Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Climate
Climate
Uploaded by
Elyssa Manansala0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views32 pagesTropical design considers the environmental impacts of wind and sun on buildings. It aims to minimize energy consumption by reducing sun exposure and maximizing wind. Some key considerations include easy access, privacy, plumbing, orientation, and using sun and wind to regulate indoor temperatures. The climate of the Philippines is tropical and humid, with high temperatures and rainfall influenced by monsoon winds and typhoons.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTropical design considers the environmental impacts of wind and sun on buildings. It aims to minimize energy consumption by reducing sun exposure and maximizing wind. Some key considerations include easy access, privacy, plumbing, orientation, and using sun and wind to regulate indoor temperatures. The climate of the Philippines is tropical and humid, with high temperatures and rainfall influenced by monsoon winds and typhoons.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views32 pagesClimate
Climate
Uploaded by
Elyssa ManansalaTropical design considers the environmental impacts of wind and sun on buildings. It aims to minimize energy consumption by reducing sun exposure and maximizing wind. Some key considerations include easy access, privacy, plumbing, orientation, and using sun and wind to regulate indoor temperatures. The climate of the Philippines is tropical and humid, with high temperatures and rainfall influenced by monsoon winds and typhoons.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 32
Tropical Design
Tropical Design
Considers the environmental impact on the building
Wind
Sun
As much as possible, less energy consumption
MINIMIZE THE SUN + MAXIMIZE THE WIND
What are your considerations when
planning?
Easy access
Carport > Kitchen
Bedroom > Toilet and Bath
Privacy
Plumbing
Orientation
Sun heat
Kitchen bacteria
Bedroom comfort
Donts
Dead ends
Two near doors*
Long hallway
Climate
Climate
Defined a region with certain temperature, dryness, wind,
light etc
An integration in time of the atmospheric environment of
a certain geographical location
Climate VS Weather
Climate is different from weather, in that weather only
describes the short-term conditions of these variables in a
given region.
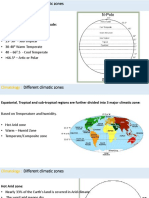
World Climates
General Types of Climate
1. Cold
2. Temperature
3. Hot Arid
4. Hot Humid (Tropical)
Cool Regions
Minimizing the surface area of a building reduces exposure
to low temperature
• Maximize absorption of solar radiation
• Reduce radiant, conductive and evaporative heat loss
• Provide wind protection
Cool
Alberta, Canada
Temperate Regions
Elongating the form of a building along the east-west axis
maximizes south-facing walls
• Minimize east and west exposures, which are generally
warmer in summer and cooler in winter than southern
exposures
• Balance solar heat gain with shade protection on a
seasonal basis
• Encourage air movement in hot weather; protect against
wind in cold weather
Temperate
Haus, Norway
Hot-Arid Regions
Building forms should enclose courtyard spaces
• Reduce solar and conductive heat gain
• Promote cooling by evaporation using water features and
plantings
• Provide solar shading for windows and outdoor spaces
“Arid”
A land or a climate having little or no rain and is typically
too dry or barren to support lush vegetation
Dry
Pheonix, Arinoza
Hot-Humid (Tropical) Regions
Building form elongated along the east-west axis minimizes
east and west exposures
• Reduce solar heat gain
• Utilize wind to promote cooling by evaporation
• Provide solar shading for windows and outdoor spaces
Tropical
Cebu, Philippines
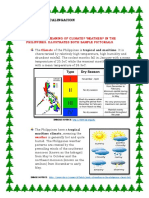
Climate of the Philippines
The climate of the Philippines is tropical and maritime
It is characterized by relatively high temperature, high
humidity and abundant rainfall
It is similar in many respects to the climate of the
countries of Central America
The most important elements of the country’s weather and
climate are the following:
Temperature
Humidity
Rainfall
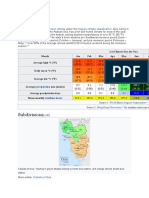
Temperature
Excluding Baguio, the mean annual temperature in the
Philippines is 26.6 ºC
The coolest months fall in January with a mean
temperature of 25.5 ºC while the warmest month occurs in
May with a mean temperature of 28.3 ºC
Humidity
Refers to the moisture content of the atmosphere
Due to high temperature and the surrounding bodies of
water, the Philippines has a high relative humidity
The average monthly relative humidity varies between
71% in March and 85% in September
Rainfall
Most important climatic element in the Philippines
Rainfall distribution throughout the country varies from
one region to another, depending upon the direction of the
moisture-bearing winds and the location of the mountain
systems
The mean annual rainfall of the Philippines varies from
965 to 4064 mm annually
Baguio City, eastern Samar, and eastern Surigao receive
the greatest amount of rainfall while the southern portion
of Cotabato receives the least amount of rain. At GSC, the
average annual rainfall is only 978 mm.
Seasons
Using temperature and rainfall as bases, the climate of the
country can be divided into two major seasons:
rainy and dry
The rainy season, from June to November
The dry season, from December to May, which may be
subdivided further into:
The cool dry season, from December to February
The hot dry season, from March to May
Prevailing Winds
Hanging amihan (N-E)
November-April
Hanging habagat (S-W)
May-October
Monsoon
A monsoon is a seasonal shift in the prevailing wind
direction, that usually brings with it a different kind of
weather
Typhoons
Have a great influence on the climate and weather
conditions of the Philippines
A great portion of the rainfall, humidity and cloudiness are
due to the influence of typhoons
They generally originate in the region of the Marianas and
Caroline Islands of the Pacific Ocean which have the same
latitudinal location as Mindanao
Their movements follow a north-westerly direction,
sparing Mindanao from being directly hit by majority of
the typhoons that cross the country
This makes the southern Philippines very desirable for
agriculture and industrial development
You might also like
- Full Download Geosystems An Introduction To Physical Geography 9th Edition PDF Version 9th Edition PDF Version PDFDocument42 pagesFull Download Geosystems An Introduction To Physical Geography 9th Edition PDF Version 9th Edition PDF Version PDFjohnny.bierman446100% (34)
- Tropical LectureDocument120 pagesTropical LectureChristian Dayne TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Tropical DesignDocument201 pagesTropical DesignFrancis Grant ReladoNo ratings yet
- Tropival Lesson 1Document70 pagesTropival Lesson 1Krichelle RamirezNo ratings yet
- APR Tropical Architecture Rev1Document57 pagesAPR Tropical Architecture Rev1Yuanne San0% (1)
- What Is ClimateDocument12 pagesWhat Is ClimateDannielyn BuayaNo ratings yet
- Science q3 Lecture 5Document22 pagesScience q3 Lecture 5jharealoNo ratings yet
- Science q3 Lecture 5Document22 pagesScience q3 Lecture 5jharealoNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument5 pagesClimate ChangeCristine Joy CalingacionNo ratings yet
- Tropical Design 1Document64 pagesTropical Design 1Ian Paolo D. RuñezNo ratings yet
- Climate 2 Grade 9Document19 pagesClimate 2 Grade 9Julius Memeg PanayoNo ratings yet
- ClimateDocument13 pagesClimateShafic RuckyNo ratings yet
- School of Architecture: S.B.S.S.T.C FZRDocument13 pagesSchool of Architecture: S.B.S.S.T.C FZRSAHIL KAUSHALNo ratings yet
- Climate Group 1Document31 pagesClimate Group 1Cristina AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Tropical DesignDocument12 pagesTropical DesignjohnNo ratings yet
- Philippine Climate Data & AnalysisDocument14 pagesPhilippine Climate Data & AnalysisJulia ObregonNo ratings yet
- Eather S Limate: Conditions in A Certain Place Over Many YearsDocument12 pagesEather S Limate: Conditions in A Certain Place Over Many YearsElle EspirituNo ratings yet
- Climate and Weather Patterns (Lessons) 1Document5 pagesClimate and Weather Patterns (Lessons) 1patcris moncadaNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Climate of The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesNotes On The Climate of The PhilippinesAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Chap 6 Weather and Climate in The Phil 1Document13 pagesChap 6 Weather and Climate in The Phil 1secretzNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Climate: Enviropedia Climate Change Global Warming Ozone Air Pollution Weather & Climate Sustainability KidsDocument5 pagesPatterns of Climate: Enviropedia Climate Change Global Warming Ozone Air Pollution Weather & Climate Sustainability KidsVimal NairNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Climate: Enviropedia Climate Change Global Warming Ozone Air Pollution Weather & Climate Sustainability KidsDocument5 pagesPatterns of Climate: Enviropedia Climate Change Global Warming Ozone Air Pollution Weather & Climate Sustainability KidsVimal NairNo ratings yet
- Weather Basics (Meteorology) : Atmospheric Waters MeteorologyDocument6 pagesWeather Basics (Meteorology) : Atmospheric Waters Meteorologyglaydelle100% (1)
- Classification of ClimateDocument54 pagesClassification of ClimateMuskan100% (1)
- Form 2 Geo-ClimateDocument8 pagesForm 2 Geo-Climatechristinekirimi46No ratings yet
- Seasons, Weather, Climate, Extreme WeatherDocument49 pagesSeasons, Weather, Climate, Extreme WeatherWeryn GómezNo ratings yet
- Types of Climates and Corresponding CharacteristecsDocument13 pagesTypes of Climates and Corresponding CharacteristecsRenhel EdradanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 ClimateDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Climatem.furqanullahNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Term 2 Geography SummaryDocument10 pagesGrade 8 Term 2 Geography Summarynnsabbas07No ratings yet
- New Weather and ClimateDocument20 pagesNew Weather and Climateshabika169No ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument12 pagesScience NotesClaire MaeNo ratings yet
- Types of ClimateDocument25 pagesTypes of ClimateVernon100% (1)
- Weatherand Climate FinalDocument48 pagesWeatherand Climate Finalvivek100% (1)
- Factorsthataffectclimate 7Document20 pagesFactorsthataffectclimate 7Juvielyn RazNo ratings yet
- Cold and Sunnny ZoneDocument19 pagesCold and Sunnny ZoneBereket ArayaNo ratings yet
- Olevel Geography Notes by Saleemferozi: Contact:03332157652Document20 pagesOlevel Geography Notes by Saleemferozi: Contact:03332157652Syed Muhammad Saleem FeroziNo ratings yet
- Climate Vs WeatherDocument7 pagesClimate Vs WeatherRossvell HiloNo ratings yet
- Architectural Design Based On Climatic DataDocument14 pagesArchitectural Design Based On Climatic DataKukishin KrimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ClimateDocument21 pagesChapter 2 Climateushez294No ratings yet
- Olevel Geography Notes by Saleemferozi: Contact:03332157652Document12 pagesOlevel Geography Notes by Saleemferozi: Contact:03332157652Syed Muhammad Saleem FeroziNo ratings yet
- Tropical Climates Are Characterized by High TemperaturesDocument2 pagesTropical Climates Are Characterized by High TemperaturesbharmkidumpNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Notes IDocument11 pagesClimate Change Notes ILucky JillaniNo ratings yet
- S3 GEOG Term 1 EXAM NotesDocument15 pagesS3 GEOG Term 1 EXAM Noteshayleychan6202007No ratings yet
- Weather and Climate ProjectDocument10 pagesWeather and Climate ProjectProject MA2No ratings yet
- Climate 1Document13 pagesClimate 1rmwalimu66No ratings yet
- Climatology: Asst. Prof. Gaurav GoyalDocument32 pagesClimatology: Asst. Prof. Gaurav GoyalMansaNo ratings yet
- Indian Climatic Conditions and Their Impact On Building DesignDocument30 pagesIndian Climatic Conditions and Their Impact On Building DesignAD ARCHITECTS100% (1)
- PrecipitationDocument5 pagesPrecipitationAndrea AbuleNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate of East AfricaDocument41 pagesWeather and Climate of East Africakenethwaiswa77No ratings yet
- Geography Notes-2 Weather, Climate, Vegetation, Soils, Hazards, LongitudeDocument26 pagesGeography Notes-2 Weather, Climate, Vegetation, Soils, Hazards, LongitudeShaquan FullertonNo ratings yet
- Hot Deserts ClimateDocument7 pagesHot Deserts Climatenicole matsikaNo ratings yet
- Philippine ClimateDocument22 pagesPhilippine ClimateJulia ObregonNo ratings yet
- 3.climates of World and NepalDocument47 pages3.climates of World and NepalAsish BarailiNo ratings yet
- 1 Geography Grade 12 Chapter Three SummaryDocument60 pages1 Geography Grade 12 Chapter Three SummarymelkamumesheshamemiruNo ratings yet
- Weather Patterns in The PhilippinesDocument18 pagesWeather Patterns in The PhilippinesChie Molina Montaña60% (10)
- Climate: Sagurit, Saraiah Luy, Camille Del Valle, Laia Villanueva, Roi Alvarez, ArvinDocument21 pagesClimate: Sagurit, Saraiah Luy, Camille Del Valle, Laia Villanueva, Roi Alvarez, ArvinSaraiah SaguritNo ratings yet
- Science9 ClimateDocument95 pagesScience9 ClimateicebeargoodbearandgrizzyesNo ratings yet
- 2023-2024 HMA G10 Week 4Document14 pages2023-2024 HMA G10 Week 4milliongtsadik3No ratings yet
- Climate, Classification, Philippine Climate Final VersionDocument38 pagesClimate, Classification, Philippine Climate Final Versionaprildina.loquinteNo ratings yet
- Low-Water Garden: How To Beat The Drought And Grow a Thriving Garden Using Low-Water TechniquesFrom EverandLow-Water Garden: How To Beat The Drought And Grow a Thriving Garden Using Low-Water TechniquesNo ratings yet
- HeinonlineDocument20 pagesHeinonlinecaiqumeloNo ratings yet
- MAT Solved Question Papers For Language Comprehension: Passage IDocument24 pagesMAT Solved Question Papers For Language Comprehension: Passage ISAMRAT DEYNo ratings yet
- Edc 273 Signature Assignment Part 2Document23 pagesEdc 273 Signature Assignment Part 2api-285995221No ratings yet
- LACEcologicalSystems PDFDocument47 pagesLACEcologicalSystems PDFMayra MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- PCXR2020 Complete 20210304Document165 pagesPCXR2020 Complete 20210304Allan SalvatusNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science 3rd Departmental TestDocument4 pagesGrade 9 Science 3rd Departmental TestLOUWELA JEAN DE LA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Aqa A2 Geography 9780340946121Document42 pagesAqa A2 Geography 9780340946121Logan Run100% (1)
- Observed Trends and Projected Climate Change in The PhilippinesDocument43 pagesObserved Trends and Projected Climate Change in The PhilippinesAnonymous zyZal72No ratings yet
- An Inconvenient Truth SummaryDocument5 pagesAn Inconvenient Truth SummaryRenaliz GonzalesNo ratings yet
- GeographyDocument13 pagesGeographyaisling murphuNo ratings yet
- Climate Extremes Indices in The CMIP5 Multimodel Ensemble Part 2.future Climate ProjectionsDocument21 pagesClimate Extremes Indices in The CMIP5 Multimodel Ensemble Part 2.future Climate ProjectionsAshraf RamadanNo ratings yet
- Subdivisions: ClimateDocument3 pagesSubdivisions: ClimateNatia SaginashviliNo ratings yet
- Climate Change and Its Impact On PakistanDocument15 pagesClimate Change and Its Impact On PakistanNauman Rashid96% (24)
- 33 Trend Analysis of Rainfall and Temperature and Its Relationship Over IndiaDocument14 pages33 Trend Analysis of Rainfall and Temperature and Its Relationship Over IndiaPtb4docNo ratings yet
- Global Warming Causes Effects and PreventionDocument2 pagesGlobal Warming Causes Effects and PreventionAnthony Cris Martin VillonesNo ratings yet
- Weather Maps and Intro To ClimateDocument39 pagesWeather Maps and Intro To Climatecmillica1176No ratings yet
- WMObulletin 58Document92 pagesWMObulletin 58v1_y4No ratings yet
- G7Q4LAS1W1Document7 pagesG7Q4LAS1W1Hazel RecañaNo ratings yet
- Climate VariabilityDocument4 pagesClimate VariabilityFaiz M TaimurNo ratings yet
- Name - Davyous Melvin - Earth Science Wind/Pressure/Weather Webquest Part 1. Air MassesDocument5 pagesName - Davyous Melvin - Earth Science Wind/Pressure/Weather Webquest Part 1. Air Massesapi-330049909No ratings yet
- q2 Week 5 Day 1 TyphoonDocument26 pagesq2 Week 5 Day 1 TyphoonGenel YutucNo ratings yet
- 2023 Solar Risk Assessment FinalDocument21 pages2023 Solar Risk Assessment FinalFake EmailNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development: 1. Read The Paragraphs Below and Match Them With The Threat They Refer ToDocument3 pagesSustainable Development: 1. Read The Paragraphs Below and Match Them With The Threat They Refer ToXs Holy SouL100% (1)
- Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) CurvesDocument18 pagesIntensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) CurvesZiaul Haq DoostNo ratings yet
- Topic - 8.2Document4 pagesTopic - 8.2Niharika ChomalNo ratings yet
- Climate A UmDocument7 pagesClimate A UmsanthakumarNo ratings yet
- Phytosociological, Bioclimatic and Biogeographical Classification of Woody Climax Communities of Western North AmericaDocument24 pagesPhytosociological, Bioclimatic and Biogeographical Classification of Woody Climax Communities of Western North AmericaHERMES CUADROS VILLALOBOSNo ratings yet
- Morrell Nature Sanctuary Guidebook - 2019Document36 pagesMorrell Nature Sanctuary Guidebook - 2019John AndersonNo ratings yet
- Tropical Meteorology and ClimatologyDocument230 pagesTropical Meteorology and ClimatologyAse NiguNo ratings yet