Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 viewsDda Drug
Dda Drug
Uploaded by
farrah hanimThe document provides information on several opioid analgesics:
- Morphine is used for moderate to severe pain and has dosage ranges from 2.5-120mg every 4 hours. It works by binding to mu-opioid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
- Pethidine is used for moderate to severe pain, reducing shivering, and acute pain management. It has similar mechanisms of action to morphine but also has local anesthetic and stimulant effects. Common side effects include tachycardia and urinary retention.
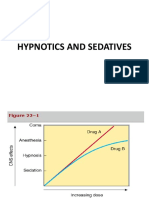
- Phenobarbitone is used as a short-term insomnia treatment, anticonvulsant, and to prevent febrile seizures. It works by prolonging the opening
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- RF 265 266 Ab Samsung Refri PDFDocument107 pagesRF 265 266 Ab Samsung Refri PDFaderlochNo ratings yet
- ZopicloneDocument2 pagesZopicloneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Pharma CardsDocument5 pagesPharma CardsazancheNo ratings yet
- O-Level Commerce PDFDocument8 pagesO-Level Commerce PDFClinton ChikengezhaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reporting-1Document32 pagesPharmacology Reporting-1Mj TalentNo ratings yet
- Barbiturate Benzodiazepine PoisoningDocument23 pagesBarbiturate Benzodiazepine PoisoningRoman MamunNo ratings yet
- Anti EpilepticsDocument29 pagesAnti Epilepticskeerthi sivayanamaNo ratings yet
- SedativesDocument21 pagesSedativesKeerthana KNo ratings yet
- AnticonvulsantDocument37 pagesAnticonvulsantPamela MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sedative/ Hypnotics: Silim, Miriam Grace DDocument29 pagesSedative/ Hypnotics: Silim, Miriam Grace DDeloria, Alma J.No ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Mental IllnessDocument60 pagesDrugs Used in Mental IllnessDixa MeNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Drugs 2Document57 pagesPsychiatry Drugs 2Abdulmajid mohamedNo ratings yet
- 7 Sedative Hypnotics Anti AnxietyDocument30 pages7 Sedative Hypnotics Anti Anxietyranjitasubedi678No ratings yet
- Antiparkinson DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinson DrugsSV SagarNo ratings yet
- Sedatives and Hypnotics LectureDocument55 pagesSedatives and Hypnotics LectureOSAKA THOMASNo ratings yet
- HypnoticsDocument27 pagesHypnoticsattu farrayalNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicDocument42 pagesAnalgesicVinayak SinghNo ratings yet
- Procaine: BupivicaineDocument7 pagesProcaine: BupivicaineBirara ChakilieNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument65 pagesParkinson's DiseaseGerald Resubal OriñaNo ratings yet
- Scribble Pad: Drugs Used To Treat Parkinson'sDocument24 pagesScribble Pad: Drugs Used To Treat Parkinson'sLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- CNS PNS DrugsDocument29 pagesCNS PNS DrugsMadel A. AlberioNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument24 pagesParkinson's Diseasejanemwanza003No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyJaessa Feliciano50% (2)
- OpioidsDocument62 pagesOpioidssourabh jakharNo ratings yet
- Sedative Hypnotic PoisoningDocument37 pagesSedative Hypnotic PoisoningDeepa WilliamNo ratings yet
- Handout 2563 OpioidsDocument84 pagesHandout 2563 OpioidsPiya TangNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson Disease - PDF - Pharmacology - AssignmentDocument11 pagesAnti Parkinson Disease - PDF - Pharmacology - AssignmentMr HotmasterNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studykarenkaren09No ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of ParkinsonismDocument28 pagesDrug Therapy of ParkinsonismZobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Cardiac EmergenciesDocument18 pagesDrugs Used in Cardiac Emergencieshakky gamyNo ratings yet
- Adjuvant AnalgesicDocument19 pagesAdjuvant AnalgesicKyra KhalidNo ratings yet
- Opiod Analgesics &antagonistsDocument58 pagesOpiod Analgesics &antagonistsVictoria ChepkorirNo ratings yet
- Block I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Antiparkisonian DrugsDocument41 pagesBlock I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Antiparkisonian DrugsOdiete EfeNo ratings yet
- Antidote Meds in Crash Cart (Naloxone, Hydrobromide, Flumazenil)Document5 pagesAntidote Meds in Crash Cart (Naloxone, Hydrobromide, Flumazenil)Still DollNo ratings yet
- Medications NHBDocument40 pagesMedications NHBAnonymous 7hJgATNo ratings yet
- MedicationDocument31 pagesMedicationMary Joy Morales BuquiranNo ratings yet
- OpioidsDocument57 pagesOpioidsSteven Okta ChandraNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument30 pagesParkinsonRebecca HarsNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia and Drugs RealDocument37 pagesAnesthesia and Drugs Realshehryarahmed1021998No ratings yet
- Drugs in ICUDocument83 pagesDrugs in ICUJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Conscious Sedation: Hayel Gharaibeh, MD. Anesthesia ConsultantDocument84 pagesConscious Sedation: Hayel Gharaibeh, MD. Anesthesia ConsultantKhaled GharaibehNo ratings yet
- Opioid AnalgesicsDocument27 pagesOpioid AnalgesicsDivya VarsiniNo ratings yet
- OpioidanalgesicsDocument30 pagesOpioidanalgesicsMr VoralpenNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Used in DentistryDocument53 pagesEmergency Drugs Used in Dentistryasmita1989No ratings yet
- Premedication: Presenter-Dr - Srishti Moderator-Dr.R.Pal (Professor) Dr.P. Jain (Associate Professor)Document34 pagesPremedication: Presenter-Dr - Srishti Moderator-Dr.R.Pal (Professor) Dr.P. Jain (Associate Professor)Viresh Upase Roll No 130. / 8th termNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson Drugs FinallDocument36 pagesAnti Parkinson Drugs FinallandrapradeshsseNo ratings yet
- Drug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsDocument57 pagesDrug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Hypnoti and SedativeDocument30 pagesHypnoti and SedativeC velmuruganNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AgonistsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic AgonistsArjay LucenaNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinson Pharma 2020Document26 pagesAntiparkinson Pharma 2020Ida Bagus Putu SwabawaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyJohn LesterNo ratings yet
- Typical Antipsychotic DrugsDocument4 pagesTypical Antipsychotic DrugsErika Blaire N. OlacaoNo ratings yet
- Archivetempfinal RevisionDocument140 pagesArchivetempfinal RevisionSheza FarooqNo ratings yet
- Influence The Opioids To ImmunityDocument13 pagesInfluence The Opioids To ImmunityoctaviasulistyaNo ratings yet
- Movement DisordersDocument28 pagesMovement DisordersAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Parkinson Disease SlidesDocument21 pagesParkinson Disease Slidessarah morley100% (2)
- FAR 381 - Opioids - 2018 - Lecture UploadDocument36 pagesFAR 381 - Opioids - 2018 - Lecture UploadHuzaifa KhanNo ratings yet
- Anastesi DrugDocument28 pagesAnastesi DrugGita KhairiyahNo ratings yet
- Analgesics: DR Mohammed Malik AfrozDocument37 pagesAnalgesics: DR Mohammed Malik AfrozMohee DawabshehNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinsonism AgentsDocument16 pagesAnti Parkinsonism AgentsLacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Rabies: Dr. Paul Bartlett, MPH., DVM., PH.DDocument45 pagesRabies: Dr. Paul Bartlett, MPH., DVM., PH.DnfrnufaNo ratings yet
- Audit ComplianceDocument10 pagesAudit ComplianceAl-Amin SarkarNo ratings yet
- JEE 2024 RoadmapDocument42 pagesJEE 2024 Roadmaplilop27557No ratings yet
- Waterworld201808 DLDocument56 pagesWaterworld201808 DLThiyagu ManogaranNo ratings yet
- Vendor: Design Information: Gas BootDocument2 pagesVendor: Design Information: Gas Boot124swadeshiNo ratings yet
- Heat Recovery Steam Generator For Cheng Cycle Application: Reprinted From 1988Document5 pagesHeat Recovery Steam Generator For Cheng Cycle Application: Reprinted From 1988Herberth SilitongaNo ratings yet
- Nivel Básico de Inglés Septiembre 2016 Comprensión de Lectura Modelo de CorrecciónDocument8 pagesNivel Básico de Inglés Septiembre 2016 Comprensión de Lectura Modelo de CorrecciónEsther León JorgeNo ratings yet
- CH PDFDocument43 pagesCH PDFBobVonCatNo ratings yet
- 7th History Workbook English Medium Maharashtra BoardDocument12 pages7th History Workbook English Medium Maharashtra Boardpankarvi6100% (1)
- Experiment No. (6) Study of Dispersion Compensation Schemes: ObjectDocument9 pagesExperiment No. (6) Study of Dispersion Compensation Schemes: ObjectFaez FawwazNo ratings yet
- Exhibitor List Foam ExpoDocument7 pagesExhibitor List Foam Expohijero7692No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae of Supramaniyan KumarDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae of Supramaniyan KumarSupramaniyan kumarNo ratings yet
- Final Stilt Floor Plan 16042022Document1 pageFinal Stilt Floor Plan 16042022rajesh lankaNo ratings yet
- The Vivago Watch A Telecare Solution For Cost-Efficient CareDocument1 pageThe Vivago Watch A Telecare Solution For Cost-Efficient CareGeronTechnoPlatformNo ratings yet
- CP7211 Advanced Databases Laboratory ManualDocument63 pagesCP7211 Advanced Databases Laboratory Manualashaheer75% (4)
- 3is FORMATDocument10 pages3is FORMATAMACIO, MARIAN JOY A.No ratings yet
- Sale Deed: ORGANISATION (AWHO), (PAN No. AABTA4251G) A Society Registered UnderDocument26 pagesSale Deed: ORGANISATION (AWHO), (PAN No. AABTA4251G) A Society Registered Undernaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Section Capacity Section Capacity: AbutmentDocument4 pagesSection Capacity Section Capacity: AbutmentGajendra SNo ratings yet
- Business English 4 - Teacher'S Lecture Notes: 2 Signposting - Page 8Document12 pagesBusiness English 4 - Teacher'S Lecture Notes: 2 Signposting - Page 8AndraStefaniaNo ratings yet
- PT ArchanaDocument9 pagesPT ArchanadhavalNo ratings yet
- Afn 2 PDFDocument5 pagesAfn 2 PDFLovely Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sri Mahila Griha Udyog Lijjat Papad: Strategic Management CourseDocument23 pagesSri Mahila Griha Udyog Lijjat Papad: Strategic Management CoursePrachit ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Doordash Agreement Contract October 25Document13 pagesDoordash Agreement Contract October 25wagaga papapaNo ratings yet
- 600 ngữ pháp chọn lọc luyện thi THPT Quốc GiaDocument32 pages600 ngữ pháp chọn lọc luyện thi THPT Quốc GiaNguyen Chi Cuong100% (1)
- Advanced Enzymes White PaperDocument16 pagesAdvanced Enzymes White PaperAnubhav TripathiNo ratings yet
- BBRC4103 Kaedah Penyelidikan September Semester 2020Document12 pagesBBRC4103 Kaedah Penyelidikan September Semester 2020SARIPAH NOOR FARAH AIN BINTI P.AFDZAL SHAH STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Risk-Return Relationship On Equity Shares in India 1Document11 pagesRisk-Return Relationship On Equity Shares in India 1Tanmaya BiswalNo ratings yet
- Smart Battery Data Specification Revision 1.1 ErrataDocument5 pagesSmart Battery Data Specification Revision 1.1 ErrataredmsbatteryNo ratings yet
Dda Drug
Dda Drug
Uploaded by
farrah hanim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views18 pagesThe document provides information on several opioid analgesics:
- Morphine is used for moderate to severe pain and has dosage ranges from 2.5-120mg every 4 hours. It works by binding to mu-opioid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
- Pethidine is used for moderate to severe pain, reducing shivering, and acute pain management. It has similar mechanisms of action to morphine but also has local anesthetic and stimulant effects. Common side effects include tachycardia and urinary retention.
- Phenobarbitone is used as a short-term insomnia treatment, anticonvulsant, and to prevent febrile seizures. It works by prolonging the opening
Original Description:
DDA DRUG USE IN CLINICAL AREA
Original Title
DDA DRUG
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information on several opioid analgesics:
- Morphine is used for moderate to severe pain and has dosage ranges from 2.5-120mg every 4 hours. It works by binding to mu-opioid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
- Pethidine is used for moderate to severe pain, reducing shivering, and acute pain management. It has similar mechanisms of action to morphine but also has local anesthetic and stimulant effects. Common side effects include tachycardia and urinary retention.
- Phenobarbitone is used as a short-term insomnia treatment, anticonvulsant, and to prevent febrile seizures. It works by prolonging the opening
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
124 views18 pagesDda Drug
Dda Drug
Uploaded by
farrah hanimThe document provides information on several opioid analgesics:
- Morphine is used for moderate to severe pain and has dosage ranges from 2.5-120mg every 4 hours. It works by binding to mu-opioid receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
- Pethidine is used for moderate to severe pain, reducing shivering, and acute pain management. It has similar mechanisms of action to morphine but also has local anesthetic and stimulant effects. Common side effects include tachycardia and urinary retention.
- Phenobarbitone is used as a short-term insomnia treatment, anticonvulsant, and to prevent febrile seizures. It works by prolonging the opening
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 18
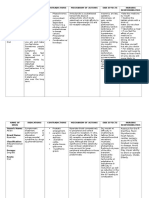
MORPHINE
• TRADE NAME: DURAMORPH, INFUMORP
• GENERIC NAME: MORPINE
• PHARMACEUTICAL PREPARATION: ORAL, INJECTION
• DOSAGE: 2.5mg – 5 – 7.5 – 10 – 15 – 20 – 30 – 40 – 60 – 80 – 100 –
120mg 4 hrly
• INDICATIONS:
moderate to severe pain that may be acute or chronic.
pain management
management of palliative/end-of-life care, active cancer treatment,
and vaso-occlusive pain during sickle cell crisis
musculoskeletal pain, abdominal pain, chest pain, arthritis
• MECHANISMS OF ACTION: This drug produces the majority of its analgesic
effects by binding to the mu-opioid receptor within the central nervous
system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).The net effect
of morphine is the activation of descending inhibitory pathways of the
CNS as well as inhibition of the nociceptive afferent neurons of the PNS,
which leads to an overall reduction of the nociceptive transmission.
PETHIDINE
• TRADE NAME: MEPERGEN, MEPERGEN FORTIS, MEPROZINE
• GENERIC NAME: PETHIDINE
• PHARMACEUTICAL PREPARATION: Injectable Solution
Oral Capsule, Oral Solution, Oral Tablet, Prefilled Syringe
• DOSAGE:
Meperidine 10 Mg/ml Injectable Solution
Meperidine 10 Mg/ml-nacl 0.9% Intravenous Solution
Meperidine 100 Mg Oral Tablet
Meperidine 100 Mg/ml Injectable Solution
Meperidine 25 Mg/ml Injectable Solution
Meperidine 50 Mg Oral Tablet
Ml Oral SyrupMeperidine 50 Mg/5
Meperidine 50 Mg/ml Injectable Solution
Meperidine 75 Mg/ml Injectable Solution
Meperidine Compounding Powder
• INDICATIONS:
treatment of moderate to severe pain.
reduce shivering
management of acute pain
the management of some patients with chronic pain.
• MECHANISM OF ACTION: same mechanism of action as morphine,
which is acting as an agonist to the mu-opioid receptor. The anti-
shivering effect may involve the stimulation of k-opioid receptors.
• Meperidine also has some local anesthetic effects because of
interactions with sodium ion channels. Also, meperidine has stimulant
effects by inhibition of the dopamine transporter (DAT) and
norepinephrine transporter (NET)
• ADVERSE REACTION/SIDE EFFECTS:
Serious Reactions Common Reactions
Shock, Tachycardia,
seizure, urinary retention,
syncope, tremor,
bradycardia, movements,
cardiac arrest, xerostomia,
severe hypotension, constipation,
apnea, dysphoria, weakness,
respiratory failure. palpitation,
PHENOBARBITONE
• TRADE NAME: Luminal, Solfoton
• GENERIC NAME: PHENOBARBITONE
• PHARMACEUTICAL PREPARATION: ORAL , INJECTION
• DOSAGE:
15 mg Tablet
30 mg Tablet
20 mg/5 ml Syrup or 20 mg/4 ml Syrup
• INDICATIONS:
Short-term treatment of insomnia;
relieve anxiety, tension & apprehension;
long-term anticonvulsant therapy for the treatment of generalised
tonic clonic & simple partial seizures.
Prophylaxis & treatment of febrile seizures.
Prevention & treatment of hyperbilirubinemia in neonates.
• MECHANISM OF ACTION:
Phenobarbitol is as an allosteric modulator
which extends the amount of time the chloride ion channel is open
by interacting with GABAA receptor subunits. Through this action,
phenobarbital increases the flow of chloride ions into the neuron
which decreases the excitability of the post-synaptic neuron.
Hyperpolarizing this post-synaptic membrane leads to a decrease in
the general excitatory aspects of the post-synaptic neuron. By
making it harder to depolarize the neuron, the
threshold for the action potential of the post-synaptic neuron will be
increased. Phenobarbital stimulates GABA to accomplish this
hyperpolarization.[36] Direct blockade of excitatory glutamate
signaling is also believed to contribute to the
hypnotic/anticonvulsant effect that is observed with the barbiturates.
• ADVERSE REACTION/SIDE EFFECTS:
Confusion,
hallucinations,
mental depression,
skin rash or hives or swelling of eye lids, face or lips,
wheezing or tightness in chest,
sore throat & fever,
unusual excitement & tiredness or weakness,
yellowing of eyes & skin, clumsiness or unsteadiness,
dizziness or lightheadedness, drowsiness,
hangover's effect, anxiety or nervousness,
constipation,headache,
nausea, vomiting,
nightmare or trouble in sleeping, unusual irritability.
DIAZEPAM
• TRADE NAME: Valium, Diastat, Diastat AcuDial
• GENERIC NAME: DIAZEPAM
• PHARMACEUTICAL PREPARATION: ORAL ,INJECTION
• DOSAGE: Rectal gel:
Tablet: 2.5 mg
2 mg 10 mg
5 mg 20 mg
10 mg Injectable solution:
Oral solution: 5mg/mL
1mg/1mL Intramuscular device:
5mg/mL 5mg/mL
• INDICATIONS
anxiety,
seizures,
alcohol withdrawal syndrome,
benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome,
muscle spasms, insomnia, and restless legs syndrome
• MECHANISM OF ACTION: bind to receptors in various regions of
the brain and spinal cord. This binding increases the inhibitory
effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABAs functions
include CNS involvement in sleep induction. Also involved in the
control of hypnosis, memory, anxiety, epilepsy and neuronal
excitability
• ADVERSE REACTION/SIDE EFFECTS:
Loss of control of bodily movements
Euphoria (rectal gel) Respiratory depression
Incoordination (rectal gel) Urinary retention
Drowsiness Depression
Rash (rectal gel) Incontinence
Diarrhea (rectal gel) Blurred vision
Low blood pressure (hypotension) Difficulty speaking
Fatigue Headache
Muscle weakness Skin rash
Changes in salivation
Codeine Phosphate
• TRADE NAME: Tylenol/Codeine TAB
• GENERIC NAME: Codeine Phosphate
• PHARMACEUTICAL PREPARATION: ORAL
• DOSAGE:
o As a solution for injection, as phosphate: 30 mg/ml
o As an oral solution, as phosphate: 25 mg/ml
o As a controlled-release tablet: 50 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg and 200
mg
o As an immediate-release tablet, codeine sulfate: 15mg, 30mg, 60
mg
• INDICATIONS:
treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea
treat mild to moderate degrees of pain.
• MECHANISM OF ACTION: Codeine is an opioid and an agonist of the
mu opioid receptor. It acts on the central nervous system to have an
analgesic effect.It is metabolised in the liver to produce morphine
which is ten times more potent against the mu receptor. Opioid
receptors are G-Protein coupled receptors that positively and
negatively regulate synaptic transmission through downstream
signalling. Binding of codeine or morphine to the mu opioid receptor
results in hyperpolarization of the neuron leading to the inhibition of
release of nociceptive neurotransmitters causing an analgesic effect
and increased pain tolerance due to reduced neuronal excitability.
• ADVERSE REACTION/SIDE EFFECTS:
stomach cramps
dry mouth less common side effects:
loss of appetite • itchy, raised or red skin rash
constipation • swelling of face
nausea (feeling sick) • muscle stiffness
vomiting • breathing difficulties
dizziness • heartbeat irregularities
drowsiness • blurred or double vision
feeling faint • difficulty in urinating (passing water)
excitability
skin rashes
unable to sleep
unusual dreams
THANK
YOU
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- RF 265 266 Ab Samsung Refri PDFDocument107 pagesRF 265 266 Ab Samsung Refri PDFaderlochNo ratings yet
- ZopicloneDocument2 pagesZopicloneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Pharma CardsDocument5 pagesPharma CardsazancheNo ratings yet
- O-Level Commerce PDFDocument8 pagesO-Level Commerce PDFClinton ChikengezhaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reporting-1Document32 pagesPharmacology Reporting-1Mj TalentNo ratings yet
- Barbiturate Benzodiazepine PoisoningDocument23 pagesBarbiturate Benzodiazepine PoisoningRoman MamunNo ratings yet
- Anti EpilepticsDocument29 pagesAnti Epilepticskeerthi sivayanamaNo ratings yet
- SedativesDocument21 pagesSedativesKeerthana KNo ratings yet
- AnticonvulsantDocument37 pagesAnticonvulsantPamela MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sedative/ Hypnotics: Silim, Miriam Grace DDocument29 pagesSedative/ Hypnotics: Silim, Miriam Grace DDeloria, Alma J.No ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Mental IllnessDocument60 pagesDrugs Used in Mental IllnessDixa MeNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Drugs 2Document57 pagesPsychiatry Drugs 2Abdulmajid mohamedNo ratings yet
- 7 Sedative Hypnotics Anti AnxietyDocument30 pages7 Sedative Hypnotics Anti Anxietyranjitasubedi678No ratings yet
- Antiparkinson DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinson DrugsSV SagarNo ratings yet
- Sedatives and Hypnotics LectureDocument55 pagesSedatives and Hypnotics LectureOSAKA THOMASNo ratings yet
- HypnoticsDocument27 pagesHypnoticsattu farrayalNo ratings yet
- AnalgesicDocument42 pagesAnalgesicVinayak SinghNo ratings yet
- Procaine: BupivicaineDocument7 pagesProcaine: BupivicaineBirara ChakilieNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument65 pagesParkinson's DiseaseGerald Resubal OriñaNo ratings yet
- Scribble Pad: Drugs Used To Treat Parkinson'sDocument24 pagesScribble Pad: Drugs Used To Treat Parkinson'sLydia Lopz MsnrncdNo ratings yet
- CNS PNS DrugsDocument29 pagesCNS PNS DrugsMadel A. AlberioNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument24 pagesParkinson's Diseasejanemwanza003No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyJaessa Feliciano50% (2)
- OpioidsDocument62 pagesOpioidssourabh jakharNo ratings yet
- Sedative Hypnotic PoisoningDocument37 pagesSedative Hypnotic PoisoningDeepa WilliamNo ratings yet
- Handout 2563 OpioidsDocument84 pagesHandout 2563 OpioidsPiya TangNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson Disease - PDF - Pharmacology - AssignmentDocument11 pagesAnti Parkinson Disease - PDF - Pharmacology - AssignmentMr HotmasterNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug Studykarenkaren09No ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of ParkinsonismDocument28 pagesDrug Therapy of ParkinsonismZobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Cardiac EmergenciesDocument18 pagesDrugs Used in Cardiac Emergencieshakky gamyNo ratings yet
- Adjuvant AnalgesicDocument19 pagesAdjuvant AnalgesicKyra KhalidNo ratings yet
- Opiod Analgesics &antagonistsDocument58 pagesOpiod Analgesics &antagonistsVictoria ChepkorirNo ratings yet
- Block I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Antiparkisonian DrugsDocument41 pagesBlock I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Antiparkisonian DrugsOdiete EfeNo ratings yet
- Antidote Meds in Crash Cart (Naloxone, Hydrobromide, Flumazenil)Document5 pagesAntidote Meds in Crash Cart (Naloxone, Hydrobromide, Flumazenil)Still DollNo ratings yet
- Medications NHBDocument40 pagesMedications NHBAnonymous 7hJgATNo ratings yet
- MedicationDocument31 pagesMedicationMary Joy Morales BuquiranNo ratings yet
- OpioidsDocument57 pagesOpioidsSteven Okta ChandraNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument30 pagesParkinsonRebecca HarsNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia and Drugs RealDocument37 pagesAnesthesia and Drugs Realshehryarahmed1021998No ratings yet
- Drugs in ICUDocument83 pagesDrugs in ICUJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Conscious Sedation: Hayel Gharaibeh, MD. Anesthesia ConsultantDocument84 pagesConscious Sedation: Hayel Gharaibeh, MD. Anesthesia ConsultantKhaled GharaibehNo ratings yet
- Opioid AnalgesicsDocument27 pagesOpioid AnalgesicsDivya VarsiniNo ratings yet
- OpioidanalgesicsDocument30 pagesOpioidanalgesicsMr VoralpenNo ratings yet
- Emergency Drugs Used in DentistryDocument53 pagesEmergency Drugs Used in Dentistryasmita1989No ratings yet
- Premedication: Presenter-Dr - Srishti Moderator-Dr.R.Pal (Professor) Dr.P. Jain (Associate Professor)Document34 pagesPremedication: Presenter-Dr - Srishti Moderator-Dr.R.Pal (Professor) Dr.P. Jain (Associate Professor)Viresh Upase Roll No 130. / 8th termNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinson Drugs FinallDocument36 pagesAnti Parkinson Drugs FinallandrapradeshsseNo ratings yet
- Drug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsDocument57 pagesDrug Presentation: Manisha M.Sc. Nursing 1 Year Con IlbsManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Hypnoti and SedativeDocument30 pagesHypnoti and SedativeC velmuruganNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AgonistsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic AgonistsArjay LucenaNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinson Pharma 2020Document26 pagesAntiparkinson Pharma 2020Ida Bagus Putu SwabawaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyJohn LesterNo ratings yet
- Typical Antipsychotic DrugsDocument4 pagesTypical Antipsychotic DrugsErika Blaire N. OlacaoNo ratings yet
- Archivetempfinal RevisionDocument140 pagesArchivetempfinal RevisionSheza FarooqNo ratings yet
- Influence The Opioids To ImmunityDocument13 pagesInfluence The Opioids To ImmunityoctaviasulistyaNo ratings yet
- Movement DisordersDocument28 pagesMovement DisordersAhmad WaliNo ratings yet
- Parkinson Disease SlidesDocument21 pagesParkinson Disease Slidessarah morley100% (2)
- FAR 381 - Opioids - 2018 - Lecture UploadDocument36 pagesFAR 381 - Opioids - 2018 - Lecture UploadHuzaifa KhanNo ratings yet
- Anastesi DrugDocument28 pagesAnastesi DrugGita KhairiyahNo ratings yet
- Analgesics: DR Mohammed Malik AfrozDocument37 pagesAnalgesics: DR Mohammed Malik AfrozMohee DawabshehNo ratings yet
- Anti Parkinsonism AgentsDocument16 pagesAnti Parkinsonism AgentsLacangan, Thea YvonneNo ratings yet
- Rabies: Dr. Paul Bartlett, MPH., DVM., PH.DDocument45 pagesRabies: Dr. Paul Bartlett, MPH., DVM., PH.DnfrnufaNo ratings yet
- Audit ComplianceDocument10 pagesAudit ComplianceAl-Amin SarkarNo ratings yet
- JEE 2024 RoadmapDocument42 pagesJEE 2024 Roadmaplilop27557No ratings yet
- Waterworld201808 DLDocument56 pagesWaterworld201808 DLThiyagu ManogaranNo ratings yet
- Vendor: Design Information: Gas BootDocument2 pagesVendor: Design Information: Gas Boot124swadeshiNo ratings yet
- Heat Recovery Steam Generator For Cheng Cycle Application: Reprinted From 1988Document5 pagesHeat Recovery Steam Generator For Cheng Cycle Application: Reprinted From 1988Herberth SilitongaNo ratings yet
- Nivel Básico de Inglés Septiembre 2016 Comprensión de Lectura Modelo de CorrecciónDocument8 pagesNivel Básico de Inglés Septiembre 2016 Comprensión de Lectura Modelo de CorrecciónEsther León JorgeNo ratings yet
- CH PDFDocument43 pagesCH PDFBobVonCatNo ratings yet
- 7th History Workbook English Medium Maharashtra BoardDocument12 pages7th History Workbook English Medium Maharashtra Boardpankarvi6100% (1)
- Experiment No. (6) Study of Dispersion Compensation Schemes: ObjectDocument9 pagesExperiment No. (6) Study of Dispersion Compensation Schemes: ObjectFaez FawwazNo ratings yet
- Exhibitor List Foam ExpoDocument7 pagesExhibitor List Foam Expohijero7692No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae of Supramaniyan KumarDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae of Supramaniyan KumarSupramaniyan kumarNo ratings yet
- Final Stilt Floor Plan 16042022Document1 pageFinal Stilt Floor Plan 16042022rajesh lankaNo ratings yet
- The Vivago Watch A Telecare Solution For Cost-Efficient CareDocument1 pageThe Vivago Watch A Telecare Solution For Cost-Efficient CareGeronTechnoPlatformNo ratings yet
- CP7211 Advanced Databases Laboratory ManualDocument63 pagesCP7211 Advanced Databases Laboratory Manualashaheer75% (4)
- 3is FORMATDocument10 pages3is FORMATAMACIO, MARIAN JOY A.No ratings yet
- Sale Deed: ORGANISATION (AWHO), (PAN No. AABTA4251G) A Society Registered UnderDocument26 pagesSale Deed: ORGANISATION (AWHO), (PAN No. AABTA4251G) A Society Registered Undernaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Section Capacity Section Capacity: AbutmentDocument4 pagesSection Capacity Section Capacity: AbutmentGajendra SNo ratings yet
- Business English 4 - Teacher'S Lecture Notes: 2 Signposting - Page 8Document12 pagesBusiness English 4 - Teacher'S Lecture Notes: 2 Signposting - Page 8AndraStefaniaNo ratings yet
- PT ArchanaDocument9 pagesPT ArchanadhavalNo ratings yet
- Afn 2 PDFDocument5 pagesAfn 2 PDFLovely Ann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sri Mahila Griha Udyog Lijjat Papad: Strategic Management CourseDocument23 pagesSri Mahila Griha Udyog Lijjat Papad: Strategic Management CoursePrachit ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Doordash Agreement Contract October 25Document13 pagesDoordash Agreement Contract October 25wagaga papapaNo ratings yet
- 600 ngữ pháp chọn lọc luyện thi THPT Quốc GiaDocument32 pages600 ngữ pháp chọn lọc luyện thi THPT Quốc GiaNguyen Chi Cuong100% (1)
- Advanced Enzymes White PaperDocument16 pagesAdvanced Enzymes White PaperAnubhav TripathiNo ratings yet
- BBRC4103 Kaedah Penyelidikan September Semester 2020Document12 pagesBBRC4103 Kaedah Penyelidikan September Semester 2020SARIPAH NOOR FARAH AIN BINTI P.AFDZAL SHAH STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Risk-Return Relationship On Equity Shares in India 1Document11 pagesRisk-Return Relationship On Equity Shares in India 1Tanmaya BiswalNo ratings yet
- Smart Battery Data Specification Revision 1.1 ErrataDocument5 pagesSmart Battery Data Specification Revision 1.1 ErrataredmsbatteryNo ratings yet