Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views14.1 Cells
14.1 Cells
Uploaded by
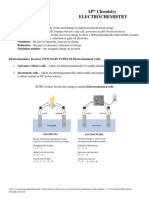
Muaaz Raza MisbahiGalvani observed frog leg twitching from current flowing through electrolytes, inspiring Volta to invent the first battery by connecting multiple cells producing consistent current from redox reactions. A cell contains liquid electrolytes and electrodes that produce electricity through spontaneous redox or use electricity to force redox. A voltaic cell produces electricity while an electrolytic cell uses it. A salt bridge maintains charge balance. Potential difference depends on materials and drives electron flow. Current is charge flow rate. Batteries combine cells' potentials. Secondary cells recharge through added electricity like lead-acid batteries. Fuel cells continuously supply reactants like hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- 14.1 CellsDocument12 pages14.1 CellsLaras FadillahNo ratings yet
- 14.1 CellsDocument12 pages14.1 CellsdeanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell: Chapter 2: Electrochemistry Chemistry For Grade 12Document8 pagesElectrochemical Cell: Chapter 2: Electrochemistry Chemistry For Grade 12Farhan Pranadarmesta MerchNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellDocument11 pagesElectrochemical CellssssNo ratings yet
- CHE 111 - Lecture 15 Electrochemistry PDFDocument62 pagesCHE 111 - Lecture 15 Electrochemistry PDFElisa MuntangaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry File XIIDocument34 pagesChemistry File XIITushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- 14.0 Electrochemical PowerPointDocument64 pages14.0 Electrochemical PowerPointhedayatinluv100% (1)
- Voltaic CellsDocument6 pagesVoltaic CellsRaj MallickNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotespvnchemNo ratings yet
- Low Volatge and BatteryDocument74 pagesLow Volatge and BatteryOladokun Sulaiman OlanrewajuNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell Project FileDocument16 pagesElectrochemical Cell Project Filevabhay22435No ratings yet
- Italian: Primary Batteries Secondary BatteriesDocument4 pagesItalian: Primary Batteries Secondary Batteriessupriyakumari7No ratings yet
- Plate # 2 Primary and Secondary BatteriesDocument14 pagesPlate # 2 Primary and Secondary Batteriesjr gajelesNo ratings yet
- Battery EeeDocument27 pagesBattery EeeNaisarg ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Cells and BatteriesDocument32 pagesCells and BatteriesMuhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- 1.ElectrochemistryPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae SheetDocument4 pages1.ElectrochemistryPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae SheetArbab MazharNo ratings yet
- Module 4 SPDocument50 pagesModule 4 SPSanskriti GuptaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Electric Potential Voltage For WeeblyDocument26 pages6 - Electric Potential Voltage For WeeblyPAYNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers (Lec) - For MergeDocument10 pagesChemistry For Engineers (Lec) - For MergeCleofe Jane P. CasasNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science & Technology University: Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument37 pagesAddis Ababa Science & Technology University: Department of Chemical EngineeringdagmawiNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument7 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry ProjectMd RehanNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument8 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry BeginingDocument5 pagesChemistry Beginingarchita1072006No ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument35 pagesElectrolysisericbattyNo ratings yet
- ECE5710 Notes01Document32 pagesECE5710 Notes01FREDERICKNo ratings yet
- CHM031 Module 1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesCHM031 Module 1 ReviewerrainNo ratings yet
- History of Electrochemical Cell: Voltaic PileDocument10 pagesHistory of Electrochemical Cell: Voltaic PileNabilah OthmanNo ratings yet
- Half-Cells Anions Anode Cations Cathode Redox Electrolyte: Luigi Galvani Leyden JarDocument3 pagesHalf-Cells Anions Anode Cations Cathode Redox Electrolyte: Luigi Galvani Leyden JarKirstie ImeldaNo ratings yet
- Chapter17 2Document27 pagesChapter17 2Mr. NaveenNo ratings yet
- Dipankar Maity Electrochemical CellDocument3 pagesDipankar Maity Electrochemical CellSk jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Bateries - InglesDocument9 pagesBateries - InglesMariana Rivas CruzNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2015-16 CP3624 26-Aug-2015 RM01 Module-6Document26 pagesFALLSEM2015-16 CP3624 26-Aug-2015 RM01 Module-6Playa 5No ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument2 pagesElectrochemical CellsQ202No ratings yet
- BatteryDocument12 pagesBatteryvinesh6No ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument1 pageQuestionsDevendraa Muniandy100% (2)
- Battery Introduction PDFDocument17 pagesBattery Introduction PDFlavanyaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument15 pagesElectrochemistrySakshi TamshettiNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument1 pageElectrochemistryJohn Carlo G. NolascoNo ratings yet
- Electric BatteryDocument17 pagesElectric Batterymohan yadavNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument76 pagesElectrochemistryRatna ThakurNo ratings yet
- Topics Covered in Introduction To Batteries The Voltaic Cell Common Types of Primary Cells Lead-Acid Wet Cell Additional Types of Secondary CellsDocument32 pagesTopics Covered in Introduction To Batteries The Voltaic Cell Common Types of Primary Cells Lead-Acid Wet Cell Additional Types of Secondary CellsArvind VNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrics - Aircraft BatteriesDocument17 pagesAircraft Electrics - Aircraft BatteriesErica Zoe BantogNo ratings yet
- Electrical System - Part1Document36 pagesElectrical System - Part1LARA JOANNE DORIANo ratings yet
- Chapter 21a Electrohem Electrolysis f08Document8 pagesChapter 21a Electrohem Electrolysis f08shalini99No ratings yet
- CELLS AND BATTERIES AllDocument18 pagesCELLS AND BATTERIES AllVictor mulotaNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument42 pagesBatterySubhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter17 2Document27 pagesChapter17 2BleZianne PugayanNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY - Voltaic Cell PDFDocument14 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY - Voltaic Cell PDFKlifford Galicia100% (2)
- 2.3 Electrochemistry R0 - 220830Document34 pages2.3 Electrochemistry R0 - 220830Kelly Roxelle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ElectrochemistryDocument25 pagesUnit 1 ElectrochemistryVasudev Gupta100% (1)
- Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis: Q Quantity of Electricity I × T Where I Is The Current T TimeDocument18 pagesFaraday's Laws of Electrolysis: Q Quantity of Electricity I × T Where I Is The Current T TimeHarshil ChangelaNo ratings yet
- All About The Electrochemical Cell and Its Different Types: July 2020Document25 pagesAll About The Electrochemical Cell and Its Different Types: July 2020SivaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument56 pagesElectrochemistry NotesAnusha PanchumarthiNo ratings yet
- Batteries and Fuel CellsDocument31 pagesBatteries and Fuel CellsUmesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- Chem AlokDocument19 pagesChem AlokRiya TiwariNo ratings yet
- 17 Electrochemistry With Answers PDFDocument15 pages17 Electrochemistry With Answers PDFFirdausia Rahma Putri100% (1)
- Stone Battery-1Document4 pagesStone Battery-1apdallhaied67No ratings yet
- III RD Maths I Preliminary Paper of HSCDocument2 pagesIII RD Maths I Preliminary Paper of HSCAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNo ratings yet
- 06 - Chapter 1 PDFDocument35 pages06 - Chapter 1 PDFcarmenNo ratings yet
- Business Case Part 1 - Phase 2 - Group 212053 - 17 FDocument14 pagesBusiness Case Part 1 - Phase 2 - Group 212053 - 17 Fkaren stefania hortua curzNo ratings yet
- FORM V Abstract Under The Payment of Wages Act, 1936 (English Version)Document2 pagesFORM V Abstract Under The Payment of Wages Act, 1936 (English Version)anant nagvekarsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Dealing With Uncertainty: General ProcedureDocument15 pagesChapter 10 Dealing With Uncertainty: General ProcedureHannan Mahmood TonmoyNo ratings yet
- Ielts Reading Test 1Document7 pagesIelts Reading Test 1Bách XuânNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Free Fall SolsDocument5 pagesKinematics Free Fall SolsDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Cd00020086 Sensorless BLDC Motor Control and Bemf Sampling Methods With St7mc StmicroelectronicsDocument35 pagesCd00020086 Sensorless BLDC Motor Control and Bemf Sampling Methods With St7mc StmicroelectronicsmortezaNo ratings yet
- Sauer90 ServiceManual PDFDocument72 pagesSauer90 ServiceManual PDFeng13100% (7)
- KMA CVDocument5 pagesKMA CVKhandoker Mostak AhamedNo ratings yet
- Howlett Paper 09182013Document6 pagesHowlett Paper 09182013FutantxxyzNo ratings yet
- Energy and Energy Transformations: Energy Makes Things HappenDocument8 pagesEnergy and Energy Transformations: Energy Makes Things HappenLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Digital Controls Improve PFC PerformanceDocument18 pagesAdvanced Digital Controls Improve PFC Performancediablo diablolordNo ratings yet
- 04353957Document5 pages04353957Ramya RNo ratings yet
- Budget Plan 2Document14 pagesBudget Plan 2Abbie BalsarzaNo ratings yet
- Geometry AssignmentDocument2 pagesGeometry AssignmentAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNo ratings yet
- CAT Test Series 2015Document2 pagesCAT Test Series 2015Nikhil SiddharthNo ratings yet
- Boli Interne Vol I Partea 1Document454 pagesBoli Interne Vol I Partea 1Murariu Diana100% (2)
- Social Class Influence & CBDocument8 pagesSocial Class Influence & CBAdityaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications Project ReportDocument14 pagesDigital Communications Project ReportSonal Pinto0% (1)
- Corporate Nvidia in BriefDocument2 pagesCorporate Nvidia in BriefakesplwebsiteNo ratings yet
- Production ManagementDocument26 pagesProduction Managementkevin punzalan100% (5)
- CyberMania 2023Document22 pagesCyberMania 2023choudhuryaarit2007No ratings yet
- HARRIS Instruction Manual 7-8 Imn-901600-E03Document268 pagesHARRIS Instruction Manual 7-8 Imn-901600-E03g_pargadeNo ratings yet
- Neverwhere by Neil Gaiman - Teacher Study GuideDocument3 pagesNeverwhere by Neil Gaiman - Teacher Study GuideHarperAcademic33% (3)
- Smallware InventoryDocument7 pagesSmallware Inventoryye min aungNo ratings yet
- Guidotti Timothy E1980Document164 pagesGuidotti Timothy E1980Samuel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Denim A New Export Item For BangladeshDocument2 pagesDenim A New Export Item For Bangladeshhabibun naharNo ratings yet
- License Exceptions Part 740 - Page 1: 740.1 IntroductionDocument82 pagesLicense Exceptions Part 740 - Page 1: 740.1 Introductiondali layouniNo ratings yet
- Allen StoneDocument4 pagesAllen StoneRubén FernándezNo ratings yet
14.1 Cells
14.1 Cells
Uploaded by
Muaaz Raza Misbahi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views12 pagesGalvani observed frog leg twitching from current flowing through electrolytes, inspiring Volta to invent the first battery by connecting multiple cells producing consistent current from redox reactions. A cell contains liquid electrolytes and electrodes that produce electricity through spontaneous redox or use electricity to force redox. A voltaic cell produces electricity while an electrolytic cell uses it. A salt bridge maintains charge balance. Potential difference depends on materials and drives electron flow. Current is charge flow rate. Batteries combine cells' potentials. Secondary cells recharge through added electricity like lead-acid batteries. Fuel cells continuously supply reactants like hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity.
Original Description:
Class 12 biology cells
Original Title
14.1 cells
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGalvani observed frog leg twitching from current flowing through electrolytes, inspiring Volta to invent the first battery by connecting multiple cells producing consistent current from redox reactions. A cell contains liquid electrolytes and electrodes that produce electricity through spontaneous redox or use electricity to force redox. A voltaic cell produces electricity while an electrolytic cell uses it. A salt bridge maintains charge balance. Potential difference depends on materials and drives electron flow. Current is charge flow rate. Batteries combine cells' potentials. Secondary cells recharge through added electricity like lead-acid batteries. Fuel cells continuously supply reactants like hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views12 pages14.1 Cells
14.1 Cells
Uploaded by
Muaaz Raza MisbahiGalvani observed frog leg twitching from current flowing through electrolytes, inspiring Volta to invent the first battery by connecting multiple cells producing consistent current from redox reactions. A cell contains liquid electrolytes and electrodes that produce electricity through spontaneous redox or use electricity to force redox. A voltaic cell produces electricity while an electrolytic cell uses it. A salt bridge maintains charge balance. Potential difference depends on materials and drives electron flow. Current is charge flow rate. Batteries combine cells' potentials. Secondary cells recharge through added electricity like lead-acid batteries. Fuel cells continuously supply reactants like hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
14.
1 Cells and Batteries
Origins of the Cell
• Galvani (late 1700’s) observed a frog’s leg
twitch when exposed to a current
• Volta (early 1800’s) realized it was due to
current flowing through electrolytes in body
• Volta invented the first battery by
connecting multiple electric cells together
• Based on spontaneous redox rxtn’s it was
able to produce a consistent current
Cell design
• “Cells” are containers of liquid with electrodes:
Source or use
of electricity
Cell Electrode
–
–
+
+
Molten or
– + aqueous
chemicals
• In “voltaic cells”, electricity is produced
spontaneously from a redox reaction
• In “electrolytic cells”, electricity is used to force
chemicals to undergo a redox reaction
Voltaic Cell
• also referred to as a “galvanic cell”
• salt bridge or porous disk(cup) used to allow for
unrelated ions to move to allow for balance of charge
Cell Properties
- driving force on electron to move them through the
wire
• electric potential difference is the energy difference
per unit charge
• depends on type of electrodes and electrolytes used in
cells
• electric current is rate of flow of charge in a circuit
• power is the rate at which electrical energy is
produced
Cell Quantities
Quantity Symbol Meter Units
Charge Q C (coulombs)
Current I ammeter A (ampere)
Potential V voltmeter V (volt)
difference
Power P W (watt)
Energy J/kg
density
Secondary Cells & Batteries
a battery is a group of galvanic cells
connected in series
the potentials of the individual cells add
to give the total battery potential
secondary cells can be recharged by
adding electricity
Figure 7 One of the Cells in a 12-V Lead Storage Battery (LSM 14.1C)
Figure 6 A Common Dry Cell Battery (LSM 14.1C)
Fuel Cells
. . . voltaic cells where the reactants are
continuously supplied.
2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l)
anode: 2H2 + 4OH 4H2O + 4e
cathode: 4e + O2 + 2H2O 4OH
Figure 8 Schematic of the Hydrogen-Oxygen Fuel Cell (LSM 14.1C)
Homework
Textbook p. 614 #1-5
Textbook p. 619 #10-15
LSM 14.1 B,C,D
You might also like
- 14.1 CellsDocument12 pages14.1 CellsLaras FadillahNo ratings yet
- 14.1 CellsDocument12 pages14.1 CellsdeanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell: Chapter 2: Electrochemistry Chemistry For Grade 12Document8 pagesElectrochemical Cell: Chapter 2: Electrochemistry Chemistry For Grade 12Farhan Pranadarmesta MerchNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellDocument11 pagesElectrochemical CellssssNo ratings yet
- CHE 111 - Lecture 15 Electrochemistry PDFDocument62 pagesCHE 111 - Lecture 15 Electrochemistry PDFElisa MuntangaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry File XIIDocument34 pagesChemistry File XIITushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- 14.0 Electrochemical PowerPointDocument64 pages14.0 Electrochemical PowerPointhedayatinluv100% (1)
- Voltaic CellsDocument6 pagesVoltaic CellsRaj MallickNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-2 Clean Energy Storage and Conversion Devices NotespvnchemNo ratings yet
- Low Volatge and BatteryDocument74 pagesLow Volatge and BatteryOladokun Sulaiman OlanrewajuNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell Project FileDocument16 pagesElectrochemical Cell Project Filevabhay22435No ratings yet
- Italian: Primary Batteries Secondary BatteriesDocument4 pagesItalian: Primary Batteries Secondary Batteriessupriyakumari7No ratings yet
- Plate # 2 Primary and Secondary BatteriesDocument14 pagesPlate # 2 Primary and Secondary Batteriesjr gajelesNo ratings yet
- Battery EeeDocument27 pagesBattery EeeNaisarg ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Cells and BatteriesDocument32 pagesCells and BatteriesMuhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- 1.ElectrochemistryPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae SheetDocument4 pages1.ElectrochemistryPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae SheetArbab MazharNo ratings yet
- Module 4 SPDocument50 pagesModule 4 SPSanskriti GuptaNo ratings yet
- 6 - Electric Potential Voltage For WeeblyDocument26 pages6 - Electric Potential Voltage For WeeblyPAYNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For Engineers (Lec) - For MergeDocument10 pagesChemistry For Engineers (Lec) - For MergeCleofe Jane P. CasasNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Science & Technology University: Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument37 pagesAddis Ababa Science & Technology University: Department of Chemical EngineeringdagmawiNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument7 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry ProjectMd RehanNo ratings yet
- Electroanalytical TechniquesDocument8 pagesElectroanalytical Techniqueszeshma iqbalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry BeginingDocument5 pagesChemistry Beginingarchita1072006No ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument35 pagesElectrolysisericbattyNo ratings yet
- ECE5710 Notes01Document32 pagesECE5710 Notes01FREDERICKNo ratings yet
- CHM031 Module 1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesCHM031 Module 1 ReviewerrainNo ratings yet
- History of Electrochemical Cell: Voltaic PileDocument10 pagesHistory of Electrochemical Cell: Voltaic PileNabilah OthmanNo ratings yet
- Half-Cells Anions Anode Cations Cathode Redox Electrolyte: Luigi Galvani Leyden JarDocument3 pagesHalf-Cells Anions Anode Cations Cathode Redox Electrolyte: Luigi Galvani Leyden JarKirstie ImeldaNo ratings yet
- Chapter17 2Document27 pagesChapter17 2Mr. NaveenNo ratings yet
- Dipankar Maity Electrochemical CellDocument3 pagesDipankar Maity Electrochemical CellSk jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Bateries - InglesDocument9 pagesBateries - InglesMariana Rivas CruzNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2015-16 CP3624 26-Aug-2015 RM01 Module-6Document26 pagesFALLSEM2015-16 CP3624 26-Aug-2015 RM01 Module-6Playa 5No ratings yet
- Electrochemical CellsDocument2 pagesElectrochemical CellsQ202No ratings yet
- BatteryDocument12 pagesBatteryvinesh6No ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument1 pageQuestionsDevendraa Muniandy100% (2)
- Battery Introduction PDFDocument17 pagesBattery Introduction PDFlavanyaNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument15 pagesElectrochemistrySakshi TamshettiNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument1 pageElectrochemistryJohn Carlo G. NolascoNo ratings yet
- Electric BatteryDocument17 pagesElectric Batterymohan yadavNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument76 pagesElectrochemistryRatna ThakurNo ratings yet
- Topics Covered in Introduction To Batteries The Voltaic Cell Common Types of Primary Cells Lead-Acid Wet Cell Additional Types of Secondary CellsDocument32 pagesTopics Covered in Introduction To Batteries The Voltaic Cell Common Types of Primary Cells Lead-Acid Wet Cell Additional Types of Secondary CellsArvind VNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Electrics - Aircraft BatteriesDocument17 pagesAircraft Electrics - Aircraft BatteriesErica Zoe BantogNo ratings yet
- Electrical System - Part1Document36 pagesElectrical System - Part1LARA JOANNE DORIANo ratings yet
- Chapter 21a Electrohem Electrolysis f08Document8 pagesChapter 21a Electrohem Electrolysis f08shalini99No ratings yet
- CELLS AND BATTERIES AllDocument18 pagesCELLS AND BATTERIES AllVictor mulotaNo ratings yet
- BatteryDocument42 pagesBatterySubhuNo ratings yet
- Chapter17 2Document27 pagesChapter17 2BleZianne PugayanNo ratings yet
- ELECTROCHEMISTRY - Voltaic Cell PDFDocument14 pagesELECTROCHEMISTRY - Voltaic Cell PDFKlifford Galicia100% (2)
- 2.3 Electrochemistry R0 - 220830Document34 pages2.3 Electrochemistry R0 - 220830Kelly Roxelle De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ElectrochemistryDocument25 pagesUnit 1 ElectrochemistryVasudev Gupta100% (1)
- Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis: Q Quantity of Electricity I × T Where I Is The Current T TimeDocument18 pagesFaraday's Laws of Electrolysis: Q Quantity of Electricity I × T Where I Is The Current T TimeHarshil ChangelaNo ratings yet
- All About The Electrochemical Cell and Its Different Types: July 2020Document25 pagesAll About The Electrochemical Cell and Its Different Types: July 2020SivaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument56 pagesElectrochemistry NotesAnusha PanchumarthiNo ratings yet
- Batteries and Fuel CellsDocument31 pagesBatteries and Fuel CellsUmesh ChandraNo ratings yet
- Chem AlokDocument19 pagesChem AlokRiya TiwariNo ratings yet
- 17 Electrochemistry With Answers PDFDocument15 pages17 Electrochemistry With Answers PDFFirdausia Rahma Putri100% (1)
- Stone Battery-1Document4 pagesStone Battery-1apdallhaied67No ratings yet
- III RD Maths I Preliminary Paper of HSCDocument2 pagesIII RD Maths I Preliminary Paper of HSCAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNo ratings yet
- 06 - Chapter 1 PDFDocument35 pages06 - Chapter 1 PDFcarmenNo ratings yet
- Business Case Part 1 - Phase 2 - Group 212053 - 17 FDocument14 pagesBusiness Case Part 1 - Phase 2 - Group 212053 - 17 Fkaren stefania hortua curzNo ratings yet
- FORM V Abstract Under The Payment of Wages Act, 1936 (English Version)Document2 pagesFORM V Abstract Under The Payment of Wages Act, 1936 (English Version)anant nagvekarsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Dealing With Uncertainty: General ProcedureDocument15 pagesChapter 10 Dealing With Uncertainty: General ProcedureHannan Mahmood TonmoyNo ratings yet
- Ielts Reading Test 1Document7 pagesIelts Reading Test 1Bách XuânNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Free Fall SolsDocument5 pagesKinematics Free Fall SolsDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Cd00020086 Sensorless BLDC Motor Control and Bemf Sampling Methods With St7mc StmicroelectronicsDocument35 pagesCd00020086 Sensorless BLDC Motor Control and Bemf Sampling Methods With St7mc StmicroelectronicsmortezaNo ratings yet
- Sauer90 ServiceManual PDFDocument72 pagesSauer90 ServiceManual PDFeng13100% (7)
- KMA CVDocument5 pagesKMA CVKhandoker Mostak AhamedNo ratings yet
- Howlett Paper 09182013Document6 pagesHowlett Paper 09182013FutantxxyzNo ratings yet
- Energy and Energy Transformations: Energy Makes Things HappenDocument8 pagesEnergy and Energy Transformations: Energy Makes Things HappenLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Digital Controls Improve PFC PerformanceDocument18 pagesAdvanced Digital Controls Improve PFC Performancediablo diablolordNo ratings yet
- 04353957Document5 pages04353957Ramya RNo ratings yet
- Budget Plan 2Document14 pagesBudget Plan 2Abbie BalsarzaNo ratings yet
- Geometry AssignmentDocument2 pagesGeometry AssignmentAMIN BUHARI ABDUL KHADERNo ratings yet
- CAT Test Series 2015Document2 pagesCAT Test Series 2015Nikhil SiddharthNo ratings yet
- Boli Interne Vol I Partea 1Document454 pagesBoli Interne Vol I Partea 1Murariu Diana100% (2)
- Social Class Influence & CBDocument8 pagesSocial Class Influence & CBAdityaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications Project ReportDocument14 pagesDigital Communications Project ReportSonal Pinto0% (1)
- Corporate Nvidia in BriefDocument2 pagesCorporate Nvidia in BriefakesplwebsiteNo ratings yet
- Production ManagementDocument26 pagesProduction Managementkevin punzalan100% (5)
- CyberMania 2023Document22 pagesCyberMania 2023choudhuryaarit2007No ratings yet
- HARRIS Instruction Manual 7-8 Imn-901600-E03Document268 pagesHARRIS Instruction Manual 7-8 Imn-901600-E03g_pargadeNo ratings yet
- Neverwhere by Neil Gaiman - Teacher Study GuideDocument3 pagesNeverwhere by Neil Gaiman - Teacher Study GuideHarperAcademic33% (3)
- Smallware InventoryDocument7 pagesSmallware Inventoryye min aungNo ratings yet
- Guidotti Timothy E1980Document164 pagesGuidotti Timothy E1980Samuel GarciaNo ratings yet
- Denim A New Export Item For BangladeshDocument2 pagesDenim A New Export Item For Bangladeshhabibun naharNo ratings yet
- License Exceptions Part 740 - Page 1: 740.1 IntroductionDocument82 pagesLicense Exceptions Part 740 - Page 1: 740.1 Introductiondali layouniNo ratings yet
- Allen StoneDocument4 pagesAllen StoneRubén FernándezNo ratings yet