Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Graphics: Overview of Graphics Systems
Computer Graphics: Overview of Graphics Systems
Uploaded by
shibina balakrishnan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views25 pagesThe document discusses various topics in computer graphics including video display devices like cathode ray tubes, color CRT monitors, flat panel displays, and 3D viewing devices. It also covers input devices, hardcopy output, and graphics software. Specifically, it provides details on how refresh cathode ray tubes work using an electron gun and magnetic coils to direct the electron beam and refresh the screen. It also explains raster scan and random scan display methods.
Original Description:
Original Title
CGppt2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various topics in computer graphics including video display devices like cathode ray tubes, color CRT monitors, flat panel displays, and 3D viewing devices. It also covers input devices, hardcopy output, and graphics software. Specifically, it provides details on how refresh cathode ray tubes work using an electron gun and magnetic coils to direct the electron beam and refresh the screen. It also explains raster scan and random scan display methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views25 pagesComputer Graphics: Overview of Graphics Systems
Computer Graphics: Overview of Graphics Systems
Uploaded by
shibina balakrishnanThe document discusses various topics in computer graphics including video display devices like cathode ray tubes, color CRT monitors, flat panel displays, and 3D viewing devices. It also covers input devices, hardcopy output, and graphics software. Specifically, it provides details on how refresh cathode ray tubes work using an electron gun and magnetic coils to direct the electron beam and refresh the screen. It also explains raster scan and random scan display methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 25
COMPUTER GRAPHICS
Overview of graphics systems
Video Display Devices
1) Refresh Cathode Ray Tube(CRT)
2) Color CRT Monitors
3) Direct View Storage Tubes (DVST)
4) Flat Panel Display
5) Three Dimensional Viewing Device
6) Stereoscopic and Virtual Reality Systems
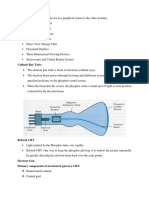
Refresh Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
Refresh Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
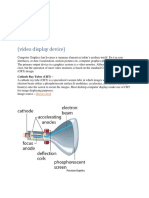
operation of most video monitors is based on the standard
cathode-ray tube (CRT) design.
electron gun emits a beam of electrons (cathode rays)
focusing and deflection systems that direct the beam toward
specified positions on the phosphor coated screen.
The phosphor then emits a small spot of light at each position
contacted by the electron beam.
Because the light emitted by the phosphor fades very rapidly,
some method is needed for maintaining the screen picture.
One way to keep the phosphor glowing is to redraw the picture
repeatedly by quickly directing the electron beam back over the
same points. This type of display is called a refresh CRT.
Magnetic Deflection Coils: to control the direction of the beam
Operation of an ELECTRON GUN with an accelerating anode:
Heated metal cathode—Heat supplied to the Cathode using a current in
filament
Causes’ electrons to be “boiled off”
Free negatively charged electrons are accelerated towards the phosphor
coated screen by a high positive voltage
Control grid: A metal cylinder which controls Intensity of the electron beam by
setting voltage levels
FOCUSING SYSTEM: Force the electron beam to strike the phosphor to
avoid the repelling and spreading of electrons
PERSISTANCE ,RESOLUTION AND ASPECT RATIO
PERSISTENCE : How long they continue to emit light after the CRT beam is
removed. Persistence is defined as the time it takes the emitted light from
the screen to decay to one-tenth of its original intensity.
Lower- persistence phosphors require higher refresh rates to maintain a
picture on the screen without flicker. A phosphor with low persistence is
useful for animation
A high-persistence phosphor is useful for displaying highly complex, static
pictures.
Some phosphors have a persistence greater than 1 second, graphics
monitors are usually constructed with a persistence in the range from 10 to
60 microseconds.
RESOLUTION: The maximum number of points that can be
displayed without overlap on a CRT is referred to as the
resolution.
A more precise definition of resolution is the number of points
per centimeter that can be plotted horizontally and vertically,
although it is often simply stated as the total number of points
in each direction.
ASPECT RATIO: This number gives the ratio of vertical points
to horizontal points necessary to produce equal-length lines in
both directions on the screen. (Sometimes aspect ratio is
stated in terms of the ratio of horizontal to vertical points.)
An aspect ratio of 3/4 means that a vertical line plotted with
three points has the same length as a horizontal line plot- ted
with four points.
There are two ways for displaying
object on a screen:
I. RASTER SCAN DISPLAY
II. RANDOM SCAN DISPLAY
RASTER SCAN DISPLAY
Most common type graphics software used in CRT
In a raster scan system, the electron beam is swept across the
screen, one row at a time from top to bottom.
As the electron beam moves across each row, the beam intensity is
turned on and off to create a pattern of illuminated spots.
Picture definition is stored in a memory area called REFRESH
BUFFER OR FRAME BUFFER which holds the intensity values
for all the screen points(pixels)
Black and White system---screen point is either ON or OFF
Bilevel system 1 indicate ON and 0 indicate OFF and additional
bits needed for color variations
BITMAP---On a black and white system with one bit per pixel,
the frame buffer is commonly called bitmap
PIXMAP---For systems with multiple bits per pixel referred to as
pixmap
Raster scan display is carried out a rate of 60 to 80 frames per
second
RANDOM SCAN DISPLAY
The electron beam is directed only to the part of the screen
where the picture is to be drawn rather than scanning from
left to right and top to bottom as in raster scan.
It is also called vector display, stroke-writing
display, or calligraphic display.
Draw a picture one line at a time
Refresh rate depends on the number of lines to be
displayed
Picturedefinition is stored as a set of line drawing
commands in an area of memory called REFRESH
DISPLAY FILE (display list or display program)
Random scan systems are designed for line
drawing applications
COLOR CRT MONITORS
Displays
color pictures using a combination of
phosphors that emit different colors of light
Range of colors is generated by combining the
emitted light from different phosphors
Two basic techniques for producing color displays
I) Beam penetration method
II) Shadow mask method
BEAM PENETRATION METHOD
Used with random scan monitors
Two layers of phosphors (red and green) are coated in the
CRT screen
Displayed color depends on how far the electron beam
penetrated in to the phosphors layer
Slow electrons exists only on the outer layer
Fast electrons penetrates through the red layer and exists in
the inner green layer
Intermediate beam speeds , combination of red green light
emitted (orange and yellow)
Disadvantage: only 4 colors are possible and quality of
picture not good as other methods
SHADOW MASK METHOD
Commonly used in raster scan systems(color TV)
Produce a much wide range of colors
Three phosphors color dots red, green, blue
Three electron guns
When three dots pass through a hole produce a
dot triangle appears as a small color spot
Equal intensity---white or gray
DIRECT VIEW STORAGE TUBES
Stores the picture information as a charge distribution just behind
the phosphor coated screen
Two electron guns are used :
(i) primary gun: Used to store picture pattern
(ii) flood gun: Maintaining the picture display
Advantage : No refreshing is needed
complex pictures can be displayed at very high resolution
Disadvantage : Do not display color and
selected parts of a picture cannot be erased
FLAT PANEL DISPLAY
Class of video devices that have reduced volume, weight and
power requirements compared to CRT
Thinner than CRT and can hang them on walls
Small TV monitors, calculators, pocket video games ,
advertisement board etc.
PLASMA PANNELS
Gas discharge displays
Constructed by filling the region between two glass plates , set of
vertical ribbons, set of horizontal ribbons
Gas at the intersection of ribbons cause a breakdown of glowing
plasma in to electrons and ions while voltage applies
Firing voltage applies to pixel position 60 times per second
LIGHT EMITTING DIODE
A matrix of diode is arranged to form the display
Picture definition is stored in refresh buffer
Scanline information is read from refresh buffer and convert to
voltage levels that are applied to diodes to produce light pattern
in display
LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY
Commonly used in small systems( calculator, watch..)
Produce picture by passing polarized light from the
surroundings through a liquid crystal material
Components have a crystalline arrangement of molecules
THREE DIMENSIONAL VIEWING DEVICE
Display of three dimensional scene
Reflects a CRT image from a vibrating flexible mirror
As it vibrate focal length changes so that each point on
the object reflected in to a specified position in the
window
Allows us to walk around an object or scene to view it
from different sides
STERIOSCOPIC AND VIRTUAL REALITY SYSTEMS
Representing three dimensional object in a stereoscopic
view
Does not provide an original three dimensional image ,only
provide a feel
Component in virtual reality systems
INPUT DEVICES
Various devices are available for data input on graphics workstations.
Most systems have a keyboard and one or more additional devices specially
designed for interactive input
Keyboard
Mouse
Trackball
Joystick
Spaceball
Dataglove
Digitizers
Touch panel
Voice system
Light pen
HARDCOPY DEVICES
We can obtain hard-copy output for images in several formats
To put images on film, we can simply photograph a scene
displayed on a video monitor.
we can put our pictures on paper by directing graphics output
to a printer or plotter.
Printers produce output by either impact or nonimpact
methods.
Impact printers press formed character faces against an inked
ribbon onto the paper. eg line printer
Nonimpact printers and plotters use laser techniques, ink-jet
sprays, xerographic process, electrostatic methods, and
electrothermal methods to get images onto Paper.
Laser device: use laser beam to print in paper
GRAPHICS SOFTWARE
Two general classifications:
1) general programming packages
used in high level programming language
Eg: Graphics library
Generating picture components, setting color and intensity values,
selecting views and applying transformations
2) special purpose application package
Designed for non programmers
User can generate displays with out worrying about software
working
Allows users to communicate their own ways
Eg : painting programs, medical and CAD systems
THANK YOU
You might also like
- Question and AnswerDocument15 pagesQuestion and AnswerIT Department HOD100% (1)
- DS4 Hydraulic Training System - RexrothDocument158 pagesDS4 Hydraulic Training System - RexrothJenny Cecilia Ureña Zuri100% (8)
- Distribution Strategy of HewlettDocument7 pagesDistribution Strategy of HewlettKumar SatvikNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 UpdatedDocument2 pagesTutorial 5 UpdatedChiraag ChiruNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Application of Computer Graphics:: Fine ArtDocument9 pagesUnit - 1 Application of Computer Graphics:: Fine ArtVathicoming Vikky100% (1)
- 1display DevicesDocument26 pages1display DevicesKrishna AnanthiNo ratings yet
- Display TechnologiesDocument8 pagesDisplay TechnologiesAshley MainaNo ratings yet
- CG Lect1Document32 pagesCG Lect1Shrishti ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CG Unit 1Document22 pagesCG Unit 1VINAYAK CODMNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Display - DevicesDocument11 pagesLecture 2 - Display - DevicesaathikahNo ratings yet
- CS6504 Computer Graphics Notes Unit IDocument23 pagesCS6504 Computer Graphics Notes Unit IAnonymous ZRinsjjWi40% (2)
- Hearn and Baker - Chapter 2Document56 pagesHearn and Baker - Chapter 2Rashika Jain100% (5)
- 2-Graphics SystemsDocument68 pages2-Graphics SystemsBEKAN FAYERANo ratings yet
- Unit I Basics of Computer GraphicsDocument37 pagesUnit I Basics of Computer GraphicsbjchwbjhNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics: Lecture - 02Document42 pagesComputer Graphics: Lecture - 02Saimo MghaseNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroDocument16 pages1 IntroranjinishreeNo ratings yet
- CG Unit 1Document37 pagesCG Unit 1Kuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- The Cathode Ray MonitorDocument24 pagesThe Cathode Ray MonitorSreshtha KashyapNo ratings yet
- Computer Graphics: Overview of Graphics I-O DeviceDocument20 pagesComputer Graphics: Overview of Graphics I-O DeviceLet’s Talk TechNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Computer GraphicsDocument41 pagesEvolution of Computer GraphicsGeetika BhardwajNo ratings yet
- CG Into ch1Document83 pagesCG Into ch1Nilesh RanaNo ratings yet
- JRNGKRJGDocument52 pagesJRNGKRJGAyush ModiNo ratings yet
- Graphics UNIT 1 NotesDocument39 pagesGraphics UNIT 1 NotesmalathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Overview of Graphics SystemsDocument9 pagesChapter 1: Overview of Graphics SystemsprincejiNo ratings yet
- Graphics NotesDocument16 pagesGraphics NotesSamuel EbenezerNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Graphics Hardware: Dhiraj ShresthaDocument35 pagesChapter-2 Graphics Hardware: Dhiraj ShresthaBinoNo ratings yet
- Cathode Ray TubeDocument13 pagesCathode Ray Tubehema eswaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- Unit I - Lecture 2Document35 pagesUnit I - Lecture 2santoshteja_69No ratings yet
- Cad Unit 2 Swayam DR K T MannanDocument9 pagesCad Unit 2 Swayam DR K T MannanHarsh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Final CG NotesDocument58 pagesFinal CG NotesVEDANSH PARGAIEN CO20366No ratings yet
- Lec-02 (A) Computer GraphicsDocument27 pagesLec-02 (A) Computer GraphicsPranil NandeshwarNo ratings yet
- C.G. Unit-1 (Part-2)Document11 pagesC.G. Unit-1 (Part-2)Shruti SharmaNo ratings yet
- DMC 1934Document160 pagesDMC 1934Kajendran KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Graphics Systems: Lecture By: S.MwongelaDocument59 pagesGraphics Systems: Lecture By: S.MwongelaDavid AdeolaNo ratings yet
- CRT NotesDocument103 pagesCRT NotesRitu KapoorNo ratings yet
- 03 Presentation and Output DeviceDocument33 pages03 Presentation and Output DeviceAjay GhugeNo ratings yet
- Display DevicesDocument78 pagesDisplay DevicesSweta SipraNo ratings yet
- I Unit CGDocument83 pagesI Unit CGYesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Part - IDocument48 pagesUnit 1 - Part - IVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- CG Assignment-2 With SolutionDocument11 pagesCG Assignment-2 With SolutionSelzer ProfitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ScriptDocument118 pagesChapter 1 ScriptSaumya SinghNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document11 pagesChap 2EmanNo ratings yet
- Unit I Lecture 2 Display DevicesDocument68 pagesUnit I Lecture 2 Display DevicesKrishan Kant ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Display DevicesDocument7 pagesDisplay DevicesPramod Theghost RawatNo ratings yet
- Assignment:-1: Introduction To Computer Graphics QuestionsDocument16 pagesAssignment:-1: Introduction To Computer Graphics QuestionsDrashti PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 GraphicsedDocument45 pagesChapter 2 GraphicsedAnteneh solomonNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes-CgDocument32 pagesLecture Notes-Cgandirajukeshavakrishna6945No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document11 pagesChapter 2ibrahin mahamedNo ratings yet
- The Video Display Unit (VDU) Is One of The Two Principal Interfaces Between The UserDocument29 pagesThe Video Display Unit (VDU) Is One of The Two Principal Interfaces Between The Userlordjebus2000No ratings yet
- 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - CRT - Random Raster - InterlacingDocument39 pages3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - CRT - Random Raster - InterlacingDr. Sanjeev PuniaNo ratings yet
- Computer Notes - Display Devices in Computer GraphicsDocument5 pagesComputer Notes - Display Devices in Computer Graphicsecomputernotes91% (11)
- Chapter 2 Graphics HardwareDocument39 pagesChapter 2 Graphics Hardwaretyv89783No ratings yet
- Video Display DevicesDocument66 pagesVideo Display DevicesshabanaNo ratings yet
- CGM Lec-4Document11 pagesCGM Lec-4RAKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- The Cathode Ray MonitorDocument20 pagesThe Cathode Ray MonitorreghunathevNo ratings yet
- Display Devices and InterfacesDocument74 pagesDisplay Devices and InterfacesPraveen SainiNo ratings yet
- Display UnitDocument28 pagesDisplay UnitGuty HuancaNo ratings yet
- 2 - DevitracesDocument14 pages2 - Devitracespraveen kumarNo ratings yet
- Overview of Graphic SystemsDocument64 pagesOverview of Graphic SystemsUzma Rukhayya ShaikNo ratings yet
- A Study of AircraftDocument2 pagesA Study of AircraftAmir AsadyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems in A BuildingDocument76 pagesElectrical Systems in A BuildingPitz Shady ShinNo ratings yet
- Philips fwt9200Document37 pagesPhilips fwt9200Alex BrazNo ratings yet
- DLS Basics PDFDocument50 pagesDLS Basics PDFAniketRaikwarNo ratings yet
- Marx Generator Design and PerformanceDocument4 pagesMarx Generator Design and PerformanceHardik PatelNo ratings yet
- QFN Packagin ReliabilityDocument3 pagesQFN Packagin ReliabilitymrbustaNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting ProfibusDocument5 pagesTroubleshooting Profibussteam100deg8229No ratings yet
- Operador Siemens Intercam PDFDocument32 pagesOperador Siemens Intercam PDFCristian Orosco ValverdeNo ratings yet
- 7 Series Product Selection GuideDocument12 pages7 Series Product Selection GuidematrixNo ratings yet
- User's Manual: SR-1000 SeriesDocument94 pagesUser's Manual: SR-1000 SeriesNiteshNo ratings yet
- 0008ph PDocument40 pages0008ph PRana HazemNo ratings yet
- Mee BookDocument165 pagesMee Bookddewashish23No ratings yet
- Water Level Controller Relay: Operating InstructionsDocument4 pagesWater Level Controller Relay: Operating InstructionsBala GangadharNo ratings yet
- Physics of VLSI Devices (ECE5018) - CAT-1 Solutions: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEDocument14 pagesPhysics of VLSI Devices (ECE5018) - CAT-1 Solutions: Dr. Rajan Pandey Associate Professor, SENSEVibha M VNo ratings yet
- Tda7294 PDFDocument16 pagesTda7294 PDFRoger NunesNo ratings yet
- 3 2 KeytermsDocument2 pages3 2 Keytermsapi-291995478No ratings yet
- Recover A Failed RAID Without Deleting Data On APG40Document11 pagesRecover A Failed RAID Without Deleting Data On APG40Alassane KafandoNo ratings yet
- How Disassemble and Reassemble A ComputerDocument35 pagesHow Disassemble and Reassemble A ComputertheoremineNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Bucket CacheDocument8 pagesIntroduction of Bucket CacheGuruprasad SridharanNo ratings yet
- 1-Transmission Line TypesDocument20 pages1-Transmission Line TypesManish YadavNo ratings yet
- CV LabDocument9 pagesCV LabtworedpartyhatsNo ratings yet
- SCRPCatalogDocument2 pagesSCRPCatalogRaul García (INNTELLIA)No ratings yet
- Android Battery DrainageDocument21 pagesAndroid Battery DrainageMehmet Fatih Yorulmaz67% (3)
- Board of Technical Education Uttar Pradesh Lucknow: Odd Semester Result December-2018 Marks SheetDocument1 pageBoard of Technical Education Uttar Pradesh Lucknow: Odd Semester Result December-2018 Marks SheetMayankNo ratings yet
- LEA ProtectPlus M600 2019 ENDocument2 pagesLEA ProtectPlus M600 2019 ENprseNo ratings yet
- BM8076-ESQA Part-B With AnswerDocument63 pagesBM8076-ESQA Part-B With Answernandhini zechNo ratings yet
- As Physics Practical Set 1 Updated April 2014Document99 pagesAs Physics Practical Set 1 Updated April 2014Pathmanathan Nadeson33% (3)