Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
284 viewsFECALYSIS
FECALYSIS
Uploaded by
marie judimor gomezThis document provides information about fecalysis, a series of tests done on stool samples to diagnose digestive conditions. Key details include: stool samples should be collected in clean, sealed containers and examined within 1 hour for liquid samples or 30 minutes for semi-formed samples. Certain medications can interfere with test results if taken within a week of the sample. Examination of stool samples under a microscope can detect parasites, eggs, larvae, blood, and mucus. Proper collection and transport of fresh stool samples is important for accurate test results.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Virtual Lab Report by Honey Noreen Belnas: The Gram Stain: Identify and DifferentiateDocument16 pagesVirtual Lab Report by Honey Noreen Belnas: The Gram Stain: Identify and DifferentiateJihil KishaNo ratings yet
- CMO14 3mt01Document75 pagesCMO14 3mt01makike100% (2)
- History of Medical Technology Education in The PhilippinesDocument45 pagesHistory of Medical Technology Education in The PhilippinesCedrickNo ratings yet
- College of Medical Laboratory Science Our Lady of Fatima University-VelenzuelaDocument33 pagesCollege of Medical Laboratory Science Our Lady of Fatima University-VelenzuelaClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- Manual AubfDocument4 pagesManual AubfNoraine Princess Tabangcora100% (2)
- FECALYSISDocument14 pagesFECALYSISMarl EstradaNo ratings yet
- Stool Concentration MethodDocument2 pagesStool Concentration Methodqwshagdvndsavsb100% (1)
- Fecalysis LaboratoryDocument7 pagesFecalysis LaboratoryFRANCESCA ALEXANDRIA PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Preservation MethodsDocument5 pagesParasitology Preservation MethodsAinah Charina TapicNo ratings yet
- Crystal Appearance/Characteristics Clinical SignificanceDocument4 pagesCrystal Appearance/Characteristics Clinical SignificanceAngela LaglivaNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesHistopath Lab ActivityRakia PillayNo ratings yet
- History of Med Tech (PPT 1)Document29 pagesHistory of Med Tech (PPT 1)Christopher CaduhadaNo ratings yet
- Principles in Medical Laboratory Science 2Document2 pagesPrinciples in Medical Laboratory Science 2lai cruzNo ratings yet
- Kato Katz TechniqueDocument35 pagesKato Katz TechniqueJohn Paul Valencia100% (2)
- Trichuris TrichiuraDocument3 pagesTrichuris TrichiuraTwish BeraldeNo ratings yet
- FECALYSISDocument43 pagesFECALYSISKen LaguiabNo ratings yet
- Immuno Hema - EX 2 ACT - Veloso, Mary Raffaele G - BSMT 3DDocument3 pagesImmuno Hema - EX 2 ACT - Veloso, Mary Raffaele G - BSMT 3DAnneNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument58 pagesMetabolismZ ZernsNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lecture Module 8 Chapter 10: SEMINALYSIS: Semen AnalysisDocument9 pagesAUBF Lecture Module 8 Chapter 10: SEMINALYSIS: Semen AnalysisColene MoresNo ratings yet
- CC 2 Activity 2Document5 pagesCC 2 Activity 2Valdez Francis ZaccheauNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number 3 Sample Preparation For Blood Banking ProcedureDocument10 pagesExperiment Number 3 Sample Preparation For Blood Banking ProcedureKriziaNo ratings yet
- CPH Lab - Prelim TransesDocument4 pagesCPH Lab - Prelim TransesLOUISSE ANNE MONIQUE L. CAYLONo ratings yet
- Fecal AnalysisDocument13 pagesFecal AnalysisYormae QuezonNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Survey of MicroorganismDocument6 pagesLab 6 - Survey of MicroorganismYusof SundangNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment-LEC/RLE Prelim Exam NCM 201 - College of Nursing San Pedro CollegeDocument6 pagesHealth Assessment-LEC/RLE Prelim Exam NCM 201 - College of Nursing San Pedro CollegeAntoniette Jane Martin PathayNo ratings yet
- The Intestinal NematodesDocument9 pagesThe Intestinal NematodesdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Media Preparation, Isolation of Pure Culture and Bacterial GrowthDocument6 pagesMedia Preparation, Isolation of Pure Culture and Bacterial Growthhamody662002No ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document6 pagesExercise 3Gwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- (HANDOUT) Phar 112 Lab - Fecalysis and Fecal Occult Blood TestDocument2 pages(HANDOUT) Phar 112 Lab - Fecalysis and Fecal Occult Blood TestHan SoloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - PSTMLS 100 - Teaching and Learning Concept of Teaching What Is Teaching? What Is Learning?Document3 pagesLesson 1 - PSTMLS 100 - Teaching and Learning Concept of Teaching What Is Teaching? What Is Learning?Angela Ammco LapezNo ratings yet
- Principles of MedtechDocument93 pagesPrinciples of MedtechAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- FAO208Document4 pagesFAO208Alverastine AnNo ratings yet
- Lipids: DDC Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDocument48 pagesLipids: DDC Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentMelody PardilloNo ratings yet
- PMLS2 - Familiarization in PhleboDocument3 pagesPMLS2 - Familiarization in PhleboCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Prelims MT LawsDocument36 pagesPrelims MT LawsErica Serrano ManguingNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 Handling and Processing of Blood Specimens For LaboratoryDocument5 pagesPMLS 2 Handling and Processing of Blood Specimens For LaboratoryXyrelle NavarroNo ratings yet
- Direct Fecal Smear 3Document16 pagesDirect Fecal Smear 3Kenesa100% (2)
- Exercise 9 PARA LABDocument9 pagesExercise 9 PARA LABBishal KunworNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuestionsTims WatsonsssNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Hematocrit DeterminationDocument7 pagesExercise 5 Hematocrit DeterminationJam RamosNo ratings yet
- Clinical Parasitology Mid Term TransDocument11 pagesClinical Parasitology Mid Term TransBelle LatNo ratings yet
- Urine Preservatives - SLUDocument2 pagesUrine Preservatives - SLUShana Flame Haze0% (1)
- Medical Technology CoursesDocument3 pagesMedical Technology CoursesAly Bint SmbsNo ratings yet
- Activity 2. Bacterial Smear PreparationDocument5 pagesActivity 2. Bacterial Smear PreparationRoan Eam TanNo ratings yet
- L E CellDocument59 pagesL E CellAvi VermaNo ratings yet
- Micro-Para Finals ReviewerDocument14 pagesMicro-Para Finals ReviewerFatima Mae MeLagroNo ratings yet
- General Approach in Investigation of Haemostasis: Lecture 2: Bleeding TimeDocument28 pagesGeneral Approach in Investigation of Haemostasis: Lecture 2: Bleeding TimeClorence John Yumul FerrerNo ratings yet
- 2 History of Medical TechnologyDocument56 pages2 History of Medical TechnologyVinz WansiNo ratings yet
- MTLB Week 1 and 2Document86 pagesMTLB Week 1 and 2Josh Buenafe Macapallag100% (1)
- Capillary Blood CollectionDocument8 pagesCapillary Blood CollectionARIF AHAMMED P100% (1)
- The Problem and Its Background: Citrofortunella Microcarpa (Calamansi) Is An Important CitrofortunellaDocument50 pagesThe Problem and Its Background: Citrofortunella Microcarpa (Calamansi) Is An Important CitrofortunellaArmylinda LaoagNo ratings yet
- Trematode SDocument4 pagesTrematode SMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Jasmin Bernadette Villaver - PRELIMINARY TERM EXAM PMLS 2 (LAB)Document12 pagesJasmin Bernadette Villaver - PRELIMINARY TERM EXAM PMLS 2 (LAB)Frankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Immunosero: Experiment # 1 - Preparation of Red Cell Suspension (Pg. 13-14)Document8 pagesImmunosero: Experiment # 1 - Preparation of Red Cell Suspension (Pg. 13-14)swfsNo ratings yet
- Aubf Case Study AbcdefDocument9 pagesAubf Case Study AbcdefChiara Kate CodillaNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 Handling and Processing of Non Blood Specimens For LaboratoryDocument8 pagesPMLS 2 Handling and Processing of Non Blood Specimens For LaboratoryXyrelle NavarroNo ratings yet
- Enterobius Vermicularis: Cellophane (Scotch) Tape MethodDocument3 pagesEnterobius Vermicularis: Cellophane (Scotch) Tape MethodThea Thei YaNo ratings yet
- Faults Occurring During TrimmingDocument4 pagesFaults Occurring During TrimmingMary Christelle100% (3)
- The politics of hunger: Protest, poverty and policy in England, <i>c.</i> 1750–<i>c.</i> 1840From EverandThe politics of hunger: Protest, poverty and policy in England, <i>c.</i> 1750–<i>c.</i> 1840No ratings yet
- Protozoa - Sample PreparationDocument31 pagesProtozoa - Sample PreparationRNo ratings yet
- Letter 1Document1 pageLetter 1marie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Research MCNPDocument57 pagesResearch MCNPmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOASSAYDocument31 pagesIMMUNOASSAYmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Dna Polymorphism and Human IdentificationDocument5 pagesDna Polymorphism and Human Identificationmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Tumor ImmunologyDocument15 pagesTumor Immunologymarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- HEMA1Document34 pagesHEMA1marie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- LibraryDocument2 pagesLibrarymarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Thesis QuestionaireDocument3 pagesThesis Questionairemarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Hema 1 ErythropoiesisDocument20 pagesHema 1 Erythropoiesismarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Library Collection InventoryDocument1 pageLibrary Collection Inventorymarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Library Inventory CollectionDocument2 pagesLibrary Inventory Collectionmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Ces Library InventoryDocument1 pageCes Library Inventorymarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Library ActivityDocument2 pagesLibrary Activitymarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To TTLDocument38 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To TTLmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- TTL 1 Prelims Handouts Part1Document15 pagesTTL 1 Prelims Handouts Part1marie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- What Is Law Page 1 Bunagan Aubrey Horiondo JD 1Document1 pageWhat Is Law Page 1 Bunagan Aubrey Horiondo JD 1marie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Diagnosi S Planning Intervention S Rational E Evaluatio NDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Diagnosi S Planning Intervention S Rational E Evaluatio Nmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Anti-Terrorism Is UnconstitutionalDocument5 pagesAnti-Terrorism Is Unconstitutionalmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- L17 Wound ExaminationDocument10 pagesL17 Wound ExaminationAhmed samirNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper On Air Pollution and Climate Change As A Global Health IssueDocument2 pagesReaction Paper On Air Pollution and Climate Change As A Global Health Issueanne marieNo ratings yet
- FNCP Inadequate Living SpaceDocument2 pagesFNCP Inadequate Living SpaceMargarette AfanNo ratings yet
- National Assessment and Certification Arrangements: ReferencesDocument25 pagesNational Assessment and Certification Arrangements: ReferencesCharlton Benedict Bernabe100% (1)
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument3 pagesMental Status ExaminationRomulo Vincent PerezNo ratings yet
- Denali Partners With Amazon and Providence To Get Oxygen and Vaccines To Employees and Hospitals in IndiaDocument3 pagesDenali Partners With Amazon and Providence To Get Oxygen and Vaccines To Employees and Hospitals in IndiaPR.comNo ratings yet
- Mr. Zoat - With This Ring (NSFW) (XenForo)Document53 pagesMr. Zoat - With This Ring (NSFW) (XenForo)Edgar PeNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Module 1st Quarter Lesson 1Document5 pagesScience 9 Module 1st Quarter Lesson 1BeverlyNo ratings yet
- Screening Tests For Anc MotherDocument20 pagesScreening Tests For Anc MotherDhrumini PatelNo ratings yet
- Journal of Public Procurement: Article InformationDocument38 pagesJournal of Public Procurement: Article Informationwalelgn eyayuNo ratings yet
- August 1896 The Katipuneros Led by Emilio Jacinto Tried Rescue RizalDocument10 pagesAugust 1896 The Katipuneros Led by Emilio Jacinto Tried Rescue RizalSatra SabbuhNo ratings yet
- Doctor ExhibitDocument110 pagesDoctor ExhibitKFORNo ratings yet
- Supergrads Test Series: Mock Test #1 (Cuet) Answer Key and ExplanationsDocument8 pagesSupergrads Test Series: Mock Test #1 (Cuet) Answer Key and ExplanationsSimran BhatiaNo ratings yet
- GATE 2022 Important DatesDocument3 pagesGATE 2022 Important DatesaviralNo ratings yet
- Admit CardDocument2 pagesAdmit CardAyesha KhanNo ratings yet
- DYP Induction BookletDocument24 pagesDYP Induction BookletdypcopakurdipuneNo ratings yet
- Manual ToolDocument5 pagesManual ToolCarlos MamaniNo ratings yet
- Richard Kradin - The Placebo Response and The Power of Unconscious Healing-Routledge (2008) PDFDocument296 pagesRichard Kradin - The Placebo Response and The Power of Unconscious Healing-Routledge (2008) PDFCamelia Teodora BuneaNo ratings yet
- Script Webs 2Document4 pagesScript Webs 2Djan TecsonNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxicity of Different Composite Resins On Human Gingival Fibroblast Cell LinesDocument8 pagesCytotoxicity of Different Composite Resins On Human Gingival Fibroblast Cell LinesLavinia GheorghitaNo ratings yet
- Eyewitness Testimony.Document6 pagesEyewitness Testimony.anorus97No ratings yet
- Methods: Ian Zelko BS, Zach Zylstra BSDocument1 pageMethods: Ian Zelko BS, Zach Zylstra BSIan ZelkoNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4Document2 pagesCase Study 4Dwaine TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Research On Honorary DoctorateDocument21 pagesResearch On Honorary DoctorateMa.Clarince ManubaNo ratings yet
- VESICULAR NEW Lession PlanDocument18 pagesVESICULAR NEW Lession PlanRaj JadhavNo ratings yet
- "Cooper Pharmaceutical" Case Submission: Submitted For Sales and Distribution Management - MKT 6009 byDocument5 pages"Cooper Pharmaceutical" Case Submission: Submitted For Sales and Distribution Management - MKT 6009 byshubhamsd3No ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet DynaplugDocument4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Dynaplugfs1640No ratings yet
- Midterm Evaluation - With CommentsDocument16 pagesMidterm Evaluation - With Commentsapi-31372043980% (5)
- The Maturing of Positive Psychology and The Emergence of PP 2.0: A Book Review of Positive Psychology (3rd Ed.) by William Compton and Edward HoffmanDocument11 pagesThe Maturing of Positive Psychology and The Emergence of PP 2.0: A Book Review of Positive Psychology (3rd Ed.) by William Compton and Edward HoffmanSefria Adistra GhandiNo ratings yet
- Vaccination CertificateDocument1 pageVaccination CertificateZiya SaifiNo ratings yet
FECALYSIS
FECALYSIS
Uploaded by
marie judimor gomez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
284 views21 pagesThis document provides information about fecalysis, a series of tests done on stool samples to diagnose digestive conditions. Key details include: stool samples should be collected in clean, sealed containers and examined within 1 hour for liquid samples or 30 minutes for semi-formed samples. Certain medications can interfere with test results if taken within a week of the sample. Examination of stool samples under a microscope can detect parasites, eggs, larvae, blood, and mucus. Proper collection and transport of fresh stool samples is important for accurate test results.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information about fecalysis, a series of tests done on stool samples to diagnose digestive conditions. Key details include: stool samples should be collected in clean, sealed containers and examined within 1 hour for liquid samples or 30 minutes for semi-formed samples. Certain medications can interfere with test results if taken within a week of the sample. Examination of stool samples under a microscope can detect parasites, eggs, larvae, blood, and mucus. Proper collection and transport of fresh stool samples is important for accurate test results.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
284 views21 pagesFECALYSIS
FECALYSIS
Uploaded by
marie judimor gomezThis document provides information about fecalysis, a series of tests done on stool samples to diagnose digestive conditions. Key details include: stool samples should be collected in clean, sealed containers and examined within 1 hour for liquid samples or 30 minutes for semi-formed samples. Certain medications can interfere with test results if taken within a week of the sample. Examination of stool samples under a microscope can detect parasites, eggs, larvae, blood, and mucus. Proper collection and transport of fresh stool samples is important for accurate test results.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 21
FECALYSIS
Fecalysis is a series of test done on a stool (feces)
sample to help diagnose certain conditions affecting
the digestive tract.
Examination of stool or Fecal Sample
• Typical stool collection protocol consist of 3 specimens.
• One specimen collected every other day or a total of 3
collected in 10 days.
The best way to collect fecal
sample is in clean, wide
mouthed containers made of
waxed card board or plastic
with a tight-fitting lid to ensure
retention of moisture and to
prevent accidental spillage.
Certain Medications
• Barium This may interfere with
• Bismuth the detection of
• Laxatives parasites. All of these
drugs have been found
• Antacids
to leave crystalline
• Anti-diarrheal residues that can
interfere with the
identification of
parasites.
Stool samples should be
collected a week after the last
intake of any of these drugs.
Intake of antibiotics decreases
the number of protozoans for
several weeks.
Routine stool examination
requires a thumb-sized six of
formed stool or about 5-6
tablespoons of watery stool.
Age of stool sample is very
important for diarrheic
specimens since trophozoites it
may contain are likely to die.
Liquid specimens be examined
within 30 minutes
Semi formed specimens be
examines within 1 hour .
Formed stool specimens are not
likely to contain trophozoites,
they can be held for 24 hours
following collection
• Liquid stool • Blood and mucus in
Protozoan trophozoites soft or watery stools
may possibly yield the
• Formed stool presence of
Cysts trophozoites.
• Any type of consistency • By gross examination ,
Helminth eggs and larvae tape worm proglottids
and adult nematodes
may be found on the
stool sample
• Temporary storage of
fecal samples in a
refrigerator (3-5C) is
acceptable.
Prolonged refrigeration can
bring about desiccation.
Trophozoites are killed by
refrigeration.
Never freeze stool samples.
Never keep them in incubators
Stool Preservatives
• When selecting a fixative, the possibility of preparing a
permanently stained slide should be considered Preservative
proportion 1 part stool:3 parts preservative
FORMALIN
• All purpose fixative. Buffered with sodium phosphate to
preserve morphological characteristics
• 5% concentration is recommended for protozoan cyst.
• 10% concentration is recommended for helminth eggs and
larvae.
Schaudinns solution
• Use to preserve fresh stool/ fresh fecal specimen in
preparation for staining the stool smears.
• Provide excellent preservation of protozoans trophozoites and
cyst.
• For many years , considered GOLD STANDARD
• Contain mercuric chloride; which is highly toxic in humans
POLYVINYL ALCHOHOL (PVA)
• Plastic resin that serves to adhere a stool sample onto a slide.
• Normally incorporated into the schaudinn’s solution.
• Main advantage : preservation of protozoans cyst and
trophozoites for permanent staining.
• Stool preserved in PVA can be concentrated using FECT.
• Disadvantage: use of mercuric chloride; some replaced with
cupric sullfate.
MERTHIOLATE IODINE FORMALINE
(MIF)
• Component both fix and provide stain color
• Contains merthiolate (THIMEROSAL)and iodine that acts as
staining components
• Formalin act as the preservative
• Useful to the fixation of intestinal protozoans, helminth eggs,
and larvae
• Disadvantage : Contains mercury compounds (THIMEROSAL)
stainong of preserved stools and MIF yields unsatisfactory
result or not as good as schaudinn’s fluid
SODIUM ACETATE ACETIC ACID
FORMALIN (SAF)
• Advantage: does note contain mercuric chloride; long shelf life
• Disadvantage: image are not sharp after staing as compared
with does fixed in PVA or schaudinn’s solutions
TEST STOOL EXAM
SYNONYMS FECALYSIS, STOOL ANALYSIS
LAB SECTION CLINICAL MICROSCOPY
AVAILABILITY DAILY ( 24 hours )
TURN AROUND TIME STAT : WITHIN 2 hours
ROUTINE : WITHIN 4 hours
PATEINTS PREPARATION NONE
SPECIMEN FRESH DIARRHEAL STOOL ,
ESPECIALLY WITH BLOOD AND
MUCUS
VOLUME OF SPECIMEN THUMB SIZE ( 3-5 grams)
CONTAINER
CLEAR, CLEAN DRY ,WIDE MOUTH SCREW CAP CONTAINER
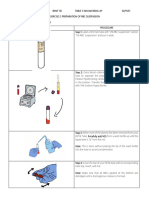
COLLECTION AND TRANSPORT
1 Collect fresh , diarrheal stool in a clean ,dry bed pan or a plastic , leak proof
container.
2 those portion of stool containing blood and mucus are especially significant and
should be transferred in to the container .
3 The patient should understand that the specimen should not be contaminated with
urine and toilet water that may contain chemicals
4 Label the specimen with patient’s full name , date and time of collection .
SPECIMEN STABILITY
Specimen must arrive at the laboratory within one hour of collection
METHODOLOGY
direct light microscopy
You might also like
- Virtual Lab Report by Honey Noreen Belnas: The Gram Stain: Identify and DifferentiateDocument16 pagesVirtual Lab Report by Honey Noreen Belnas: The Gram Stain: Identify and DifferentiateJihil KishaNo ratings yet
- CMO14 3mt01Document75 pagesCMO14 3mt01makike100% (2)
- History of Medical Technology Education in The PhilippinesDocument45 pagesHistory of Medical Technology Education in The PhilippinesCedrickNo ratings yet
- College of Medical Laboratory Science Our Lady of Fatima University-VelenzuelaDocument33 pagesCollege of Medical Laboratory Science Our Lady of Fatima University-VelenzuelaClaire GonoNo ratings yet
- Manual AubfDocument4 pagesManual AubfNoraine Princess Tabangcora100% (2)
- FECALYSISDocument14 pagesFECALYSISMarl EstradaNo ratings yet
- Stool Concentration MethodDocument2 pagesStool Concentration Methodqwshagdvndsavsb100% (1)
- Fecalysis LaboratoryDocument7 pagesFecalysis LaboratoryFRANCESCA ALEXANDRIA PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Preservation MethodsDocument5 pagesParasitology Preservation MethodsAinah Charina TapicNo ratings yet
- Crystal Appearance/Characteristics Clinical SignificanceDocument4 pagesCrystal Appearance/Characteristics Clinical SignificanceAngela LaglivaNo ratings yet
- Histopath Lab ActivityDocument5 pagesHistopath Lab ActivityRakia PillayNo ratings yet
- History of Med Tech (PPT 1)Document29 pagesHistory of Med Tech (PPT 1)Christopher CaduhadaNo ratings yet
- Principles in Medical Laboratory Science 2Document2 pagesPrinciples in Medical Laboratory Science 2lai cruzNo ratings yet
- Kato Katz TechniqueDocument35 pagesKato Katz TechniqueJohn Paul Valencia100% (2)
- Trichuris TrichiuraDocument3 pagesTrichuris TrichiuraTwish BeraldeNo ratings yet
- FECALYSISDocument43 pagesFECALYSISKen LaguiabNo ratings yet
- Immuno Hema - EX 2 ACT - Veloso, Mary Raffaele G - BSMT 3DDocument3 pagesImmuno Hema - EX 2 ACT - Veloso, Mary Raffaele G - BSMT 3DAnneNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument58 pagesMetabolismZ ZernsNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lecture Module 8 Chapter 10: SEMINALYSIS: Semen AnalysisDocument9 pagesAUBF Lecture Module 8 Chapter 10: SEMINALYSIS: Semen AnalysisColene MoresNo ratings yet
- CC 2 Activity 2Document5 pagesCC 2 Activity 2Valdez Francis ZaccheauNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number 3 Sample Preparation For Blood Banking ProcedureDocument10 pagesExperiment Number 3 Sample Preparation For Blood Banking ProcedureKriziaNo ratings yet
- CPH Lab - Prelim TransesDocument4 pagesCPH Lab - Prelim TransesLOUISSE ANNE MONIQUE L. CAYLONo ratings yet
- Fecal AnalysisDocument13 pagesFecal AnalysisYormae QuezonNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - Survey of MicroorganismDocument6 pagesLab 6 - Survey of MicroorganismYusof SundangNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment-LEC/RLE Prelim Exam NCM 201 - College of Nursing San Pedro CollegeDocument6 pagesHealth Assessment-LEC/RLE Prelim Exam NCM 201 - College of Nursing San Pedro CollegeAntoniette Jane Martin PathayNo ratings yet
- The Intestinal NematodesDocument9 pagesThe Intestinal NematodesdhaineyNo ratings yet
- Media Preparation, Isolation of Pure Culture and Bacterial GrowthDocument6 pagesMedia Preparation, Isolation of Pure Culture and Bacterial Growthhamody662002No ratings yet
- Exercise 3Document6 pagesExercise 3Gwyneth Marie DayaganNo ratings yet
- (HANDOUT) Phar 112 Lab - Fecalysis and Fecal Occult Blood TestDocument2 pages(HANDOUT) Phar 112 Lab - Fecalysis and Fecal Occult Blood TestHan SoloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - PSTMLS 100 - Teaching and Learning Concept of Teaching What Is Teaching? What Is Learning?Document3 pagesLesson 1 - PSTMLS 100 - Teaching and Learning Concept of Teaching What Is Teaching? What Is Learning?Angela Ammco LapezNo ratings yet
- Principles of MedtechDocument93 pagesPrinciples of MedtechAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- FAO208Document4 pagesFAO208Alverastine AnNo ratings yet
- Lipids: DDC Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentDocument48 pagesLipids: DDC Medical Laboratory Science DepartmentMelody PardilloNo ratings yet
- PMLS2 - Familiarization in PhleboDocument3 pagesPMLS2 - Familiarization in PhleboCorinne Bautista RenivaNo ratings yet
- Prelims MT LawsDocument36 pagesPrelims MT LawsErica Serrano ManguingNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 Handling and Processing of Blood Specimens For LaboratoryDocument5 pagesPMLS 2 Handling and Processing of Blood Specimens For LaboratoryXyrelle NavarroNo ratings yet
- Direct Fecal Smear 3Document16 pagesDirect Fecal Smear 3Kenesa100% (2)
- Exercise 9 PARA LABDocument9 pagesExercise 9 PARA LABBishal KunworNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument5 pagesQuestionsTims WatsonsssNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5 Hematocrit DeterminationDocument7 pagesExercise 5 Hematocrit DeterminationJam RamosNo ratings yet
- Clinical Parasitology Mid Term TransDocument11 pagesClinical Parasitology Mid Term TransBelle LatNo ratings yet
- Urine Preservatives - SLUDocument2 pagesUrine Preservatives - SLUShana Flame Haze0% (1)
- Medical Technology CoursesDocument3 pagesMedical Technology CoursesAly Bint SmbsNo ratings yet
- Activity 2. Bacterial Smear PreparationDocument5 pagesActivity 2. Bacterial Smear PreparationRoan Eam TanNo ratings yet
- L E CellDocument59 pagesL E CellAvi VermaNo ratings yet
- Micro-Para Finals ReviewerDocument14 pagesMicro-Para Finals ReviewerFatima Mae MeLagroNo ratings yet
- General Approach in Investigation of Haemostasis: Lecture 2: Bleeding TimeDocument28 pagesGeneral Approach in Investigation of Haemostasis: Lecture 2: Bleeding TimeClorence John Yumul FerrerNo ratings yet
- 2 History of Medical TechnologyDocument56 pages2 History of Medical TechnologyVinz WansiNo ratings yet
- MTLB Week 1 and 2Document86 pagesMTLB Week 1 and 2Josh Buenafe Macapallag100% (1)
- Capillary Blood CollectionDocument8 pagesCapillary Blood CollectionARIF AHAMMED P100% (1)
- The Problem and Its Background: Citrofortunella Microcarpa (Calamansi) Is An Important CitrofortunellaDocument50 pagesThe Problem and Its Background: Citrofortunella Microcarpa (Calamansi) Is An Important CitrofortunellaArmylinda LaoagNo ratings yet
- Trematode SDocument4 pagesTrematode SMaria Charlene OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Jasmin Bernadette Villaver - PRELIMINARY TERM EXAM PMLS 2 (LAB)Document12 pagesJasmin Bernadette Villaver - PRELIMINARY TERM EXAM PMLS 2 (LAB)Frankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- Immunosero: Experiment # 1 - Preparation of Red Cell Suspension (Pg. 13-14)Document8 pagesImmunosero: Experiment # 1 - Preparation of Red Cell Suspension (Pg. 13-14)swfsNo ratings yet
- Aubf Case Study AbcdefDocument9 pagesAubf Case Study AbcdefChiara Kate CodillaNo ratings yet
- PMLS 2 Handling and Processing of Non Blood Specimens For LaboratoryDocument8 pagesPMLS 2 Handling and Processing of Non Blood Specimens For LaboratoryXyrelle NavarroNo ratings yet
- Enterobius Vermicularis: Cellophane (Scotch) Tape MethodDocument3 pagesEnterobius Vermicularis: Cellophane (Scotch) Tape MethodThea Thei YaNo ratings yet
- Faults Occurring During TrimmingDocument4 pagesFaults Occurring During TrimmingMary Christelle100% (3)
- The politics of hunger: Protest, poverty and policy in England, <i>c.</i> 1750–<i>c.</i> 1840From EverandThe politics of hunger: Protest, poverty and policy in England, <i>c.</i> 1750–<i>c.</i> 1840No ratings yet
- Protozoa - Sample PreparationDocument31 pagesProtozoa - Sample PreparationRNo ratings yet
- Letter 1Document1 pageLetter 1marie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Research MCNPDocument57 pagesResearch MCNPmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOASSAYDocument31 pagesIMMUNOASSAYmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Dna Polymorphism and Human IdentificationDocument5 pagesDna Polymorphism and Human Identificationmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Tumor ImmunologyDocument15 pagesTumor Immunologymarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- HEMA1Document34 pagesHEMA1marie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- LibraryDocument2 pagesLibrarymarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Thesis QuestionaireDocument3 pagesThesis Questionairemarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Hema 1 ErythropoiesisDocument20 pagesHema 1 Erythropoiesismarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Library Collection InventoryDocument1 pageLibrary Collection Inventorymarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Library Inventory CollectionDocument2 pagesLibrary Inventory Collectionmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Ces Library InventoryDocument1 pageCes Library Inventorymarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Library ActivityDocument2 pagesLibrary Activitymarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To TTLDocument38 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To TTLmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- TTL 1 Prelims Handouts Part1Document15 pagesTTL 1 Prelims Handouts Part1marie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- What Is Law Page 1 Bunagan Aubrey Horiondo JD 1Document1 pageWhat Is Law Page 1 Bunagan Aubrey Horiondo JD 1marie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Diagnosi S Planning Intervention S Rational E Evaluatio NDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Diagnosi S Planning Intervention S Rational E Evaluatio Nmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- Anti-Terrorism Is UnconstitutionalDocument5 pagesAnti-Terrorism Is Unconstitutionalmarie judimor gomezNo ratings yet
- L17 Wound ExaminationDocument10 pagesL17 Wound ExaminationAhmed samirNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper On Air Pollution and Climate Change As A Global Health IssueDocument2 pagesReaction Paper On Air Pollution and Climate Change As A Global Health Issueanne marieNo ratings yet
- FNCP Inadequate Living SpaceDocument2 pagesFNCP Inadequate Living SpaceMargarette AfanNo ratings yet
- National Assessment and Certification Arrangements: ReferencesDocument25 pagesNational Assessment and Certification Arrangements: ReferencesCharlton Benedict Bernabe100% (1)
- Mental Status ExaminationDocument3 pagesMental Status ExaminationRomulo Vincent PerezNo ratings yet
- Denali Partners With Amazon and Providence To Get Oxygen and Vaccines To Employees and Hospitals in IndiaDocument3 pagesDenali Partners With Amazon and Providence To Get Oxygen and Vaccines To Employees and Hospitals in IndiaPR.comNo ratings yet
- Mr. Zoat - With This Ring (NSFW) (XenForo)Document53 pagesMr. Zoat - With This Ring (NSFW) (XenForo)Edgar PeNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Module 1st Quarter Lesson 1Document5 pagesScience 9 Module 1st Quarter Lesson 1BeverlyNo ratings yet
- Screening Tests For Anc MotherDocument20 pagesScreening Tests For Anc MotherDhrumini PatelNo ratings yet
- Journal of Public Procurement: Article InformationDocument38 pagesJournal of Public Procurement: Article Informationwalelgn eyayuNo ratings yet
- August 1896 The Katipuneros Led by Emilio Jacinto Tried Rescue RizalDocument10 pagesAugust 1896 The Katipuneros Led by Emilio Jacinto Tried Rescue RizalSatra SabbuhNo ratings yet
- Doctor ExhibitDocument110 pagesDoctor ExhibitKFORNo ratings yet
- Supergrads Test Series: Mock Test #1 (Cuet) Answer Key and ExplanationsDocument8 pagesSupergrads Test Series: Mock Test #1 (Cuet) Answer Key and ExplanationsSimran BhatiaNo ratings yet
- GATE 2022 Important DatesDocument3 pagesGATE 2022 Important DatesaviralNo ratings yet
- Admit CardDocument2 pagesAdmit CardAyesha KhanNo ratings yet
- DYP Induction BookletDocument24 pagesDYP Induction BookletdypcopakurdipuneNo ratings yet
- Manual ToolDocument5 pagesManual ToolCarlos MamaniNo ratings yet
- Richard Kradin - The Placebo Response and The Power of Unconscious Healing-Routledge (2008) PDFDocument296 pagesRichard Kradin - The Placebo Response and The Power of Unconscious Healing-Routledge (2008) PDFCamelia Teodora BuneaNo ratings yet
- Script Webs 2Document4 pagesScript Webs 2Djan TecsonNo ratings yet
- Cytotoxicity of Different Composite Resins On Human Gingival Fibroblast Cell LinesDocument8 pagesCytotoxicity of Different Composite Resins On Human Gingival Fibroblast Cell LinesLavinia GheorghitaNo ratings yet
- Eyewitness Testimony.Document6 pagesEyewitness Testimony.anorus97No ratings yet
- Methods: Ian Zelko BS, Zach Zylstra BSDocument1 pageMethods: Ian Zelko BS, Zach Zylstra BSIan ZelkoNo ratings yet
- Case Study 4Document2 pagesCase Study 4Dwaine TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Research On Honorary DoctorateDocument21 pagesResearch On Honorary DoctorateMa.Clarince ManubaNo ratings yet
- VESICULAR NEW Lession PlanDocument18 pagesVESICULAR NEW Lession PlanRaj JadhavNo ratings yet
- "Cooper Pharmaceutical" Case Submission: Submitted For Sales and Distribution Management - MKT 6009 byDocument5 pages"Cooper Pharmaceutical" Case Submission: Submitted For Sales and Distribution Management - MKT 6009 byshubhamsd3No ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet DynaplugDocument4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Dynaplugfs1640No ratings yet
- Midterm Evaluation - With CommentsDocument16 pagesMidterm Evaluation - With Commentsapi-31372043980% (5)
- The Maturing of Positive Psychology and The Emergence of PP 2.0: A Book Review of Positive Psychology (3rd Ed.) by William Compton and Edward HoffmanDocument11 pagesThe Maturing of Positive Psychology and The Emergence of PP 2.0: A Book Review of Positive Psychology (3rd Ed.) by William Compton and Edward HoffmanSefria Adistra GhandiNo ratings yet
- Vaccination CertificateDocument1 pageVaccination CertificateZiya SaifiNo ratings yet