Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Future Tense
The Future Tense
Uploaded by
Rahela Folt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views15 pagesThe document discusses various ways to express future tense in English including will + verb, be/am/are + going to + verb, will be + verb+ing, simple present, and present continuous. It contrasts uses of will and future continuous, and explains how be going to, present continuous, and simple present can be used to express different types of future plans, intentions, predictions and scheduled events.
Original Description:
Original Title
the_future_tense
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various ways to express future tense in English including will + verb, be/am/are + going to + verb, will be + verb+ing, simple present, and present continuous. It contrasts uses of will and future continuous, and explains how be going to, present continuous, and simple present can be used to express different types of future plans, intentions, predictions and scheduled events.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views15 pagesThe Future Tense
The Future Tense
Uploaded by
Rahela FoltThe document discusses various ways to express future tense in English including will + verb, be/am/are + going to + verb, will be + verb+ing, simple present, and present continuous. It contrasts uses of will and future continuous, and explains how be going to, present continuous, and simple present can be used to express different types of future plans, intentions, predictions and scheduled events.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
The Future Tense
I’m playing golf with my boss after work
next Tuesday.
I’m going to play golf at least once a week
this year - I want to get fit.
I think I’ll play golf after work tomorrow.
At this time next week I’ll be playing golf on
the first day of my vacation.
I have a busy schedule next week: on
Tuesday I arrive in New York, on
Wednesday I play golf with the Marketing
Manager ..
What tenses can be used to
express the future?
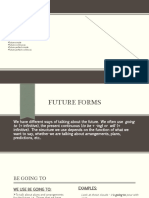
Will + verb
is/are/am+ going to+ verb
Will be+ verb+ ing
Simple present
Present continuous
Future Time Clauses
After you get home, I am leaving for work.
I’ll probably leave for work when you get
home.
I am going to call you as soon as I arrive
home
Before I leave for work, I’ll do the dishes
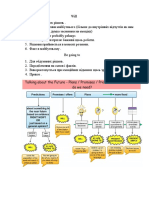
Future forms can occur in the main clause
with future time clauses.
Future time clauses begin with a time
word such as when, before, after, as
soon as, until, once, next time, etc.
In most cases, the main clause uses the
simple present. The main clause uses a
future form.
Contrasting will and the future
continuous
Don’t worry. I’ll pick up the kids after work.
I’ll be picking up the kids after work. Then
I’ll be going straight home.
Don’t call Bob at six. He’ll probably be
eating dinner then
Don’t call Bob at six. He’ll probably eat
dinner then.
Future Continuous
The future continuous expresses an
activity in progress at a specific time in the
future.
At this time tomorrow, I’ll be leaving for
Hawaii.
I’ll be staying in Hawaii for three weeks.
Promises and Requests vs. Plans
and Expectations
Future with Will Future Continuous
(a Promise) (a Plan or Expectation)
I’ll finish this tomorrow. I’ll be finishing this
tomorrow.
Future Continuous
Future with Will (a Question About a
(a Request) Plan)
A: Will you stop at the A: Will you be
post office to send this stopping at the post
package tomorrow? office tomorrow?
B: Sure. B: Yes, I will.
A: Could you send
this package?
Be going to, the present
continuous as future, and the
simple present as future
Be going to & the present
continuous as future
Both be going to and the present
continuous as future are used to talk about
a planned event or future intention.
I am not going to take classes this summer.
I am going to work full-time.
I am not taking classes this summer. I am
working full-time.
Be going to & the present
continuous as future
With be going to, the With the present
speaker may not have continuous as future,
an exact plan the plan is often more
definite
I am going to leave my I am leaving my job
job (someday). I am (next week). I’ve been
just so unhappy. unhappy for too long.
Be going to & the present
continuous as future
We use be going to make perditions. We
don’t use the present continuous or the
simple present to predict events.
They are going to win tonight. Everyone
thinks so.
They are winning tonight. X
It’s going to rain later.
It is raining later. X
The Simple Present as Future
The simple present as future is used for
scheduled events that usually cannot be
changed. It is common in more formal
contexts.
Printed program: The conference starts on
Tuesday evening and ends on Saturday
afternoon.
Trip itinerary: The flight leaves Chicago at
10:02 and arrives in Palm Beach at 12:36.
The Present continuous as future and be going
to can ALSO be used to talk about scheduled
events. However, the simple present as future
is more likely to imply that the schedule is
beyond the control of the speaker.
Student: I am leaving at midnight. That’s my
plan.
I am going to leave at midnight. That’s
my plan.
Soldier: I leave at midnight. Those are my
orders.
You might also like
- FUTURE Tenses - PPTDocument37 pagesFUTURE Tenses - PPTi.diana100% (1)
- Subject Verb Agreement2 PDFDocument8 pagesSubject Verb Agreement2 PDFzhakunthala_gekNo ratings yet
- Future TimeDocument18 pagesFuture Timeapi-252190418No ratings yet
- Future (Pt. 2)Document25 pagesFuture (Pt. 2)Mariana BlancoNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument7 pagesFutureAndreiAlexandruNo ratings yet
- Talking About FutureDocument21 pagesTalking About FutureAnuradha SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Future VerbsDocument6 pagesFuture VerbsElia Miranda CorralesNo ratings yet
- PPT. Expressing The FutureDocument53 pagesPPT. Expressing The FutureHanizar Rachman100% (1)
- Future Tenses: Lecturer: Mr. Vinh SovannDocument18 pagesFuture Tenses: Lecturer: Mr. Vinh SovannStudent Sokha ChanchesdaNo ratings yet
- Be Going To BE GOING TO For IntentionsDocument5 pagesBe Going To BE GOING TO For IntentionsAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- FUTUREDocument15 pagesFUTURENicola PrinNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument30 pagesFutureStefanDribler998No ratings yet
- Future All FormsDocument19 pagesFuture All FormsCamila GualuchicoNo ratings yet
- The Future (Predictions, Decisions and Intentions, Arrangements, Other Future MeaningsDocument12 pagesThe Future (Predictions, Decisions and Intentions, Arrangements, Other Future MeaningsYulia SidelnykNo ratings yet
- Simple Future Tense (Will) : FunctionDocument3 pagesSimple Future Tense (Will) : FunctionMaitane Ladislao BilbaoNo ratings yet
- Meeting VI Tiia: Lecturer: Sepsy Caroline T H. S. SS., M.HumDocument19 pagesMeeting VI Tiia: Lecturer: Sepsy Caroline T H. S. SS., M.HumAjeng WakimNo ratings yet
- The Present Continuous TenseDocument6 pagesThe Present Continuous TenselepromNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument26 pagesFutureMariana BlancoNo ratings yet
- Meeting VI-VII Tiia: Lecturer: Sepsy Caroline T H. S. SS., M.HumDocument19 pagesMeeting VI-VII Tiia: Lecturer: Sepsy Caroline T H. S. SS., M.HumAjeng WakimNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument52 pagesFuture TensesTấn Tài VõNo ratings yet
- Engleski (Future Forms)Document12 pagesEngleski (Future Forms)Kozmetika Amina-Mirnesa SubašićNo ratings yet
- Worksheet For PracticeDocument8 pagesWorksheet For Practiceishika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Future Forms PresentationDocument10 pagesFuture Forms PresentationKatya GeorgievaNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument5 pagesFuture Tensesnato.kharshiladze.1No ratings yet
- Expressing The FutureDocument3 pagesExpressing The FuturetyysiaNo ratings yet
- Future Tense - THEORYDocument7 pagesFuture Tense - THEORYRoxana Caia GheboianuNo ratings yet
- Les 6 Unit 19, 20, 21, 22, 23grammar Verb Forms 5 Will Work, Am Going To Work (Student Version For HUbl)Document11 pagesLes 6 Unit 19, 20, 21, 22, 23grammar Verb Forms 5 Will Work, Am Going To Work (Student Version For HUbl)MerveNo ratings yet
- Future Tense in EnglishDocument20 pagesFuture Tense in Englisht7kx7p92mqNo ratings yet
- Give You A Pay RiseDocument4 pagesGive You A Pay RiseAnca ȘtefănescuNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses in EnglishDocument11 pagesFuture Tenses in EnglishNagyKatalinNo ratings yet
- What The Future HoldsDocument11 pagesWhat The Future HoldsAtta BatulNo ratings yet
- Will - Going ToDocument35 pagesWill - Going ToDiana Carolina Castillo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Will - Going ToDocument35 pagesWill - Going ToDiana Carolina Castillo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Future TensesDocument4 pagesFuture TensesSusana BettúNo ratings yet
- FUTURE TENSESDocument27 pagesFUTURE TENSESdaliaNo ratings yet
- English III - Student - S TextbookDocument82 pagesEnglish III - Student - S TextbookEdier BravoNo ratings yet
- Grammar Notes-Future FormsDocument3 pagesGrammar Notes-Future FormsInés PerazzaNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument20 pagesFutureAli AteeqNo ratings yet
- Future Continuous and Future PerfectDocument23 pagesFuture Continuous and Future PerfectZI-CHEM INDOCHINANo ratings yet
- Future Continuous and Future PerfectDocument23 pagesFuture Continuous and Future PerfectZI-CHEM INDOCHINANo ratings yet
- Future FormsDocument3 pagesFuture FormsRaso RasovicNo ratings yet
- Expressing The Future TenseDocument7 pagesExpressing The Future TenseBobuinNo ratings yet
- Future - Tenses - M2Document20 pagesFuture - Tenses - M2Matteo 1510No ratings yet
- GUIA 11-02 THIRD TERM OkDocument9 pagesGUIA 11-02 THIRD TERM OkJhon Alexander Palacios MorenoNo ratings yet
- Session 13. Grammar. Future Tense and Going To. P1-P203Document19 pagesSession 13. Grammar. Future Tense and Going To. P1-P203Roxana Mollinedo ArteagaNo ratings yet
- The FutureDocument14 pagesThe FutureFatima valentina romeroNo ratings yet
- Using The Future Continuous TenseDocument4 pagesUsing The Future Continuous TenseTRACY NGU HUI SIENo ratings yet
- Libro de Ingles (Tercer Nivel)Document75 pagesLibro de Ingles (Tercer Nivel)Mig EngelNo ratings yet
- Expressing Future in EnglishDocument4 pagesExpressing Future in EnglishTamara PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Future: Future: Will and ShallDocument1 pageFuture: Future: Will and Shallorion_scoNo ratings yet
- Semana 06 - PPT Sesión Presencial English IVDocument34 pagesSemana 06 - PPT Sesión Presencial English IVIvan CotrinaNo ratings yet
- Furure ContinuousDocument2 pagesFurure ContinuousAnna JanczewskaNo ratings yet
- FutureDocument6 pagesFutureelmoatassimNo ratings yet
- DoneDocument7 pagesDoneYasmin Putri MaharaniNo ratings yet
- HM Future Tenses ExplanationDocument3 pagesHM Future Tenses ExplanationVinícius CorreaNo ratings yet
- Basic Contrasts: Will, Going To, Present Continuous: I'll Be Late Home This EveningDocument3 pagesBasic Contrasts: Will, Going To, Present Continuous: I'll Be Late Home This EveningSamantha RamosNo ratings yet
- FuturesDocument12 pagesFuturesYazmin TitoNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Microsoft WordDocument18 pagesEnglish Grammar Microsoft WordMarysia AndrunyszynNo ratings yet
- Future Progressive HoroscopeDocument16 pagesFuture Progressive Horoscopeapi-267540571No ratings yet
- B1 Word Order WO003: Write Affirmative Sentences in The Correct Word OrderDocument2 pagesB1 Word Order WO003: Write Affirmative Sentences in The Correct Word OrderRahela Folt100% (1)
- Ad014 Comparison of AdjectivesDocument2 pagesAd014 Comparison of AdjectivesRahela FoltNo ratings yet
- Indefinite and Definite ArticlesDocument11 pagesIndefinite and Definite ArticlesRahela FoltNo ratings yet
- The Past Perfect The Past Perfect ContinuousDocument17 pagesThe Past Perfect The Past Perfect ContinuousRahela FoltNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Present Continuous: Discuss With Your Partner Why The Following Sentences Are Grammatically WrongDocument10 pagesSimple Present and Present Continuous: Discuss With Your Partner Why The Following Sentences Are Grammatically WrongRahela FoltNo ratings yet
- The Present Perfect ContinuousDocument20 pagesThe Present Perfect ContinuousRahela FoltNo ratings yet
- Creative Powerpoint: Information ServicesDocument24 pagesCreative Powerpoint: Information ServicesRahela FoltNo ratings yet
- January - December 2022Document12 pagesJanuary - December 2022Rahela FoltNo ratings yet
- Bloor & Bloor - Chapter 5 - Grammar and TextDocument18 pagesBloor & Bloor - Chapter 5 - Grammar and TextRomero FlaviaNo ratings yet
- 3-3 - Gile - The Effort Models of InterpretingDocument2 pages3-3 - Gile - The Effort Models of InterpretingPaz EtchanchuNo ratings yet
- Y12 - Really Useful Spanish BookletDocument15 pagesY12 - Really Useful Spanish BookletH M Whiteside GillibrandNo ratings yet
- Session 5 - C1 Advanced Reading Use of English Part 1Document9 pagesSession 5 - C1 Advanced Reading Use of English Part 1Israel OlayaNo ratings yet
- Ovc Eng1 Unit3ab BlendedDocument20 pagesOvc Eng1 Unit3ab BlendedJoffrey Itamar Valdivia FarromequeNo ratings yet
- Adjective Clause English by Titik Nol CourseDocument4 pagesAdjective Clause English by Titik Nol CourseWardatulChamroNo ratings yet
- Brief Description (Translatian&Interpretation)Document2 pagesBrief Description (Translatian&Interpretation)Baiq IrmaNo ratings yet
- Tema 3 - MagisterDocument5 pagesTema 3 - Magistervanesa_duque_3No ratings yet
- Book Bands Flyer PDFDocument2 pagesBook Bands Flyer PDFClaudia MacarieNo ratings yet
- Modal Verbs: That Means You Make Negatives by Adding Not' To The End of The Verb. For ExampleDocument3 pagesModal Verbs: That Means You Make Negatives by Adding Not' To The End of The Verb. For ExampleGiang LêNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Guide To 2BAC EnglishDocument7 pagesComprehensive Guide To 2BAC EnglishYounes LouziNo ratings yet
- Statement On The Amendment To Law No. 270/1995 Coll. On The State Language (2009.07.15.)Document3 pagesStatement On The Amendment To Law No. 270/1995 Coll. On The State Language (2009.07.15.)kerekasztalNo ratings yet
- A Relative Pronoun Is Used To Connect A Clause or Phrase To A Noun or PronounDocument34 pagesA Relative Pronoun Is Used To Connect A Clause or Phrase To A Noun or PronounKidu YabeNo ratings yet
- Raj Khati 2011 PDFDocument10 pagesRaj Khati 2011 PDFJessieRealistaNo ratings yet
- A1PLUS U3 Extra Grammar Practice ReinforcementDocument1 pageA1PLUS U3 Extra Grammar Practice ReinforcementjanNo ratings yet
- Random Choices - A PowerPoint Randomizer - TekhnologicDocument11 pagesRandom Choices - A PowerPoint Randomizer - TekhnologicABoseLopusoNo ratings yet
- Quick Navigation: Section 113: English Speaking and ConversationDocument1 pageQuick Navigation: Section 113: English Speaking and ConversationAlejandro Perez PerezNo ratings yet
- Basics of English Grammar: Comparative and Superlative Forms of AdjectivesDocument17 pagesBasics of English Grammar: Comparative and Superlative Forms of AdjectivesFadzillah AhmadNo ratings yet
- ModifiedCRLA G3 Scoresheet v3 3 - BANANA1Document57 pagesModifiedCRLA G3 Scoresheet v3 3 - BANANA1rozel.lopezNo ratings yet
- Rojhano Lesson 6Document3 pagesRojhano Lesson 6Bela NovitaNo ratings yet
- CB5 U12EF AnswerDocument15 pagesCB5 U12EF AnswerTrà Giang Lê100% (1)
- 7 - Polite - British InsultsDocument3 pages7 - Polite - British InsultsLeonardo GüthsNo ratings yet
- Perdoo OKR EbookDocument33 pagesPerdoo OKR EbookFrancesco ParaggioNo ratings yet
- Performance Monitoring and Coaching Form'2023Document2 pagesPerformance Monitoring and Coaching Form'2023remely ubungen100% (1)
- Present Continuous Tense: Agus BudiarteDocument11 pagesPresent Continuous Tense: Agus Budiarteilyas sefriansyah harahapNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Focus On The LearnerDocument1 pageAssignment 1 - Focus On The LearnerZaher Al-SaltiNo ratings yet
- Scienceofetymolo 00 SkeauoftDocument274 pagesScienceofetymolo 00 SkeauoftRon GaylesNo ratings yet
- Final Notes Social Dimension of EducationDocument6 pagesFinal Notes Social Dimension of EducationChristian LeonesNo ratings yet