroDocument28 pages1.database IntroAjiSetiajiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Databases Transparencies: © Pearson Education Limited, 2004 1Document22 pagesIntroduction To Databases Transparencies: © Pearson Education Limited, 2004 1ArbabAmjadNo ratings yet
- Managing Data ResourcesDocument51 pagesManaging Data ResourcesDebabrata PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document43 pagesChapter 11Anonymous 3BpcKiFBUNo ratings yet
- Relational Database Management Systems: UNIT-1Document120 pagesRelational Database Management Systems: UNIT-1Srinivas KanakalaNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Database - 2021 T1Document33 pagesWeek 3 - Database - 2021 T1Odria ArshianaNo ratings yet
- Managing Data ResourcesDocument50 pagesManaging Data Resourcesmicroman_123No ratings yet
- Rdbms (Unit 1)Document13 pagesRdbms (Unit 1)hari karanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Database NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Database NotesDibyeshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Databases: © Pearson Education Limited, 2004 1Document22 pagesIntroduction To Databases: © Pearson Education Limited, 2004 1hardeepcharmingNo ratings yet
- Principles of Information Systems Eighth Edition: Organizing Data and InformationDocument60 pagesPrinciples of Information Systems Eighth Edition: Organizing Data and InformationHope..!No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Information: Systems, Sixth EditionDocument56 pagesFundamentals of Information: Systems, Sixth EditionVengie BragaNo ratings yet
- 05 DatabaseDocument29 pages05 DatabaseShivangi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Database Management System: Unit-I The Database Environment: Basic Concepts and Definitions: Data, Information, MetadataDocument70 pagesDatabase Management System: Unit-I The Database Environment: Basic Concepts and Definitions: Data, Information, MetadataDeekonda AshwiniNo ratings yet
- DBMS MaterialDocument70 pagesDBMS MaterialMitesh PujaraNo ratings yet
- MIS: Database, Lecture-1Document81 pagesMIS: Database, Lecture-1Sunjida EnamNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Files Vs DatabasesDocument36 pagesWeek 4 Files Vs Databaseskobamelo LetowaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Database Systems Lect 1Document14 pagesFundamentals of Database Systems Lect 1YabNo ratings yet
- DBMS (Part 1)Document57 pagesDBMS (Part 1)Harsh WaghelaNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementDocument36 pagesFoundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information Management Foundations of Business Intelligence: Databases and Information ManagementTanvi MittalNo ratings yet
- Managing Data ResourcesDocument47 pagesManaging Data ResourcesErnst OtienoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Database SystemDocument94 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To Database SystemNabil Syahmi100% (3)
- ME DBMS Unit1 FinalDocument139 pagesME DBMS Unit1 FinalSendurusrinivas NadarNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 IDBDocument21 pagesLecture03 IDBhudaiNo ratings yet
- Dbms NotesDocument20 pagesDbms NotesSangeeta PalNo ratings yet
- 8 9dayDocument23 pages8 9dayGuess WhoNo ratings yet
- Laudon Mis15 PPT Ch06Document40 pagesLaudon Mis15 PPT Ch06Amar NsouliNo ratings yet
- DBMS ConceptsDocument38 pagesDBMS ConceptsRahul RaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DatabaseDocument61 pagesIntroduction To DatabasezainabNo ratings yet
- INT 306 Database Management SystemDocument43 pagesINT 306 Database Management SystemAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Oracle ch1Document88 pagesOracle ch1Jenner Patrick Lopes BrasilNo ratings yet
- Database Management: Dr. Md. Rakibul Hoque University of DhakaDocument57 pagesDatabase Management: Dr. Md. Rakibul Hoque University of DhakaShahriar HaqueNo ratings yet
- Sistem Informasi AkuntansiDocument40 pagesSistem Informasi AkuntansiAngga SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Database Systems: Module TitleDocument17 pagesAdvanced Database Systems: Module TitleMclab MedcollegeNo ratings yet
- Database Design and ManagementDocument45 pagesDatabase Design and ManagementJeneath TahilNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Database ConceptsDocument64 pages7.1 Database ConceptsTawanda MahereNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4 Databse Basics - For JCOsDocument35 pagesLecture-4 Databse Basics - For JCOscbhavelianNo ratings yet
- Module 16 Introduction To Database Management SystemDocument32 pagesModule 16 Introduction To Database Management SystemMadaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Database Design Process PDFDocument19 pagesLecture 6 - Database Design Process PDFChia Wei HanNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 08: Class: BBA 5 Credit HoursDocument49 pagesLecture # 08: Class: BBA 5 Credit HoursMuiz SaddozaiNo ratings yet
- BRT Chapter 1Document49 pagesBRT Chapter 1yonasante2121No ratings yet
- Data Base EnggDocument116 pagesData Base EnggPendem Sai SrujanNo ratings yet
- PPT ch05Document60 pagesPPT ch05Felicia Lee Li ErnNo ratings yet
- 279 - DBMS Complete1Document121 pages279 - DBMS Complete1Pratiksha BhosaleNo ratings yet
- 1st Chap Data ModelsDocument47 pages1st Chap Data ModelsGuru DarshanNo ratings yet
- Databases: System Concepts, Designs, Management, and ImplementationFrom EverandDatabases: System Concepts, Designs, Management, and ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Real-Time Analytics: Techniques to Analyze and Visualize Streaming DataFrom EverandReal-Time Analytics: Techniques to Analyze and Visualize Streaming DataNo ratings yet
- THE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)From EverandTHE SQL LANGUAGE: Master Database Management and Unlock the Power of Data (2024 Beginner's Guide)No ratings yet
- 10 Things A Real Man Does When He's in A Relationship PDFDocument12 pages10 Things A Real Man Does When He's in A Relationship PDFAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- 14 App - Sci - Computer ApplicationDocument8 pages14 App - Sci - Computer ApplicationAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- User Manual Enrollment StationDocument20 pagesUser Manual Enrollment StationAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- ESD Best PracticesDocument23 pagesESD Best PracticesAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Excel WorksheetDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Office Excel WorksheetAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Rsa Softtoken InstructionsDocument7 pagesRsa Softtoken InstructionsAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Bells and WhistesDocument1 pageBells and WhistesAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Sr. No. Topic Name Roll No. (B2804) Sig1 Sig2Document1 pageSr. No. Topic Name Roll No. (B2804) Sig1 Sig2Aayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Video Compression: Principles, Practice, and Standards: SumberDocument41 pagesVideo Compression: Principles, Practice, and Standards: SumberAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: Chandra Prakash Assistant Professor LPUDocument65 pagesArtificial Intelligence: Chandra Prakash Assistant Professor LPUAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Home Work 1 Part ADocument1 pageHome Work 1 Part AAayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Question 6.16 Page 186: ( ( ( Employee) ) - X - ( ( Works - On) ) - X - ( ( Project) ) )Document8 pagesQuestion 6.16 Page 186: ( ( ( Employee) ) - X - ( ( Works - On) ) - X - ( ( Project) ) )Aayush ManubanshNo ratings yet
- Srs ProjectDocument40 pagesSrs ProjectFATIMA NASIR AWANNo ratings yet
- ClassXI CS SampleQuestionPaperDocument9 pagesClassXI CS SampleQuestionPaperAnimesh SirNo ratings yet
- Conditional State NotesDocument12 pagesConditional State NotesSamrudh MysoreNo ratings yet
- Software Requirements Specification FOR: Book Shop Automation SoftwareDocument17 pagesSoftware Requirements Specification FOR: Book Shop Automation SoftwareGowtham SaiNo ratings yet
- SPL 161 Assignment 1 - Cybersecurity Simulation: 1 Before You StartDocument6 pagesSPL 161 Assignment 1 - Cybersecurity Simulation: 1 Before You StartMizie TarmizieNo ratings yet
- System Programming NotesDocument63 pagesSystem Programming NotesSAM CYRILNo ratings yet
- Vmware Site Recovery Manager DatasheetDocument3 pagesVmware Site Recovery Manager Datasheetmani224537No ratings yet
- The Art of Agile MarketingDocument32 pagesThe Art of Agile MarketingKatherine CastroNo ratings yet
- Assignment 0 OOPDocument11 pagesAssignment 0 OOPHUZAIFA SAEEDNo ratings yet
- 00877a - DeviceNet™ Group 2 Slave Firmware For PIC18 With CANDocument34 pages00877a - DeviceNet™ Group 2 Slave Firmware For PIC18 With CANFernando PeixeiroNo ratings yet
- PHP Answer 1Document5 pagesPHP Answer 1Dhiraj ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 360 Peoplesoft Interview QuestionsDocument10 pages360 Peoplesoft Interview QuestionsRaghu Nandepu100% (1)
- Unit 5 Procedures & Functions: Stored ProcedureDocument6 pagesUnit 5 Procedures & Functions: Stored ProcedureishuNo ratings yet
- 3.BADI Implementation For Transaction FB60Document12 pages3.BADI Implementation For Transaction FB60kiranmeesalaNo ratings yet
- 4 Reverse Engineer's Blog (KDSBest)Document5 pages4 Reverse Engineer's Blog (KDSBest)Mohammad Mohsen AmiriNo ratings yet
- Semantic HTML Use CasesDocument9 pagesSemantic HTML Use CasesHruday charanNo ratings yet
- Object-Oriented Programming (C++) Topic:-InheritanceDocument14 pagesObject-Oriented Programming (C++) Topic:-InheritanceMitul Kuvadiya 58No ratings yet
- AL 2012 Sample Questions ATM v1.3 QuestionsDocument41 pagesAL 2012 Sample Questions ATM v1.3 QuestionsPraful KaulNo ratings yet
- Sorting and Reversing A Linked ListDocument4 pagesSorting and Reversing A Linked ListhasibujtabaNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Force Com Enterprise Architecture 2Nd Edition Andrew Fawcett Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument38 pages(Download PDF) Force Com Enterprise Architecture 2Nd Edition Andrew Fawcett Online Ebook All Chapter PDFhelen.white772100% (11)
- Scratch Programming and Digital Literacy - WorksheetDocument5 pagesScratch Programming and Digital Literacy - WorksheetSamiNo ratings yet
- Name Synopsis: Italic TextDocument10 pagesName Synopsis: Italic TextbubbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Overview of Operating System (8 M)Document20 pagesChapter 1 Overview of Operating System (8 M)Abhi RajNo ratings yet
- Amazon SrsDocument45 pagesAmazon SrsLalam CharanNo ratings yet
- 8Th Sem Internship Report Final BSC CSITDocument20 pages8Th Sem Internship Report Final BSC CSITVishal PurkutiNo ratings yet
- Software Validation and Verification PlanDocument4 pagesSoftware Validation and Verification PlanDaniel AdesegunNo ratings yet
- Mike Driscoll - Python Interviews - Discussions With Python Experts (2018, Packt Publishing)Document367 pagesMike Driscoll - Python Interviews - Discussions With Python Experts (2018, Packt Publishing)FelipNo ratings yet
- PDF Table ExtractorDocument17 pagesPDF Table ExtractorJaneNo ratings yet