Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 viewsScaffolding
Scaffolding
Uploaded by
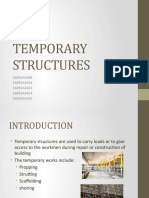
Zubir AbdullahThere are several types of scaffolding described in the document:
1) Step scaffolding uses platforms supported by outriggers, brackets, poles or other rigid supports.
2) Suspended scaffolding uses platforms suspended by ropes or other non-rigid means from an overhead structure.
3) Single scaffolding is used for bricklaying and comprises standards, putlogs and ledgers spaced about 1.2 meters apart to support the scaffold against a wall.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Shear Wall SeminarDocument12 pagesShear Wall SeminarJithu SukumaranNo ratings yet
- BLD 212 Lecture 1Document10 pagesBLD 212 Lecture 1Umar Bello NuhuNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document4 pagesModule 6Felamae BaynosaNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldingDocument9 pagesScaffoldingxnazmiexNo ratings yet
- Safe Scaffold1Document40 pagesSafe Scaffold1Anonymous 3VTQm3Tgyb100% (1)
- Building Construction and Technology IV: Forth Semester, B.ArchDocument14 pagesBuilding Construction and Technology IV: Forth Semester, B.ArchRAVATNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding - LECTURE 2Document47 pagesScaffolding - LECTURE 2MichaelKiprono100% (2)
- SCAFFOLDINGDocument24 pagesSCAFFOLDINGivorykeyzzNo ratings yet
- Types of ShoringDocument2 pagesTypes of ShoringAhmad MustaqeemNo ratings yet
- Excavation, WAH, ScaffoldingDocument30 pagesExcavation, WAH, ScaffoldingManohar KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of ScaffoldingDocument14 pagesTypes of ScaffoldingJohn Ceasar PascoNo ratings yet
- Anshumi ScaffoldingDocument6 pagesAnshumi ScaffoldingAnshumi TannaNo ratings yet
- Temporary WorksDocument25 pagesTemporary Workscraig burey100% (1)
- WALL," Around The BuildingDocument1 pageWALL," Around The BuildingVinay SoniNo ratings yet
- SCAFFOLDINGDocument13 pagesSCAFFOLDINGyonasjova21No ratings yet
- SCAFOLDINGDocument49 pagesSCAFOLDINGKHAIRINA FIKRIAH KHAIRUDDINNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldingDocument6 pagesScaffoldingUmar Bello NuhuNo ratings yet
- Foundation Part B PDFDocument11 pagesFoundation Part B PDFKiprono VincentNo ratings yet
- Shoring and UnderpinningDocument35 pagesShoring and UnderpinningAnySikaNo ratings yet
- Shoring and UnderpinningDocument35 pagesShoring and UnderpinningAnySikaNo ratings yet
- Shear WallDocument19 pagesShear WallVasu MevawalaNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall PDFDocument18 pagesShear Wall PDFRubina Hannure100% (1)
- Temporary Structures: 16091AA008 16091AA018 16091AA021 16091AA024 16091AA029Document27 pagesTemporary Structures: 16091AA008 16091AA018 16091AA021 16091AA024 16091AA029KaushikJainNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding PPT EditedDocument28 pagesScaffolding PPT EditedKhiZra ShahZad50% (2)
- Shoring: Shoring Is The Construction of A Temporary Structure To Support Temporarily AnDocument8 pagesShoring: Shoring Is The Construction of A Temporary Structure To Support Temporarily Anweston chegeNo ratings yet
- Shoring UnderpiningDocument21 pagesShoring UnderpiningMumtahina MouliNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding: Scaffolding Is A Temporary Framework Used ToDocument38 pagesScaffolding: Scaffolding Is A Temporary Framework Used ToNagakrishna SamanasaNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldingDocument37 pagesScaffoldingsoumyasonawaneNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall StructuresDocument25 pagesShear Wall StructuresSameera Simha100% (4)
- RT4 4a Wall CoreDocument10 pagesRT4 4a Wall CoreHamNo ratings yet
- Form WorkDocument72 pagesForm WorkNimmy BennyNo ratings yet
- Topic-Temporary Works (Btech)Document9 pagesTopic-Temporary Works (Btech)victorNo ratings yet
- Types of Shoring: Unsafe Structure. These Support Walls Laterally. They Can Be Used Under The Following CircumstancesDocument7 pagesTypes of Shoring: Unsafe Structure. These Support Walls Laterally. They Can Be Used Under The Following CircumstancesEdward RiderNo ratings yet
- ShoringDocument8 pagesShoringJeo LawrenceNo ratings yet
- LGS Erection Methodology by Nabeel AmjadDocument14 pagesLGS Erection Methodology by Nabeel AmjadNabeel SheikhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document20 pagesAssignment 2Raj MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Temporary ConstructionDocument65 pagesChapter 7 Temporary Constructionnabin prasaiNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Structure Detailing: Anusha. R Sneha AuteDocument26 pagesEarthquake Resistant Structure Detailing: Anusha. R Sneha AuteHana SiddNo ratings yet
- Access Birdcage ScaffoldsDocument22 pagesAccess Birdcage ScaffoldsJitendra Kumar AnandNo ratings yet
- Adv Mat PresentDocument65 pagesAdv Mat PresentShee JaNo ratings yet
- Reporter: Silo, Jeter Gabayan, Lorence Batayo, Jayson Pasco, John Caesar RDocument14 pagesReporter: Silo, Jeter Gabayan, Lorence Batayo, Jayson Pasco, John Caesar RJohn Ceasar PascoNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldingDocument11 pagesScaffoldingGarima MehtaNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding, Shoring & Underpinning: Applications of ScaffoldsDocument14 pagesScaffolding, Shoring & Underpinning: Applications of Scaffoldssmugler 123100% (2)
- High Rise Building Structure SystemDocument35 pagesHigh Rise Building Structure SystemZanyar S. MuhamadNo ratings yet
- High Rise Building Construction: BY-Ruksardeep Kaur Rohit Devgan Srishti SharmaDocument86 pagesHigh Rise Building Construction: BY-Ruksardeep Kaur Rohit Devgan Srishti SharmaruksarNo ratings yet
- Scaffoldings, Bonds in Bricks and Masonry WallsDocument30 pagesScaffoldings, Bonds in Bricks and Masonry WallsDeepak Singh100% (1)
- Reviewer (Building Technology)Document27 pagesReviewer (Building Technology)Jully GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Temporary ConstructionDocument14 pagesTemporary ConstructionDevesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lift Shear Walls Individual Compression Shear WallsDocument19 pagesLift Shear Walls Individual Compression Shear Wallssaurabh singhNo ratings yet
- Basic Scaffolding Elements: TransomsDocument2 pagesBasic Scaffolding Elements: TransomsAnonymous v5QjDW2eHxNo ratings yet
- High Rise Structural Systems: Presented byDocument35 pagesHigh Rise Structural Systems: Presented byvidi herdianaNo ratings yet
- DF Chapter 1Document40 pagesDF Chapter 1Rajesh MarvadaNo ratings yet
- Lintels and ArchesDocument27 pagesLintels and Archesguneet100% (1)
- High Rise Structural Systems: Presented byDocument35 pagesHigh Rise Structural Systems: Presented byiqbalNo ratings yet
- Transportation and Hosting of PrefabricatesDocument9 pagesTransportation and Hosting of Prefabricatescse udtNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding PDFDocument12 pagesScaffolding PDFChinki Rockzz.. ..No ratings yet
- Shear WallDocument23 pagesShear WallSamit RajakNo ratings yet
- Stair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareFrom EverandStair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareNo ratings yet
- St-Nerf-25 - Reinforcememt DetailsDocument1 pageSt-Nerf-25 - Reinforcememt Detailsmhazarath murariNo ratings yet
- Abonalla Final A1Document1 pageAbonalla Final A1vern pam0% (1)
- ACI 318 08 Design of Retaining Wall With Counterfort Rev1Document3 pagesACI 318 08 Design of Retaining Wall With Counterfort Rev1januarto jamadiNo ratings yet
- منصور حسين الحريصي انشائيDocument21 pagesمنصور حسين الحريصي انشائيSales ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Howe Truss Computation Analysis2Document11 pagesHowe Truss Computation Analysis2Wingartz Vendiola PosedioNo ratings yet
- Southern Tier Bridges - Steuben CountyDocument13 pagesSouthern Tier Bridges - Steuben CountyGeorge StockburgerNo ratings yet
- One-Way Joist SlabDocument11 pagesOne-Way Joist SlabGui Per100% (1)
- Floor Plan Roof Plan: Schedule of Doors and WindowsDocument1 pageFloor Plan Roof Plan: Schedule of Doors and WindowsAngelo AmarNo ratings yet
- Introducing Two Most Common Types of Shear Walls and Their Construction MethodsDocument6 pagesIntroducing Two Most Common Types of Shear Walls and Their Construction MethodsVictor OmotoriogunNo ratings yet
- RFPLANDocument1 pageRFPLANDIAMA, JOYCE LYNN MAE B.No ratings yet
- Super StructureDocument2 pagesSuper StructureHarshita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Column RebarDocument5 pagesColumn RebarAlyssa Marie AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Product Brochure enDocument24 pagesProduct Brochure encatalinpascariuNo ratings yet
- 275 THK Slab Design 1 .Document4 pages275 THK Slab Design 1 .bittuchintuNo ratings yet
- Rustic Shingle Instalation InstructionsDocument9 pagesRustic Shingle Instalation InstructionsgeorgeksmithNo ratings yet
- Construction Activities For 10 Door Housing UnitsDocument4 pagesConstruction Activities For 10 Door Housing Unitsbroomer27100% (1)
- Ene Getenet G+8 BOQDocument96 pagesEne Getenet G+8 BOQsifu asratNo ratings yet
- Sunway Big Box Office - C&S Design Write Up 20 02 13Document3 pagesSunway Big Box Office - C&S Design Write Up 20 02 13hauzhiNo ratings yet
- Bolts - For Fill Out - KateDocument118 pagesBolts - For Fill Out - KateKate PerezNo ratings yet
- AUS Triboard ManuaDocument112 pagesAUS Triboard ManuaWan RidsNo ratings yet
- Metsec Design GuideDocument86 pagesMetsec Design GuideRm1262No ratings yet
- Typical Beam Elevation DetailDocument1 pageTypical Beam Elevation DetailPrince QuimnoNo ratings yet
- The House Designers - THD-9690, JoshuaDocument4 pagesThe House Designers - THD-9690, JoshuajodgeNo ratings yet
- Problem Set1 (Quiz1)Document13 pagesProblem Set1 (Quiz1)JAMESNo ratings yet
- RC Design U 2017 v12.7Document73 pagesRC Design U 2017 v12.7AmjedMassamjedNo ratings yet
- Terms Used in RoofDocument2 pagesTerms Used in Roofrahul_5587_265238786No ratings yet
- Construction Technology 1 Group AssignmentDocument25 pagesConstruction Technology 1 Group Assignmentdixondj_9433% (3)
- Structure, Form, and Architecture: The Synergy: Lecture 18: Tensile StructuresDocument21 pagesStructure, Form, and Architecture: The Synergy: Lecture 18: Tensile StructuresVrushi PatelNo ratings yet
- Bölüm 5 CevaplarDocument165 pagesBölüm 5 Cevaplarbaris.usta04No ratings yet
- Dumpdata A50Document224 pagesDumpdata A50KillburnNo ratings yet
Scaffolding
Scaffolding
Uploaded by
Zubir Abdullah0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views9 pagesThere are several types of scaffolding described in the document:
1) Step scaffolding uses platforms supported by outriggers, brackets, poles or other rigid supports.
2) Suspended scaffolding uses platforms suspended by ropes or other non-rigid means from an overhead structure.
3) Single scaffolding is used for bricklaying and comprises standards, putlogs and ledgers spaced about 1.2 meters apart to support the scaffold against a wall.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThere are several types of scaffolding described in the document:
1) Step scaffolding uses platforms supported by outriggers, brackets, poles or other rigid supports.
2) Suspended scaffolding uses platforms suspended by ropes or other non-rigid means from an overhead structure.
3) Single scaffolding is used for bricklaying and comprises standards, putlogs and ledgers spaced about 1.2 meters apart to support the scaffold against a wall.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views9 pagesScaffolding
Scaffolding
Uploaded by
Zubir AbdullahThere are several types of scaffolding described in the document:
1) Step scaffolding uses platforms supported by outriggers, brackets, poles or other rigid supports.
2) Suspended scaffolding uses platforms suspended by ropes or other non-rigid means from an overhead structure.
3) Single scaffolding is used for bricklaying and comprises standards, putlogs and ledgers spaced about 1.2 meters apart to support the scaffold against a wall.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 9
STEP SCAFFOLDING
Consist of one or more platforms supported by
outrigger beams, brackets, poles, legs, uprights, posts,
frames, or similar rigid support.
SUSPENDED SCAFFOLDING
Suspended scaffolds are platforms suspended by
ropes, or other non-rigid means, from an overhead
structure. Because two-point scaffolds are the most
common type of suspended scaffold, this E-tool uses
the two-point module to describe requirements that
apply to all suspended scaffolds. Requirements specific
to other types are described only in their respective
modules.
SINGLE SCAFFOLDING
Usually used for brick masonry and so it is also known
as brick layer’s scaffolding. Single scaffolding
comprises of standards, putlogs, ledgers etc, which
corresponds to the wall at a distance of around 1.2
meter. Distance amongst the standards is around 2 –
2.5 meter. Ledgers join the standards at an upright gap
of 1.2 to 1.5 meter. Putlogs are extracted from the gap
remaining in the wall to one end of the ledgers.
Putlogs are positioned at a gap of 1.2 to 1.5 meter.
DOUBLE SCAFFOLDING
Usually used for stone masonry job, therefore , it is
also known as mason’s scaffolding. Its is also known as
the independent scaffolding. Typically, in stone walls,
it is tough to make holes in the wall for supporting
putlogs; thus, two scaffolding rows are made to make
it robust. Basically, the first row is about 20 – 30 cm
away from the wall, and another one is 1 meter away
from the first row. Then after putlogs are positioned
that are supported by both the frames. In order to
make it sturdier, cross braces and rakers are supplied.
CANTALIVER SCAFFOLDING
This is a type of independent scaffold which is erected
on cantilever beams and secured to a building at only
one end. The other side is left hanging or exposed.
This type of scaffold is efficient in that it provides
access to areas that would be difficult or uneconomic
to reach using a scaffold system erected from ground
level. Worker operating on cantilever scaffold system
must be fitted with safety harnesses.
BIRDCAGE SCAFFOLDING
This is a type of independent scaffold which is
typically used for interior work in large buildings such
as halls, mosque, museums and so on. It is generally
only used for one level, typically to provide easy access
to ceilings and soffits. It consists of parallel rows of
standards connected by ledgers in both directions and
supporting a single working platform.
RAKING STRUT
A shoring technique deploys rakers, or scaffolding tube,
set at an incline from the ground to the top of the wall and
providing support from the side along the way. The rakers
originate from a sole plate embedded in the ground and
continue upward to link to a wall plate screwed into the
structure near its top. Rakers should be angled at 45
degrees, though an incline of up to 75 degrees is also
acceptable. Rakers must be secured at intervals with
braces that bolt into cleats on the wall. Experts advise
against using construction wedges to connect rakers to
sole plates, because wedges can fail if the building vibrates
or shakes.
HORIZONTAL STRUT
Uses shores that don’t touch the ground, but rather
span in mid-air the widths between the walls you’re
propping up. The flying shoring technique focuses on
a horizontal strut or shore placed between the walls,
secured to wall plates and supported by a network of
needles, or shorter beams, and steel construction
cleats. Additional inclined struts brace into wall plates
and angle upward to the horizontal shore to provide
additional strength. Inclined struts gain extra support
from needles at the top and straining pieces, or
straining sills, at the bottom.
DEAD STRUT
Provide vertical support to roofs and floors. The method
is designed to arrange a system of beams and posts that
can both support a building’s weight and transfer the
weight to a foundation on the ground. Builders install
dead shores by cutting holes into walls and inserting
vertical beams or girders to prop up the structure above.
Dead shores, which are vertical props, are braced to a
sole plate on the ground, and needles are secured
horizontally to the tops of the dead shores. Builders
should leave enough distance between the dead shores
and the walls to allow workers to pass through the space.
You might also like
- Shear Wall SeminarDocument12 pagesShear Wall SeminarJithu SukumaranNo ratings yet
- BLD 212 Lecture 1Document10 pagesBLD 212 Lecture 1Umar Bello NuhuNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document4 pagesModule 6Felamae BaynosaNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldingDocument9 pagesScaffoldingxnazmiexNo ratings yet
- Safe Scaffold1Document40 pagesSafe Scaffold1Anonymous 3VTQm3Tgyb100% (1)
- Building Construction and Technology IV: Forth Semester, B.ArchDocument14 pagesBuilding Construction and Technology IV: Forth Semester, B.ArchRAVATNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding - LECTURE 2Document47 pagesScaffolding - LECTURE 2MichaelKiprono100% (2)
- SCAFFOLDINGDocument24 pagesSCAFFOLDINGivorykeyzzNo ratings yet
- Types of ShoringDocument2 pagesTypes of ShoringAhmad MustaqeemNo ratings yet
- Excavation, WAH, ScaffoldingDocument30 pagesExcavation, WAH, ScaffoldingManohar KumarNo ratings yet
- Types of ScaffoldingDocument14 pagesTypes of ScaffoldingJohn Ceasar PascoNo ratings yet
- Anshumi ScaffoldingDocument6 pagesAnshumi ScaffoldingAnshumi TannaNo ratings yet
- Temporary WorksDocument25 pagesTemporary Workscraig burey100% (1)
- WALL," Around The BuildingDocument1 pageWALL," Around The BuildingVinay SoniNo ratings yet
- SCAFFOLDINGDocument13 pagesSCAFFOLDINGyonasjova21No ratings yet
- SCAFOLDINGDocument49 pagesSCAFOLDINGKHAIRINA FIKRIAH KHAIRUDDINNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldingDocument6 pagesScaffoldingUmar Bello NuhuNo ratings yet
- Foundation Part B PDFDocument11 pagesFoundation Part B PDFKiprono VincentNo ratings yet
- Shoring and UnderpinningDocument35 pagesShoring and UnderpinningAnySikaNo ratings yet
- Shoring and UnderpinningDocument35 pagesShoring and UnderpinningAnySikaNo ratings yet
- Shear WallDocument19 pagesShear WallVasu MevawalaNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall PDFDocument18 pagesShear Wall PDFRubina Hannure100% (1)
- Temporary Structures: 16091AA008 16091AA018 16091AA021 16091AA024 16091AA029Document27 pagesTemporary Structures: 16091AA008 16091AA018 16091AA021 16091AA024 16091AA029KaushikJainNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding PPT EditedDocument28 pagesScaffolding PPT EditedKhiZra ShahZad50% (2)
- Shoring: Shoring Is The Construction of A Temporary Structure To Support Temporarily AnDocument8 pagesShoring: Shoring Is The Construction of A Temporary Structure To Support Temporarily Anweston chegeNo ratings yet
- Shoring UnderpiningDocument21 pagesShoring UnderpiningMumtahina MouliNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding: Scaffolding Is A Temporary Framework Used ToDocument38 pagesScaffolding: Scaffolding Is A Temporary Framework Used ToNagakrishna SamanasaNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldingDocument37 pagesScaffoldingsoumyasonawaneNo ratings yet
- Shear Wall StructuresDocument25 pagesShear Wall StructuresSameera Simha100% (4)
- RT4 4a Wall CoreDocument10 pagesRT4 4a Wall CoreHamNo ratings yet
- Form WorkDocument72 pagesForm WorkNimmy BennyNo ratings yet
- Topic-Temporary Works (Btech)Document9 pagesTopic-Temporary Works (Btech)victorNo ratings yet
- Types of Shoring: Unsafe Structure. These Support Walls Laterally. They Can Be Used Under The Following CircumstancesDocument7 pagesTypes of Shoring: Unsafe Structure. These Support Walls Laterally. They Can Be Used Under The Following CircumstancesEdward RiderNo ratings yet
- ShoringDocument8 pagesShoringJeo LawrenceNo ratings yet
- LGS Erection Methodology by Nabeel AmjadDocument14 pagesLGS Erection Methodology by Nabeel AmjadNabeel SheikhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document20 pagesAssignment 2Raj MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Temporary ConstructionDocument65 pagesChapter 7 Temporary Constructionnabin prasaiNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Structure Detailing: Anusha. R Sneha AuteDocument26 pagesEarthquake Resistant Structure Detailing: Anusha. R Sneha AuteHana SiddNo ratings yet
- Access Birdcage ScaffoldsDocument22 pagesAccess Birdcage ScaffoldsJitendra Kumar AnandNo ratings yet
- Adv Mat PresentDocument65 pagesAdv Mat PresentShee JaNo ratings yet
- Reporter: Silo, Jeter Gabayan, Lorence Batayo, Jayson Pasco, John Caesar RDocument14 pagesReporter: Silo, Jeter Gabayan, Lorence Batayo, Jayson Pasco, John Caesar RJohn Ceasar PascoNo ratings yet
- ScaffoldingDocument11 pagesScaffoldingGarima MehtaNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding, Shoring & Underpinning: Applications of ScaffoldsDocument14 pagesScaffolding, Shoring & Underpinning: Applications of Scaffoldssmugler 123100% (2)
- High Rise Building Structure SystemDocument35 pagesHigh Rise Building Structure SystemZanyar S. MuhamadNo ratings yet
- High Rise Building Construction: BY-Ruksardeep Kaur Rohit Devgan Srishti SharmaDocument86 pagesHigh Rise Building Construction: BY-Ruksardeep Kaur Rohit Devgan Srishti SharmaruksarNo ratings yet
- Scaffoldings, Bonds in Bricks and Masonry WallsDocument30 pagesScaffoldings, Bonds in Bricks and Masonry WallsDeepak Singh100% (1)
- Reviewer (Building Technology)Document27 pagesReviewer (Building Technology)Jully GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Temporary ConstructionDocument14 pagesTemporary ConstructionDevesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lift Shear Walls Individual Compression Shear WallsDocument19 pagesLift Shear Walls Individual Compression Shear Wallssaurabh singhNo ratings yet
- Basic Scaffolding Elements: TransomsDocument2 pagesBasic Scaffolding Elements: TransomsAnonymous v5QjDW2eHxNo ratings yet
- High Rise Structural Systems: Presented byDocument35 pagesHigh Rise Structural Systems: Presented byvidi herdianaNo ratings yet
- DF Chapter 1Document40 pagesDF Chapter 1Rajesh MarvadaNo ratings yet
- Lintels and ArchesDocument27 pagesLintels and Archesguneet100% (1)
- High Rise Structural Systems: Presented byDocument35 pagesHigh Rise Structural Systems: Presented byiqbalNo ratings yet
- Transportation and Hosting of PrefabricatesDocument9 pagesTransportation and Hosting of Prefabricatescse udtNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding PDFDocument12 pagesScaffolding PDFChinki Rockzz.. ..No ratings yet
- Shear WallDocument23 pagesShear WallSamit RajakNo ratings yet
- Stair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareFrom EverandStair-Building and the Steel Square: A Manual of Practical Instruction in the Art of Stair-Building and Hand-Railing, and the Manifold Uses of the Steel SquareNo ratings yet
- St-Nerf-25 - Reinforcememt DetailsDocument1 pageSt-Nerf-25 - Reinforcememt Detailsmhazarath murariNo ratings yet
- Abonalla Final A1Document1 pageAbonalla Final A1vern pam0% (1)
- ACI 318 08 Design of Retaining Wall With Counterfort Rev1Document3 pagesACI 318 08 Design of Retaining Wall With Counterfort Rev1januarto jamadiNo ratings yet
- منصور حسين الحريصي انشائيDocument21 pagesمنصور حسين الحريصي انشائيSales ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Howe Truss Computation Analysis2Document11 pagesHowe Truss Computation Analysis2Wingartz Vendiola PosedioNo ratings yet
- Southern Tier Bridges - Steuben CountyDocument13 pagesSouthern Tier Bridges - Steuben CountyGeorge StockburgerNo ratings yet
- One-Way Joist SlabDocument11 pagesOne-Way Joist SlabGui Per100% (1)
- Floor Plan Roof Plan: Schedule of Doors and WindowsDocument1 pageFloor Plan Roof Plan: Schedule of Doors and WindowsAngelo AmarNo ratings yet
- Introducing Two Most Common Types of Shear Walls and Their Construction MethodsDocument6 pagesIntroducing Two Most Common Types of Shear Walls and Their Construction MethodsVictor OmotoriogunNo ratings yet
- RFPLANDocument1 pageRFPLANDIAMA, JOYCE LYNN MAE B.No ratings yet
- Super StructureDocument2 pagesSuper StructureHarshita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Column RebarDocument5 pagesColumn RebarAlyssa Marie AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Product Brochure enDocument24 pagesProduct Brochure encatalinpascariuNo ratings yet
- 275 THK Slab Design 1 .Document4 pages275 THK Slab Design 1 .bittuchintuNo ratings yet
- Rustic Shingle Instalation InstructionsDocument9 pagesRustic Shingle Instalation InstructionsgeorgeksmithNo ratings yet
- Construction Activities For 10 Door Housing UnitsDocument4 pagesConstruction Activities For 10 Door Housing Unitsbroomer27100% (1)
- Ene Getenet G+8 BOQDocument96 pagesEne Getenet G+8 BOQsifu asratNo ratings yet
- Sunway Big Box Office - C&S Design Write Up 20 02 13Document3 pagesSunway Big Box Office - C&S Design Write Up 20 02 13hauzhiNo ratings yet
- Bolts - For Fill Out - KateDocument118 pagesBolts - For Fill Out - KateKate PerezNo ratings yet
- AUS Triboard ManuaDocument112 pagesAUS Triboard ManuaWan RidsNo ratings yet
- Metsec Design GuideDocument86 pagesMetsec Design GuideRm1262No ratings yet
- Typical Beam Elevation DetailDocument1 pageTypical Beam Elevation DetailPrince QuimnoNo ratings yet
- The House Designers - THD-9690, JoshuaDocument4 pagesThe House Designers - THD-9690, JoshuajodgeNo ratings yet
- Problem Set1 (Quiz1)Document13 pagesProblem Set1 (Quiz1)JAMESNo ratings yet
- RC Design U 2017 v12.7Document73 pagesRC Design U 2017 v12.7AmjedMassamjedNo ratings yet
- Terms Used in RoofDocument2 pagesTerms Used in Roofrahul_5587_265238786No ratings yet
- Construction Technology 1 Group AssignmentDocument25 pagesConstruction Technology 1 Group Assignmentdixondj_9433% (3)
- Structure, Form, and Architecture: The Synergy: Lecture 18: Tensile StructuresDocument21 pagesStructure, Form, and Architecture: The Synergy: Lecture 18: Tensile StructuresVrushi PatelNo ratings yet
- Bölüm 5 CevaplarDocument165 pagesBölüm 5 Cevaplarbaris.usta04No ratings yet
- Dumpdata A50Document224 pagesDumpdata A50KillburnNo ratings yet