Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit-I p3
Unit-I p3
Uploaded by
Girraj DohareOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit-I p3
Unit-I p3
Uploaded by
Girraj DohareCopyright:
Available Formats
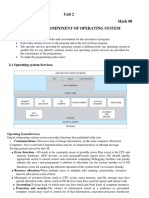
Common System Components
Process Management
Main Memory Management
File Management
I/O System Management
Secondary Management
Networking
Protection System
Command-Interpreter System
Operating System Concepts
Process Management
A process is a program in execution. A process needs certain
resources, including CPU time, memory, files, and I/O
devices, to accomplish its task.
The operating system is responsible for the following
activities in connection with process management.
Process creation and deletion.
process suspension and resumption.
Provision of mechanisms for:
process synchronization
process communication
Operating System Concepts
Main-Memory Management
Memory is a large array of words or bytes, each with its own
address. It is a repository of quickly accessible data shared by the
CPU and I/O devices.
Main memory is a volatile storage device. It loses its contents in
the case of system failure.
The operating system is responsible for the following activities in
connections with memory management:
Keep track of which parts of memory are currently being used
and by whom.
Decide which processes to load when memory space becomes
available.
Allocate and deallocate memory space as needed.
Operating System Concepts
File Management
A file is a collection of related information defined by its
creator. Commonly, files represent programs (both source
and object forms) and data.
The operating system is responsible for the following
activities in connections with file management:
File creation and deletion.
Directory creation and deletion.
Support of primitives for manipulating files and directories.
Mapping files onto secondary storage.
File backup on stable (nonvolatile) storage media.
Operating System Concepts
I/O System Management
The I/O system consists of:
A buffer-caching system
A general device-driver interface
Drivers for specific hardware devices
Operating System Concepts
Secondary-Storage Management
Since main memory (primary storage) is volatile and too
small to accommodate all data and programs permanently,
the computer system must provide secondary storage to back
up main memory.
Most modern computer systems use disks as the principle
on-line storage medium, for both programs and data.
The operating system is responsible for the following
activities in connection with disk management:
Free space management
Storage allocation
Disk scheduling
Operating System Concepts
Networking (Distributed Systems)
A distributed system is a collection processors that do not share memory
or a clock. Each processor has its own local memory.
The processors in the system are connected through a communication
network.
Communication takes place using a protocol.
A distributed system provides user access to various system resources.
Access to a shared resource allows:
Computation speed-up
Increased data availability
Enhanced reliability
Operating System Concepts
Protection System
Protection refers to a mechanism for controlling
access by programs, processes, or users to both
system and user resources.
The protection mechanism must:
distinguish between authorized and unauthorized usage.
specify the controls to be imposed.
provide a means of enforcement.
Operating System Concepts
Command-Interpreter System
Many commands are given to the operating system by
control statements which deal with:
process creation and management
I/O handling
secondary-storage management
main-memory management
file-system access
protection
networking
Operating System Concepts
Command-Interpreter System (Cont.)
The program that reads and interprets control
statements is called variously:
command-line interpreter
shell (in UNIX)
Its function is to get and execute the next command
statement.
Operating System Concepts
Operating System Services
Program execution – system capability to load a program into memory
and to run it.
I/O operations – since user programs cannot execute I/O operations
directly, the operating system must provide some means to perform I/O.
File-system manipulation – program capability to read, write, create, and
delete files.
Communications – exchange of information between processes executing
either on the same computer or on different systems tied together by a
network. Implemented via shared memory or message passing.
Error detection – ensure correct computing by detecting errors in the
CPU and memory hardware, in I/O devices, or in user programs.
Operating System Concepts
Additional Operating System Functions
Additional functions exist not for helping the user, but
rather for ensuring efficient system operations.
Resource allocation – allocating resources to multiple users
or multiple jobs running at the same time.
Accounting – keep track of and record which users use how
much and what kinds of computer resources for account
billing or for accumulating usage statistics.
Protection – ensuring that all access to system resources is
controlled.
Operating System Concepts
System Calls
System calls provide the interface between a running program and the operating
system.
Generally available as assembly-language instructions.
Languages defined to replace assembly language for systems programming allow
system calls to be made directly (e.g., C, C++)
Three general methods are used to pass parameters between a running program and
the operating system.
Pass parameters in registers.
Store the parameters in a table in memory, and the table address is passed as a
parameter in a register.
Push (store) the parameters onto the stack by the program, and pop off the stack by
operating system.
Operating System Concepts
Passing of Parameters As A Table
Operating System Concepts
Types of System Calls
Process control
File management
Device management
Information maintenance
Communications
Operating System Concepts
MS-DOS Execution
At System Start-up Running a Program
Operating System Concepts
UNIX Running Multiple Programs
Operating System Concepts
Communication Models
Communication may take place using either message passing or shared
memory.
Msg Passing Shared Memory
Operating System Concepts
System Programs
System programs provide a convenient environment for program development and
execution. The can be divided into:
File manipulation
Status information
File modification
Programming language support
Program loading and execution
Communications
Application programs
Most users’ view of the operation system is defined by system programs, not the actual
system calls.
Operating System Concepts
You might also like
- (Ebook - PDF) Software Testing Fundamentals (Wiley)Document315 pages(Ebook - PDF) Software Testing Fundamentals (Wiley)rajiprateesh100% (1)
- Operating Systems Lecture Notes-1Document15 pagesOperating Systems Lecture Notes-1Arun Sasidharan100% (1)
- Hytera ProgrammingDocument6 pagesHytera ProgrammingChrisNo ratings yet
- TCI1835 Student Guide 2of2 PDFDocument222 pagesTCI1835 Student Guide 2of2 PDFJohnny Stengaard HansenNo ratings yet
- CompatibilitymodeDocument42 pagesCompatibilitymodeAnil KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Operating-System StructuresDocument31 pagesChapter 3: Operating-System StructuresDiamond MindglanceNo ratings yet
- Os Unit 1Document41 pagesOs Unit 1saumya patelNo ratings yet
- 2.services and Component of OS NotesDocument11 pages2.services and Component of OS NoteshshsgNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument38 pagesChapter Oneadugnaw azanawNo ratings yet
- Slides Ch1 Basics Overview of Operating SystemsDocument26 pagesSlides Ch1 Basics Overview of Operating SystemsAbuky Ye AmanNo ratings yet
- Services and Component of Operating System1Document6 pagesServices and Component of Operating System1Nisarg GugaleNo ratings yet
- Itec55 - Operating System StructureDocument4 pagesItec55 - Operating System StructureaescarlannNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review: CMSC 421 Fall 05Document75 pagesMidterm Review: CMSC 421 Fall 05asdNo ratings yet
- Operating System U-1Document40 pagesOperating System U-1BCA03114202019 YASHARORANo ratings yet
- Operating SystemDocument49 pagesOperating SystemBCA03114202019 YASHARORANo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document33 pagesChapter 1dejenehundaol91No ratings yet
- Module 1Document41 pagesModule 1japesh dixitNo ratings yet
- Components of Operating SystemDocument6 pagesComponents of Operating SystemVaibhav PearsonNo ratings yet
- Program Execution: Operating System System Operating Systems SystemsDocument3 pagesProgram Execution: Operating System System Operating Systems SystemsMUHAMMAD ATTIQUENo ratings yet
- 1OS StructureDocument8 pages1OS StructurePianic PelmaNo ratings yet
- Components of Operating System2Document8 pagesComponents of Operating System2gsssbheemsanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Operating SystemsDocument7 pagesLecture Notes On Operating SystemsrrrollroxNo ratings yet
- OS Unit 1 NotesDocument48 pagesOS Unit 1 NotesHARSHA VINAY KOTNI HU21CSEN0100574No ratings yet
- Chapter#01 - Introduction To OSDocument52 pagesChapter#01 - Introduction To OSManzar AliNo ratings yet
- Cs6401 Operating System Part BDocument27 pagesCs6401 Operating System Part BAk-Bollywood SeriesNo ratings yet
- Components of Operating SystemDocument5 pagesComponents of Operating SystemMARY JOY VILLARUEL100% (1)
- OS Lecture 01Document24 pagesOS Lecture 01anaana71233No ratings yet
- unit_1_part_2_Document13 pagesunit_1_part_2_aman jatainNo ratings yet
- Note 4Document5 pagesNote 4DEBUGH247 ON TELEGRAMNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledNana Saoudou LoicNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Operating System StructuresDocument51 pagesUnit 2 - Operating System Structuresyuki tetsuNo ratings yet
- CSE 4th - OSDocument68 pagesCSE 4th - OSPrajwal MeshramNo ratings yet
- Operating SystemsDocument4 pagesOperating SystemsRohith PeddiNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems Concepts: Lecture 1 - IntroductionDocument18 pagesOperating Systems Concepts: Lecture 1 - IntroductionRashda KhanzadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document3 pagesChapter 2Abhi RajNo ratings yet
- Os Unit-1 (Bca)Document54 pagesOs Unit-1 (Bca)Bot IdNo ratings yet
- OS and NW BasicDocument64 pagesOS and NW BasicApurva SinghNo ratings yet
- Learning Materials-Chapter-2-OSDocument8 pagesLearning Materials-Chapter-2-OSSheeraz ArifNo ratings yet
- Ch02 (Compatibility Mode)Document51 pagesCh02 (Compatibility Mode)Raja MasoodNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems: Lecture NotesDocument222 pagesOperating Systems: Lecture NotesMinuJose JojyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Operating-System StructuresDocument41 pagesChapter 3: Operating-System StructuresAnushree kumawatNo ratings yet
- Unit OneDocument13 pagesUnit OneAkshat JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two OSDocument13 pagesChapter Two OShiruttesfay67No ratings yet
- Chapter1 IntroductionDocument40 pagesChapter1 IntroductionDeep ChavanNo ratings yet
- Operating System Lecture Note Module-1Document32 pagesOperating System Lecture Note Module-1Kefelegn GulintNo ratings yet
- OS unit 1 answer keyDocument21 pagesOS unit 1 answer keysaitejakasani091No ratings yet
- CF Unit-3 OSDocument17 pagesCF Unit-3 OSMr. MANTRANo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Operating SystemsDocument17 pagesUnit - 2 Operating Systemsimran hameerNo ratings yet
- COS 331 Operating System2 LectureNotes 2023Document70 pagesCOS 331 Operating System2 LectureNotes 2023eze.pleasant001No ratings yet
- Chapter - 01 - Overview of Operating SystemDocument34 pagesChapter - 01 - Overview of Operating SystemDuy Bùi LêNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 01 - Overview of Operating SystemDocument34 pagesChapter - 01 - Overview of Operating SystemcuonghuynhNo ratings yet
- Operating System CompleteDocument59 pagesOperating System CompleteJasperFabella100% (1)
- Operating Systems Notes by S DhallDocument124 pagesOperating Systems Notes by S DhallSALMAN KHANNo ratings yet
- Unit1 - Introduction To OSDocument7 pagesUnit1 - Introduction To OSAdarsh PandeyNo ratings yet
- 01 04 OS OperationsDocument2 pages01 04 OS OperationsMarlo CapalaNo ratings yet
- Operating System Services: One Set of Operating-System Services Provides Functions That Are Helpful To The UserDocument26 pagesOperating System Services: One Set of Operating-System Services Provides Functions That Are Helpful To The UserAnonymous hzr2fbc1zMNo ratings yet
- Operating System Components - Lesson 2-1Document6 pagesOperating System Components - Lesson 2-1Bright Alike ChiwevuNo ratings yet
- Operating-System StructuresDocument17 pagesOperating-System StructuresAshok OrugantiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: IntroductionDocument16 pagesChapter 1: IntroductionYogesh DevgunNo ratings yet
- OS Chapter 2 - 1 16 17Document63 pagesOS Chapter 2 - 1 16 17nasa stickNo ratings yet
- Operations of Operating System: Dr. Tapas K. MishraDocument17 pagesOperations of Operating System: Dr. Tapas K. MishraDale sharmaNo ratings yet
- Operating Systems: Concepts to Save Money, Time, and FrustrationFrom EverandOperating Systems: Concepts to Save Money, Time, and FrustrationNo ratings yet
- Computer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignFrom EverandComputer Science: Learn about Algorithms, Cybersecurity, Databases, Operating Systems, and Web DesignNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Part 2Document24 pagesUnit 4 Part 2Girraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Part 1Document62 pagesUnit 4 Part 1Girraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Unit - V: Statistical Technique & DistributionDocument20 pagesUnit - V: Statistical Technique & DistributionGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Part 4Document8 pagesUnit 3 Part 4Girraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 1Document18 pagesUnit 1 Part 1Girraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Python BasicsDocument15 pagesPython BasicsGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- 3pandas IpynbDocument26 pages3pandas IpynbGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Madhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior Department of CSE & ITDocument16 pagesMadhav Institute of Technology & Science, Gwalior Department of CSE & ITGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Network Layer: The Control Plane: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachDocument102 pagesNetwork Layer: The Control Plane: Computer Networking: A Top Down ApproachGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Digital ElectronicsDocument37 pagesUnit 2 Digital ElectronicsGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 2Document85 pagesUnit 1 Part 2Girraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design 230201 (Dc-1) : PPTS: Unit - 1Document50 pagesDigital Logic Design 230201 (Dc-1) : PPTS: Unit - 1Girraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Introduction Of: Operating SystemDocument14 pagesIntroduction Of: Operating SystemGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument23 pagesUnit 4 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- CSO (160311) - Unit 1Document134 pagesCSO (160311) - Unit 1Girraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument27 pagesUnit 5 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument38 pagesUnit 3 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inGirraj DohareNo ratings yet
- MCA T113 PrinciplesofProgrammingwithCDocument30 pagesMCA T113 PrinciplesofProgrammingwithCBhaskar MondalNo ratings yet
- Impressions of The HP 12C PlatinumDocument4 pagesImpressions of The HP 12C PlatinumJordi HidalgoNo ratings yet
- PKS - TDC 3000 Customer Resource Manual: PFC (Power Factor Corrected) Power Supply KitsDocument3 pagesPKS - TDC 3000 Customer Resource Manual: PFC (Power Factor Corrected) Power Supply KitsPudnaNo ratings yet
- EE312 Old Exam Study GuideDocument6 pagesEE312 Old Exam Study GuideWilliam YangNo ratings yet
- Principles of Digital Transmission: With Wireless ApplicationsDocument16 pagesPrinciples of Digital Transmission: With Wireless ApplicationsCristian VargasNo ratings yet
- 1 Whole Sheet (LAS)Document14 pages1 Whole Sheet (LAS)amet hystNo ratings yet
- Self Balancing RobotDocument48 pagesSelf Balancing RobotHiếu TrầnNo ratings yet
- Cisco-to-Juniper Show CommandsDocument4 pagesCisco-to-Juniper Show Commandsakarki77No ratings yet
- 3468 Compiler ConstructionDocument5 pages3468 Compiler ConstructionSyed HumairNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor KF5N50P/F/PZ/FZ: Technical DataDocument7 pagesSemiconductor KF5N50P/F/PZ/FZ: Technical DatatallertecuNo ratings yet
- Cranex DimensionsDocument1 pageCranex DimensionsanasNo ratings yet
- 945GCT-M V30-OK (ComunidadeTecnica - Com.br) PDFDocument35 pages945GCT-M V30-OK (ComunidadeTecnica - Com.br) PDFjoseto_441No ratings yet
- Clif-Cbuslc Interface: FeaturesDocument2 pagesClif-Cbuslc Interface: FeaturesErmiasNo ratings yet
- ProfileService LuaDocument40 pagesProfileService Luaegg container b28348No ratings yet
- 2011 ZX-10r FI Cal Tool ManualDocument101 pages2011 ZX-10r FI Cal Tool ManualAlon LellisNo ratings yet
- Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (Igbts) : Lecture NotesDocument17 pagesInsulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (Igbts) : Lecture NotesVERONICA TALIA GUANOLUISA MORETANo ratings yet
- Kumpulan Serial Number Windows XPDocument4 pagesKumpulan Serial Number Windows XPspsc66No ratings yet
- Hoja de Datos Gal22v10 PDFDocument27 pagesHoja de Datos Gal22v10 PDFCadHomeNo ratings yet
- ATmega328 Timer-Counter1 Compare Match BDocument1 pageATmega328 Timer-Counter1 Compare Match BSajad DehghanNo ratings yet
- 173504-Khadja-Tul-Kubra - Online Hostel Management System-1Document74 pages173504-Khadja-Tul-Kubra - Online Hostel Management System-1RabiaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 PythonDocument89 pagesUnit-4 PythonBessy Bijo100% (2)
- Teradata Developer Track Bootcamp TrainingDocument2 pagesTeradata Developer Track Bootcamp TrainingAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- SAP Notes: Note Assistant (Transaction SNOTE) Helps You When Working WithDocument2 pagesSAP Notes: Note Assistant (Transaction SNOTE) Helps You When Working Withaniruddha_2012No ratings yet
- JAVA All MergedDocument227 pagesJAVA All MergedKioniNo ratings yet
- ISTQB Software Testing Certification Sample Question Paper With Answers - Part IIDocument1 pageISTQB Software Testing Certification Sample Question Paper With Answers - Part IISenthil Kumar SivamNo ratings yet
- Porting GuideDocument7 pagesPorting GuideKevin CheowNo ratings yet
- Seg2Mat: SEG-2 To MATLAB File ConverterDocument5 pagesSeg2Mat: SEG-2 To MATLAB File ConverterAnand BesraNo ratings yet