Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 viewsUnit-I 80386DX Architecture
Unit-I 80386DX Architecture
Uploaded by
josephThe document summarizes the architecture of the Intel 8086 microprocessor. It describes the 8086's functional blocks including the Execution Unit (EU) and Bus Interface Unit (BIU). The EU contains an ALU, general purpose registers including AX, BX, CX, DX, and flags that are set based on arithmetic/logic operations. The BIU handles fetching instructions and data from memory to pass to the EU for processing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Central On-Board Computer 2 (ZBR2) A302Document40 pagesCentral On-Board Computer 2 (ZBR2) A302Dan Rosoiu50% (4)
- Assembly Language:Simple, Short, And Straightforward Way Of Learning Assembly ProgrammingFrom EverandAssembly Language:Simple, Short, And Straightforward Way Of Learning Assembly ProgrammingRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Substation Automation SystemDocument44 pagesSubstation Automation SystemKASHIFNo ratings yet
- Unit II Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor 8086 ArchitectureDocument34 pagesUnit II Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor 8086 ArchitectureabhitilluNo ratings yet
- Unit II Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor 8086 ArchitectureDocument34 pagesUnit II Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor 8086 ArchitectureGetachew ShambelNo ratings yet
- Execution Unit and BIUDocument29 pagesExecution Unit and BIUMohammad ZakirNo ratings yet
- Ec 8691-Microprocessors and Microcontrollers: Prepared by N.Beaula Ap/Ece ACEW, ManavilaiDocument39 pagesEc 8691-Microprocessors and Microcontrollers: Prepared by N.Beaula Ap/Ece ACEW, ManavilaibeaulajenishNo ratings yet
- Internal Architecture of Intel 8086, FinalDocument24 pagesInternal Architecture of Intel 8086, FinalAshek E Elahi SohanNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 8086Document17 pagesArchitecture of 8086sreenimolNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document31 pagesUnit 1VELU KNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor: Prof. Niraj Kumar, Assistant Professor, Vellore Institute of Technology, ChennaiDocument50 pagesIntroduction To 8086 Microprocessor: Prof. Niraj Kumar, Assistant Professor, Vellore Institute of Technology, ChennaiAyyeeeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Part III) - The 8086 MicroprocessorDocument34 pagesChapter 3 (Part III) - The 8086 MicroprocessorKirubel EsayasNo ratings yet
- Aim: Apparatus: Theory:: 8086 Trainer KitDocument8 pagesAim: Apparatus: Theory:: 8086 Trainer Kitdeepa9bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Unit-1 PART ADocument12 pagesMicroprocessor Unit-1 PART ASasi BhushanNo ratings yet
- Detailed BIU and CUDocument5 pagesDetailed BIU and CUhago sohaniNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 8086 PDFDocument39 pagesArchitecture of 8086 PDFSourabh DasNo ratings yet
- E-Notes Compiled SrinathDocument24 pagesE-Notes Compiled SrinathArjun SvNo ratings yet
- Advanced Processor: B.E. Semester V (CE)Document130 pagesAdvanced Processor: B.E. Semester V (CE)JAAPANo ratings yet
- 14 12 31 10 21 13 2925 SabarishDocument72 pages14 12 31 10 21 13 2925 Sabarishprof_ktNo ratings yet
- 8086 Microprocessor CheatsheetDocument17 pages8086 Microprocessor Cheatsheetdz15dzNo ratings yet
- Internal Block Diagram of 8086Document33 pagesInternal Block Diagram of 8086Salitha100% (1)
- Unit I The 8086 MicroprocessorDocument21 pagesUnit I The 8086 Microprocessor16211a0470100% (1)
- CHAP - I MicroprocessorDocument49 pagesCHAP - I MicroprocessorVuggam VenkateshNo ratings yet
- 8086 Architecture Addressing ModesDocument10 pages8086 Architecture Addressing ModesKumaran GNo ratings yet
- Execution Unit (EU)Document5 pagesExecution Unit (EU)Megha GargNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document3 pagesExperiment 1brajeshkumar.jha.litsNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8086 NewDocument15 pagesMicroprocessor 8086 NewShyamasree DuttaNo ratings yet
- MP Module 1 - ModifiedDocument15 pagesMP Module 1 - Modifiedakhil krishnanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1&3Document18 pagesUnit 1&3Sreekanth PagadapalliNo ratings yet
- 8086 arch-SNKDocument7 pages8086 arch-SNKzelalem2022No ratings yet
- 8086 Notes NITW2020Document76 pages8086 Notes NITW2020ka21ecb0f27No ratings yet
- 8086 MicroprocessorDocument25 pages8086 Microprocessorابن اليمنNo ratings yet
- 8086 Unit IIDocument49 pages8086 Unit IISai Sreenath100% (1)
- Introduction to 8086Document14 pagesIntroduction to 8086Sasi BhushanNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8086Document14 pagesMicroprocessor 8086vshlvvkNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument22 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers6012 ANILNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Intel 8086Document135 pagesChapter 3: Intel 8086singhrps8483% (6)
- Unit-Vi Lecture Notes: - 8086 MICROPROCESSOR: 8086 ArchitectureDocument29 pagesUnit-Vi Lecture Notes: - 8086 MICROPROCESSOR: 8086 Architectureramarao pagadalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Ree602Document235 pagesUnit 3 Ree602Praveen YadavNo ratings yet
- 8086 ArchitectureDocument28 pages8086 ArchitectureSUHANA PATELNo ratings yet
- EC 6513 Microprocessor and Microcontroller ManualDocument121 pagesEC 6513 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Manualsaravanantec100% (1)
- Micro 8086Document119 pagesMicro 8086Md Fairuz SiddiqueeNo ratings yet
- Register Organization of 8086 PDFDocument10 pagesRegister Organization of 8086 PDFDevikaNo ratings yet
- 16 Bit Microprocessor 8086Document11 pages16 Bit Microprocessor 8086Yogesh KuteNo ratings yet
- Sewp Zc413 Computer Organization & ArchitectureDocument16 pagesSewp Zc413 Computer Organization & Architectureshravanr500No ratings yet
- 8086 ArchDocument19 pages8086 Archapi-3848496100% (1)
- Unit-1,2,3 MP&MC NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-1,2,3 MP&MC NotesHyma Prasad GelliNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 8086 Microprocessor: Microprocessors LabDocument7 pagesArchitecture of 8086 Microprocessor: Microprocessors LabljjbNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document18 pagesLec 4عمیر بن اصغرNo ratings yet
- 8086 Architecture: 8086 FeaturesDocument26 pages8086 Architecture: 8086 FeaturesVedhaVyas MahasivaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor SystemsDocument26 pagesMicroprocessor SystemsHaseeb shaikhNo ratings yet
- Significance of QueueDocument6 pagesSignificance of QueueJun Alfred Alba100% (1)
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument15 pagesMicroprocessors and MicrocontrollerslekaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document67 pagesChapter 2Micha'el AbebeNo ratings yet
- Mpi Unit 1Document22 pagesMpi Unit 1sree ramyaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Helpful NotesDocument234 pagesMicroprocessor Helpful NotesNevin HardyNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 ThirdmicroprocessorcDocument22 pagesLecture2 Thirdmicroprocessorcxkurt358792100% (2)
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationFrom EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationNo ratings yet
- Electronic & Precision Equipment Repair & Maintenance Lines World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandElectronic & Precision Equipment Repair & Maintenance Lines World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Full Segment DefinitionDocument18 pagesFull Segment DefinitionjosephNo ratings yet
- Up 4Document27 pagesUp 4josephNo ratings yet
- Interrupt Programming With CDocument18 pagesInterrupt Programming With CjosephNo ratings yet
- Program Segments: - It Has Only 16 Pins For The Address Lines (2 64K)Document18 pagesProgram Segments: - It Has Only 16 Pins For The Address Lines (2 64K)josephNo ratings yet
- Up 7Document14 pagesUp 7josephNo ratings yet
- Assembly Language ProgrammingDocument19 pagesAssembly Language ProgrammingjosephNo ratings yet
- Up 5Document17 pagesUp 5josephNo ratings yet
- General Registers I: - Accumulator'Document8 pagesGeneral Registers I: - Accumulator'josephNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of 8086Document19 pagesBlock Diagram of 8086josephNo ratings yet
- Execution Unit - PointersDocument12 pagesExecution Unit - PointersjosephNo ratings yet
- SYSC3601 Microprocessor Systems: Unit 8: Direct Memory Access (DMA)Document14 pagesSYSC3601 Microprocessor Systems: Unit 8: Direct Memory Access (DMA)josephNo ratings yet
- Developing A Generic Hard Fault Handler For ARM Cortex M3/M4Document21 pagesDeveloping A Generic Hard Fault Handler For ARM Cortex M3/M4Hassaan ShahNo ratings yet
- Mac On FigDocument449 pagesMac On Figvuk_vucko_vukovicNo ratings yet
- Original Commodore Business Machines Plus 4 Docs, The, (2003) (Lidovski, V)Document40 pagesOriginal Commodore Business Machines Plus 4 Docs, The, (2003) (Lidovski, V)BASILEIOS KATHOLOSNo ratings yet
- Opti 320techspecsDocument6 pagesOpti 320techspecsHùng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesMicroprocessor Interview QuestionsYedu SujithNo ratings yet
- Exfire360 Fire&Gas Control PanelDocument6 pagesExfire360 Fire&Gas Control PanelKorichiKarimNo ratings yet
- Section A: Operating System and Computer Architecture 1 of 7Document7 pagesSection A: Operating System and Computer Architecture 1 of 7arun neupaneNo ratings yet
- EPLAN PropertiesDocument40 pagesEPLAN Propertiesflash_90697638No ratings yet
- Model Based E/E Architecture Development at Daimler: ... and A Look at The Broader PictureDocument16 pagesModel Based E/E Architecture Development at Daimler: ... and A Look at The Broader PictureRandy Collins100% (1)
- Motherboard - 11Document58 pagesMotherboard - 11jmkcbeNo ratings yet
- EGCP 2 Installation and Operation Manual en TechManDocument234 pagesEGCP 2 Installation and Operation Manual en TechManRigoberto Lozano100% (2)
- GR CHECK Module 4 Exam Style Answers Processor Fundamentals CUPDocument3 pagesGR CHECK Module 4 Exam Style Answers Processor Fundamentals CUPKanishk T.R.No ratings yet
- Motion Control: 7344/7334 Hardware User ManualDocument66 pagesMotion Control: 7344/7334 Hardware User ManualChecho260493No ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Architecture of 8086Document45 pagesUNIT-1: Architecture of 8086amoghNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Grade 8 Curriculum Design 1Document91 pagesComputer Science Grade 8 Curriculum Design 1kinyanjui_eNo ratings yet
- GE Fanuc Automation: Series 0i-Model C Series 0i Mate-Model CDocument366 pagesGE Fanuc Automation: Series 0i-Model C Series 0i Mate-Model CkiemkhachvotinhNo ratings yet
- Atmega 2560 Ingles (031-060)Document30 pagesAtmega 2560 Ingles (031-060)Yovan MamaniNo ratings yet
- The Relatively Simple Cpu SimulatorDocument9 pagesThe Relatively Simple Cpu SimulatorTrendkill Trendkill TrendkillNo ratings yet
- 01 IntroductionDocument15 pages01 IntroductionDeepak ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 8085 Note-3Document21 pages8085 Note-3Anonymous dxqddDNo ratings yet
- MX Component Ver.4 - Programming Manual SH (NA) - 081085-G (04.15)Document586 pagesMX Component Ver.4 - Programming Manual SH (NA) - 081085-G (04.15)ngoxuannghiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Functioning of A Computer: Structure Page NoDocument16 pagesUnit 2 Functioning of A Computer: Structure Page NoanuragNo ratings yet
- Product-Overview 2012 ESU-KG en EbookDocument64 pagesProduct-Overview 2012 ESU-KG en EbookstefanofagnaniNo ratings yet
- Intel Desktop Board D865PERC/D865PESO: Technical Product SpecificationDocument130 pagesIntel Desktop Board D865PERC/D865PESO: Technical Product SpecificationMichael PuentesNo ratings yet
- Data Flow ModelDocument3 pagesData Flow ModelJyothsnaNo ratings yet
- El 6752 enDocument111 pagesEl 6752 enLuis Alberto Zapata OjedaNo ratings yet
- Co 18cs34 Notes FinalDocument141 pagesCo 18cs34 Notes FinalAshishNo ratings yet
- CSE Graphics Processing UnitDocument26 pagesCSE Graphics Processing UnitYash AgrawalNo ratings yet
Unit-I 80386DX Architecture
Unit-I 80386DX Architecture
Uploaded by
joseph0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views14 pagesThe document summarizes the architecture of the Intel 8086 microprocessor. It describes the 8086's functional blocks including the Execution Unit (EU) and Bus Interface Unit (BIU). The EU contains an ALU, general purpose registers including AX, BX, CX, DX, and flags that are set based on arithmetic/logic operations. The BIU handles fetching instructions and data from memory to pass to the EU for processing.
Original Description:
Original Title
up 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the architecture of the Intel 8086 microprocessor. It describes the 8086's functional blocks including the Execution Unit (EU) and Bus Interface Unit (BIU). The EU contains an ALU, general purpose registers including AX, BX, CX, DX, and flags that are set based on arithmetic/logic operations. The BIU handles fetching instructions and data from memory to pass to the EU for processing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views14 pagesUnit-I 80386DX Architecture
Unit-I 80386DX Architecture
Uploaded by
josephThe document summarizes the architecture of the Intel 8086 microprocessor. It describes the 8086's functional blocks including the Execution Unit (EU) and Bus Interface Unit (BIU). The EU contains an ALU, general purpose registers including AX, BX, CX, DX, and flags that are set based on arithmetic/logic operations. The BIU handles fetching instructions and data from memory to pass to the EU for processing.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Unit-I 80386DX Architecture
History of 8086 microprocessor, Concept of
segmentation in 8086, 8086 Register block diagram
80386DX functional Block Diagram, PIN Description,
Register set, Flags, Physical address space, Data types
History of 8086
Architecture of 8086
The architecture of 8086 includes
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Flags
General registers
Instruction byte queue
Segment registers
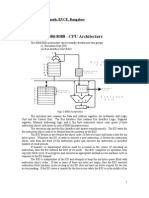
EU & BIU
The 8086 CPU logic has been partitioned into two
functional units namely Bus Interface Unit (BIU) and
Execution Unit (EU)
The major reason for this separation is to increase the
processing speed of the processor
The BIU has to interact with memory and input and
output devices in fetching the instructions and data
required by the EU
EU is responsible for executing the instructions of the
programs and to carry out the required processing
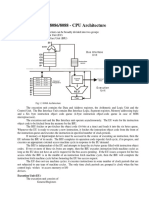
Architecture Diagram
Execution Unit
The Execution Unit (EU) has
Control unit
Instruction decoder
Arithmetic and Logical Unit (ALU)
General registers
Flag register
Pointers
Index registers
Execution Unit
Control unit is responsible for the co-ordination of all
other units of the processor.
ALU performs various arithmetic and logical
operations over the data.
The instruction decoder translates the instructions
fetched from the memory into a series of actions that
are carried out by the EU.
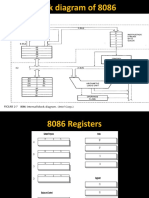
Execution Unit - Registers
General registers are used for temporary storage and
manipulation of data and instructions
Accumulator register consists of two 8-bit registers AL
and AH, which can be combined together and used as
a 16-bit register AX
Accumulator can be used for I/O operations and
string manipulation
Execution Unit - Registers
Base register consists of two 8-bit registers BL and BH,
which can be combined together and used as a 16-bit
register BX .
BX register usually contains a data pointer used for based,
based indexed or register indirect addressing.
Count register consists of two 8-bit registers CL and CH,
which can be combined together and used as a 16-bit
register CX .
Count register can be used as a counter in string
manipulation and shift/rotate instructions.
Execution Unit - Registers
Data register consists of two 8-bit registers DL and
DH, which can be combined together and used as a 16-
bit register DX.
Data register can be used as a port number in I/O
operations.
In integer 32-bit multiply and divide instruction the
DX register contains high-order word of the initial or
resulting number .
Execution Unit - Registers
Execution Unit - Flags
Execution Unit - Flags
Flags
Conditional Flags:
Set or reset by EU on the basis of the results of
arithmetic or logic operation
Control Flags (TF,IF,DF)
You might also like
- Central On-Board Computer 2 (ZBR2) A302Document40 pagesCentral On-Board Computer 2 (ZBR2) A302Dan Rosoiu50% (4)
- Assembly Language:Simple, Short, And Straightforward Way Of Learning Assembly ProgrammingFrom EverandAssembly Language:Simple, Short, And Straightforward Way Of Learning Assembly ProgrammingRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Substation Automation SystemDocument44 pagesSubstation Automation SystemKASHIFNo ratings yet
- Unit II Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor 8086 ArchitectureDocument34 pagesUnit II Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor 8086 ArchitectureabhitilluNo ratings yet
- Unit II Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor 8086 ArchitectureDocument34 pagesUnit II Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor 8086 ArchitectureGetachew ShambelNo ratings yet
- Execution Unit and BIUDocument29 pagesExecution Unit and BIUMohammad ZakirNo ratings yet
- Ec 8691-Microprocessors and Microcontrollers: Prepared by N.Beaula Ap/Ece ACEW, ManavilaiDocument39 pagesEc 8691-Microprocessors and Microcontrollers: Prepared by N.Beaula Ap/Ece ACEW, ManavilaibeaulajenishNo ratings yet
- Internal Architecture of Intel 8086, FinalDocument24 pagesInternal Architecture of Intel 8086, FinalAshek E Elahi SohanNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 8086Document17 pagesArchitecture of 8086sreenimolNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document31 pagesUnit 1VELU KNo ratings yet
- Introduction To 8086 Microprocessor: Prof. Niraj Kumar, Assistant Professor, Vellore Institute of Technology, ChennaiDocument50 pagesIntroduction To 8086 Microprocessor: Prof. Niraj Kumar, Assistant Professor, Vellore Institute of Technology, ChennaiAyyeeeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Part III) - The 8086 MicroprocessorDocument34 pagesChapter 3 (Part III) - The 8086 MicroprocessorKirubel EsayasNo ratings yet
- Aim: Apparatus: Theory:: 8086 Trainer KitDocument8 pagesAim: Apparatus: Theory:: 8086 Trainer Kitdeepa9bhardwajNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Unit-1 PART ADocument12 pagesMicroprocessor Unit-1 PART ASasi BhushanNo ratings yet
- Detailed BIU and CUDocument5 pagesDetailed BIU and CUhago sohaniNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 8086 PDFDocument39 pagesArchitecture of 8086 PDFSourabh DasNo ratings yet
- E-Notes Compiled SrinathDocument24 pagesE-Notes Compiled SrinathArjun SvNo ratings yet
- Advanced Processor: B.E. Semester V (CE)Document130 pagesAdvanced Processor: B.E. Semester V (CE)JAAPANo ratings yet
- 14 12 31 10 21 13 2925 SabarishDocument72 pages14 12 31 10 21 13 2925 Sabarishprof_ktNo ratings yet
- 8086 Microprocessor CheatsheetDocument17 pages8086 Microprocessor Cheatsheetdz15dzNo ratings yet
- Internal Block Diagram of 8086Document33 pagesInternal Block Diagram of 8086Salitha100% (1)
- Unit I The 8086 MicroprocessorDocument21 pagesUnit I The 8086 Microprocessor16211a0470100% (1)
- CHAP - I MicroprocessorDocument49 pagesCHAP - I MicroprocessorVuggam VenkateshNo ratings yet
- 8086 Architecture Addressing ModesDocument10 pages8086 Architecture Addressing ModesKumaran GNo ratings yet
- Execution Unit (EU)Document5 pagesExecution Unit (EU)Megha GargNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document3 pagesExperiment 1brajeshkumar.jha.litsNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8086 NewDocument15 pagesMicroprocessor 8086 NewShyamasree DuttaNo ratings yet
- MP Module 1 - ModifiedDocument15 pagesMP Module 1 - Modifiedakhil krishnanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1&3Document18 pagesUnit 1&3Sreekanth PagadapalliNo ratings yet
- 8086 arch-SNKDocument7 pages8086 arch-SNKzelalem2022No ratings yet
- 8086 Notes NITW2020Document76 pages8086 Notes NITW2020ka21ecb0f27No ratings yet
- 8086 MicroprocessorDocument25 pages8086 Microprocessorابن اليمنNo ratings yet
- 8086 Unit IIDocument49 pages8086 Unit IISai Sreenath100% (1)
- Introduction to 8086Document14 pagesIntroduction to 8086Sasi BhushanNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8086Document14 pagesMicroprocessor 8086vshlvvkNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument22 pagesMicroprocessors and Microcontrollers6012 ANILNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Intel 8086Document135 pagesChapter 3: Intel 8086singhrps8483% (6)
- Unit-Vi Lecture Notes: - 8086 MICROPROCESSOR: 8086 ArchitectureDocument29 pagesUnit-Vi Lecture Notes: - 8086 MICROPROCESSOR: 8086 Architectureramarao pagadalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Ree602Document235 pagesUnit 3 Ree602Praveen YadavNo ratings yet
- 8086 ArchitectureDocument28 pages8086 ArchitectureSUHANA PATELNo ratings yet
- EC 6513 Microprocessor and Microcontroller ManualDocument121 pagesEC 6513 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Manualsaravanantec100% (1)
- Micro 8086Document119 pagesMicro 8086Md Fairuz SiddiqueeNo ratings yet
- Register Organization of 8086 PDFDocument10 pagesRegister Organization of 8086 PDFDevikaNo ratings yet
- 16 Bit Microprocessor 8086Document11 pages16 Bit Microprocessor 8086Yogesh KuteNo ratings yet
- Sewp Zc413 Computer Organization & ArchitectureDocument16 pagesSewp Zc413 Computer Organization & Architectureshravanr500No ratings yet
- 8086 ArchDocument19 pages8086 Archapi-3848496100% (1)
- Unit-1,2,3 MP&MC NotesDocument25 pagesUnit-1,2,3 MP&MC NotesHyma Prasad GelliNo ratings yet
- Architecture of 8086 Microprocessor: Microprocessors LabDocument7 pagesArchitecture of 8086 Microprocessor: Microprocessors LabljjbNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document18 pagesLec 4عمیر بن اصغرNo ratings yet
- 8086 Architecture: 8086 FeaturesDocument26 pages8086 Architecture: 8086 FeaturesVedhaVyas MahasivaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor SystemsDocument26 pagesMicroprocessor SystemsHaseeb shaikhNo ratings yet
- Significance of QueueDocument6 pagesSignificance of QueueJun Alfred Alba100% (1)
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument15 pagesMicroprocessors and MicrocontrollerslekaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document67 pagesChapter 2Micha'el AbebeNo ratings yet
- Mpi Unit 1Document22 pagesMpi Unit 1sree ramyaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Helpful NotesDocument234 pagesMicroprocessor Helpful NotesNevin HardyNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 ThirdmicroprocessorcDocument22 pagesLecture2 Thirdmicroprocessorcxkurt358792100% (2)
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- Practical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationFrom EverandPractical Reverse Engineering: x86, x64, ARM, Windows Kernel, Reversing Tools, and ObfuscationNo ratings yet
- Electronic & Precision Equipment Repair & Maintenance Lines World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryFrom EverandElectronic & Precision Equipment Repair & Maintenance Lines World Summary: Market Values & Financials by CountryNo ratings yet
- Full Segment DefinitionDocument18 pagesFull Segment DefinitionjosephNo ratings yet
- Up 4Document27 pagesUp 4josephNo ratings yet
- Interrupt Programming With CDocument18 pagesInterrupt Programming With CjosephNo ratings yet
- Program Segments: - It Has Only 16 Pins For The Address Lines (2 64K)Document18 pagesProgram Segments: - It Has Only 16 Pins For The Address Lines (2 64K)josephNo ratings yet
- Up 7Document14 pagesUp 7josephNo ratings yet
- Assembly Language ProgrammingDocument19 pagesAssembly Language ProgrammingjosephNo ratings yet
- Up 5Document17 pagesUp 5josephNo ratings yet
- General Registers I: - Accumulator'Document8 pagesGeneral Registers I: - Accumulator'josephNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of 8086Document19 pagesBlock Diagram of 8086josephNo ratings yet
- Execution Unit - PointersDocument12 pagesExecution Unit - PointersjosephNo ratings yet
- SYSC3601 Microprocessor Systems: Unit 8: Direct Memory Access (DMA)Document14 pagesSYSC3601 Microprocessor Systems: Unit 8: Direct Memory Access (DMA)josephNo ratings yet
- Developing A Generic Hard Fault Handler For ARM Cortex M3/M4Document21 pagesDeveloping A Generic Hard Fault Handler For ARM Cortex M3/M4Hassaan ShahNo ratings yet
- Mac On FigDocument449 pagesMac On Figvuk_vucko_vukovicNo ratings yet
- Original Commodore Business Machines Plus 4 Docs, The, (2003) (Lidovski, V)Document40 pagesOriginal Commodore Business Machines Plus 4 Docs, The, (2003) (Lidovski, V)BASILEIOS KATHOLOSNo ratings yet
- Opti 320techspecsDocument6 pagesOpti 320techspecsHùng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Interview QuestionsDocument7 pagesMicroprocessor Interview QuestionsYedu SujithNo ratings yet
- Exfire360 Fire&Gas Control PanelDocument6 pagesExfire360 Fire&Gas Control PanelKorichiKarimNo ratings yet
- Section A: Operating System and Computer Architecture 1 of 7Document7 pagesSection A: Operating System and Computer Architecture 1 of 7arun neupaneNo ratings yet
- EPLAN PropertiesDocument40 pagesEPLAN Propertiesflash_90697638No ratings yet
- Model Based E/E Architecture Development at Daimler: ... and A Look at The Broader PictureDocument16 pagesModel Based E/E Architecture Development at Daimler: ... and A Look at The Broader PictureRandy Collins100% (1)
- Motherboard - 11Document58 pagesMotherboard - 11jmkcbeNo ratings yet
- EGCP 2 Installation and Operation Manual en TechManDocument234 pagesEGCP 2 Installation and Operation Manual en TechManRigoberto Lozano100% (2)
- GR CHECK Module 4 Exam Style Answers Processor Fundamentals CUPDocument3 pagesGR CHECK Module 4 Exam Style Answers Processor Fundamentals CUPKanishk T.R.No ratings yet
- Motion Control: 7344/7334 Hardware User ManualDocument66 pagesMotion Control: 7344/7334 Hardware User ManualChecho260493No ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Architecture of 8086Document45 pagesUNIT-1: Architecture of 8086amoghNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Grade 8 Curriculum Design 1Document91 pagesComputer Science Grade 8 Curriculum Design 1kinyanjui_eNo ratings yet
- GE Fanuc Automation: Series 0i-Model C Series 0i Mate-Model CDocument366 pagesGE Fanuc Automation: Series 0i-Model C Series 0i Mate-Model CkiemkhachvotinhNo ratings yet
- Atmega 2560 Ingles (031-060)Document30 pagesAtmega 2560 Ingles (031-060)Yovan MamaniNo ratings yet
- The Relatively Simple Cpu SimulatorDocument9 pagesThe Relatively Simple Cpu SimulatorTrendkill Trendkill TrendkillNo ratings yet
- 01 IntroductionDocument15 pages01 IntroductionDeepak ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 8085 Note-3Document21 pages8085 Note-3Anonymous dxqddDNo ratings yet
- MX Component Ver.4 - Programming Manual SH (NA) - 081085-G (04.15)Document586 pagesMX Component Ver.4 - Programming Manual SH (NA) - 081085-G (04.15)ngoxuannghiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Functioning of A Computer: Structure Page NoDocument16 pagesUnit 2 Functioning of A Computer: Structure Page NoanuragNo ratings yet
- Product-Overview 2012 ESU-KG en EbookDocument64 pagesProduct-Overview 2012 ESU-KG en EbookstefanofagnaniNo ratings yet
- Intel Desktop Board D865PERC/D865PESO: Technical Product SpecificationDocument130 pagesIntel Desktop Board D865PERC/D865PESO: Technical Product SpecificationMichael PuentesNo ratings yet
- Data Flow ModelDocument3 pagesData Flow ModelJyothsnaNo ratings yet
- El 6752 enDocument111 pagesEl 6752 enLuis Alberto Zapata OjedaNo ratings yet
- Co 18cs34 Notes FinalDocument141 pagesCo 18cs34 Notes FinalAshishNo ratings yet
- CSE Graphics Processing UnitDocument26 pagesCSE Graphics Processing UnitYash AgrawalNo ratings yet