Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 viewsCloud Computing: By: Sharad Singh
Cloud Computing: By: Sharad Singh
Uploaded by
nitin goswamiThis document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its evolution, models, and benefits compared to traditional computing. Specifically:
- Cloud computing evolved from mainframe computers accessed by "dummy terminals" in the 1950s to virtualization technologies in the 1970s that allowed multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on one machine.
- The main models of cloud services are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). SaaS delivers applications via the web, PaaS provides platforms for app development, and IaaS provides basic computing infrastructure.
- Cloud computing provides benefits like increased flexibility and scalability, lower costs,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Pertamina Digital Transformation PDFDocument11 pagesPertamina Digital Transformation PDFAries Rahmanto100% (1)
- Cloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersDocument38 pagesCloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersPraveen Madupu100% (1)
- Cloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will LearnDocument11 pagesCloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will Learnsangeet83No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Notes For BSC and BCADocument48 pagesCloud Computing Notes For BSC and BCAPvlsowjanya100% (4)
- Unit-2.PDF Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesUnit-2.PDF Cloud ComputingManya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- CC Lab FileDocument42 pagesCC Lab FileRitika SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputingDillip Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CCDocument11 pagesIntroduction To CCHAFIZ AMEENUDDINNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesCloud ComputingZinzy MNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 - Cloud Computing FundamentalsDocument51 pagesCH - 1 - Cloud Computing FundamentalsBarney StinsonNo ratings yet
- Cloud and Network Securityt10Document19 pagesCloud and Network Securityt10Md. EmdadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Cloud Computinghemasrik2508No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument10 pagesCloud ComputingJiru AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesUnit I Introduction To Cloud Computingkomalpopatshinde2345No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Presented By: Nirjala HadaDocument18 pagesCloud Computing: Presented By: Nirjala HadaNirjala HadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document13 pagesUnit 1Bnod MsraNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Pros and Cons For Business and IT ProfessionalsDocument7 pagesCloud Computing Pros and Cons For Business and IT ProfessionalsKarla Isael AscNo ratings yet
- Why To Use Cloud Solution?: Types of Cloud ServicesDocument5 pagesWhy To Use Cloud Solution?: Types of Cloud ServicesSyeda Malika AnjumNo ratings yet
- Anurag CC LAB File CompleteDocument27 pagesAnurag CC LAB File CompleteBaby SauravNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument12 pagesCloud ComputingELSADNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Benefits of Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesAssignment On Benefits of Cloud ComputingMonir HossainNo ratings yet
- Azure FundamentalsDocument38 pagesAzure Fundamentalsumakant bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Book (2017-Regulation) PDF-1-89 Unit - I & IIDocument89 pagesCloud Computing Book (2017-Regulation) PDF-1-89 Unit - I & IIVishnu Kumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Introduction To Cloud)Document15 pagesUnit-1 (Introduction To Cloud)Binay YadavNo ratings yet
- CC 1Document58 pagesCC 1VISHNU VASHISHTHNo ratings yet
- CEO - Final Exam PrepDocument32 pagesCEO - Final Exam PrepublehkogeniusNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Interview Questions and Answersਰਜਨੀ ਖਜੂਰਿਆNo ratings yet
- 1.4. Cloud CharacteristicsDocument33 pages1.4. Cloud CharacteristicsASWINI BNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 New Trends in MISDocument31 pagesLecture 4 New Trends in MISmaryallaine02No ratings yet
- What Exactly Is Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesWhat Exactly Is Cloud ComputingrahulNo ratings yet
- ETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingSheshrao LandgeNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAmRkmvZIyh8RjvaErPGd4NFOqw0T21AQxjqCt Wtz7-Yt io1Gdv5jrsGNqXCCWgQclmeF NQjx8NvyYBelD762ZYqlbfYhx4VqDcIeKO99dJ2WrzqgO6MprXwc-iIbaVpexhxGzXTLLn1Document30 pagesACFrOgAmRkmvZIyh8RjvaErPGd4NFOqw0T21AQxjqCt Wtz7-Yt io1Gdv5jrsGNqXCCWgQclmeF NQjx8NvyYBelD762ZYqlbfYhx4VqDcIeKO99dJ2WrzqgO6MprXwc-iIbaVpexhxGzXTLLn1tanishNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesCloud Computingsubhayanmanna1234No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesCloud ComputingAnjali SoniNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputingVictor ImarhiagbeNo ratings yet
- IIIT Allahabad: Software Testing & Quality Assurance Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesIIIT Allahabad: Software Testing & Quality Assurance Cloud ComputingRohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Technology That Uses The Internet and Central Remote Servers To Maintain Data andDocument11 pagesCloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Technology That Uses The Internet and Central Remote Servers To Maintain Data androhan7801No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing NIST Model: Essential CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesCloud Computing NIST Model: Essential CharacteristicsDrishti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesCloud ComputingFLAMENo ratings yet
- Introduction - What Is ItDocument9 pagesIntroduction - What Is ItLalit KundaliaNo ratings yet
- Network Essentials Group 10 Assignment-1 PDFDocument16 pagesNetwork Essentials Group 10 Assignment-1 PDFelvisNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing AssignmentDocument2 pagesCloud Computing Assignmentgoyalshabnam19No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing DocumentationDocument11 pagesCloud Computing DocumentationSailaja MannemNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing1Document32 pagesCloud Computing1NiharikaNo ratings yet
- CC Unit IDocument31 pagesCC Unit ISuriyaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing AUDocument11 pagesCloud Computing AUTHANGA DURAINo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesCloud ComputingChuru iddyNo ratings yet
- The New Age of Computing: Presented By: Mansi Tomer B.Tech (IT) 3rd Year 1512813020Document17 pagesThe New Age of Computing: Presented By: Mansi Tomer B.Tech (IT) 3rd Year 1512813020jaishree jainNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing and Big DataDocument17 pagesCloud Computing and Big Datashweta sinhaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing YasirDocument3 pagesCloud Computing Yasiryasir shahNo ratings yet
- CSE-420 Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesCSE-420 Cloud ComputingRMG ComplianceNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Assignment 3Document6 pagesCloud Computing Assignment 3Dipesh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Unit1 1Document30 pagesUnit1 1HimajanaiduNo ratings yet
- Public-Private-Hybrid CCDocument28 pagesPublic-Private-Hybrid CCharry HarithaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Means Using Multiple: ServerDocument13 pagesCloud Computing Means Using Multiple: ServerEkta TayalNo ratings yet
- CSIT409 ExaminationDocument9 pagesCSIT409 ExaminationSelormNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Class Notes CEDocument24 pagesUNIT-4 Class Notes CE21R25A1202 DESETTY VINEETHNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - Lecture MaterialDocument14 pagesCloud Computing - Lecture Materialchirayush chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing IntroductionDocument16 pagesCloud Computing IntroductionVicNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureFrom EverandCloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureNo ratings yet
- OOP Slides (Updated)Document111 pagesOOP Slides (Updated)nitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing vs. Traditional IT Infrastructure - Leading EdgeDocument4 pagesCloud Computing vs. Traditional IT Infrastructure - Leading Edgenitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Concept of VirtualizationDocument25 pagesConcept of Virtualizationnitin goswami100% (1)
- Cloud Computing (CSE8146) : Working With Private CloudDocument83 pagesCloud Computing (CSE8146) : Working With Private Cloudnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing (CSE8146) : Prepared byDocument35 pagesCloud Computing (CSE8146) : Prepared bynitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Virtualization: Ambrish GangalDocument32 pagesVirtualization: Ambrish Gangalnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Case Study On AWSDocument51 pagesCase Study On AWSnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Virtualization: Ambrish GangalDocument32 pagesVirtualization: Ambrish Gangalnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- AWS Storage TypesDocument10 pagesAWS Storage Typesnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Virtual Machine MigrationDocument10 pagesVirtual Machine Migrationnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To JavaDocument23 pagesWelcome To JavanadeemsoftwaredesignerNo ratings yet
- Ipsec ConfigurationDocument12 pagesIpsec Configurationharshit asharaNo ratings yet
- Business Technology Report 2023 - FinalDocument49 pagesBusiness Technology Report 2023 - FinalAbdelmadjid djibrineNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 MisDocument17 pagesUnit-3 Misuttkarshpandey0018No ratings yet
- Lyva Labs Manufacturing Cluster - SME Adoption of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies by Sujita PurushothamanDocument10 pagesLyva Labs Manufacturing Cluster - SME Adoption of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies by Sujita Purushothamansujita.purushothamanNo ratings yet
- Homomorphic Encryption: Aarushi Gupta 1RV18EC001Document14 pagesHomomorphic Encryption: Aarushi Gupta 1RV18EC001crayonNo ratings yet
- Case Study LegoDocument6 pagesCase Study LegoIvaAmelyaPutri0% (1)
- Reflections On Integrating With EAI or ESBDocument2 pagesReflections On Integrating With EAI or ESBMoganedi SekeleNo ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics For Healthcare Recommendation SystemsDocument6 pagesBig Data Analytics For Healthcare Recommendation SystemsNirosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Touch Screen Chain Men Hair Salon Project ProposalDocument8 pagesTouch Screen Chain Men Hair Salon Project ProposalAhmed A Major Aminu0% (1)
- Ref 6 - What Is IT Governance - A Formal Way To Align IT - Business Strategy - CIODocument4 pagesRef 6 - What Is IT Governance - A Formal Way To Align IT - Business Strategy - CIOTowhidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Sophos - Considerations For Deploying Sophos Firewall in Common ScenariosDocument22 pagesSophos - Considerations For Deploying Sophos Firewall in Common ScenariosMiguel António ManuelNo ratings yet
- UIDAI Letter Dated 27 01 2023 Phase Out of Existing Fingerprint L0 Registered Devices From Aadhaar Authentication EcosystemDocument17 pagesUIDAI Letter Dated 27 01 2023 Phase Out of Existing Fingerprint L0 Registered Devices From Aadhaar Authentication EcosystemgtcesevaNo ratings yet
- SAP MDG Technical Concept:-: (Type The Company Name)Document16 pagesSAP MDG Technical Concept:-: (Type The Company Name)Lionelkeneth12100% (1)
- 3 GmcomDocument12 pages3 GmcombaliyanrohitbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Web Communication-1Document30 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Web Communication-1St WxyNo ratings yet
- Hacking Exposed Cisco Networks - Cisco Security Secrets & Solutions by Andrew Vladimirov, Konstantin Gavrilenko and Andrei MikhailovskyDocument1,096 pagesHacking Exposed Cisco Networks - Cisco Security Secrets & Solutions by Andrew Vladimirov, Konstantin Gavrilenko and Andrei MikhailovskyUli UliNo ratings yet
- Plan For ReleaseDocument6 pagesPlan For ReleasetestscribdnewNo ratings yet
- Ota Apis GeneralDocument13 pagesOta Apis Generaljack_rzmNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security ReportDocument24 pagesCyber Security ReportAakash Jain100% (1)
- Tecsec 3004Document299 pagesTecsec 3004wahyu baganNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document30 pagesCH 6Joycelyne ZangNo ratings yet
- Lock-Up Device With: Dynamic Measurement Option (Dmo)Document1 pageLock-Up Device With: Dynamic Measurement Option (Dmo)wenpinNo ratings yet
- Saurav Kumar Singh: Software Engineer Accenture Services Pvt. LTD."Document2 pagesSaurav Kumar Singh: Software Engineer Accenture Services Pvt. LTD."SauravSinghNo ratings yet
- PGDIT 2013 ProjectGuidelines ITDocument3 pagesPGDIT 2013 ProjectGuidelines ITdev_thecoolboyNo ratings yet
- Traffic Software Requirement Specification SrsDocument13 pagesTraffic Software Requirement Specification SrsJahnavi Prasad SrirampurapuNo ratings yet
- Computer Viruses: Everything You Wanted To Know AboutDocument35 pagesComputer Viruses: Everything You Wanted To Know AboutSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- G7 WORKSHEET ICT Week 5 NEWDocument4 pagesG7 WORKSHEET ICT Week 5 NEWEbb Lian AninoNo ratings yet
- NetScreen-to-SRX Series Migration Service Sales PresentationDocument19 pagesNetScreen-to-SRX Series Migration Service Sales PresentationLi KangNo ratings yet
Cloud Computing: By: Sharad Singh
Cloud Computing: By: Sharad Singh
Uploaded by
nitin goswami0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views57 pagesThis document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its evolution, models, and benefits compared to traditional computing. Specifically:
- Cloud computing evolved from mainframe computers accessed by "dummy terminals" in the 1950s to virtualization technologies in the 1970s that allowed multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on one machine.
- The main models of cloud services are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). SaaS delivers applications via the web, PaaS provides platforms for app development, and IaaS provides basic computing infrastructure.
- Cloud computing provides benefits like increased flexibility and scalability, lower costs,
Original Description:
Original Title
Cloud Computing
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its evolution, models, and benefits compared to traditional computing. Specifically:
- Cloud computing evolved from mainframe computers accessed by "dummy terminals" in the 1950s to virtualization technologies in the 1970s that allowed multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on one machine.
- The main models of cloud services are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). SaaS delivers applications via the web, PaaS provides platforms for app development, and IaaS provides basic computing infrastructure.
- Cloud computing provides benefits like increased flexibility and scalability, lower costs,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views57 pagesCloud Computing: By: Sharad Singh
Cloud Computing: By: Sharad Singh
Uploaded by
nitin goswamiThis document provides an overview of cloud computing, including its evolution, models, and benefits compared to traditional computing. Specifically:
- Cloud computing evolved from mainframe computers accessed by "dummy terminals" in the 1950s to virtualization technologies in the 1970s that allowed multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on one machine.
- The main models of cloud services are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). SaaS delivers applications via the web, PaaS provides platforms for app development, and IaaS provides basic computing infrastructure.
- Cloud computing provides benefits like increased flexibility and scalability, lower costs,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 57
Cloud Computing
By: Sharad Singh
Evolution of Cloud:
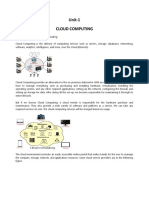
Cloud computing is a process that entails accessing of
services, including, storage, applications and servers
through the Internet, making use of another
company's remote services for a fee.
This enables a company to store and access data or
programs virtually, i.e. in a cloud, rather than on local
hard,drives,or,servers.
Contd…
In 1950 At that time, several users accessed the central
computer via dummy terminals. The only task these
dummy terminals could perform was to enable users
access the mainframe computer.
In 1970s, IBM came out with an operating system (OS)
named VM. This allowed for simultaneous operation
of more than one OS.
Contd..
Guest Operating Systems could be run on every VM,
with their own memory and other infrastructure,
making it possible to share these resources.
This caused the concept of virtualization in
computing to gain popularity.
Traditional Computing vs Cloud Computing:
Traditional computing:
Traditional data centers consist of various pieces of
hardware, such as a desktop computer, which are
connected to a network via a remote server.
This server is typically installed on the premises, and
provides all employees using the hardware, access to
the business’s stored data and applications.
Contd..
Businesses with this IT model must purchase
additional hardware and upgrades in order to scale up
their data storage and services to support more users.
Mandatory software upgrades are also required with
traditional IT infrastructure to ensure fail safe systems
are in place to in case a hardware failure occurs.
Contd..
For many businesses with IT data centers, an in-house
IT department is needed to install and maintain the
hardware.
Cloud Computing vs Traditional IT
infrastructure:
Resilience and Elasticity:
The information and applications hosted in the cloud are
evenly distributed across all the servers, which are
connected to work as one.
Therefore, if one server fails, no data is lost and
downtime is avoided. The cloud also offers more
storage space and server resources, including better
computing power. This means your software and
applications will perform faster
Contd…
Traditional IT systems are not so resilient and cannot
guarantee a consistently high level of server
performance.
They have limited capacity and are susceptible to
downtime, which can greatly hinder workplace
productivity.
Flexibility and Scalability:
Cloud hosting offers an enhanced level of flexibility
and scalability in comparison to traditional data
centers.
The on-demand virtual space of cloud computing has
unlimited storage space and more server resources.
Cloud servers can scale up or down depending on the
level of traffic your website receives, and you will have
full control to install any software as and when you
need to. This provides more flexibility for your
business to grow.
Contd..
With traditional IT infrastructure, you can only use
the resources that are already available to you. If you
run out of storage space, the only solution is to
purchase or rent another server.
Automation:
A key difference between cloud computing and
traditional IT infrastructure is how they are managed.
Cloud hosting is managed by the storage provider who
takes care of all the necessary hardware, ensures
security measures are in place, and keeps it running
smoothly.
Contd..
Traditional data centers require heavy administration
in house, which can be costly and time consuming for
your business. Fully trained IT personnel may be
needed to ensure regular monitoring and maintenance
of your servers – such as upgrades, configuration
problems, threat protection and installations.
Running Cost:
Cloud computing is more cost effective than
traditional IT infrastructure due to methods of
payment for the data storage services. With cloud
based services, you only pay for what is used –
similarly to how you pay for utilities such as electricity
Furthermore, the decreased likelihood of downtime
means improved workplace performance and
increased profits in the long run.
Importance of Cloud Computing:
The cloud, and the flexibility it provides is fast
becoming a necessity for innovative and daring
organizations.
When you use a cloud computing service you don’t
have to worry about maintaining the system yourself.
All of this is done for you, and the cloud computing
service will deal with all security and software updates
as well, which means far less for you to worry about.
Benefits by using Cloud:
Increased flexibility: If your bandwidth requirements
tend to fluctuate, using the cloud makes perfect sense.
This is because you can upgrade in line with your needs,
so you do not pay for more storage than you actually need.
Recovery of data: With cloud based computing, recovery
of data is far easier and this means that you can enjoy
greater peace of mind. When it comes to backing up
information, a smaller business may not have the
necessary tools and resources so cloud computing could
be the perfect solution.
Contd…
No maintenance: When you use a cloud computing
service you don’t have to worry about maintaining the
system yourself. All of this is done for you, and the
cloud computing service will deal with all security and
software updates as well.
Contd…
Easy access: Using the cloud gives you far easier access
to your documents.
This benefits you and your employees, as you can
access your work no matter where you are.
You can provide your employees with greater
flexibility and continue running operations no matter
where you are as long as you have internet access.
Contd..
Higher level of security: Cloud computing gives you a
higher level of security.
For instance, if you lose your mobile device or laptop you
can still access everything you have on the cloud using
another machine or device.
Easy to share information: You can share information
with colleagues and employees far more easily using the
cloud.
It means that you don’t have to send emails back and forth
when it comes to sharing document access as you can all
access it on the cloud.
Models of Cloud Services:
There are usually three models of cloud service :
1.Software as a Service (SaaS),
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
3.Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
S aaS: Software as a Service:
SaaS utilizes the internet to deliver applications to its
users, which are managed by a third-party vendor.
A majority of SaaS applications are run directly
through the web browser, and do not require any
downloads or installations on the client side.
Contd:
Due to its web delivery model, SaaS eliminates the
need to download and install applications on each
individual computer; a nightmare for IT staff.
With SaaS, vendors manage all of the potential
technical issues, such as data, middleware, servers,
and storage, while businesses can simply streamline
their maintenance and support.
SaaS Advantages:
SaaS provides numerous advantages to employees and
companies by greatly reducing the time and money
spent on tedious tasks such as installing, managing,
and upgrading software.
This frees up a lot of time for technical staff to spend
on more pressing matters and issues within the
organization.
SaaS Characteristics:
There are a few ways to help you determine when SaaS
is being utilized:
Managed from a central location.
Hosted on a remote server.
• Accessible over the internet.
Users not responsible for hardware or software
updates.
When to Use SaaS:
There are many different situations in which SaaS may
be the most beneficial, including:
If you are a startup or small company that needs to
launch ecommerce quickly and don’t have time for
server issues or software.
For short-term projects that require collaboration.
If you use applications that aren’t in-demand very
often, such as tax software.
For applications that need both web and mobile
access.
Examples of SaaS
Google Apps, Drop box, Sales force, Cisco WebEx,
Concur, GoToMeeting.
PaaS: Platform as a Service:
Cloud platform services, or Platform as a Service
(PaaS), provide cloud components to certain software
while being used mainly for applications.
PaaS provides a framework for developers that they can
build upon and use to create customized applications .
• All servers, storage, and networking can be managed
by the enterprise or a third-party provider while the
developers can maintain management of the
applications.
Contd..
The delivery model of PaaS is similar to SaaS, except
instead of delivering the software over the internet,
PaaS provides a platform for software creation.
This platform is delivered over the web, and gives
developers the freedom to concentrate on building the
software while still not having to worry about
operating systems, software updates, storage, or
infrastructure.
PaaS Advantages:
No matter what size of company you may be in, there
are numerous advantages for using PaaS:
Makes the development and deployment of apps
simple and cost-effective.
Scalable.
Highly available.
Gives developers the ability to create customized apps
without the headache of maintaining the software.
Greatly reduces the amount of coding.
Automates business policy.
When to Use PaaS:
There are many situations that utilizing PaaS is
beneficial or even necessary.
If there are multiple developers working on the same
development project, or if other vendors must be
included as well, PaaS can provide great speed and
flexibility to the entire process.
Examples of PaaS:
AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Windows Azure, Heroku,
Force.com, Google App Engine, Apache Stratos,
OpenShift.
IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service:
Cloud infrastructure services, known as Infrastructure
as a Service (IaaS), are made of highly scalable and
automated compute resources.
IaaS is fully self-service for accessing and monitoring
things like compute, networking, storage, and other
services, and it allows businesses to purchase
resources on-demand and as-needed instead of having
to buy hardware outright.
Contd…
IaaS delivers Cloud Computing infrastructure to
organizations, including things such as servers,
network, operating systems, and storage, through
virtualization technology.
These cloud servers are typically provided to the client
through a dashboard or an API, and IaaS clients have
complete control over the entire infrastructure.
Contd…
As opposed to SaaS or PaaS, IaaS clients are
responsible for managing aspects such as applications,
runtime, OSes, middleware, and data.
However, providers of the IaaS manage the servers,
hard drives, networking, virtualization, and storage.
IaaS Advantages:
There are many benefits of choosing IaaS, such as that it:
Is the most flexible cloud computing model.
Easily allows for automated deployment of storage,
networking, servers, and processing power.
Hardware can be purchased based on consumption.
Gives clients complete control of their infrastructure.
Resources can be purchased as-needed.
Is highly scalable.
IaaS Characteristics:
Some characteristics to look for when considering IaaS
are:
Resources are available as a service
The cost varies depending on consumption
Services are highly scalable.
Typically includes multiple users on a single piece of
hardware.
Provides complete control of the infrastructure to
organizations.
Dynamic and flexible.
When to Use IaaS:
Just as with SaaS and PaaS, there are specific
situations when it is the most advantageous to use
IaaS.
If you are a startup or a small company, IaaS is a great
option so you don’t have to spend the time or money
trying to create hardware and software.
IaaS is also beneficial for large organizations who wish
to have complete control over their applications and
infrastructures, but are looking to only purchase what
is actually consumed or needed.
Contd..
For rapidly growing companies, IaaS can be a good
option as you don’t have to commit to a specific
hardware or software as your needs change and evolve.
It also helps if you are unsure what demands a new
application will need as there is a lot of flexibility to
scale up or down as needed.
Examples of IaaS
Digital Ocean, Linode, Rackspace, Amazon Web
Services (AWS), Cisco Metapod, Microsoft Azure,
Google Compute Engine (GCE).
Deployment Model of Cloud:
1.Public Cloud
2.Private Cloud
3. Hybrid Cloud
Public Cloud:
Public Cloud:
Public clouds are the most common way of deploying
cloud computing.
The cloud resources (like servers and storage) are
owned and operated by a third-party
cloud service provider and delivered over the Internet.
Microsoft Azure is an example of a public cloud.
Contd…
With a public cloud, all hardware, software and other
supporting infrastructure is owned and managed by
the cloud provider.
In a public cloud, you share the same hardware,
storage and network devices with other organizations
or cloud “tenants.” You access services and manage
your account using a web browser.
Contd..
Public cloud deployments are frequently used to
provide web-based email, online office applications,
storage and testing and development environments.
Advantage of Public Cloud:
Lower costs—no need to purchase hardware or
software and you pay only for the service you use.
No maintenance—your service provider provides the
maintenance.
Near-unlimited scalability—on-demand resources
are available to meet your business needs.
Contd..
High reliability—a vast network of servers ensures
against failure.
Private Cloud:
Private cloud:
A private cloud consists of computing resources used
exclusively by one business or organization.
The private cloud can be physically located at your
organization's on-site data center or it can be hosted
by a third-party service provider.
But in a private cloud, the services and infrastructure
are always maintained on a private network and the
hardware and software are dedicated solely to your
organization.
Contd…
In this way, a private cloud can make it easier for an
organization to customize its resources to meet
specific IT requirements.
Private clouds are often used by government agencies,
financial institutions, any other mid- to large-size
organizations with business-critical operations
seeking enhanced control over their environment
Advantages of a private clouds:
More flexibility—your organization can customize its
cloud environment to meet specific business needs.
Improved security—resources are not shared with
others, so higher levels of control and security are
possible.
High scalability—private clouds still afford the
scalability and efficiency of a public cloud.
Hybrid:
Hybrid Cloud:
Often called “the best of both worlds,” hybrid clouds
combine on-premises infrastructure, or private clouds,
with public clouds so organizations can reap the
advantages of both.
In a hybrid cloud, data and applications can move
between private and public clouds for greater
flexibility and more deployment options.
Contd:
For instance, you can use the public cloud for high-
volume, lower-security needs such as web-based email
and the private cloud (or other on-premises
infrastructure) for sensitive, business-critical
operations like financial reporting.
In a hybrid cloud, “cloud bursting” is also an option.
Contd
This is when an application or resource runs in the
private cloud until there is a spike in demand (such as
seasonal event like online shopping or tax filing), at
which point the organization can “burst through” to
the public cloud to tap into additional computing
resources.
Advantages of hybrid clouds:
Control—your organization can maintain a private
infrastructure for sensitive assets.
Flexibility—you can take advantage of additional
resources in the public cloud when you need them.
Cost-effectiveness—with the ability to scale to the public
cloud, you pay for extra computing power only when
needed.
Ease—transitioning to the cloud does not have to be
overwhelming because you can migrate gradually—
phasing in workloads over time.
Differences between Private and
Public Cloud:
You might also like
- Pertamina Digital Transformation PDFDocument11 pagesPertamina Digital Transformation PDFAries Rahmanto100% (1)
- Cloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersDocument38 pagesCloud Computing Tutorial For BeginnersPraveen Madupu100% (1)
- Cloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will LearnDocument11 pagesCloud Computing For Beginners: in This Tutorial, You Will Learnsangeet83No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Notes For BSC and BCADocument48 pagesCloud Computing Notes For BSC and BCAPvlsowjanya100% (4)
- Unit-2.PDF Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesUnit-2.PDF Cloud ComputingManya JaiswalNo ratings yet
- CC Lab FileDocument42 pagesCC Lab FileRitika SinghNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputingDillip Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CCDocument11 pagesIntroduction To CCHAFIZ AMEENUDDINNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesCloud ComputingZinzy MNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 - Cloud Computing FundamentalsDocument51 pagesCH - 1 - Cloud Computing FundamentalsBarney StinsonNo ratings yet
- Cloud and Network Securityt10Document19 pagesCloud and Network Securityt10Md. EmdadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Cloud Computinghemasrik2508No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument10 pagesCloud ComputingJiru AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesUnit I Introduction To Cloud Computingkomalpopatshinde2345No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Presented By: Nirjala HadaDocument18 pagesCloud Computing: Presented By: Nirjala HadaNirjala HadaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document13 pagesUnit 1Bnod MsraNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Pros and Cons For Business and IT ProfessionalsDocument7 pagesCloud Computing Pros and Cons For Business and IT ProfessionalsKarla Isael AscNo ratings yet
- Why To Use Cloud Solution?: Types of Cloud ServicesDocument5 pagesWhy To Use Cloud Solution?: Types of Cloud ServicesSyeda Malika AnjumNo ratings yet
- Anurag CC LAB File CompleteDocument27 pagesAnurag CC LAB File CompleteBaby SauravNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument12 pagesCloud ComputingELSADNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Benefits of Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesAssignment On Benefits of Cloud ComputingMonir HossainNo ratings yet
- Azure FundamentalsDocument38 pagesAzure Fundamentalsumakant bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Book (2017-Regulation) PDF-1-89 Unit - I & IIDocument89 pagesCloud Computing Book (2017-Regulation) PDF-1-89 Unit - I & IIVishnu Kumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Introduction To Cloud)Document15 pagesUnit-1 (Introduction To Cloud)Binay YadavNo ratings yet
- CC 1Document58 pagesCC 1VISHNU VASHISHTHNo ratings yet
- CEO - Final Exam PrepDocument32 pagesCEO - Final Exam PrepublehkogeniusNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Interview Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesCloud Computing Interview Questions and Answersਰਜਨੀ ਖਜੂਰਿਆNo ratings yet
- 1.4. Cloud CharacteristicsDocument33 pages1.4. Cloud CharacteristicsASWINI BNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 New Trends in MISDocument31 pagesLecture 4 New Trends in MISmaryallaine02No ratings yet
- What Exactly Is Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesWhat Exactly Is Cloud ComputingrahulNo ratings yet
- ETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingDocument6 pagesETI Micro Project Cloud ComputingSheshrao LandgeNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAmRkmvZIyh8RjvaErPGd4NFOqw0T21AQxjqCt Wtz7-Yt io1Gdv5jrsGNqXCCWgQclmeF NQjx8NvyYBelD762ZYqlbfYhx4VqDcIeKO99dJ2WrzqgO6MprXwc-iIbaVpexhxGzXTLLn1Document30 pagesACFrOgAmRkmvZIyh8RjvaErPGd4NFOqw0T21AQxjqCt Wtz7-Yt io1Gdv5jrsGNqXCCWgQclmeF NQjx8NvyYBelD762ZYqlbfYhx4VqDcIeKO99dJ2WrzqgO6MprXwc-iIbaVpexhxGzXTLLn1tanishNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument36 pagesCloud Computingsubhayanmanna1234No ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument8 pagesCloud ComputingAnjali SoniNo ratings yet
- What Is Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesWhat Is Cloud ComputingVictor ImarhiagbeNo ratings yet
- IIIT Allahabad: Software Testing & Quality Assurance Cloud ComputingDocument9 pagesIIIT Allahabad: Software Testing & Quality Assurance Cloud ComputingRohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Technology That Uses The Internet and Central Remote Servers To Maintain Data andDocument11 pagesCloud Computing: Cloud Computing Is A Technology That Uses The Internet and Central Remote Servers To Maintain Data androhan7801No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing NIST Model: Essential CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesCloud Computing NIST Model: Essential CharacteristicsDrishti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument17 pagesCloud ComputingFLAMENo ratings yet
- Introduction - What Is ItDocument9 pagesIntroduction - What Is ItLalit KundaliaNo ratings yet
- Network Essentials Group 10 Assignment-1 PDFDocument16 pagesNetwork Essentials Group 10 Assignment-1 PDFelvisNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing AssignmentDocument2 pagesCloud Computing Assignmentgoyalshabnam19No ratings yet
- Cloud Computing DocumentationDocument11 pagesCloud Computing DocumentationSailaja MannemNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing1Document32 pagesCloud Computing1NiharikaNo ratings yet
- CC Unit IDocument31 pagesCC Unit ISuriyaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing AUDocument11 pagesCloud Computing AUTHANGA DURAINo ratings yet
- Cloud ComputingDocument4 pagesCloud ComputingChuru iddyNo ratings yet
- The New Age of Computing: Presented By: Mansi Tomer B.Tech (IT) 3rd Year 1512813020Document17 pagesThe New Age of Computing: Presented By: Mansi Tomer B.Tech (IT) 3rd Year 1512813020jaishree jainNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing and Big DataDocument17 pagesCloud Computing and Big Datashweta sinhaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing YasirDocument3 pagesCloud Computing Yasiryasir shahNo ratings yet
- CSE-420 Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesCSE-420 Cloud ComputingRMG ComplianceNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Assignment 3Document6 pagesCloud Computing Assignment 3Dipesh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Unit1 1Document30 pagesUnit1 1HimajanaiduNo ratings yet
- Public-Private-Hybrid CCDocument28 pagesPublic-Private-Hybrid CCharry HarithaNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Means Using Multiple: ServerDocument13 pagesCloud Computing Means Using Multiple: ServerEkta TayalNo ratings yet
- CSIT409 ExaminationDocument9 pagesCSIT409 ExaminationSelormNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Class Notes CEDocument24 pagesUNIT-4 Class Notes CE21R25A1202 DESETTY VINEETHNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing - Lecture MaterialDocument14 pagesCloud Computing - Lecture Materialchirayush chakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing IntroductionDocument16 pagesCloud Computing IntroductionVicNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingFrom EverandCloud Computing Made Simple: Navigating the Cloud: A Practical Guide to Cloud ComputingNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureFrom EverandCloud Computing and Virtualization: Streamlining Your IT InfrastructureNo ratings yet
- OOP Slides (Updated)Document111 pagesOOP Slides (Updated)nitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing vs. Traditional IT Infrastructure - Leading EdgeDocument4 pagesCloud Computing vs. Traditional IT Infrastructure - Leading Edgenitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Concept of VirtualizationDocument25 pagesConcept of Virtualizationnitin goswami100% (1)
- Cloud Computing (CSE8146) : Working With Private CloudDocument83 pagesCloud Computing (CSE8146) : Working With Private Cloudnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Computing (CSE8146) : Prepared byDocument35 pagesCloud Computing (CSE8146) : Prepared bynitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Virtualization: Ambrish GangalDocument32 pagesVirtualization: Ambrish Gangalnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Case Study On AWSDocument51 pagesCase Study On AWSnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Virtualization: Ambrish GangalDocument32 pagesVirtualization: Ambrish Gangalnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- AWS Storage TypesDocument10 pagesAWS Storage Typesnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Virtual Machine MigrationDocument10 pagesVirtual Machine Migrationnitin goswamiNo ratings yet
- Welcome To JavaDocument23 pagesWelcome To JavanadeemsoftwaredesignerNo ratings yet
- Ipsec ConfigurationDocument12 pagesIpsec Configurationharshit asharaNo ratings yet
- Business Technology Report 2023 - FinalDocument49 pagesBusiness Technology Report 2023 - FinalAbdelmadjid djibrineNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 MisDocument17 pagesUnit-3 Misuttkarshpandey0018No ratings yet
- Lyva Labs Manufacturing Cluster - SME Adoption of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies by Sujita PurushothamanDocument10 pagesLyva Labs Manufacturing Cluster - SME Adoption of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies by Sujita Purushothamansujita.purushothamanNo ratings yet
- Homomorphic Encryption: Aarushi Gupta 1RV18EC001Document14 pagesHomomorphic Encryption: Aarushi Gupta 1RV18EC001crayonNo ratings yet
- Case Study LegoDocument6 pagesCase Study LegoIvaAmelyaPutri0% (1)
- Reflections On Integrating With EAI or ESBDocument2 pagesReflections On Integrating With EAI or ESBMoganedi SekeleNo ratings yet
- Big Data Analytics For Healthcare Recommendation SystemsDocument6 pagesBig Data Analytics For Healthcare Recommendation SystemsNirosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Touch Screen Chain Men Hair Salon Project ProposalDocument8 pagesTouch Screen Chain Men Hair Salon Project ProposalAhmed A Major Aminu0% (1)
- Ref 6 - What Is IT Governance - A Formal Way To Align IT - Business Strategy - CIODocument4 pagesRef 6 - What Is IT Governance - A Formal Way To Align IT - Business Strategy - CIOTowhidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Sophos - Considerations For Deploying Sophos Firewall in Common ScenariosDocument22 pagesSophos - Considerations For Deploying Sophos Firewall in Common ScenariosMiguel António ManuelNo ratings yet
- UIDAI Letter Dated 27 01 2023 Phase Out of Existing Fingerprint L0 Registered Devices From Aadhaar Authentication EcosystemDocument17 pagesUIDAI Letter Dated 27 01 2023 Phase Out of Existing Fingerprint L0 Registered Devices From Aadhaar Authentication EcosystemgtcesevaNo ratings yet
- SAP MDG Technical Concept:-: (Type The Company Name)Document16 pagesSAP MDG Technical Concept:-: (Type The Company Name)Lionelkeneth12100% (1)
- 3 GmcomDocument12 pages3 GmcombaliyanrohitbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Web Communication-1Document30 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Web Communication-1St WxyNo ratings yet
- Hacking Exposed Cisco Networks - Cisco Security Secrets & Solutions by Andrew Vladimirov, Konstantin Gavrilenko and Andrei MikhailovskyDocument1,096 pagesHacking Exposed Cisco Networks - Cisco Security Secrets & Solutions by Andrew Vladimirov, Konstantin Gavrilenko and Andrei MikhailovskyUli UliNo ratings yet
- Plan For ReleaseDocument6 pagesPlan For ReleasetestscribdnewNo ratings yet
- Ota Apis GeneralDocument13 pagesOta Apis Generaljack_rzmNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security ReportDocument24 pagesCyber Security ReportAakash Jain100% (1)
- Tecsec 3004Document299 pagesTecsec 3004wahyu baganNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document30 pagesCH 6Joycelyne ZangNo ratings yet
- Lock-Up Device With: Dynamic Measurement Option (Dmo)Document1 pageLock-Up Device With: Dynamic Measurement Option (Dmo)wenpinNo ratings yet
- Saurav Kumar Singh: Software Engineer Accenture Services Pvt. LTD."Document2 pagesSaurav Kumar Singh: Software Engineer Accenture Services Pvt. LTD."SauravSinghNo ratings yet
- PGDIT 2013 ProjectGuidelines ITDocument3 pagesPGDIT 2013 ProjectGuidelines ITdev_thecoolboyNo ratings yet
- Traffic Software Requirement Specification SrsDocument13 pagesTraffic Software Requirement Specification SrsJahnavi Prasad SrirampurapuNo ratings yet
- Computer Viruses: Everything You Wanted To Know AboutDocument35 pagesComputer Viruses: Everything You Wanted To Know AboutSanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- G7 WORKSHEET ICT Week 5 NEWDocument4 pagesG7 WORKSHEET ICT Week 5 NEWEbb Lian AninoNo ratings yet
- NetScreen-to-SRX Series Migration Service Sales PresentationDocument19 pagesNetScreen-to-SRX Series Migration Service Sales PresentationLi KangNo ratings yet