Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation 1
Presentation 1
Uploaded by
Maryam ZainalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation 1
Presentation 1
Uploaded by
Maryam ZainalCopyright:
Available Formats
THE BETHESDA SYSTEM AND EVALUATION OF ABNORMAL PAP SMEARS IN HIGH GRADE SQUAMOUS INTRAEPHITELIAL LESION
WAN IDA YAZMIN , NUR IZZA NAIM, NUR FARAH AIDA, NOR NASUHA, SHAZANA, NORSYAZWANI, NUR FAZILAH,
Department of Medical Laboratory Technology, Faculty of Health Science, UiTM, Puncak Alam Campus.
INTRODUCTION DIFFERENTIATION BETWEEN HSIL AND ASC-H
Coarse Chromatin
The Bethesda System (TBS) Dense cytoplasm Irregular nuclear contour
System reporting cervical cytological diagnose in Pap Smear which Hyperchromasia
describe precancerous changes in cervical cells for squamous
intraepithelial lesion (SIL) (Apgar et Al. 2003).
Scanty cytoplasm Thick nuclear membrane
BETHESDA SYSTEM 1991 BETHESDA SYSTEM 2001
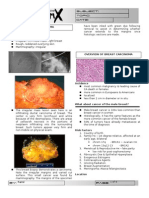
Figure 1: High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesion (HSIL) (CP) High
Magnification (100x)
HSIL encompasses SIL consist of ASC-US, Severe dysplastic cells with some variation in cell size and high N/C ratio.
moderate and severe LSIL, ASC-H and HSIL. Central, enlarged nuclei Metaplastic cell with
Hyperchromasia , coarse chromatin, scanty cytoplasm and thick nuclear
dysplasia, carcinoma in with coarse chromatin enlarged nuclei
membrane.
situ and CIN 2, 3. (American Society of Cytopathology)
Figure 4: HSIL. Evenly Figure 5: ASC-H. Metaplastic cells
distributed coarse chromatin, with enlarged nuclei, nuclear
ATYPICAL SQUAMOUS CELL- “CANNOT EXCLUDE” HSIL
Table 1: Comparison between Bethesda System 1991 and centrally placed enlarged nuclei, contour irregularities variation in
(ASC-H) and dense cytoplasmic. (CP) size, shape, and ratio of nuclear to
Bethesda System 2001
(American Family Physician Journal, 2003) High Magnification (100x) cytoplasmic area. (CP) Medium
MORPHOLOGY ASC-H Magnification
HSIL: Condition characterized by a number of immature cells, General Number of Fewer atypical cells (American Society of Cytopathology)
precancerous and if not removed may progress to invasive cells
cancer (http://www.bd.comp, 2010). Appearance Singly cell or discohesive
ALGORITHM
ASC-H: Atypical squamous cells that exhibit few similar features Nucleus Size 1-2 times larger than normal
suggestive of but not sufficient to report HSIL (Chivukula M Chromasia Hyperchromasia
& Shidham VB, 2006) Chromatin Coarse and unevenly
dispersed chromatin
Membrane Prominent nuclear
HIGH SQUAMOUS INTRAEPITHELIAL LESION (HSIL) membrane irregularities
Nucleoli Lack of nucleoli
MORPHOLOGY HSIL
Cytoplasm Staining Cyanophilic
General Cell size Small parabasal cell sizes Appearance Scanty cytoplasm
Aggregate In sheets or in syncytial- Less dense
like aggregates N/C ratio High
Nucleus Size Variation in nuclear size Diathesis Absent
Moderate enlarge
Shape Round to oval Table 3: Characteristics of ASC-H
(Chivukula M & Shidham VB, 2006)
Chromasia Hyperchromasia
SUMMARY
Chromatin Fine or coarsely granular
and evenly distributed High N/C ratio Cytologic changes of ASC-H is likely suggestive of HSIL but
Membrane Thick nuclear membrane exhibit features that are not sufficient to report as HSIL.
Nucleoli Absent Irregular nuclear contour
Early detection of HSIL can prevent cervical cancer.
Cytoplasm Staining Cyanophilic
REFERENCES
Appearanc Scanty cytoplasm
Coarse chromatin
e Lacy and delicate •American Society of Cytopathology. (n.d.). Retrieved October 12, 2010, from NCI Bethesda System:
http://nih.techriver.net/atlas.php
Densely metaplastic •Apgar, B. S., Zoschnick, L., & Wright, T. C. (2003). The 2001 Bethesda System terminology.
American family physician , 1992-1998.
N/C ratio Markedly high •Chivukula, M., & Shidham, V. B. (2006). ASC-H in Pap test--definitive categorization of
Figure 2: ASC-H. Singly cell show Figure 3: ASC-H. High N/C ratios
Diathesis Absent nuclei have coarse chromatin
cytomorphological spectrum. CytoJournal , 14.
and nuclear contour irregularities. •Solomon, D., & Nayar, R. (2004). The Bethesda System for Reporting Cervical Cytology (2 ed.). New
Table 2: Characteristics of HSIL without nucleoli. High N/C ratios. (LBP) High Magnification (100x)
York: Springer.
•Vassilakos, P., Petignat, P., Boulvain, M., & Campana, A. (2002). Primary screening for cervical
(Solomon & Nayar, 2004) (LBP) High Magnification (100x) cancer precursors by the combined use of liquid-based cytology, computer-assisted cytology and HPV
(Chivukula M & Shidham VB, 2006) DNA testing. British Journal of Cancer , 382-388.
You might also like
- MCQs NDAEBDocument75 pagesMCQs NDAEBTariq Khalid100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Pott's DiseaseDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Pott's Diseasederic95% (21)
- German New Medicine® (GNM) The New Medical Paradigm: Scientific Chart GNM BookstoreDocument13 pagesGerman New Medicine® (GNM) The New Medical Paradigm: Scientific Chart GNM Bookstoremayanekita100% (10)
- REPORTING CERVICAL CYTOLOGY, The Bethesda SystemDocument3 pagesREPORTING CERVICAL CYTOLOGY, The Bethesda SystemNgotelo FunwiNo ratings yet
- Plus Plastic Tubes Wallchart Order of Draw VS5729Document1 pagePlus Plastic Tubes Wallchart Order of Draw VS5729Dave DucharmeNo ratings yet
- Department of Pathology, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Medical College and Hospital, Siruvachur, Perambalur, Tamil Nadu, IndiaDocument14 pagesDepartment of Pathology, Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Medical College and Hospital, Siruvachur, Perambalur, Tamil Nadu, IndiaaishaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory Management - OrganizationDocument26 pagesClinical Laboratory Management - OrganizationMaryam Zainal67% (3)
- LSIL (Bethesda System)Document1 pageLSIL (Bethesda System)Maryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- Final Cyto Presentation BaruuuuDocument1 pageFinal Cyto Presentation BaruuuuMaryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls in Diagnosis of HsilDocument1 pagePitfalls in Diagnosis of HsilMaryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- FRCPath+picture-based+questions (1)Document39 pagesFRCPath+picture-based+questions (1)Marvi UmairNo ratings yet
- Renal BiopsyDocument53 pagesRenal Biopsybusiness onlyyouNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument31 pagesBone Marrow ExaminationMonique BorresNo ratings yet
- Cytology II: Gynae and Non-Gynae CytologyDocument126 pagesCytology II: Gynae and Non-Gynae Cytologybusiness onlyyouNo ratings yet
- (6-7) PATH - Colonic Polyps and CarcinomaDocument11 pages(6-7) PATH - Colonic Polyps and Carcinomaaaron mbindyoNo ratings yet
- Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence As The Next Chapter in Diagnostic HematopathologyDocument7 pagesDigital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence As The Next Chapter in Diagnostic HematopathologyKira Cao0% (1)
- BD Complete Solution PreAnalitycal System ProductDocument49 pagesBD Complete Solution PreAnalitycal System ProductHendyAnax Anax PointBlankNo ratings yet
- Reedsternberg CellDocument2 pagesReedsternberg CellYakan AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow Pathology 2 PDFDocument69 pagesBone Marrow Pathology 2 PDFJorge VenturaNo ratings yet
- (MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyDocument6 pages(MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyHenryboi CañasNo ratings yet
- Plus Plastic Tubes Instructions Drawvolguide VS5944-1Document2 pagesPlus Plastic Tubes Instructions Drawvolguide VS5944-1Coria Denisse ElsaNo ratings yet
- Cytopreparatory Technique: Ama AfrahDocument49 pagesCytopreparatory Technique: Ama Afrahreuben kwotaNo ratings yet
- Anti EpCAM Antibodies For Detection of Metastatic CarcinomaDocument6 pagesAnti EpCAM Antibodies For Detection of Metastatic CarcinomaIulia Alexandra PredaNo ratings yet
- Faquin Milian System and Molecular Advances in Diagnosis Salivary Gland TumorsDocument87 pagesFaquin Milian System and Molecular Advances in Diagnosis Salivary Gland TumorsJoanna Marie100% (1)
- Body Fluid Cell Counts by Automated MethodsDocument11 pagesBody Fluid Cell Counts by Automated MethodsntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Tissue ProcessingDocument7 pages1 Introduction To Tissue ProcessingAngel RamosNo ratings yet
- Infectious Disease (Part 1) : Viral DiseasesDocument11 pagesInfectious Disease (Part 1) : Viral Diseasesmiguel gaquitNo ratings yet
- Gross Examination of Surgical SpecimensDocument7 pagesGross Examination of Surgical SpecimensMahmoud AbouelsoudNo ratings yet
- Haematology SAQDocument16 pagesHaematology SAQPowell KitagwaNo ratings yet
- Cytology I - Techniques and Application: Peter NG Cyto Lab Ic, MT, PYNEHDocument201 pagesCytology I - Techniques and Application: Peter NG Cyto Lab Ic, MT, PYNEHbusiness onlyyouNo ratings yet
- Haemolytic AnaemiaDocument44 pagesHaemolytic AnaemiaMark DemNo ratings yet
- Granulomatous Inflammation ThyroidDocument55 pagesGranulomatous Inflammation ThyroidKamlesh PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 27kiran Body FluidsDocument33 pages27kiran Body FluidsABHINABA GUPTANo ratings yet
- 3 Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument105 pages3 Bone Marrow ExaminationShourav SarkarNo ratings yet
- Squash CytologyDocument66 pagesSquash CytologyMarvi UmairNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic AnemiaDocument1 pageHemolytic AnemiaTeus FatamorganaNo ratings yet
- Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.DDocument47 pagesMa. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.Djulo_05100% (1)
- Bethesda SystemDocument186 pagesBethesda SystemJoyce Pardo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Module 2 HistopathologyDocument34 pagesModule 2 HistopathologyKim RuizNo ratings yet
- CytologyDocument12 pagesCytologyEsther HutagalungNo ratings yet
- Bethesda System-ThyroidDocument11 pagesBethesda System-ThyroidSonam JoshiNo ratings yet
- 1 Products of Conception - Libre PathologyDocument8 pages1 Products of Conception - Libre PathologyfadoNo ratings yet
- Liver AbscessDocument14 pagesLiver AbscessMariaOeiNo ratings yet
- Effusion Cytology 2Document6 pagesEffusion Cytology 2PranayNo ratings yet
- Oncology Revision: Paul BaillieDocument299 pagesOncology Revision: Paul BaillieMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Cytology SpecimensDocument2 pagesChapter 17 Cytology SpecimensHalidah Rahawarin100% (1)
- Breast CancerDocument6 pagesBreast Cancersarguss14No ratings yet
- Urine Collection in CytologyDocument12 pagesUrine Collection in CytologyjunaidiabdhalimNo ratings yet
- Oncology Pathology Tanuvas NotesDocument17 pagesOncology Pathology Tanuvas NotesNagesh NNo ratings yet
- 04 AntigenDocument30 pages04 AntigenVivin Syamsul ArifinNo ratings yet
- 1pathology Limfnode UnimalDocument85 pages1pathology Limfnode UnimalJefry SNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Sysmex XN 1000 Hematology Analyzer.49Document4 pagesEvaluation of Sysmex XN 1000 Hematology Analyzer.49ivanNo ratings yet
- Pathology Revision E6.5Document130 pagesPathology Revision E6.5vikashchahal1987No ratings yet
- Platelet CountsDocument35 pagesPlatelet Countsshikhar623No ratings yet
- CELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Document7 pagesCELL OVERVIEW PREVENTION Notes 2015Alexander LukashenkoNo ratings yet
- Clinpath-04.-Disorders of Hemostasis and Blood CoagulationDocument11 pagesClinpath-04.-Disorders of Hemostasis and Blood CoagulationCharisse Angelica MacedaNo ratings yet
- IT 1 - Introduction To Anatomical PathologyDocument54 pagesIT 1 - Introduction To Anatomical Pathologyezra soNo ratings yet
- Cytology and Cytological TechniquesDocument29 pagesCytology and Cytological TechniquesNgotelo FunwiNo ratings yet
- Hema - Cytochemistry With TablesDocument4 pagesHema - Cytochemistry With TablesAce TardoNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Blood TransfusionDocument1 pageEthics in Blood TransfusionGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Systemic Pathology Study NotesDocument33 pagesSystemic Pathology Study NotesLaura BourqueNo ratings yet
- IKD9 - Radiological Evaluation of Renal CystsDocument26 pagesIKD9 - Radiological Evaluation of Renal CystsRenal Association MauritiusNo ratings yet
- Ihc PDFDocument28 pagesIhc PDFJean Bosco ByendaNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls in Diagnosis of HsilDocument1 pagePitfalls in Diagnosis of HsilMaryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- Poster of Conization Surgical Procedure-LEEP (TERBARU)Document1 pagePoster of Conization Surgical Procedure-LEEP (TERBARU)Maryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- LSIL (Bethesda System)Document1 pageLSIL (Bethesda System)Maryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- Final Cyto Presentation BaruuuuDocument1 pageFinal Cyto Presentation BaruuuuMaryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- Apr 10 Ent 600Document3 pagesApr 10 Ent 600Syamsul Syawal HosnonNo ratings yet
- Apr 2008Document4 pagesApr 2008Aidil JuhataNo ratings yet
- Mlt503 Continuous AssessmentDocument4 pagesMlt503 Continuous AssessmentMaryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- Template For Lab Report - MLT525Document1 pageTemplate For Lab Report - MLT525Maryam ZainalNo ratings yet
- OBGM0291208 EditorialDocument5 pagesOBGM0291208 EditorialRuben SimatupangNo ratings yet
- Chronic EpididymitisDocument4 pagesChronic EpididymitisdidiNo ratings yet
- 03 Art Uses of Seaweeds in The Indian... by Vinod K. Dhargalkar Pg.192Document11 pages03 Art Uses of Seaweeds in The Indian... by Vinod K. Dhargalkar Pg.192Chris JamesNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases in ChildrenDocument263 pagesCommon Diseases in ChildrenSuneethaVangala100% (1)
- GENERAL HEALTH CAMP Word Document Final September (1) 1111Document43 pagesGENERAL HEALTH CAMP Word Document Final September (1) 1111dkNo ratings yet
- Sequence: Respiratory-Triggered Inversion Recovery-HASTE (IRHASTE) (31) Sequence With 4Document6 pagesSequence: Respiratory-Triggered Inversion Recovery-HASTE (IRHASTE) (31) Sequence With 4kingpintamNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Report Card: About The Probably Hidden ProblemsDocument1 pageComprehensive Report Card: About The Probably Hidden ProblemsJhunry AllabaNo ratings yet
- ImmunohistochemistryDocument29 pagesImmunohistochemistryAvi VermaNo ratings yet
- CT Scan in Radiology: Made By: Beland Khalil MA1709ODocument7 pagesCT Scan in Radiology: Made By: Beland Khalil MA1709OBilind KhalilNo ratings yet
- Laryngology and Rhinology McqsDocument33 pagesLaryngology and Rhinology McqsAbouzr Mohammed Elsaid0% (1)
- Carcinoma of The Breast: Nur ZulaikhaDocument12 pagesCarcinoma of The Breast: Nur ZulaikhaCahaya Al-HazeenillahNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument5 pagesHepatitis BAmple CasaclangNo ratings yet
- Oralpatho SEQDocument16 pagesOralpatho SEQKhushboo e ZehraNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Drug Utilization Study of Gynecology OPD in A Tertiary Care HospitalDocument8 pages1.6 Drug Utilization Study of Gynecology OPD in A Tertiary Care HospitalNikole PetersonNo ratings yet
- Feras Al Kharouf CVDocument3 pagesFeras Al Kharouf CVFeras Jawad AlkharoufNo ratings yet
- Complete Blood CountDocument19 pagesComplete Blood CountIrene Andriani Halim100% (2)
- 2 2 1Document14 pages2 2 1LaurenGoNo ratings yet
- Local Flap Reconstruction of Large Scalp DefectsDocument5 pagesLocal Flap Reconstruction of Large Scalp DefectsPalwasha MalikNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Epidemiology and Public Health - AnswersDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Epidemiology and Public Health - Answersjackwisher hastingNo ratings yet
- Practice Guidelines For Family Physicians Volume 3Document105 pagesPractice Guidelines For Family Physicians Volume 3Varun Arunagiri100% (1)
- Y3b3 Ong Groupd B - 13Document15 pagesY3b3 Ong Groupd B - 13Akmal ZaimNo ratings yet
- Discharge Slip Errors (DR Muhammad Ahmad, Islamabad, Pakistan)Document5 pagesDischarge Slip Errors (DR Muhammad Ahmad, Islamabad, Pakistan)plasticsurgeon9999468No ratings yet
- Vel CadeDocument20 pagesVel CadeSerly MarcelinaNo ratings yet
- Eye To Eye BCQsDocument23 pagesEye To Eye BCQsLoveKumarNo ratings yet
- Hodgkin's LymphomaDocument21 pagesHodgkin's LymphomaRavi K N100% (1)
- Voc in UseDocument67 pagesVoc in UseliesjevanhaasterNo ratings yet
- Urogenital SystemDocument111 pagesUrogenital Systemhamdan hamimNo ratings yet