Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module:2 Procurement of HR
Module:2 Procurement of HR
Uploaded by
seena150 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views39 pagesThe document discusses job analysis, which is defined as a systematic process of studying and collecting information about the tasks, duties, and requirements of a specific job. It describes the objectives and uses of job analysis, which include organizational design, recruitment and selection, employee training, and performance evaluation. The key steps in conducting a job analysis are identified as determining the purpose, collecting background information, selecting jobs, gathering data, processing information, creating job descriptions and specifications. Common methods of job analysis mentioned are interviews, participant diaries/logs, critical incidents, and technical conferences.
Original Description:
Original Title
JOB ANALYSIS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses job analysis, which is defined as a systematic process of studying and collecting information about the tasks, duties, and requirements of a specific job. It describes the objectives and uses of job analysis, which include organizational design, recruitment and selection, employee training, and performance evaluation. The key steps in conducting a job analysis are identified as determining the purpose, collecting background information, selecting jobs, gathering data, processing information, creating job descriptions and specifications. Common methods of job analysis mentioned are interviews, participant diaries/logs, critical incidents, and technical conferences.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views39 pagesModule:2 Procurement of HR
Module:2 Procurement of HR
Uploaded by
seena15The document discusses job analysis, which is defined as a systematic process of studying and collecting information about the tasks, duties, and requirements of a specific job. It describes the objectives and uses of job analysis, which include organizational design, recruitment and selection, employee training, and performance evaluation. The key steps in conducting a job analysis are identified as determining the purpose, collecting background information, selecting jobs, gathering data, processing information, creating job descriptions and specifications. Common methods of job analysis mentioned are interviews, participant diaries/logs, critical incidents, and technical conferences.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 39
Module:2 Procurement of HR
• Module II : Procurement of HR: Meaning and
Importance of HR planning ; Job analysis---
process of job analysis, job description, job
specification, methods of job analysis;
Conventional Vs strategic planning;
Recruitment – concept, sources ; Selection –
concept , Difference between recruitment and
selection, process- test, interview, placement,
induction and socialization; retention
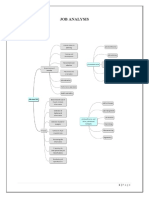
Job Job
Determine recruitment analysi
Analysis
HRP And selection s and job
& job
design
design
JOB ANALYSIS
• Job analysis is a detailed and systematic study
of jobs to know the nature and characteristics of
the people to be employed on various jobs.
• It is the process of discovering and identifying
the pertinent information relating to the nature of
a specific job.
• It is the determination of tasks which comprises
the job and of the skills, knowledge, abilities and
attitude required of the worker for the successful
performance of the job.
DEFINITION OF JOB ANALYSIS
• EDWIN B.FLIPPO
“Job analysis is the process of
studying and collecting information relating
to the operations and responsibilities of a
specific job”
Objectives of job analysis
1.Work simplification
2.Establishment of standard performance
3.Support personnel activities.
Uses of Job Analysis
• 1. Achievement of Goals:Jobs are at the
core of every organization’s productivity, if
they are designed well and done right, the
organization makes progress towards its
objectives. Otherwise, productivity suffers,
profits fall, and the organization is less
able to meet the demands of society,
customer, employees, and other with a
stake in its success.
• 2. Organizational Design: Job analysis will be
useful in classifying the jobs and the
interrelationships among the jobs. On the basis
of information obtained through job analysis,
sound decisions regarding hierarchical positions
and functional differentiation can be taken and
this will improve operational efficiency.
• 3. Organization and Manpower Planning: It is
helpful in organization planning, for it defines
labour in concrete terms and co-ordinates the
activities of the work force, and clearly divides
duties and responsibilities.
• 4. Recruitment and Selection: Job analysis
provides you with information on what the
job entails and what human requirements
are required to carry out these activities.
This information is the basis on which you
decide what sort of people to recruit and
hire
• 5. Placement and Orientation: Job
analysis helps in matching the job
requirements with the abilities, interests
and aptitudes of people. Jobs will be
assigned to persons on the basis of
suitability for the job. The orientation
programme will help the employee in
learning the activities and understanding
duties that are required to perform a given
job more effectively
• 6. Employee Training and Management
Development: Job analysis provides the
necessary information to the management
of training and development programmes.
It helps in to determine the content and
subject matter of in training courses. It
also helps in checking application
information, interviewing test results and in
checking references.
• 7. Job Evaluation and Compensation: Job
evaluation is the process of determining
the relative worth of different jobs in an
organization with a view to link
compensation, both basic and
supplementary, with the worth of the jobs.
The worth of a job is determined on the
basis of job characteristics and job holder
characteristics. Job analysis provides both
in the forms of job description and job
specification.
• 8. Performance Appraisal: Performance
appraisal involves comparing each employee’s
actual performance with his or her desired
performance. Through job analysis industrial
engineers and other experts determine
standards to be achieved and specific activities
to be performed.
• 9. Health and Safety: It provides an opportunity
for identifying hazardous conditions and
unhealthy environmental factors so that
corrective measures may be taken to minimize
and avoid the possibility of accidents
• 10. Employee Counseling: Job analysis
provides information about career choices
and personal limitation. Such information
is helpful in vocational guidance and
rehabilitation counseling. Employees who
are unable to cope with the hazards and
demands of given jobs may be advised to
opt for subsidiary jobs or to seek
premature retirement.
JOB ANALYSIS PROCESS
1) Determine the Use of the Job Analysis
Information
2) Collection of Background Information
3) Selection of Jobs for Analysis
4) Collection of Job Analysis Data
5) Processing the Information
6) Preparing Job Descriptions and Job
Classifications
7) Developing Job Specifications
Steps in Job Analysis
• 1. Determine the Use of the Job Analysis
Information: Start by identifying the use to
which the information will be put, since this
will determine the type of data you collect
and the technique you use to collect them.
• 2. Collection of Background Information: This
information can be had by reviewing available
background information such as organization
charts (which show how the job in question
relates to other jobs and where they fit into the
overall organization); class specifications (which
describe the general requirements of the class of
job to which the job under analysis belongs); and
the existing job descriptions which provide a
starting point from which to build the revised job
description.
• 3. Selection of Jobs for Analysis: To do job
analysis is a costly and time consuming
process. It is hence, necessary to select a
representative sample of jobs for purposes
of analysis. Priorities of various jobs can
also be determined. A job may be selected
because it has undergone undocumented
changes in job content. The request for
analysis of a job may originate with the
employee, supervisor, or a manager
• 4. Collection of Job Analysis Data: Job data on
features of the job, requited employee qualification
and requirements, should be collected either form
the employees who actually perform a job; or from
other employees (such as foremen or supervisors)
who watch the workers doing a job and there by
acquire knowledge about it; or from the outside
persons, known as the trade job analysis who are
appointed to watch employees performing a job
• 5. Processing the Information: Once job
analysis information has been collected,
the next step is to place it in a form that
will make it useful to those charged with
the various personnel functions. Several
issues arise with respect to this. First, how
much detail is needed? Second, can the
job analysis information be expressed in
quantitative terms? These must be
considered properly.
• 6. Preparing Job Descriptions and Job
Classifications: Job information which has
been collected must be processed to
prepare the job description form. It is a
statement showing full details of the
activities of the job. Separate job description
forms may be used for various activities in
the job and may be compiled later on. The
job analysis is made with the help of these
description forms. These forms may be used
as reference for the future.
• 7. Developing Job Specifications: Job
specifications are also prepared on the basis
of information collected. It is a statement of
minimum acceptable qualities of the person
to be placed on the job. It specifies the
standard by which the qualities of the person
are measured. Job analyst prepares such
statement taking into consideration the skills
required in performing the job properly. Such
statement is used in selecting a person
matching with the job
METHODS OF JOB ANALYSIS
• 1. Participant Diary/Logs: Workers can be to keep
participant diary/long or lists of things they do during
the day. For every activity he or she engages in, the
employee records the activity (along with the time) in
a log. This can provide you with a very
comprehensive picture of the job, especially when it’s
supplemented with subsequent interviews with the
worker and his or her supervisor. This method
provides more accurate information if done faithfully.
• 2. Interview: There are three types of interviews you
can use to collect job analysis data: individual
interviews with each employee; group interviews
with groups of employees having the same job; and
supervisor interviews with one or more supervisors
who are thoroughly knowledgeable about the job
being analyzed. The group interview is used when a
large number of employees are performing similar or
identical work, since this can be a quick and
inexpensive way of learning about the job
• 3. Critical Incidents: In this method, job
holders are asked to describe incidents
concerning the job on the basis of their
past experience. The incidents so
collected are analyzed and classified
according to the job areas they describe, A
fairly picture of actual job requirements
can be obtained by distinguishing between
effective and ineffective behaviors of
workers on the job
• 4. Technical Conference Method: This method
utilizes supervisors with extensive knowledge of
the job. Here, specific characteristics of a job are
obtained from the “experts.”
• 5. Job Performance: Under this method, the job
analyst actually performs the job under study to
get first-hand experience of the actual tasks, and
physical and social demands of the job. This
method can be used only for jobs where skill
requirements are low and can be learnt quickly
and easily.
• 6. Functional Job Analysis: Functional job
analysis (FJA) is employee- oriented analytical approach
of job analysis. This approach attempts to describe the
whole person on the job.
• The main features of FJA include the following:
The extent to which specific instruction are necessary to
perform the task
The extent to which reasoning and judgment are
required to perform the task
The mathematical ability required to perform the task and
The verbal and language facilities required to perform
the task.
• 7. Observation Method: Using this method, a
job analyst watches employees directly on the
job. Observations are made on various tasks,
activities, the pace at which tasks are carried
out, and the way different activities are
performed. This method is suitable for jobs
that involve manual, standardized, and short
job cycle activities
• 8. Questionnaires: The method is usually
employed by engineering consultants.
Properly drafted questionnaires are sent out
to job-holders for completion and are returned
to supervisors.
• a. Position Analysis Questionnaire. Position
analysis questionnaire (PAQ) is a highly
specialized instrument for analyzing a job in terms
of employee activities. The PAQ developed by
Purdue University is a comprehensive
questionnaire for collecting information for job
analysis
Position Analysis Questionnaire
Job Aspects No. of elements
Information input - Where and how do 35
employee get information to do their job?
Mental processes- what reasoning, 14
planning, organizing, and decision making
is done?
Work output – what physical activities, 49
tools and machines are used?
Relationships – what contact with other 36
people, both in the company and outside is
maintained or developed?
Job context- what is the physical and social 19
context in which the job is maintained?
Other job characteristics – what other 42
activities, conditions or Characteristics not
covered by the categories are relevant?
• b. Management Position Description
Questionnaire: Management position
description is a highly structured
questionnaire containing 208 items
relating to managerial responsibilities,
restrictions, demands and other
miscellaneous position characteristics.
Components of job analysis
Components of job analysis
Job description Job specification
(It is the statement of task, duties , (It is the knowledge ,skill and abilities
responsibilities and context of the job)
required to perform the job satisfactorily
Job Description
• It is a written record of the duties,
responsibilities and requirements of a
particular job. It is concerned with the job
itself and not with the job holders. It is a
statement describing the job in such terms
as its title, location, duties, working
conditions and hazards
Definition
• Flippo has Defined Job Description as, “A job
description is an organized, factual statement
of duties and responsibilities of a specific job.
In brief, it should tell what is to be done. How
it is done why. It is a standard of function, in
that defines the appropriate and authorized
content of a job.
Job Specification
• The job specification states the minimum
acceptable qualifications that the
incumbent must possess to perform the
job successfully. Based on the information
acquired through job analysis, the job
specification identifies the knowledge,
skills, and abilities needed to do the job
effectively.
Definition
• Flippo has defined job specification as,
“Job specification is a statement of the
minimum acceptable human qualities
necessary to perform a job properly
………….. It is a standard of personnel
and designates the qualities required for
acceptable performance.”
• A Job Specification should include:
(i) Physical characteristics, which include health, strength,
endurance, age, height, weight, vision, voice, eye, hand
and foot co-ordination, motor co-ordination, and colour
discrimination.
(ii) Psychological and social characteristics such as
emotional stability, flexibility, decision making ability,
analytical view, mental ability, pleasing manners,
initiative, conversational ability etc.
(iii) Mental Characteristics such as general intelligence,
memory, judgement, ability to concentrate, foresight etc.
(iv) Personal Characteristics such as sex, education, family
background, job experience, hobbies, extracurricular
activities etc.
Job description Job specification
Job title Education
Location Experience
Job summery Training
Duties Initiative
Machines, tools and Physical effort
equipments Responsibilities
Materials and forms used Communication skill
Working condition Emotional
Supervision given or characteristics
received Unusual sensory
demands such as
sight,hearing,smell etc
You might also like
- Job Analysis and The Talent Management ProcessDocument27 pagesJob Analysis and The Talent Management Processabdullah islamNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis, Job Design and Quality of Work LifeDocument14 pagesJob Analysis, Job Design and Quality of Work Lifes1103294475% (8)
- Devin J Simon 2004 MOHAWK RD APT. 321 Pueblo, Co 81001: Employer Use Only Corp. DeptDocument2 pagesDevin J Simon 2004 MOHAWK RD APT. 321 Pueblo, Co 81001: Employer Use Only Corp. DeptemtteachNo ratings yet
- BSBMGT502 Manage People Performance Assessment Task 1-InstructionsDocument15 pagesBSBMGT502 Manage People Performance Assessment Task 1-InstructionsImran WaheedNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument31 pagesJob AnalysisAlamgir HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two1Document66 pagesChapter Two1Aklilu GirmaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Topic 4 - JOB ANALYSISDocument12 pagesUNIT 4 Topic 4 - JOB ANALYSISshubhamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 RSDocument16 pagesUnit 1 RSNingambika G MNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument6 pagesJob AnalysisAreeba ArifNo ratings yet
- 4 Job Analysis and Job DesignDocument45 pages4 Job Analysis and Job DesignAyanav BaruahNo ratings yet
- CH 02 Job Analysis and The Talent Management ProcessDocument66 pagesCH 02 Job Analysis and The Talent Management Processzahid583156No ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument5 pagesJob Analysissan291076No ratings yet
- HRM (Chapter No - 2)Document17 pagesHRM (Chapter No - 2)sujalmore9823No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - TM - Job AnalysisDocument33 pagesUnit 2 - TM - Job AnalysisMansi sharmaNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis And: The Talent Management ProcessDocument27 pagesJob Analysis And: The Talent Management ProcessKhairul Basher SujonNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis and Job DesignDocument17 pagesJob Analysis and Job DesignSufyan Ranjha100% (1)
- Concept of Job Analysis: Pcms-Bba 5 Sem HRMDocument12 pagesConcept of Job Analysis: Pcms-Bba 5 Sem HRMraazoo19No ratings yet
- Job Analysis and DescriptionDocument19 pagesJob Analysis and Descriptionheba abd elazizNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 (HR Notes)Document25 pagesUnit - 2 (HR Notes)Rohit GoyalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document11 pagesChapter 3Gizaw BelayNo ratings yet
- Shirin Chandraker 1Document31 pagesShirin Chandraker 1Shirin ChandrakerNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis ProjectDocument44 pagesJob Analysis Projectshaik karishmaNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis CHDocument42 pagesJob Analysis CHshefa AlsubaieNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis Work, Job, TaskDocument15 pagesJob Analysis Work, Job, TaskmanjushreeNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis HRDocument5 pagesJob Analysis HRSanjay Chandra SikakolluNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - 0Document12 pagesCH 3 - 0wubeNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - 0Document12 pagesCH 3 - 0Ebsa AdemeNo ratings yet
- IHRM WK 04 Lec 07 08Document9 pagesIHRM WK 04 Lec 07 08Khuzaima JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Training On SOP For JDDocument61 pagesTraining On SOP For JDMulugeta GebremedhinNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and Selection Module 1Document64 pagesRecruitment and Selection Module 1ningegowdaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - HRMDocument33 pagesChapter 2 - HRMMeagan ManiboNo ratings yet
- HRM 3Document11 pagesHRM 3Hasanuzzaman AnasNo ratings yet
- Block 4 - Job AnalysisDocument24 pagesBlock 4 - Job AnalysisChandan MazumdarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2, HRMDocument27 pagesChapter 2, HRMAryan Bin RezaNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument26 pagesJob AnalysisimdadhoNo ratings yet
- HRM Tutorial 4Document7 pagesHRM Tutorial 4Santania syebaNo ratings yet
- 6.job AnalysisDocument22 pages6.job AnalysisAbhijeet100% (1)
- "Job Analysis": University of PunjabDocument11 pages"Job Analysis": University of PunjabZain ul AbdinNo ratings yet
- Presentation Job AnalysisDocument10 pagesPresentation Job Analysismosturkyplaystation2024No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Job AnalysisDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Job Analysisjennifer abad100% (1)
- 6 18MBA331 Unit 1 2020Document233 pages6 18MBA331 Unit 1 2020Aishwarya SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- HRM 1015 - Job Analysis Notes 2024Document39 pagesHRM 1015 - Job Analysis Notes 2024kaloloeliza2003No ratings yet
- HRM Assignment (Midsem)Document3 pagesHRM Assignment (Midsem)samuwadhwaNo ratings yet
- Recruitment Selection and Placement FunctionDocument18 pagesRecruitment Selection and Placement FunctionGabriel ManuelNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3. HRMDocument8 pagesCh. 3. HRMneway gobachewNo ratings yet
- Talent ManagementDocument15 pagesTalent Managementricha sharma291No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Job AnalysisDocument2 pagesChapter 2: Job AnalysisBasco Martin JrNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document46 pagesSession 2Gellie Rose PorthreeyesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 2 Job Analysis and DesignDocument14 pagesUnit 2 2 Job Analysis and DesignAsfawosen Dingama100% (1)
- Job Analysis and Talent Management ProcessDocument5 pagesJob Analysis and Talent Management ProcessMarischiel SablanNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis: Group Member Bansi HemanshuDocument19 pagesJob Analysis: Group Member Bansi HemanshuRukmani GuptaNo ratings yet
- HR Unit 2 Mba 2nd SemDocument102 pagesHR Unit 2 Mba 2nd Semudit.cool111No ratings yet
- U2 - Job Analysis, Design, EvaluationDocument13 pagesU2 - Job Analysis, Design, EvaluationjyotiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 BY Jaffar PNM HRMDocument25 pagesUNIT 2 BY Jaffar PNM HRMSachin NNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument5 pagesJob AnalysisFaisal RasheedNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Staffing Candidate Screening and Interviewing HandbookFrom EverandHealthcare Staffing Candidate Screening and Interviewing HandbookNo ratings yet
- How to Make the Most of Your Performance Appraisal: Adopt a winning attitude and reap the benefitsFrom EverandHow to Make the Most of Your Performance Appraisal: Adopt a winning attitude and reap the benefitsNo ratings yet
- PromotionDocument6 pagesPromotionseena15No ratings yet
- MODULE 2 e LearningDocument70 pagesMODULE 2 e Learningseena15No ratings yet
- Module:3 Training and DevelopmentDocument26 pagesModule:3 Training and Developmentseena15No ratings yet
- Branches of Economics: Asst - Prof.Seena Alappatt Department of Management StudiesDocument8 pagesBranches of Economics: Asst - Prof.Seena Alappatt Department of Management Studiesseena15No ratings yet
- Demand ForcastingDocument13 pagesDemand Forcastingseena15No ratings yet
- Investment & GamblingDocument18 pagesInvestment & Gamblingseena15No ratings yet
- Institutional Support To Entrepreneurs: Asst - Prof.Seena Alappatt Dept - MGMT StudiesDocument3 pagesInstitutional Support To Entrepreneurs: Asst - Prof.Seena Alappatt Dept - MGMT Studiesseena15No ratings yet
- Investment & Gambling: Asst - Prof .Seena Alappatt Dept of Management StudiesDocument24 pagesInvestment & Gambling: Asst - Prof .Seena Alappatt Dept of Management Studiesseena15No ratings yet
- Measurement & Scaling: Asst - Prof .Seena Alappatt Dept - Management StudiesDocument13 pagesMeasurement & Scaling: Asst - Prof .Seena Alappatt Dept - Management Studiesseena15No ratings yet
- 05 RequirementanalysisDocument11 pages05 Requirementanalysisseena15No ratings yet
- Mainframe Developer COBOL Java in NYC Resume Peter RosenblumDocument3 pagesMainframe Developer COBOL Java in NYC Resume Peter RosenblumPeterRosenblumNo ratings yet
- Safety PerformanceDocument12 pagesSafety PerformanceFatih D. Prasetio100% (1)
- A Career in HR Can Take You Further: Speaker NameDocument12 pagesA Career in HR Can Take You Further: Speaker NameSharath NagNo ratings yet
- TE Ch13Document10 pagesTE Ch131anthonyanthony7No ratings yet
- Chap005 Labor EconomicsDocument15 pagesChap005 Labor EconomicsKoki Mostafa100% (1)
- Job Satisfaction in State Bank of India in Namakkal DistrictDocument8 pagesJob Satisfaction in State Bank of India in Namakkal DistrictShubham DhondsekarNo ratings yet
- Human Capital Management - LupinDocument4 pagesHuman Capital Management - LupinLAKSHMI BALAKRISHNAN MBA19-21No ratings yet
- Avinash Kumar Chitrada Offer LetterDocument2 pagesAvinash Kumar Chitrada Offer Letterwarewolf786No ratings yet
- How To Become A Competent Person Certified Environmental ProfessionalDocument5 pagesHow To Become A Competent Person Certified Environmental Professionalneer_butterfly100% (1)
- Victaulic LubDocument8 pagesVictaulic LubSopon SrirattanapiboonNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety: Safety Related Work PracticesDocument68 pagesElectrical Safety: Safety Related Work PracticesBappy PaulNo ratings yet
- Labour Law AssignmentDocument9 pagesLabour Law AssignmentChoudhary Shadab phalwanNo ratings yet
- DTR January 1-15, 2024Document2 pagesDTR January 1-15, 2024julietoNo ratings yet
- HlurbDocument112 pagesHlurbisaias l tan jrNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Moods and EmotionsDocument22 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Moods and EmotionsWasim Jamali100% (1)
- Sec A - Group4 - New Union Wellington Associates - FinalDocument13 pagesSec A - Group4 - New Union Wellington Associates - FinalVijay KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Human Resourse Management ProjectDocument16 pagesHuman Resourse Management ProjectRashmita AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Sales Management - Final Report - Group 2Document22 pagesSales Management - Final Report - Group 2Duy Nguyễn Lê NhậtNo ratings yet
- Personal Data Sheet CS Form No. 212 Revised 2017Document5 pagesPersonal Data Sheet CS Form No. 212 Revised 2017Fernando P FetalinoNo ratings yet
- Recruitment Manual 2022 For Construction CompanyDocument18 pagesRecruitment Manual 2022 For Construction CompanyNgọc HuyềnNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Business Letter 1 PDFDocument20 pagesHow To Write A Business Letter 1 PDFJoanna Michelle PelaezNo ratings yet
- Erection, Testing, Commissioning, Trial OperationDocument131 pagesErection, Testing, Commissioning, Trial OperationTufan Maity100% (1)
- Healthcare and Pharma - PPT by Atul MishraDocument21 pagesHealthcare and Pharma - PPT by Atul MishraAbhidha BhattNo ratings yet
- Resume Writing and Its Types Sem IIIDocument36 pagesResume Writing and Its Types Sem IIISyeda NishaNo ratings yet
- Employee Referral PolicyDocument2 pagesEmployee Referral Policyvarma511No ratings yet
- Public Office (First Exam)Document83 pagesPublic Office (First Exam)Karen Joy MasapolNo ratings yet
- ACCT3050 Comprehensive Question Graded (20%) Updated 28 March 2021Document3 pagesACCT3050 Comprehensive Question Graded (20%) Updated 28 March 2021TashaNo ratings yet
- Planning and Organising For SafetyDocument25 pagesPlanning and Organising For SafetyenvsandyNo ratings yet