Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Swing Motor PW200 220-7
Swing Motor PW200 220-7
Uploaded by
Teknik Makina100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
76 views7 pagesThe document describes the swing motor and related components used in machinery. It includes:
- Details of the swing motor type and capacity specifications.
- Diagrams and explanations of how the swing brake, safety valve, check valves, and rock prevention valve function to regulate pressure and prevent excessive forces during swinging motions.
- Descriptions of how oil flows through the motor and control valve to power swinging while allowing the brake to engage when controls return to neutral.
Original Description:
Original Title
Swing_Motor_PW200_220-7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the swing motor and related components used in machinery. It includes:
- Details of the swing motor type and capacity specifications.
- Diagrams and explanations of how the swing brake, safety valve, check valves, and rock prevention valve function to regulate pressure and prevent excessive forces during swinging motions.
- Descriptions of how oil flows through the motor and control valve to power swinging while allowing the brake to engage when controls return to neutral.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
76 views7 pagesSwing Motor PW200 220-7
Swing Motor PW200 220-7
Uploaded by
Teknik MakinaThe document describes the swing motor and related components used in machinery. It includes:
- Details of the swing motor type and capacity specifications.
- Diagrams and explanations of how the swing brake, safety valve, check valves, and rock prevention valve function to regulate pressure and prevent excessive forces during swinging motions.
- Descriptions of how oil flows through the motor and control valve to power swinging while allowing the brake to engage when controls return to neutral.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
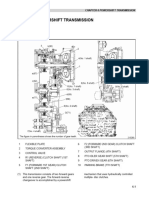
Swing Motor
Swing Motor PW200/ 220-7 Page 1
Swing Machinery
PC210-7 PW200/220-7
Motor Type KMF125ABE-5 KMF125ABE-5
Motor Capacity (cc/rev) 125 125
Machinery reduction ratio 18.627 18.627
750
Swing Motor PW200/ 220-7 Page 2
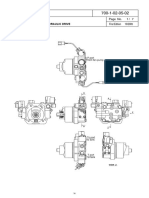
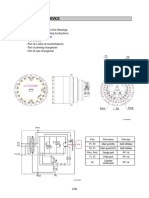
Swing Motor
Return (T)
Signal for swing brake (B)
Check valve
Swing rock prevention valve
Swing motor drain (S)
Safety valve 285 +5 bar
Check valve
Dip stick and oil fill tube for
swing machinery
Swing Motor PW200/ 220-7 Page 3
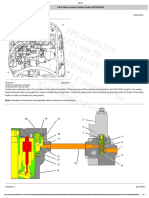
Swing Brake
To release the swing brake the swing brake solenoid
is energized. This happens if swing or any other PPC
lever is operated.
PPC pressure pushes piston (7) against springs (1)
and releases the swing brake.
If swing or any other PPC lever returns to neutral the
swing brake solenoid remains energized for 5
seconds.
After this the swing brake solenoid is de-energized
and PPC pressure from (B) is drained to tank.
Spring force (1) pushes piston (7) against the disks
(5) and plates (6) of the swing brake and the swing
brake is closed.
Swing Motor PW200/ 220-7 Page 4
Swing Motor
During swing oil flows from the control valve to
port (MA) of the swing motor.
If swing pressure exceeds the set pressure of
the safety valve (1), swing oil pressure is reliefed
to port (S).
At the same time swing oil pressure keeps
check valve (4) closed.
When the swing PPC lever returns to neutral oil
supply at port (MA) is stopped, because the
swing spool has returned to neutral, too.
Now the swing motor is acting as a pump and
generates a pressure peak at port (MB).
The pressure peak opens check valve (4) and
closes valve (5) and is reliefed across the safety
valve (1).
To prevent cavitation suction valve (3) opens
and oil flows from port (S) to (MA).
Swing Motor PW200/ 220-7 Page 5
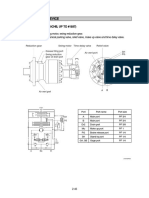
Swing Rock Prevention Valve
Pressure at (MB) and in chamber (e) pushes
spool (d) against spring (6), because surface
(D1) is larger. The upper structure swings
back and the pressure at (MA) and in
chamber (b) increases. Spool (2) is pushed
against spring (3). Oil flows from port (MA),
chamber (b) and a orifice in spool (d) to tank
(T).
The enclosed oil is drained and another rise in
pressure prevented.
Swing Motor PW200/ 220-7 Page 6
Swing Motor PW200/ 220-7 Page 7
You might also like
- 05 d155 Power TrainDocument38 pages05 d155 Power Trainghitacrainic100% (9)
- Wiring Schematic (Manual Machine) S770 (S/N AT5A11001 - AT5A11533) S770 (S/N B3BV11001 - B3BV11242) Sheet 1 of 18Document18 pagesWiring Schematic (Manual Machine) S770 (S/N AT5A11001 - AT5A11533) S770 (S/N B3BV11001 - B3BV11242) Sheet 1 of 18Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- 120 Ad4 ServicemanualDocument438 pages120 Ad4 ServicemanualTeknik Makina100% (2)
- Bw216d4-101583-Service ManualDocument974 pagesBw216d4-101583-Service ManualTeknik Makina100% (3)
- Shop Manual: 97SF11205 Backhoe Loader WB97S-2Document582 pagesShop Manual: 97SF11205 Backhoe Loader WB97S-2Teknik Makina100% (4)
- NEF ENGINES E Ed 01 - 2005Document788 pagesNEF ENGINES E Ed 01 - 2005Teknik Makina100% (3)
- B25C Omm EnglishDocument167 pagesB25C Omm EnglishTeknik Makina100% (1)
- Motor Transmisie Volvo Ec140Document14 pagesMotor Transmisie Volvo Ec140Michael Davenport100% (1)
- 06 d155 Hyd Fan CircuitDocument12 pages06 d155 Hyd Fan Circuitghitacrainic100% (6)
- Group 2. Swing DeviceDocument17 pagesGroup 2. Swing DeviceAhmad Mubarok100% (1)
- Hyundai R450LC-7 Pilot CircuitDocument20 pagesHyundai R450LC-7 Pilot CircuitHai VanNo ratings yet
- WA380-6 Brake SystemDocument26 pagesWA380-6 Brake SystemCharlene Diocadiz100% (1)
- Hydraulics: Outside DrawingDocument7 pagesHydraulics: Outside Drawingarum nadaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Swing Device: 1. StructureDocument11 pagesGroup 3 Swing Device: 1. StructurethierrylindoNo ratings yet
- 2-3 Swing DeviceDocument21 pages2-3 Swing Devicejesus silva100% (2)
- 09 Travel MotorDocument58 pages09 Travel Motorkampungsaya79No ratings yet
- D85EX-15 Hydraulic FanDocument9 pagesD85EX-15 Hydraulic FanQuy Le Thanh67% (3)
- Piston Pumo (Hoist, Ster, Brake) Cat 745Document4 pagesPiston Pumo (Hoist, Ster, Brake) Cat 745Thahirullah KhalidNo ratings yet
- Bomba Multiples ConexionesDocument2 pagesBomba Multiples ConexionesLucía Salazar de TeránNo ratings yet
- GF07.02-W-2110-01MP PLD Unit Pump, LocationDocument31 pagesGF07.02-W-2110-01MP PLD Unit Pump, LocationCostel Caraman100% (1)
- Pivot Arm Turning GearDocument24 pagesPivot Arm Turning Gearoom_tgw100% (1)
- Group 3 Swing Device ( #0408) : 1. StructureDocument22 pagesGroup 3 Swing Device ( #0408) : 1. Structuredeniden2013No ratings yet
- Electrohydraulic Pilot ManifoldDocument5 pagesElectrohydraulic Pilot ManifoldBroCactusNo ratings yet
- Hyd Sytem OperationDocument14 pagesHyd Sytem OperationBng ElektroNo ratings yet
- Solenoid Valve (Proportional Reducing) - Power Shift System: Operación de SistemasDocument5 pagesSolenoid Valve (Proportional Reducing) - Power Shift System: Operación de Sistemasgalvis1020No ratings yet
- Sis 2.0Document2 pagesSis 2.0Mohamed OmarNo ratings yet
- D375A-6 Power Train Rev3Document62 pagesD375A-6 Power Train Rev3alcowo100% (5)
- Retro 9Document7 pagesRetro 9Henry MonteagudoNo ratings yet
- 2-1 Pump DeviceDocument21 pages2-1 Pump Devicejesus silvaNo ratings yet
- PLD Unit Pump, FunctionDocument2 pagesPLD Unit Pump, FunctionTamer MoustafaNo ratings yet
- A 10 VDocument10 pagesA 10 VLeandro SalNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Ex550-5 Section 3 Component OperationDocument53 pagesHitachi Ex550-5 Section 3 Component OperationdatphuongNo ratings yet
- Retro 8Document5 pagesRetro 8Henry MonteagudoNo ratings yet
- Metering Pump (Steering)Document8 pagesMetering Pump (Steering)hidekel crafort vinicioNo ratings yet
- Pump Control OperationDocument3 pagesPump Control Operationaras aliNo ratings yet
- Pto 00Document74 pagesPto 00JipsonCuevaNo ratings yet
- Pump, Description: Model CodeDocument4 pagesPump, Description: Model CodeNaing Min HtunNo ratings yet
- Modulação Da ValvulaDocument5 pagesModulação Da Valvulavaldelei limaNo ratings yet
- WA380 480-5 Structure 2713Document27 pagesWA380 480-5 Structure 2713Mhmood QadouraNo ratings yet
- VOLVO EW160B-4 Power TransmissionDocument81 pagesVOLVO EW160B-4 Power TransmissionPIKO MOBNo ratings yet
- Power Train Hydraulic System (SENR9159-10)Document3 pagesPower Train Hydraulic System (SENR9159-10)Anderson Oliveira SilvaNo ratings yet
- Steering System SDLG 936L PDFDocument36 pagesSteering System SDLG 936L PDFjuanchilo29100% (2)
- Descripción Motor de Traslación EC350DDocument9 pagesDescripción Motor de Traslación EC350DHugo Alejandro Bello ParraNo ratings yet
- Transmision Power ShiftDocument88 pagesTransmision Power ShiftMARCO ANTONIO CURO CAMPOSNo ratings yet
- Volvo Ew160b Wheeled ExcavatorDocument23 pagesVolvo Ew160b Wheeled ExcavatorМирбек Майрыков100% (2)
- Boom Hyd SystemDocument5 pagesBoom Hyd SystemSherlock HolmesNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Travel Device: 1. StructureDocument11 pagesGroup 4 Travel Device: 1. Structurehamdi galipNo ratings yet
- 05Document64 pages05LuisTocora100% (1)
- Technical Service Information: Mercedes Benz 722.6 Shift GroupsDocument9 pagesTechnical Service Information: Mercedes Benz 722.6 Shift GroupsMario MastronardiNo ratings yet
- Sis 2.0Document3 pagesSis 2.0fjhernandez_76No ratings yet
- CAT993K Steering SystemDocument11 pagesCAT993K Steering SystemRafael RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Rotary Actuator (Transmission) : Operación de SistemasDocument3 pagesRotary Actuator (Transmission) : Operación de SistemasenriqueNo ratings yet
- Rotary Actuator (Transmission) : Operación de SistemasDocument3 pagesRotary Actuator (Transmission) : Operación de SistemasenriqueNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Shematic FonctionDocument10 pagesHydraulic Shematic FonctionatelierNo ratings yet
- Transmission: Dakar Training CenterDocument33 pagesTransmission: Dakar Training CenterMed EkahNo ratings yet
- X QH MG E3 QDocument90 pagesX QH MG E3 Qjuarez5geronimosilvaNo ratings yet
- Systems Operation Piston Pump ImplementDocument12 pagesSystems Operation Piston Pump Implementالبراق للتوريدات وصيانة المعداتNo ratings yet
- Piston Pump (Brake, Hydraulic Fan)Document7 pagesPiston Pump (Brake, Hydraulic Fan)EVER DAVID SAAVEDRA HUAYHUANo ratings yet
- ECD-V4 OutlineDocument4 pagesECD-V4 OutlineВячеслав ГлушакNo ratings yet
- Retro 13Document5 pagesRetro 13Henry MonteagudoNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-06-26 at 3.36.28 PMDocument22 pagesScreenshot 2021-06-26 at 3.36.28 PMAbdalla issa100% (2)
- 24M Motor Grader B9300001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY C18 Engine (SEBP6378 - 46) - Controle Hidráulico de TransmissãoDocument3 pages24M Motor Grader B9300001-UP (MACHINE) POWERED BY C18 Engine (SEBP6378 - 46) - Controle Hidráulico de TransmissãoDouglas GomesNo ratings yet
- Lubrication System: Systems OperationDocument5 pagesLubrication System: Systems OperationbejoythomasNo ratings yet
- Alivio Implementos 994FDocument4 pagesAlivio Implementos 994FF Diaz BarreraNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- S770 Hyd Std-Op V-1604Document2 pagesS770 Hyd Std-Op V-1604Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- S770 Hyd Std-Op V-1676Document2 pagesS770 Hyd Std-Op V-1676Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- S770 Hyd SJC V-1605Document2 pagesS770 Hyd SJC V-1605Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- Service - Manual: Catalogue NumberDocument406 pagesService - Manual: Catalogue NumberTeknik Makina100% (1)
- Wiring Schematic (Kit and Option Harness) All Models Sheet 1 of 8Document8 pagesWiring Schematic (Kit and Option Harness) All Models Sheet 1 of 8Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- S770 Hyd Sjc-Op V-1606Document2 pagesS770 Hyd Sjc-Op V-1606Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- DH Serisi Arıza Kodları.Document71 pagesDH Serisi Arıza Kodları.Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- S770 Hyd STD V-1603Document2 pagesS770 Hyd STD V-1603Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- BC 672772 RBRS Service TraningDocument385 pagesBC 672772 RBRS Service TraningTeknik Makina100% (2)
- Wiring Schematic (Acs/Sjc Machine) S770 (S/N AT5A11001 - AT5A11533) S770 (S/N B3BV11001 - B3BV11242) Sheet 1 of 20Document20 pagesWiring Schematic (Acs/Sjc Machine) S770 (S/N AT5A11001 - AT5A11533) S770 (S/N B3BV11001 - B3BV11242) Sheet 1 of 20Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- Cover Sheet 4812026582 /GDocument97 pagesCover Sheet 4812026582 /GTeknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- Bw120ad3 Service TrainingDocument89 pagesBw120ad3 Service TrainingTeknik Makina100% (2)
- Shop Manual: 97F21409 Backhoe Loader WB97R-2Document570 pagesShop Manual: 97F21409 Backhoe Loader WB97R-2Teknik Makina100% (1)
- Cover Sheet 4812038520 /IDocument52 pagesCover Sheet 4812038520 /ITeknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- Failure Code of The PLC From SAUER For The BF / MF 571 C BF / MF 691 C CrawlerDocument15 pagesFailure Code of The PLC From SAUER For The BF / MF 571 C BF / MF 691 C CrawlerTeknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- Cover Sheet 4812031680 /HDocument72 pagesCover Sheet 4812031680 /HTeknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- B30D 2Document150 pagesB30D 2Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- Cover Sheet 4812026580 /GDocument50 pagesCover Sheet 4812026580 /GTeknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- B30D 3Document150 pagesB30D 3Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- BELL35DDocument801 pagesBELL35DTeknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- Parts Manual: B30D & B25D 6X6 MKV AdtDocument150 pagesParts Manual: B30D & B25D 6X6 MKV AdtTeknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- B30D 4Document150 pagesB30D 4Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- B30D 5Document150 pagesB30D 5Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- B30D 6Document143 pagesB30D 6Teknik MakinaNo ratings yet
- Cut 120Document128 pagesCut 120Jimmy MyNo ratings yet
- GR 6 Voc Words 4th QTRDocument5 pagesGR 6 Voc Words 4th QTRAzlynn Courtney FernandezNo ratings yet
- Bir Regulations MonitoringDocument87 pagesBir Regulations MonitoringErica NicolasuraNo ratings yet
- The Expanding Universe - Sir Arthur Stanley Eddington - Cambridge University Press - 1987Document153 pagesThe Expanding Universe - Sir Arthur Stanley Eddington - Cambridge University Press - 1987cramerps2084No ratings yet
- AppsDocument6 pagesAppsxxres4lifexxNo ratings yet
- DI - 2021 Tech TrendsDocument166 pagesDI - 2021 Tech TrendsramapvkNo ratings yet
- DBEBEE601Document4 pagesDBEBEE601bariNo ratings yet
- The Crest of The Tide of Renascence: Sankaradeva's Kirttan-GhosāDocument30 pagesThe Crest of The Tide of Renascence: Sankaradeva's Kirttan-GhosāBhargavNo ratings yet
- Phlebotomist TrackerDocument62 pagesPhlebotomist Trackertarun sharmaNo ratings yet
- 22 Nb-Iot: 22.1 GeneralDocument574 pages22 Nb-Iot: 22.1 GeneralganeshNo ratings yet
- Form MOUDocument4 pagesForm MOUDouglas SugimotoNo ratings yet
- (With Script) June 2021 Saturday WSF Teaching GuideDocument3 pages(With Script) June 2021 Saturday WSF Teaching GuideMichael T. BelloNo ratings yet
- A Handbook of English Literature by Faizal Risdianto: P Oetr YDocument24 pagesA Handbook of English Literature by Faizal Risdianto: P Oetr YaYu pradhitiyanNo ratings yet
- Weather Forecast: by Vass Tunde Juen, 1 Verbal and Non-Verbal CommunicationDocument5 pagesWeather Forecast: by Vass Tunde Juen, 1 Verbal and Non-Verbal CommunicationAlina-Cristina CotoiNo ratings yet
- 2 LandDocument50 pages2 LandJose Jess AmaoNo ratings yet
- COP2800 MidtermStudyGuideDocument31 pagesCOP2800 MidtermStudyGuideCatherine CrutcherNo ratings yet
- IDC POS Lab Project Plan 2 2Document471 pagesIDC POS Lab Project Plan 2 2shiramkkNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Manual2Document106 pagesGreenhouse Manual2Amit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Nilai Konversi Uji Kuat Tekan Variasi Bentuk Paving Block Terhadap Bentuk Sampel Uji Sni 03-0691-1996Document9 pagesNilai Konversi Uji Kuat Tekan Variasi Bentuk Paving Block Terhadap Bentuk Sampel Uji Sni 03-0691-1996MiratulHazanahNo ratings yet
- Pag-Iimahen Sa Batang Katutubo Sa Ilang PDFDocument28 pagesPag-Iimahen Sa Batang Katutubo Sa Ilang PDFLui BrionesNo ratings yet
- POSTMODERN, 253s '12Document270 pagesPOSTMODERN, 253s '12Raluca Gîlcă100% (1)
- (!court: Laepublic of Tbe !lbilippines FflanilaDocument14 pages(!court: Laepublic of Tbe !lbilippines FflanilaGladys Bustria OrlinoNo ratings yet
- Jordanian Arabic Grammar For BeginnersDocument54 pagesJordanian Arabic Grammar For BeginnersAlaor Lopes100% (1)
- Advent Jesse Tree - 2013Document35 pagesAdvent Jesse Tree - 2013Chad Bragg100% (1)
- Demonstrating Value With BMC Server Automation (Bladelogic)Document56 pagesDemonstrating Value With BMC Server Automation (Bladelogic)abishekvsNo ratings yet
- Fuji ManualDocument166 pagesFuji Manualasbel gamNo ratings yet
- Floyd Edwrads Memorial Scholarship Terms of Reference 2017Document3 pagesFloyd Edwrads Memorial Scholarship Terms of Reference 2017Aswin HarishNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Phosphide, A Highly Hazardous Pesticide, and A Suicide Poison in Southern Province of ZambiaDocument2 pagesAluminium Phosphide, A Highly Hazardous Pesticide, and A Suicide Poison in Southern Province of ZambiaSimon TemboNo ratings yet
- 4 Statistics and Probability g11 Quarter 4 Module 4 Identifying The Appropriate Test Statistics Involving Population MeanDocument28 pages4 Statistics and Probability g11 Quarter 4 Module 4 Identifying The Appropriate Test Statistics Involving Population MeanISKA COMMISSIONNo ratings yet
- Classroom ArrangementsDocument5 pagesClassroom Arrangementsapi-427868008No ratings yet