Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 viewsChemistry
Chemistry
Uploaded by
nniiaa1) Polarity in bonds exists on a spectrum from completely ionic to completely covalent. Heteronuclear molecules like HF form polar covalent bonds with the electrons displaced towards the more electronegative atom.
2) Dipole moment is a measure of separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule. It is calculated as the product of the charge and distance between the charges. Molecules like H2O have a net dipole moment due to its bent shape.
3) Fajan's rules from 1923 use cation size and charge to predict bond type, with smaller cations having more polarizing power leading to increased covalent character in ionic compounds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Acetic Acid Production ReportDocument15 pagesAcetic Acid Production ReportArya Lodha100% (1)
- Design. Construction of A Charcoal Backing OvenDocument6 pagesDesign. Construction of A Charcoal Backing OvenraduonoNo ratings yet
- Why Water Is A DipoleDocument50 pagesWhy Water Is A DipoleRaviverma077No ratings yet
- Nonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryDocument9 pagesNonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Nonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryDocument9 pagesNonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- A Dipole Moment Arises in Any System in Which There Is A Separation of ChargeDocument5 pagesA Dipole Moment Arises in Any System in Which There Is A Separation of ChargehuesosNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bondind and Molecular StructureDocument33 pagesChemical Bondind and Molecular StructureSaadNo ratings yet
- Chemical PolarityDocument6 pagesChemical PolarityPavan TejNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument11 pagesPhysical ScienceSieg BelfortNo ratings yet
- Unit4 Chem Bond-Full Notes 2018Document30 pagesUnit4 Chem Bond-Full Notes 2018Krishiv RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Materials Lecture 4Document24 pagesChemistry of Materials Lecture 4sanjunaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Ionic CrystalDocument24 pagesAtomic Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Ionic CrystalDr-Sushant GuptaNo ratings yet
- ° Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds 3Document23 pages° Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds 3Zayyan AliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument12 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSatyam MittalNo ratings yet
- Diploe Moment and Inductive Effect Final VersionDocument45 pagesDiploe Moment and Inductive Effect Final VersionIqra BaigNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Short Notes by MTHDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding Short Notes by MTHmanthangoel11jeeNo ratings yet
- Physical State Melting Point and Boiling PointDocument6 pagesPhysical State Melting Point and Boiling Pointru ruNo ratings yet
- Physical State Melting Point and Boiling PointDocument6 pagesPhysical State Melting Point and Boiling Pointru ruNo ratings yet
- Physical State Melting Point and Boiling PointDocument6 pagesPhysical State Melting Point and Boiling Pointru ruNo ratings yet
- Notes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesNotes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Bonding: Ionic Bond OR Electrovalent BondDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Bonding: Ionic Bond OR Electrovalent Bondanon_397573801No ratings yet
- Say Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesSay Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structuresivaranjini S.VNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Document88 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Damz RtgNo ratings yet
- Chemical Polarity PDFDocument33 pagesChemical Polarity PDFEG Tiolo AbadNo ratings yet
- E1Document10 pagesE1Vita Dini AviyanaNo ratings yet
- 8.4 - EdlineDocument20 pages8.4 - EdlineHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document20 pagesChemical Bonding 1ahmedNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: Polarity of Molecules: Seventh Course (General Chemistry) by Dr. IstadiDocument23 pagesIntermolecular Forces: Polarity of Molecules: Seventh Course (General Chemistry) by Dr. IstadiBINTANGNo ratings yet
- PPT8Document29 pagesPPT8Adugnaw BiksNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science-Module 5 Polarity and Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument45 pagesPhysical-Science-Module 5 Polarity and Intermolecular Forces of AttractionJoana CastilloNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Polarity - FactsDocument9 pagesElectronegativity and Polarity - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- Bonding Question AnswersDocument23 pagesBonding Question Answersgyogi1989No ratings yet
- Bond Characteristics: Class 11Document19 pagesBond Characteristics: Class 11sabin MandalNo ratings yet
- Ach 2101 Lesson 5Document19 pagesAch 2101 Lesson 5Lawrence MajaliwaNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Its ApplicationsDocument6 pagesElectronegativity and Its ApplicationsShamzaSeemin100% (1)
- Lo5 1) Chemical BondsDocument9 pagesLo5 1) Chemical BondsabdogamreNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument51 pagesChemical BondsagnamolathNo ratings yet
- Chap 1.2Document47 pagesChap 1.2Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular ForcesDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forcesnoreen doraniNo ratings yet
- Chem402 Tonny WeDocument7 pagesChem402 Tonny WeRuth CheropNo ratings yet
- Electron AffinityDocument15 pagesElectron AffinitydarknesspersonifiedNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument68 pagesChemical BondingAnkur Agarwal100% (4)
- UNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2Document13 pagesUNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2KARTIKAY LADDHANo ratings yet
- Lectures - Biochemistry 1 - 2021-2022 Prof Version 6.01 - 23-24-1-30Document30 pagesLectures - Biochemistry 1 - 2021-2022 Prof Version 6.01 - 23-24-1-30Ken M'voulaboloNo ratings yet
- Z6Document5 pagesZ6turnija2030No ratings yet
- 6 Chapter Chemical Bonding Short Question With AnswersDocument16 pages6 Chapter Chemical Bonding Short Question With AnswersBilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Dipole Moment: Special Reference To Alkyl HalidesDocument8 pagesDipole Moment: Special Reference To Alkyl HalidesMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- 4.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 2016Document10 pages4.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 2016Karanvir Singh 6No ratings yet
- 04 Chemical Bonding Formula SheetsDocument9 pages04 Chemical Bonding Formula SheetsRushil PahwaNo ratings yet
- Enc Encoded ex7XDZYZXOqmbH1FNJmXNKobRl vzOD3CVnwfk7ZNedEJAZXdKoLTMWdDocument49 pagesEnc Encoded ex7XDZYZXOqmbH1FNJmXNKobRl vzOD3CVnwfk7ZNedEJAZXdKoLTMWdSri VanyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument7 pagesChemical BondingSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bonding and Molecular Sructure I Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Bonding and Molecular Sructure I Chemical BondingJonathan SaydeNo ratings yet
- Figure of Towels Sewn and Velcroed Representing Bonds Between Hydrogen and Chlorine AtomsDocument12 pagesFigure of Towels Sewn and Velcroed Representing Bonds Between Hydrogen and Chlorine AtomsW Ayu DewiNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondsDocument5 pagesIonic and Covalent BondsFern HofileñaNo ratings yet
- Polarity and Intermolecular FDocument5 pagesPolarity and Intermolecular Ftgeorgina630No ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- ASSOCIATIVE INTERACTIONS SASTRA University First YearDocument28 pagesASSOCIATIVE INTERACTIONS SASTRA University First Yearstar100% (1)
- A Chemical Bond Is An Attraction Between Atoms That Allows The Formation of Chemical Substances That Contain Two or More AtomsDocument2 pagesA Chemical Bond Is An Attraction Between Atoms That Allows The Formation of Chemical Substances That Contain Two or More Atomscaguioajulius12No ratings yet
- 3B.2 Electronegativity and Bond PolarityDocument10 pages3B.2 Electronegativity and Bond Polarityzerus ddaasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes KhraDocument24 pagesChemistry Notes KhraMohamed WageehNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshusa harshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 SUBSTITUTION REACTIONDocument35 pagesChapter 4 SUBSTITUTION REACTIONHalimatun MustafaNo ratings yet
- Cap - 1 - Heat Conduction in 3D Solids PDFDocument10 pagesCap - 1 - Heat Conduction in 3D Solids PDFmaurizio.desio4992No ratings yet
- Mir Junaid-1 PDFDocument5 pagesMir Junaid-1 PDFMir Junaid Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ImmobilizationDocument27 pagesEnzyme Immobilizationsabuz pataNo ratings yet
- The Atom Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesThe Atom Lesson Planapi-351677864No ratings yet
- OlinDocument16 pagesOlinA AhmedNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Reaction Rate Expression With Equilibrium AssumptionDocument6 pagesDerivation of Reaction Rate Expression With Equilibrium AssumptionViaTS13No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Experiment 4Document5 pagesPhysical Chemistry Experiment 4Suzanne Clariz M. BaltazarNo ratings yet
- D. C. Blackley B.sc. Ph.D. F.P.R.I. Auth. - Synthetic Rubbers Their Chemistry and Technology-Springer Netherlands 1983Document380 pagesD. C. Blackley B.sc. Ph.D. F.P.R.I. Auth. - Synthetic Rubbers Their Chemistry and Technology-Springer Netherlands 1983Minh Tran100% (3)
- 01-03 - Effect of Thickness On The Opticar Properties of GaAs Thin FilmsDocument9 pages01-03 - Effect of Thickness On The Opticar Properties of GaAs Thin FilmsFerRazzónNo ratings yet
- Electrochimica Acta Volume 37 Issue 12 1992 (Doi 10.1016 - 0013-4686 (92) 85104-s) Sergio Trasatti - Adsorption of Organic Substances at Electrodes - Recent AdvancesDocument8 pagesElectrochimica Acta Volume 37 Issue 12 1992 (Doi 10.1016 - 0013-4686 (92) 85104-s) Sergio Trasatti - Adsorption of Organic Substances at Electrodes - Recent AdvancesNumitor Tor Aten JilNo ratings yet
- hw5Document3 pageshw5Ryle ArbonNo ratings yet
- Calculation Sheet Document No. Page No. Revision No. Date Prepared by Approved by Plant PlaceDocument22 pagesCalculation Sheet Document No. Page No. Revision No. Date Prepared by Approved by Plant PlaceSwapnil Pratap Singh100% (1)
- Lecture Notes On Thermodynamics. Joseph M. PowersDocument383 pagesLecture Notes On Thermodynamics. Joseph M. PowersGustavo CoronelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31Document8 pagesLecture 31Miguel RochaNo ratings yet
- Test Glo-Qc-Tm-0744Document6 pagesTest Glo-Qc-Tm-0744rx bafnaNo ratings yet
- Qalco Q-Jetcool 153Document1 pageQalco Q-Jetcool 153Deepak JoyNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Exam MCQ'sDocument2 pagesMid Term Exam MCQ'sAbdul Khaliq KhanNo ratings yet
- EDTADocument12 pagesEDTAPrabhatNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument41 pages3.0 Laws of ThermodynamicsBrandon LubegaNo ratings yet
- Ae708 Question Bank 2Document5 pagesAe708 Question Bank 2pRoBoTRoGe OPNo ratings yet
- Properties of SteamDocument7 pagesProperties of SteamRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- ONYECHI CHINENYE ADAOBI M.Eng. THESIS CombinedDocument253 pagesONYECHI CHINENYE ADAOBI M.Eng. THESIS Combinedchinenye igwegbeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1 - ExergyDocument27 pagesLesson 1.1 - ExergyBilly JhunNo ratings yet
- FY BTech Lab Manaul 2021/01/01Document46 pagesFY BTech Lab Manaul 2021/01/01harshNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting EvaporationDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting EvaporationKaram Abd El-Aal100% (5)
- Voltaic Cell Lab Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesVoltaic Cell Lab Assignment PDFalexrilenNo ratings yet
- Surface PolarizabilityDocument21 pagesSurface PolarizabilityMike de Guzman0% (1)
Chemistry
Chemistry
Uploaded by
nniiaa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views12 pages1) Polarity in bonds exists on a spectrum from completely ionic to completely covalent. Heteronuclear molecules like HF form polar covalent bonds with the electrons displaced towards the more electronegative atom.
2) Dipole moment is a measure of separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule. It is calculated as the product of the charge and distance between the charges. Molecules like H2O have a net dipole moment due to its bent shape.
3) Fajan's rules from 1923 use cation size and charge to predict bond type, with smaller cations having more polarizing power leading to increased covalent character in ionic compounds.
Original Description:
Original Title
Chemistry Ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Polarity in bonds exists on a spectrum from completely ionic to completely covalent. Heteronuclear molecules like HF form polar covalent bonds with the electrons displaced towards the more electronegative atom.
2) Dipole moment is a measure of separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule. It is calculated as the product of the charge and distance between the charges. Molecules like H2O have a net dipole moment due to its bent shape.
3) Fajan's rules from 1923 use cation size and charge to predict bond type, with smaller cations having more polarizing power leading to increased covalent character in ionic compounds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views12 pagesChemistry
Chemistry
Uploaded by
nniiaa1) Polarity in bonds exists on a spectrum from completely ionic to completely covalent. Heteronuclear molecules like HF form polar covalent bonds with the electrons displaced towards the more electronegative atom.
2) Dipole moment is a measure of separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule. It is calculated as the product of the charge and distance between the charges. Molecules like H2O have a net dipole moment due to its bent shape.
3) Fajan's rules from 1923 use cation size and charge to predict bond type, with smaller cations having more polarizing power leading to increased covalent character in ionic compounds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Chemical bonding and molecular
structure
By -Ishita , Aishwarya , Shriya , Prashashree , Pranati and Akansha
XI-B
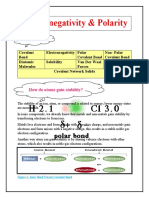
Polarity of bonds
The existence of a hundred percent covalent bond represents an
ideal situation. In reality no bond or a compound is either
completely covalent or ionic . There exists Some ionic character
or covalent character.
When a covalent bond is formed between two similar atoms , the
shared pair of electrons is equally attracted by the two atoms . As
a result the electron pair is situated exactly between the two
identical nuclei . The bond so formed is called Nonpolar
Covalent Bond .
Contrary to this , in case of a heteronuclear
molecule like HF the shared pair of
electrons between the two atoms gets
displaced more towards fluorine since the
electronegativity of fluorine is far greater
than that of hydrogen thus the resultant
covalent bond is Polar Covalent Bond.
Dipole moment
As a result of polarisation , the molecule possesses the Dipole
moment.
It is defined as the product of the magnitude of the charge and
the distance between the centres of positive and negative charge .
It is designated by a Greek letter ‘μ’
Dipole moment (μ) = charge (Q) × distance of
separation (r)
Dipole moment is usually expressed in Debts units (D) .
The conversation factor is :-
1D = 3.33564 × 10-30 C m
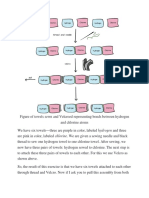
A dipole moment arises in any system in which there is a separation of charge. They can,
therefore, arise in ionic bonds as well as in covalent bonds. Dipole moments occur due
to the difference in electronegativity between two chemically bonded atoms.
The bond dipole moment is a vector quantity since it has both magnitude and direction
The above figure shows the electron cloud distribution in the dipole of Hydrogen
Chloride
The symbols 𝛿+ and 𝛿– represent the two electric charges that arise in a molecule which
are equal in magnitude but are of opposite signs
Dipole moment of BeF 2
In a beryllium fluoride molecule, the bond angle between the two
beryllium-fluorine bonds is 180o. Fluorine, being the more
electronegative atom, shifts the electron density towards itself.
The individual bond dipole moments in a BeF2 molecule are
illustrated below.
From the illustration provided above, it can be understood that
the two individual bond dipole moments cancel each other out in
a BeF2 molecule because they are equal in magnitude but are
opposite in direction. Therefore, the net dipole moment of a
BeF2 molecule is zero.
Dipole Moment of H2O (Water)
In a water molecule, the electrons are localized around the oxygen atom
since it is much more electronegative than the hydrogen atom. However,
the presence of a lone pair of electrons in the oxygen atom causes the
water molecule to have a bent shape (as per the VSEPR theory).
Therefore, the individual bond dipole moments do not cancel each other
out as is the case in the BeF2 molecule. An illustration describing the
dipole moment in a water molecule is provided below.
The bond angle in a water molecule is 104.5o. The individual bond
moment of an oxygen-hydrogen bond is 1.5 D. The net dipole moment in
a water molecule is found to be 1.84D.
Fajan’s Rule
In inorganic chemistry, Fajans' rules, formulated by Kazimierz
Fajans in 1923, are used to predict whether a chemical bond will
be covalent or ionic, and depend on the charge on the cation and the
relative sizes of the cation and anion.
Definition-
Fajan rule is actually polarisation of an anion by a cation that actually
determines the percentage of covalent character in ionic compound .
Smaller the size of cation more is its polarising power on an anion and
vice versa.
When cation and an anion approaches each other to form an
ionic bond . Then due to high effective nuclear charge on cation,
it starts attracting electron cloud of anion towards itself due to
which sharing of electron cloud takes place and hence covalent
character develops.
NOTE- No compound is 100 percent ionic and 100 percent
covalent . Ionic and covalent are relative terms .Polarizing power
of cation and polarizing power of anion are the two factors that
govern the Fazans rule .
Test your Knowledge:
Which of the following is not correct for dipole moment?
a) lone pair of electrons present on central atom can give rise to dipole moment
b) dipole moment is a vector quantity
c) CO2 molecule has no dipole moment since C-O bonds are nonpolar
d) difference in electronegativities of combining atoms can lead to dipole
moment
What is dipole moment?
When was Fajan’s rule given?
What is the net dipole moment of water?
State the difference between nonpolar covalent
bond and polar covalent bond.
Thank You
You might also like
- Acetic Acid Production ReportDocument15 pagesAcetic Acid Production ReportArya Lodha100% (1)
- Design. Construction of A Charcoal Backing OvenDocument6 pagesDesign. Construction of A Charcoal Backing OvenraduonoNo ratings yet
- Why Water Is A DipoleDocument50 pagesWhy Water Is A DipoleRaviverma077No ratings yet
- Nonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryDocument9 pagesNonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Nonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryDocument9 pagesNonpolar Covalent Bonds: ChemistryRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- A Dipole Moment Arises in Any System in Which There Is A Separation of ChargeDocument5 pagesA Dipole Moment Arises in Any System in Which There Is A Separation of ChargehuesosNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bondind and Molecular StructureDocument33 pagesChemical Bondind and Molecular StructureSaadNo ratings yet
- Chemical PolarityDocument6 pagesChemical PolarityPavan TejNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument11 pagesPhysical ScienceSieg BelfortNo ratings yet
- Unit4 Chem Bond-Full Notes 2018Document30 pagesUnit4 Chem Bond-Full Notes 2018Krishiv RajkumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Materials Lecture 4Document24 pagesChemistry of Materials Lecture 4sanjunaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Ionic CrystalDocument24 pagesAtomic Bonding: Ionic Bonding and Ionic CrystalDr-Sushant GuptaNo ratings yet
- ° Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds 3Document23 pages° Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds 3Zayyan AliNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument12 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureSatyam MittalNo ratings yet
- Diploe Moment and Inductive Effect Final VersionDocument45 pagesDiploe Moment and Inductive Effect Final VersionIqra BaigNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Short Notes by MTHDocument8 pagesChemical Bonding Short Notes by MTHmanthangoel11jeeNo ratings yet
- Physical State Melting Point and Boiling PointDocument6 pagesPhysical State Melting Point and Boiling Pointru ruNo ratings yet
- Physical State Melting Point and Boiling PointDocument6 pagesPhysical State Melting Point and Boiling Pointru ruNo ratings yet
- Physical State Melting Point and Boiling PointDocument6 pagesPhysical State Melting Point and Boiling Pointru ruNo ratings yet
- Notes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument17 pagesNotes On Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical Bonding: Ionic Bond OR Electrovalent BondDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Chemical Bonding: Ionic Bond OR Electrovalent Bondanon_397573801No ratings yet
- Say Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument13 pagesSay Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structuresivaranjini S.VNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Document88 pagesUnit 4 Chemical Bonding 2021Damz RtgNo ratings yet
- Chemical Polarity PDFDocument33 pagesChemical Polarity PDFEG Tiolo AbadNo ratings yet
- E1Document10 pagesE1Vita Dini AviyanaNo ratings yet
- 8.4 - EdlineDocument20 pages8.4 - EdlineHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document20 pagesChemical Bonding 1ahmedNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: Polarity of Molecules: Seventh Course (General Chemistry) by Dr. IstadiDocument23 pagesIntermolecular Forces: Polarity of Molecules: Seventh Course (General Chemistry) by Dr. IstadiBINTANGNo ratings yet
- PPT8Document29 pagesPPT8Adugnaw BiksNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science-Module 5 Polarity and Intermolecular Forces of AttractionDocument45 pagesPhysical-Science-Module 5 Polarity and Intermolecular Forces of AttractionJoana CastilloNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Polarity - FactsDocument9 pagesElectronegativity and Polarity - FactsAlshaimaa SolimanNo ratings yet
- Bonding Question AnswersDocument23 pagesBonding Question Answersgyogi1989No ratings yet
- Bond Characteristics: Class 11Document19 pagesBond Characteristics: Class 11sabin MandalNo ratings yet
- Ach 2101 Lesson 5Document19 pagesAch 2101 Lesson 5Lawrence MajaliwaNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Its ApplicationsDocument6 pagesElectronegativity and Its ApplicationsShamzaSeemin100% (1)
- Lo5 1) Chemical BondsDocument9 pagesLo5 1) Chemical BondsabdogamreNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument51 pagesChemical BondsagnamolathNo ratings yet
- Chap 1.2Document47 pagesChap 1.2Irfan AzaharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular ForcesDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forcesnoreen doraniNo ratings yet
- Chem402 Tonny WeDocument7 pagesChem402 Tonny WeRuth CheropNo ratings yet
- Electron AffinityDocument15 pagesElectron AffinitydarknesspersonifiedNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument68 pagesChemical BondingAnkur Agarwal100% (4)
- UNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2Document13 pagesUNIT-2 Chem Bonding-2KARTIKAY LADDHANo ratings yet
- Lectures - Biochemistry 1 - 2021-2022 Prof Version 6.01 - 23-24-1-30Document30 pagesLectures - Biochemistry 1 - 2021-2022 Prof Version 6.01 - 23-24-1-30Ken M'voulaboloNo ratings yet
- Z6Document5 pagesZ6turnija2030No ratings yet
- 6 Chapter Chemical Bonding Short Question With AnswersDocument16 pages6 Chapter Chemical Bonding Short Question With AnswersBilal KhanNo ratings yet
- Dipole Moment: Special Reference To Alkyl HalidesDocument8 pagesDipole Moment: Special Reference To Alkyl HalidesMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- 4.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 2016Document10 pages4.chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - 2016Karanvir Singh 6No ratings yet
- 04 Chemical Bonding Formula SheetsDocument9 pages04 Chemical Bonding Formula SheetsRushil PahwaNo ratings yet
- Enc Encoded ex7XDZYZXOqmbH1FNJmXNKobRl vzOD3CVnwfk7ZNedEJAZXdKoLTMWdDocument49 pagesEnc Encoded ex7XDZYZXOqmbH1FNJmXNKobRl vzOD3CVnwfk7ZNedEJAZXdKoLTMWdSri VanyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument7 pagesChemical BondingSanaa SamkoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bonding and Molecular Sructure I Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Bonding and Molecular Sructure I Chemical BondingJonathan SaydeNo ratings yet
- Figure of Towels Sewn and Velcroed Representing Bonds Between Hydrogen and Chlorine AtomsDocument12 pagesFigure of Towels Sewn and Velcroed Representing Bonds Between Hydrogen and Chlorine AtomsW Ayu DewiNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent BondsDocument5 pagesIonic and Covalent BondsFern HofileñaNo ratings yet
- Polarity and Intermolecular FDocument5 pagesPolarity and Intermolecular Ftgeorgina630No ratings yet
- Chemical Bond 21Document16 pagesChemical Bond 21Thanks OdoiNo ratings yet
- ASSOCIATIVE INTERACTIONS SASTRA University First YearDocument28 pagesASSOCIATIVE INTERACTIONS SASTRA University First Yearstar100% (1)
- A Chemical Bond Is An Attraction Between Atoms That Allows The Formation of Chemical Substances That Contain Two or More AtomsDocument2 pagesA Chemical Bond Is An Attraction Between Atoms That Allows The Formation of Chemical Substances That Contain Two or More Atomscaguioajulius12No ratings yet
- 3B.2 Electronegativity and Bond PolarityDocument10 pages3B.2 Electronegativity and Bond Polarityzerus ddaasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes KhraDocument24 pagesChemistry Notes KhraMohamed WageehNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureshusa harshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 SUBSTITUTION REACTIONDocument35 pagesChapter 4 SUBSTITUTION REACTIONHalimatun MustafaNo ratings yet
- Cap - 1 - Heat Conduction in 3D Solids PDFDocument10 pagesCap - 1 - Heat Conduction in 3D Solids PDFmaurizio.desio4992No ratings yet
- Mir Junaid-1 PDFDocument5 pagesMir Junaid-1 PDFMir Junaid Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Enzyme ImmobilizationDocument27 pagesEnzyme Immobilizationsabuz pataNo ratings yet
- The Atom Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesThe Atom Lesson Planapi-351677864No ratings yet
- OlinDocument16 pagesOlinA AhmedNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Reaction Rate Expression With Equilibrium AssumptionDocument6 pagesDerivation of Reaction Rate Expression With Equilibrium AssumptionViaTS13No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Experiment 4Document5 pagesPhysical Chemistry Experiment 4Suzanne Clariz M. BaltazarNo ratings yet
- D. C. Blackley B.sc. Ph.D. F.P.R.I. Auth. - Synthetic Rubbers Their Chemistry and Technology-Springer Netherlands 1983Document380 pagesD. C. Blackley B.sc. Ph.D. F.P.R.I. Auth. - Synthetic Rubbers Their Chemistry and Technology-Springer Netherlands 1983Minh Tran100% (3)
- 01-03 - Effect of Thickness On The Opticar Properties of GaAs Thin FilmsDocument9 pages01-03 - Effect of Thickness On The Opticar Properties of GaAs Thin FilmsFerRazzónNo ratings yet
- Electrochimica Acta Volume 37 Issue 12 1992 (Doi 10.1016 - 0013-4686 (92) 85104-s) Sergio Trasatti - Adsorption of Organic Substances at Electrodes - Recent AdvancesDocument8 pagesElectrochimica Acta Volume 37 Issue 12 1992 (Doi 10.1016 - 0013-4686 (92) 85104-s) Sergio Trasatti - Adsorption of Organic Substances at Electrodes - Recent AdvancesNumitor Tor Aten JilNo ratings yet
- hw5Document3 pageshw5Ryle ArbonNo ratings yet
- Calculation Sheet Document No. Page No. Revision No. Date Prepared by Approved by Plant PlaceDocument22 pagesCalculation Sheet Document No. Page No. Revision No. Date Prepared by Approved by Plant PlaceSwapnil Pratap Singh100% (1)
- Lecture Notes On Thermodynamics. Joseph M. PowersDocument383 pagesLecture Notes On Thermodynamics. Joseph M. PowersGustavo CoronelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 31Document8 pagesLecture 31Miguel RochaNo ratings yet
- Test Glo-Qc-Tm-0744Document6 pagesTest Glo-Qc-Tm-0744rx bafnaNo ratings yet
- Qalco Q-Jetcool 153Document1 pageQalco Q-Jetcool 153Deepak JoyNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Exam MCQ'sDocument2 pagesMid Term Exam MCQ'sAbdul Khaliq KhanNo ratings yet
- EDTADocument12 pagesEDTAPrabhatNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument41 pages3.0 Laws of ThermodynamicsBrandon LubegaNo ratings yet
- Ae708 Question Bank 2Document5 pagesAe708 Question Bank 2pRoBoTRoGe OPNo ratings yet
- Properties of SteamDocument7 pagesProperties of SteamRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- ONYECHI CHINENYE ADAOBI M.Eng. THESIS CombinedDocument253 pagesONYECHI CHINENYE ADAOBI M.Eng. THESIS Combinedchinenye igwegbeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1 - ExergyDocument27 pagesLesson 1.1 - ExergyBilly JhunNo ratings yet
- FY BTech Lab Manaul 2021/01/01Document46 pagesFY BTech Lab Manaul 2021/01/01harshNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting EvaporationDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting EvaporationKaram Abd El-Aal100% (5)
- Voltaic Cell Lab Assignment PDFDocument6 pagesVoltaic Cell Lab Assignment PDFalexrilenNo ratings yet
- Surface PolarizabilityDocument21 pagesSurface PolarizabilityMike de Guzman0% (1)