Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jamal Abdul Ansari University of India - Nawab Ali Khan University of India
Jamal Abdul Ansari University of India - Nawab Ali Khan University of India
Uploaded by
ashlie garciaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- TMA01 Handout Planner For Final Work 1Document11 pagesTMA01 Handout Planner For Final Work 1Eland ExamsNo ratings yet
- Article Critique Essay - Social Media in LearningDocument3 pagesArticle Critique Essay - Social Media in LearningAlexandra Sofia86% (7)
- Technology Resources Improvement PlanDocument2 pagesTechnology Resources Improvement PlanChristine De San Jose80% (10)
- Training CurriculumDocument2 pagesTraining CurriculumGeetliM100% (5)
- Succeed in Cambridge Cae 10 Practice Tests Key Scribd PDFDocument3 pagesSucceed in Cambridge Cae 10 Practice Tests Key Scribd PDFGiulia ChireaNo ratings yet
- 01 Gonzales Et Al 1-16Document16 pages01 Gonzales Et Al 1-16JM SanchezNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Social Media Assisted Course On Learning Self EfficacyDocument12 pagesEffectiveness of Social Media Assisted Course On Learning Self EfficacyleandroNo ratings yet
- School Counselors' Use of Technology For Program ManagementDocument10 pagesSchool Counselors' Use of Technology For Program ManagementAdam ZiyyadNo ratings yet
- Poster en InglesDocument1 pagePoster en InglesAnonymous 4QjI1ccqNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social Media Usage On Students AcademicDocument7 pagesImpact of Social Media Usage On Students AcademicSu Kings AbetoNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Education and Teaching InternationalDocument12 pagesInnovations in Education and Teaching InternationalNis NosNo ratings yet
- RMB - Research Proposal A6Document10 pagesRMB - Research Proposal A6Harshit ShubhankarNo ratings yet
- 10 1108 - Jrit 10 2022 0061Document22 pages10 1108 - Jrit 10 2022 0061cjscarecrew34No ratings yet
- Taggart Wheeler 2023 Collaborative Learning As Constructivist Practice An Exploratory Qualitative Descriptive Study ofDocument18 pagesTaggart Wheeler 2023 Collaborative Learning As Constructivist Practice An Exploratory Qualitative Descriptive Study ofmargaridaNo ratings yet
- The Relationships Between Self-Efficacy, Task Value, and Self-Regulated Learning Strategies in Massive Open Online CoursesDocument18 pagesThe Relationships Between Self-Efficacy, Task Value, and Self-Regulated Learning Strategies in Massive Open Online CoursesLarry PalaganasNo ratings yet
- F10470476S519Document5 pagesF10470476S519sanya kundraNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Role ofDocument15 pagesExploring The Role ofSparsha SNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of The Key Components of Online Pee - 2024 - Educational ResDocument27 pagesA Systematic Review of The Key Components of Online Pee - 2024 - Educational ResYOHANES KURNIAWANNo ratings yet
- Deng, Tavares - 2013 - From Moodle To Facebook Exploring Students' Motivation and Experiences in Online CommunitiesDocument10 pagesDeng, Tavares - 2013 - From Moodle To Facebook Exploring Students' Motivation and Experiences in Online CommunitiesjuliaNo ratings yet
- Investigating Students' Perceptions of Motivating Factors of Online Class DiscussionsDocument26 pagesInvestigating Students' Perceptions of Motivating Factors of Online Class DiscussionsMaxine Leslie EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Learning Behavioral Patterns of Students With Varying Performance in A High School Mathematics Course Using An Ebook SystemDocument24 pagesLearning Behavioral Patterns of Students With Varying Performance in A High School Mathematics Course Using An Ebook SystemAlejandraNo ratings yet
- Comparing Online Discussion Forums To Traditional In-Person DiscussionsDocument5 pagesComparing Online Discussion Forums To Traditional In-Person DiscussionsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social Media in Academic PerformanceDocument6 pagesImpact of Social Media in Academic PerformanceLaura BarriosNo ratings yet
- 05 Jurnalijevssiti APDocument6 pages05 Jurnalijevssiti APNURUL HAZIQAH MD BADRUL HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Teknologi: O C L E P A O P B C L MDocument6 pagesJurnal Teknologi: O C L E P A O P B C L MLisdayantiNo ratings yet
- PracDocument5 pagesPracJAMES HAROLD GUMOLON MAGHANOYNo ratings yet
- Usage of Social Media Tools For Collaborative Learning: The Effect On Learning Success With The Moderating Role of CyberbullyingDocument35 pagesUsage of Social Media Tools For Collaborative Learning: The Effect On Learning Success With The Moderating Role of CyberbullyingJhon Raymart BorrerosNo ratings yet
- Sumida Garcia 2017Document25 pagesSumida Garcia 2017MohammedJibrinNo ratings yet
- Title and AuthorDocument3 pagesTitle and Authoredsonmamaradlo23No ratings yet
- Social Media Usage and Academic Performance From A Cognitive Loading PerspectiveDocument16 pagesSocial Media Usage and Academic Performance From A Cognitive Loading PerspectiveVcore MusicNo ratings yet
- Integrated Three Theories Academic PerformanceDocument22 pagesIntegrated Three Theories Academic Performanceapi-560536000No ratings yet
- Angel I Data MiningDocument18 pagesAngel I Data MiningHani DewiNo ratings yet
- Review 20 ArticelsDocument16 pagesReview 20 ArticelsVigo DikaprioNo ratings yet
- Impact of Students Attitudes TowardsDocument14 pagesImpact of Students Attitudes Towardsangelica de jesusNo ratings yet
- Siddhardha RPDocument5 pagesSiddhardha RPkhyathiswaroop2002No ratings yet
- EducDocument16 pagesEducSaplan, Jezrell Evan AganaNo ratings yet
- Benefitsofusing Social MediaDocument4 pagesBenefitsofusing Social Mediatheresa crawfordNo ratings yet
- 645pm - 4.epra Journals .E-5207Document4 pages645pm - 4.epra Journals .E-5207Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Effects of E-Learning On Students MotivationDocument9 pagesEffects of E-Learning On Students MotivationReffy AnyatiNo ratings yet
- Computers & Education: Qing-Ke Fu, Gwo-Jen HwangDocument15 pagesComputers & Education: Qing-Ke Fu, Gwo-Jen HwangBaha'ul WardahNo ratings yet
- Brit J Educational Tech - 2021 - OuyangDocument21 pagesBrit J Educational Tech - 2021 - OuyangVivi MauritaniaNo ratings yet
- 61d6ce7d1f9625 97045802Document8 pages61d6ce7d1f9625 97045802shresthanikhil078No ratings yet
- Engagement Detection in Online Learning: A ReviewDocument20 pagesEngagement Detection in Online Learning: A ReviewRamón PérezNo ratings yet
- Benefitsofusing Social MediaDocument4 pagesBenefitsofusing Social MediaRayhane EljraidiNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Using Social Media: January 2018Document4 pagesBenefits of Using Social Media: January 2018Saima KhatunNo ratings yet
- Effects of E-Learning On Students' MotivationDocument9 pagesEffects of E-Learning On Students' Motivationg-21543720No ratings yet
- Usage of Social MediaDocument34 pagesUsage of Social Mediaapi-563385491No ratings yet
- Jurnal InggrisDocument14 pagesJurnal InggrisLivia SyafhiraNo ratings yet
- Influence of Social MediaDocument5 pagesInfluence of Social MediaManjiri NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Article CritiqueDocument2 pagesArticle CritiqueAlexandra SofiaNo ratings yet
- Perceptions of Higher Education Students Towards E-Learning and Face-to-Face Learning in Pakistani ContextDocument8 pagesPerceptions of Higher Education Students Towards E-Learning and Face-to-Face Learning in Pakistani ContextInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Social Media Effect On Students Academic Performance Based On Their Usage1Document7 pagesSocial Media Effect On Students Academic Performance Based On Their Usage1SoPe MeNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Students Online Learning Behavior in Blended Courses Using MoodleDocument17 pagesAnalyzing Students Online Learning Behavior in Blended Courses Using MoodlesandraNo ratings yet
- 2022 OthDocument16 pages2022 OthglennmedidasNo ratings yet
- Tugas Itkao Bab 9 NajiaDocument2 pagesTugas Itkao Bab 9 Najiaetirah32No ratings yet
- Learningstyles AdetailedliteraturereviewDocument10 pagesLearningstyles AdetailedliteraturereviewNur Aliyah AisyahNo ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom Research and Trends From Different Fields of StudyDocument29 pagesFlipped Classroom Research and Trends From Different Fields of StudyTio HartantoNo ratings yet
- Social Networking Practices Its Influence To The Study Habits of College StudentsDocument10 pagesSocial Networking Practices Its Influence To The Study Habits of College StudentsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Carless2020 From Teacher TransmissionDocument11 pagesCarless2020 From Teacher TransmissionFHAIRODZ DAEN ALAMADANo ratings yet
- 10 17718-Tojde 471918-556241Document14 pages10 17718-Tojde 471918-556241Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- SSRN 3785511Document12 pagesSSRN 3785511francessihebom10No ratings yet
- Retaining Learners by Establishing Harmonious Relationships in E-Learning EnvironmentDocument15 pagesRetaining Learners by Establishing Harmonious Relationships in E-Learning EnvironmentBrittany Caroline BlackNo ratings yet
- Quick Hits for Teaching with Technology: Successful Strategies by Award-Winning TeachersFrom EverandQuick Hits for Teaching with Technology: Successful Strategies by Award-Winning TeachersNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technologies for the Classroom: A Learning Sciences PerspectiveFrom EverandEmerging Technologies for the Classroom: A Learning Sciences PerspectiveNo ratings yet
- EDUC 108 - Ecological LiteracyDocument17 pagesEDUC 108 - Ecological LiteracyLee DuquiatanNo ratings yet
- CT: Biennial Report On School Districts' EffortsDocument108 pagesCT: Biennial Report On School Districts' EffortsPatricia DillonNo ratings yet
- DISASTER RESPONSE AND RISK REDUCTION - Q3 - SLM11-without Answer KeyDocument15 pagesDISASTER RESPONSE AND RISK REDUCTION - Q3 - SLM11-without Answer KeyDeceree Mae RemeticadoNo ratings yet
- TIP Mod.4 2020 2021 Output To Be AccomplishedDocument47 pagesTIP Mod.4 2020 2021 Output To Be AccomplishedBelle Herminigildo AngelesNo ratings yet
- PDCA ManamentDocument14 pagesPDCA ManamentLalitSinghNo ratings yet
- Seminar in Teaching: Osias College, IncDocument4 pagesSeminar in Teaching: Osias College, Incclara dupitasNo ratings yet
- Elsa Andrew Hilarion 930120-12-5598 Pismp Tesl SK (1) Teaching Grammar Task 4: Academic WritingDocument4 pagesElsa Andrew Hilarion 930120-12-5598 Pismp Tesl SK (1) Teaching Grammar Task 4: Academic WritingBryan AndrewNo ratings yet
- Sample Book ReviewDocument4 pagesSample Book ReviewApril Vargas100% (1)
- Final Teaching of Literacy Skills (EDU410) Complete Handout..Document154 pagesFinal Teaching of Literacy Skills (EDU410) Complete Handout..Rashid Ishfaq100% (1)
- El-113-Lpjhea FinalDocument8 pagesEl-113-Lpjhea Finaljheacawayan1018No ratings yet
- Creative Thinking in Mathematics PDFDocument6 pagesCreative Thinking in Mathematics PDFriadimazz_910414786No ratings yet
- Microcurricular Planning by Skills and Performance Criteria: Commented (A1)Document6 pagesMicrocurricular Planning by Skills and Performance Criteria: Commented (A1)Rous Illescas100% (1)
- Health-6-Cot Lesson Plan 4TH QuarterDocument3 pagesHealth-6-Cot Lesson Plan 4TH Quarterivy marie gaga-aNo ratings yet
- Le Waijiao Magazine Volume 9Document52 pagesLe Waijiao Magazine Volume 9Le Waijiao - CEO OfficeNo ratings yet
- Ed 6055 Wiat-Iii Presentation - Kayla LentzDocument13 pagesEd 6055 Wiat-Iii Presentation - Kayla Lentzapi-543728028No ratings yet
- Tqi - Evidence Map - ConciseDocument1 pageTqi - Evidence Map - Conciseapi-243028886No ratings yet
- Supervisor Observation 1 Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesSupervisor Observation 1 Lesson Planapi-325281014No ratings yet
- NCBSSH-TDNA Guide and Tools December2012Document49 pagesNCBSSH-TDNA Guide and Tools December2012Roderick Gatdula100% (33)
- g8 t1 Pretechnical Studies MidtermDocument2 pagesg8 t1 Pretechnical Studies Midtermjaynerose gacheriNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Dynamic Physical Education For Elementary School Children 17th Edition Pangzazi Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Dynamic Physical Education For Elementary School Children 17th Edition Pangzazi Test Bank PDFantiquateouterlyhxhkwv100% (16)
- Choreographing The High School Musical:: Teaching Methods For Teaching Choreography To A High School Theatre CompanyDocument14 pagesChoreographing The High School Musical:: Teaching Methods For Teaching Choreography To A High School Theatre Companyapi-341643700No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: at The End of The Lesson, The Learners CANDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: at The End of The Lesson, The Learners CANyezzhNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans - Weebly Cirg 644 l1Document2 pagesLesson Plans - Weebly Cirg 644 l1api-542550614No ratings yet
- KSSR Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesKSSR Lesson PlanHasdey HariminNo ratings yet
- Univ 1001 Unit 2 Written AssignmentDocument3 pagesUniv 1001 Unit 2 Written AssignmentKareem ObeidNo ratings yet
- Internship+Report-BUS498 8+Ishtiaque+Sarowar+Utsho+1912681630Document45 pagesInternship+Report-BUS498 8+Ishtiaque+Sarowar+Utsho+1912681630Fahrisah TazreeNo ratings yet
Jamal Abdul Ansari University of India - Nawab Ali Khan University of India
Jamal Abdul Ansari University of India - Nawab Ali Khan University of India
Uploaded by
ashlie garciaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jamal Abdul Ansari University of India - Nawab Ali Khan University of India
Jamal Abdul Ansari University of India - Nawab Ali Khan University of India
Uploaded by
ashlie garciaCopyright:
Available Formats
Exploring the role of social media in collaborative learning the new domain
of learning
Jamal Abdul Ansari University of India | Nawab Ali Khan University of India
Ashlie García 10138827
Materials Results Conclusion
Abstract Many kinds of research confronted on the applicability of social media
it was observed that seven out of the seven proposed hypotheses were
and mobile devices in higher education for interaction with Based on the empirical investigation, it could be noted that application
This study is an attempt to examine the application and usefulness of accepted and 78% of the explained variance in students’ academic
colleagues.90% of faculty members use some social media in courses and usefulness of the social media in transferring the resource materials,
performance, 60% explained variance in interactivity with teachers, 48%
social media and mobile devices in transferring the resources and interaction they were usually teaching or professional purposes out of the campus collaborative learning and interaction with the colleagues as well as
variance in interactivity with peers, 43% variance in online knowledge
with academicians in higher education institutions across the boundary wall, life. Facebook and YouTube are the most visited sites for the teachers would facilitate students to be more enthusiastic and dynamic.
sharing behavior and 79% variance in students’ engagement.
a hitherto unexplained area of research. professional outcomes. This study provides guidelines to the corporate world in formulating
strategies regarding the use of social media for collaborative learning.
This empirical study is based on the survey of 360 students at a university in
eastern India, cognizing students’ perception on social media and mobile
devices through collaborative learning, interactivity with peers, teachers and
its significant impact on students’ academic performance.
The study revealed that online social media used for collaborative learning
had a significant impact on interactivity with peers, teachers and online
knowledge sharing behavior. References
Akçayır, G. (2017). Why do faculty members use or not use social
it would be valuable to mention that use of online social media for
networking sites for education? Computers in Human Behavior, 71, 378–
collaborative learning facilitate students to be more creative, dynamic and
385.
research-oriented. It is purely a domain of knowledge. Methodology Use of social media for collaborating learning has a significant positive Al-Alwan, A. F. (2014). Modeling the relations among parental
association with online knowledge sharing behavior, meaning thereby involvement, school engagement and academic performance of high
To check the students’ perception on social media for collaborative
that the more intense use of social media for collaborative learning by school students. International Education Studies, 7(4), 47–56.
learning in higher education institutions, Data were gathered both offline
university students, the more knowledge sharing between peers and Al-Rahmi, W. M., Alias, N., Othman, M. S., Marin, V. I., & Tur, G.
and online survey administered to students from one public university in
colleagues. (2018). A model of factors affecting learning performance through the
Eastern India.
use of social media in Malaysian higher education. Computers &
Also, interaction with the teacher seen the significant statistical positive Education, 121, 59–72.
A sample of 360 undergraduate students was collected by convenience
association with students' engagement, saying that the more conversation Arbuckle, J. (2008). Amos 17.0 user's guide. Chicago: SPSS Inc..
sampling method of a public university in Eastern India. The proposed
with teachers, leads to a high level of student's engagement. Barnes, N. G., & Lescault, A. M. (2011). Social media adoption soars as
model of study was measured and evaluated using variance based
higher-ed experiments and reevaluates its use of new communications
structured equation model.
Introduction The practical interpretation of this result is that there is an expected 4.5% tools. North Dartmouth: Center for Marketing Research. University of
increase in student’s participation for every 10% increase in interaction Massachusetts Dartmouth.
The Educause Center for Applied Research [ECAR] (2012) surveyed with teachers. Interaction with peers has a significant positive Bertheussen, B. A., & Myrland, Ø. (2016). Relation between academic
students in higher education mentioned that students are pouring the association with students' engagement. Practically, the finding revealed performance and students’ engagement in digital learning
acceptance of mobile computing devices (cellphones, smartphones, and that 10% upturn in student’s involvement, there is a 2.1% increase in activities. Journal of Education for Business, 91(3), 125–131.
tablet) in Higher Education Institutions (HEIs), roughly 67% surveyed peer’s interaction. There is a significant positive association between Bogdanov, E., Limpens, F., Li, N., El Helou, S., Salzmann, C., & Gillet,
students accepted that mobile devices and social media play a vital role online knowledge sharing behavior and students' engagement, and D. (2012). A social media platform in higher education. In Proceedings
in their academic performance and career enhancement. finally students' engagement has been a statistically significant positive of the 2012 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference
relationship with students’ academic performance, this is the clear (EDUCON) (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Use of social media and mobile devices presents both advantages as well indication that more engaged students in collaborative learning via social Byrne, B. M. (1994). Structural equation modeling with EQS and
as challenges, mostly its benefits seen in terms of accessing course media leads to better students’ academic performance. EQS/windows: basic concepts, applications, and programming.
contents, video clip, transfer of the instructional notes etc. Overall Thousand Oaks: Sage.
students feel that social media and mobile devices are the cheap and Accordingly, the use of online social media for collaborative learning, Cain, J. (2008). Online social networking issues within academia and
convenient tools of obtaining relevant information. Studies in western interaction with mentors and colleagues lead better student’s engagement pharmacy education. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education.
countries have confronted that online social media use for collaborative which consequently affects student’s academic performance. The higher Cao, Y., Ajjan, H., & Hong, P. (2013). Using social media applications
learning has a significant contribution to students’ academic performance education authority should provide such a platform which can nurture for educational outcomes in college teaching: a structural equation
and satisfaction. When the students were asked for what reason did, they use social the student’s intellectual talents. Based on the empirical investigation, it analysis. British Journal of Educational Technology, 44(4), 581–593.
media, it was seen that rarely using for self-promotion, very frequently would be said that students’ engagement, social media communication Cavus, N., & Ibrahim, D. (2008). A mobile tool for learning English
The purpose of this research project was to explore how learning and using for self-education, often used for passing the time with friends, and devices facilitate students to retrieve information and interact with others words, Online Submission (pp. 6–9)
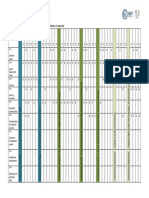
teaching activities in higher education institutions were affected by the so many fruitful information the image mentioned above depicting. in real-time regarding sharing teaching materials contents. Chemers, M. M., Hu, L. T., & Garcia, B. F. (2001). Academic self-
integration and application of mobile devices in sharing the resource efficacy and first-year college student performance and
materials, interaction with colleagues and students’ academic This study was conducted on university students, ignoring the faculty adjustment. Journal of Educational Psychology, 93(1), 55–64.
performance. The broad goal of this research was to contemporize the in- members, it might be possible that the faculty members would not have Field, A. (2013). Factor analysis using SPSS. Scientific Research and
depth perspectives of students’ perception of mobile devices and social been interested in interacting with the students. Thus, future research Essays, 22(June), 1–26
media in learning and teaching activities. could be possible towards faculty members in different higher education Jackson, C. (2011). Your students love social media… and so can
institutions. you. Teaching Tolerance, 39, 38–41.
Social media and mobile devices allow the students to create, edit and Lenhart, A., Arafeh, S., & Smith, A. (2008). Writing, technology and
share the course contents in textual, video or audio forms. These teens. Pew Internet & American Life Project.
technological innovations give birth to a new kind of learning cultures,
learning based on the principles of collective exploration and interaction.
You might also like
- TMA01 Handout Planner For Final Work 1Document11 pagesTMA01 Handout Planner For Final Work 1Eland ExamsNo ratings yet
- Article Critique Essay - Social Media in LearningDocument3 pagesArticle Critique Essay - Social Media in LearningAlexandra Sofia86% (7)
- Technology Resources Improvement PlanDocument2 pagesTechnology Resources Improvement PlanChristine De San Jose80% (10)
- Training CurriculumDocument2 pagesTraining CurriculumGeetliM100% (5)
- Succeed in Cambridge Cae 10 Practice Tests Key Scribd PDFDocument3 pagesSucceed in Cambridge Cae 10 Practice Tests Key Scribd PDFGiulia ChireaNo ratings yet
- 01 Gonzales Et Al 1-16Document16 pages01 Gonzales Et Al 1-16JM SanchezNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Social Media Assisted Course On Learning Self EfficacyDocument12 pagesEffectiveness of Social Media Assisted Course On Learning Self EfficacyleandroNo ratings yet
- School Counselors' Use of Technology For Program ManagementDocument10 pagesSchool Counselors' Use of Technology For Program ManagementAdam ZiyyadNo ratings yet
- Poster en InglesDocument1 pagePoster en InglesAnonymous 4QjI1ccqNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social Media Usage On Students AcademicDocument7 pagesImpact of Social Media Usage On Students AcademicSu Kings AbetoNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Education and Teaching InternationalDocument12 pagesInnovations in Education and Teaching InternationalNis NosNo ratings yet
- RMB - Research Proposal A6Document10 pagesRMB - Research Proposal A6Harshit ShubhankarNo ratings yet
- 10 1108 - Jrit 10 2022 0061Document22 pages10 1108 - Jrit 10 2022 0061cjscarecrew34No ratings yet
- Taggart Wheeler 2023 Collaborative Learning As Constructivist Practice An Exploratory Qualitative Descriptive Study ofDocument18 pagesTaggart Wheeler 2023 Collaborative Learning As Constructivist Practice An Exploratory Qualitative Descriptive Study ofmargaridaNo ratings yet
- The Relationships Between Self-Efficacy, Task Value, and Self-Regulated Learning Strategies in Massive Open Online CoursesDocument18 pagesThe Relationships Between Self-Efficacy, Task Value, and Self-Regulated Learning Strategies in Massive Open Online CoursesLarry PalaganasNo ratings yet
- F10470476S519Document5 pagesF10470476S519sanya kundraNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Role ofDocument15 pagesExploring The Role ofSparsha SNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of The Key Components of Online Pee - 2024 - Educational ResDocument27 pagesA Systematic Review of The Key Components of Online Pee - 2024 - Educational ResYOHANES KURNIAWANNo ratings yet
- Deng, Tavares - 2013 - From Moodle To Facebook Exploring Students' Motivation and Experiences in Online CommunitiesDocument10 pagesDeng, Tavares - 2013 - From Moodle To Facebook Exploring Students' Motivation and Experiences in Online CommunitiesjuliaNo ratings yet
- Investigating Students' Perceptions of Motivating Factors of Online Class DiscussionsDocument26 pagesInvestigating Students' Perceptions of Motivating Factors of Online Class DiscussionsMaxine Leslie EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Learning Behavioral Patterns of Students With Varying Performance in A High School Mathematics Course Using An Ebook SystemDocument24 pagesLearning Behavioral Patterns of Students With Varying Performance in A High School Mathematics Course Using An Ebook SystemAlejandraNo ratings yet
- Comparing Online Discussion Forums To Traditional In-Person DiscussionsDocument5 pagesComparing Online Discussion Forums To Traditional In-Person DiscussionsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social Media in Academic PerformanceDocument6 pagesImpact of Social Media in Academic PerformanceLaura BarriosNo ratings yet
- 05 Jurnalijevssiti APDocument6 pages05 Jurnalijevssiti APNURUL HAZIQAH MD BADRUL HISHAMNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Teknologi: O C L E P A O P B C L MDocument6 pagesJurnal Teknologi: O C L E P A O P B C L MLisdayantiNo ratings yet
- PracDocument5 pagesPracJAMES HAROLD GUMOLON MAGHANOYNo ratings yet
- Usage of Social Media Tools For Collaborative Learning: The Effect On Learning Success With The Moderating Role of CyberbullyingDocument35 pagesUsage of Social Media Tools For Collaborative Learning: The Effect On Learning Success With The Moderating Role of CyberbullyingJhon Raymart BorrerosNo ratings yet
- Sumida Garcia 2017Document25 pagesSumida Garcia 2017MohammedJibrinNo ratings yet
- Title and AuthorDocument3 pagesTitle and Authoredsonmamaradlo23No ratings yet
- Social Media Usage and Academic Performance From A Cognitive Loading PerspectiveDocument16 pagesSocial Media Usage and Academic Performance From A Cognitive Loading PerspectiveVcore MusicNo ratings yet
- Integrated Three Theories Academic PerformanceDocument22 pagesIntegrated Three Theories Academic Performanceapi-560536000No ratings yet
- Angel I Data MiningDocument18 pagesAngel I Data MiningHani DewiNo ratings yet
- Review 20 ArticelsDocument16 pagesReview 20 ArticelsVigo DikaprioNo ratings yet
- Impact of Students Attitudes TowardsDocument14 pagesImpact of Students Attitudes Towardsangelica de jesusNo ratings yet
- Siddhardha RPDocument5 pagesSiddhardha RPkhyathiswaroop2002No ratings yet
- EducDocument16 pagesEducSaplan, Jezrell Evan AganaNo ratings yet
- Benefitsofusing Social MediaDocument4 pagesBenefitsofusing Social Mediatheresa crawfordNo ratings yet
- 645pm - 4.epra Journals .E-5207Document4 pages645pm - 4.epra Journals .E-5207Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- Effects of E-Learning On Students MotivationDocument9 pagesEffects of E-Learning On Students MotivationReffy AnyatiNo ratings yet
- Computers & Education: Qing-Ke Fu, Gwo-Jen HwangDocument15 pagesComputers & Education: Qing-Ke Fu, Gwo-Jen HwangBaha'ul WardahNo ratings yet
- Brit J Educational Tech - 2021 - OuyangDocument21 pagesBrit J Educational Tech - 2021 - OuyangVivi MauritaniaNo ratings yet
- 61d6ce7d1f9625 97045802Document8 pages61d6ce7d1f9625 97045802shresthanikhil078No ratings yet
- Engagement Detection in Online Learning: A ReviewDocument20 pagesEngagement Detection in Online Learning: A ReviewRamón PérezNo ratings yet
- Benefitsofusing Social MediaDocument4 pagesBenefitsofusing Social MediaRayhane EljraidiNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Using Social Media: January 2018Document4 pagesBenefits of Using Social Media: January 2018Saima KhatunNo ratings yet
- Effects of E-Learning On Students' MotivationDocument9 pagesEffects of E-Learning On Students' Motivationg-21543720No ratings yet
- Usage of Social MediaDocument34 pagesUsage of Social Mediaapi-563385491No ratings yet
- Jurnal InggrisDocument14 pagesJurnal InggrisLivia SyafhiraNo ratings yet
- Influence of Social MediaDocument5 pagesInfluence of Social MediaManjiri NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Article CritiqueDocument2 pagesArticle CritiqueAlexandra SofiaNo ratings yet
- Perceptions of Higher Education Students Towards E-Learning and Face-to-Face Learning in Pakistani ContextDocument8 pagesPerceptions of Higher Education Students Towards E-Learning and Face-to-Face Learning in Pakistani ContextInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Social Media Effect On Students Academic Performance Based On Their Usage1Document7 pagesSocial Media Effect On Students Academic Performance Based On Their Usage1SoPe MeNo ratings yet
- Analyzing Students Online Learning Behavior in Blended Courses Using MoodleDocument17 pagesAnalyzing Students Online Learning Behavior in Blended Courses Using MoodlesandraNo ratings yet
- 2022 OthDocument16 pages2022 OthglennmedidasNo ratings yet
- Tugas Itkao Bab 9 NajiaDocument2 pagesTugas Itkao Bab 9 Najiaetirah32No ratings yet
- Learningstyles AdetailedliteraturereviewDocument10 pagesLearningstyles AdetailedliteraturereviewNur Aliyah AisyahNo ratings yet
- Flipped Classroom Research and Trends From Different Fields of StudyDocument29 pagesFlipped Classroom Research and Trends From Different Fields of StudyTio HartantoNo ratings yet
- Social Networking Practices Its Influence To The Study Habits of College StudentsDocument10 pagesSocial Networking Practices Its Influence To The Study Habits of College StudentsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Carless2020 From Teacher TransmissionDocument11 pagesCarless2020 From Teacher TransmissionFHAIRODZ DAEN ALAMADANo ratings yet
- 10 17718-Tojde 471918-556241Document14 pages10 17718-Tojde 471918-556241Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- SSRN 3785511Document12 pagesSSRN 3785511francessihebom10No ratings yet
- Retaining Learners by Establishing Harmonious Relationships in E-Learning EnvironmentDocument15 pagesRetaining Learners by Establishing Harmonious Relationships in E-Learning EnvironmentBrittany Caroline BlackNo ratings yet
- Quick Hits for Teaching with Technology: Successful Strategies by Award-Winning TeachersFrom EverandQuick Hits for Teaching with Technology: Successful Strategies by Award-Winning TeachersNo ratings yet
- Emerging Technologies for the Classroom: A Learning Sciences PerspectiveFrom EverandEmerging Technologies for the Classroom: A Learning Sciences PerspectiveNo ratings yet
- EDUC 108 - Ecological LiteracyDocument17 pagesEDUC 108 - Ecological LiteracyLee DuquiatanNo ratings yet
- CT: Biennial Report On School Districts' EffortsDocument108 pagesCT: Biennial Report On School Districts' EffortsPatricia DillonNo ratings yet
- DISASTER RESPONSE AND RISK REDUCTION - Q3 - SLM11-without Answer KeyDocument15 pagesDISASTER RESPONSE AND RISK REDUCTION - Q3 - SLM11-without Answer KeyDeceree Mae RemeticadoNo ratings yet
- TIP Mod.4 2020 2021 Output To Be AccomplishedDocument47 pagesTIP Mod.4 2020 2021 Output To Be AccomplishedBelle Herminigildo AngelesNo ratings yet
- PDCA ManamentDocument14 pagesPDCA ManamentLalitSinghNo ratings yet
- Seminar in Teaching: Osias College, IncDocument4 pagesSeminar in Teaching: Osias College, Incclara dupitasNo ratings yet
- Elsa Andrew Hilarion 930120-12-5598 Pismp Tesl SK (1) Teaching Grammar Task 4: Academic WritingDocument4 pagesElsa Andrew Hilarion 930120-12-5598 Pismp Tesl SK (1) Teaching Grammar Task 4: Academic WritingBryan AndrewNo ratings yet
- Sample Book ReviewDocument4 pagesSample Book ReviewApril Vargas100% (1)
- Final Teaching of Literacy Skills (EDU410) Complete Handout..Document154 pagesFinal Teaching of Literacy Skills (EDU410) Complete Handout..Rashid Ishfaq100% (1)
- El-113-Lpjhea FinalDocument8 pagesEl-113-Lpjhea Finaljheacawayan1018No ratings yet
- Creative Thinking in Mathematics PDFDocument6 pagesCreative Thinking in Mathematics PDFriadimazz_910414786No ratings yet
- Microcurricular Planning by Skills and Performance Criteria: Commented (A1)Document6 pagesMicrocurricular Planning by Skills and Performance Criteria: Commented (A1)Rous Illescas100% (1)
- Health-6-Cot Lesson Plan 4TH QuarterDocument3 pagesHealth-6-Cot Lesson Plan 4TH Quarterivy marie gaga-aNo ratings yet
- Le Waijiao Magazine Volume 9Document52 pagesLe Waijiao Magazine Volume 9Le Waijiao - CEO OfficeNo ratings yet
- Ed 6055 Wiat-Iii Presentation - Kayla LentzDocument13 pagesEd 6055 Wiat-Iii Presentation - Kayla Lentzapi-543728028No ratings yet
- Tqi - Evidence Map - ConciseDocument1 pageTqi - Evidence Map - Conciseapi-243028886No ratings yet
- Supervisor Observation 1 Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesSupervisor Observation 1 Lesson Planapi-325281014No ratings yet
- NCBSSH-TDNA Guide and Tools December2012Document49 pagesNCBSSH-TDNA Guide and Tools December2012Roderick Gatdula100% (33)
- g8 t1 Pretechnical Studies MidtermDocument2 pagesg8 t1 Pretechnical Studies Midtermjaynerose gacheriNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Dynamic Physical Education For Elementary School Children 17th Edition Pangzazi Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Dynamic Physical Education For Elementary School Children 17th Edition Pangzazi Test Bank PDFantiquateouterlyhxhkwv100% (16)
- Choreographing The High School Musical:: Teaching Methods For Teaching Choreography To A High School Theatre CompanyDocument14 pagesChoreographing The High School Musical:: Teaching Methods For Teaching Choreography To A High School Theatre Companyapi-341643700No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: at The End of The Lesson, The Learners CANDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: at The End of The Lesson, The Learners CANyezzhNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans - Weebly Cirg 644 l1Document2 pagesLesson Plans - Weebly Cirg 644 l1api-542550614No ratings yet
- KSSR Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesKSSR Lesson PlanHasdey HariminNo ratings yet
- Univ 1001 Unit 2 Written AssignmentDocument3 pagesUniv 1001 Unit 2 Written AssignmentKareem ObeidNo ratings yet
- Internship+Report-BUS498 8+Ishtiaque+Sarowar+Utsho+1912681630Document45 pagesInternship+Report-BUS498 8+Ishtiaque+Sarowar+Utsho+1912681630Fahrisah TazreeNo ratings yet