Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsStudy of Ultrastructural Pathology of Microtubules and Microfilaments in Various Cell Types (Electronograms)
Study of Ultrastructural Pathology of Microtubules and Microfilaments in Various Cell Types (Electronograms)
Uploaded by
shyngysThe document discusses the study of ultrastructural pathology of microtubules and microfilaments in various cell types. It provides details on microtubules and microfilaments, which are intracellular structures that form part of the cytoskeleton. Microtubules are hollow cylinders composed of tubulin dimers. They play an important structural role in many cellular processes and transport particles along their surface using motor proteins. The study examines microtubule and microfilament structures at the ultrastructural level in different cell types to understand pathology using electron microscopy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Edward de Bono - 5 Day Course in ThinkingDocument158 pagesEdward de Bono - 5 Day Course in ThinkingNway Moe Saung100% (2)
- BSCS Final CN 2021 Spring 6th ADocument2 pagesBSCS Final CN 2021 Spring 6th AwaheedNo ratings yet
- Histology: Lecture NotesDocument97 pagesHistology: Lecture Notessky100% (4)
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- Assignment 1594125502 SmsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1594125502 Smsanulorance98No ratings yet
- 2cytology Cytoskel Receptor Transp (3) 1Document43 pages2cytology Cytoskel Receptor Transp (3) 1m.mansoor3377No ratings yet
- Microtubules: Organization: Single Microtubules Are Distributed Within The Cytoplasm. Also, MicrotubulesDocument6 pagesMicrotubules: Organization: Single Microtubules Are Distributed Within The Cytoplasm. Also, MicrotubulesArif NabeelNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument65 pagesCytoskeletonSapana SubediNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument31 pagesCELLtan shin meiNo ratings yet
- MicrotubuleDocument4 pagesMicrotubuleAbhishek DasNo ratings yet
- BCH 4107 - Plant BiochemistryDocument13 pagesBCH 4107 - Plant BiochemistryOLUWASEGUN K AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CellDocument17 pagesChapter 2 CellSirWin AmidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument42 pagesChapter 3: Cell Structure and FunctionHanifa ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:-: Priyanka Yadav M.Sc. Life Sciences Ist SemDocument37 pagesPrepared By:-: Priyanka Yadav M.Sc. Life Sciences Ist SemleartaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - CytoskeletonDocument38 pagesLecture 6 - CytoskeletonNL DearestNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton Actividad 28-03 PDFDocument9 pagesCytoskeleton Actividad 28-03 PDFCatalina YáñezNo ratings yet
- Assignment II: Macaranas, Mar SDocument7 pagesAssignment II: Macaranas, Mar SMar MacaranasNo ratings yet
- MicrotubulesDocument39 pagesMicrotubulesAdnan QureshiNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument9 pagesCytoskeletonGordon YapNo ratings yet
- 1 7 CytoskeletonDocument31 pages1 7 CytoskeletonAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Cytoskeleton STDocument18 pagesLecture 6 - Cytoskeleton STminhph.23bi14469No ratings yet
- Week 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021Document4 pagesWeek 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021yui kirigayayuukiNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document42 pagesCell Organelles 2James IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.animal Cell StructureDocument25 pagesTopic 2.animal Cell StructureJanine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- The Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellDocument9 pagesThe Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellHania GulNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 006 Chapter 3Document7 pagesZoology Notes: 006 Chapter 3humanupgrade100% (1)
- Name: Course: Registration Number: Assignment One: Describe The Structure Function and Adaptation of Animal CellsDocument5 pagesName: Course: Registration Number: Assignment One: Describe The Structure Function and Adaptation of Animal CellsDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton (1) HBHHHHGGH, HGDocument24 pagesCytoskeleton (1) HBHHHHGGH, HGrohanv4712No ratings yet
- Enumerating The Structure of Major Protein, Describe The Eukaryotic CytoskeletonDocument10 pagesEnumerating The Structure of Major Protein, Describe The Eukaryotic CytoskeletonTathagata ChakravarttyNo ratings yet
- Microtubules - The Cell - NCBI BookshelfDocument5 pagesMicrotubules - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelfanulorance98No ratings yet
- Biomed 05Document12 pagesBiomed 05api-3706483No ratings yet
- February 27, 2012 - Chapter 7: Inside The CellDocument4 pagesFebruary 27, 2012 - Chapter 7: Inside The CellVincent Troy SantosNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Prepared by Dr. Sana AslamDocument41 pagesCell Structure: Prepared by Dr. Sana Aslamsajjad Ali balouch100% (1)
- Cell Organelles - Biology Class 11 - NEETDocument18 pagesCell Organelles - Biology Class 11 - NEETsanjNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: How Are Eukaryotic Cells Organized Into Smaller Parts?Document6 pagesUnit 3: How Are Eukaryotic Cells Organized Into Smaller Parts?juan mondaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Cell CytoskeletonDocument7 pagesCell Cytoskeletonandersonmack047No ratings yet
- MicrotubuleDocument12 pagesMicrotubuleGordon YapNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Section 4-2, Parts of The Eukaryotic CellDocument20 pagesImmunology: Section 4-2, Parts of The Eukaryotic CellJoia De LeonNo ratings yet
- The CytoskeletonDocument3 pagesThe CytoskeletonMark Lorenz LorillaNo ratings yet
- Flagellar Restoration in C. ReinhardiDocument8 pagesFlagellar Restoration in C. Reinhardinasek22No ratings yet
- BIOL 202 Lab 2 Animal Cells and Tissues: Cell StructureDocument15 pagesBIOL 202 Lab 2 Animal Cells and Tissues: Cell StructureKate Anne Montallana RamosNo ratings yet
- Intro, Cell, TissueDocument29 pagesIntro, Cell, Tissueanisa930804No ratings yet
- Biochem AssignmentDocument2 pagesBiochem AssignmentAngel GoNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton DADocument35 pagesCytoskeleton DAAnonymous NVBCqKWHNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton: Jetro P. MagnayonDocument66 pagesCytoskeleton: Jetro P. MagnayonChristian Santiago100% (1)
- CytoskeletonDocument9 pagesCytoskeletonQuoc KhanhNo ratings yet
- Cyto SkeletonDocument3 pagesCyto SkeletonRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-The CellDocument43 pagesLecture 2-The CellMatende husseinNo ratings yet
- Microtubule Oranizing CenterDocument5 pagesMicrotubule Oranizing CenterSasha GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 14 The CytoskeletonDocument7 pages14 The Cytoskeletonsatriamanullang880No ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Plant CellDocument3 pagesParts and Function of Plant CellAmy A. OgnayonNo ratings yet
- Study of Ultrastructural Pathology of Mitochondria and Changes in Cell Bioenergetics (Electronograms)Document9 pagesStudy of Ultrastructural Pathology of Mitochondria and Changes in Cell Bioenergetics (Electronograms)shyngysNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 BioA 3201Document6 pagesAssign 2 BioA 3201Princess CabardoNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 1 SummaryDocument8 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 1 SummaryDana PorterNo ratings yet
- Keerthana H PDocument22 pagesKeerthana H PVidya shree GNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton 2Document7 pagesCytoskeleton 2Basil Francis AlajidNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure by Sabir.h.nDocument15 pagesCell Structure by Sabir.h.nprinceaimy.bestNo ratings yet
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Cell and Molecular Biology 1Document38 pagesLecture 1 Cell and Molecular Biology 1Martin HangasNo ratings yet
- Cell OrgenellesDocument10 pagesCell OrgenellesShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- Liver Disease Modelling: Zhexenbin Shynggys BB-1908 in The Subject: Differentiation of CellsDocument8 pagesLiver Disease Modelling: Zhexenbin Shynggys BB-1908 in The Subject: Differentiation of CellsshyngysNo ratings yet
- Organoids in Developmental Biology Research and ApplicationDocument8 pagesOrganoids in Developmental Biology Research and ApplicationshyngysNo ratings yet
- Study of Ultrastructural Pathology of Mitochondria and Changes in Cell Bioenergetics (Electronograms)Document9 pagesStudy of Ultrastructural Pathology of Mitochondria and Changes in Cell Bioenergetics (Electronograms)shyngysNo ratings yet
- Study of Cellular Processes (Proliferation, Polyploidy, Hypertrohy) During Reparative Regeneration of Various OrgansDocument8 pagesStudy of Cellular Processes (Proliferation, Polyploidy, Hypertrohy) During Reparative Regeneration of Various OrgansshyngysNo ratings yet
- FELCOM 12 Operator's Manual M2 1-22-03Document182 pagesFELCOM 12 Operator's Manual M2 1-22-03smartstepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PDFDocument37 pagesChapter 13 PDFZerlyndaBunga'alloNo ratings yet
- Multi Storey Steel Building 01Document19 pagesMulti Storey Steel Building 01Dan AlexandrescuNo ratings yet
- RSSI-Based Indoor Localization With The Internet of ThingsDocument13 pagesRSSI-Based Indoor Localization With The Internet of ThingsEmi SaharaNo ratings yet
- The Molecules of LifeDocument13 pagesThe Molecules of LifeZen Garcia100% (1)
- Dcm292 Dock For Iphone/ Ipod Sleek Micro SystemDocument17 pagesDcm292 Dock For Iphone/ Ipod Sleek Micro SystemRafael SuarezNo ratings yet
- Mtap 2015Document10 pagesMtap 2015irec100% (2)
- General Circulation: Thermal Circulation and Earth's RotationDocument3 pagesGeneral Circulation: Thermal Circulation and Earth's RotationGie AndalNo ratings yet
- Map Design PDFDocument35 pagesMap Design PDFShahin NescoNo ratings yet
- Elasticity WireDocument8 pagesElasticity WiremksayshiNo ratings yet
- Sast Vs Dast Vs Iast Infographic FinalDocument1 pageSast Vs Dast Vs Iast Infographic Finalpunzango73No ratings yet
- The CircleDocument9 pagesThe CircleavislgNo ratings yet
- Example:: Practice Personal Hygiene Protocols at All Times. 1Document11 pagesExample:: Practice Personal Hygiene Protocols at All Times. 1Christopher GunsatNo ratings yet
- Standard Base Course Soil ModulusDocument14 pagesStandard Base Course Soil ModulusphatmatNo ratings yet
- College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3rd Edition Knight Test BankDocument39 pagesCollege Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3rd Edition Knight Test Bankgretchenmilesdxeh3100% (13)
- Various Cases and Studies of Direct Stroke Lightning Protection On Different Substation IJERTV5IS040692 PDFDocument4 pagesVarious Cases and Studies of Direct Stroke Lightning Protection On Different Substation IJERTV5IS040692 PDFHasnain AwanNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Fixtures & Appliances: Building Services 1Document12 pagesPlumbing Fixtures & Appliances: Building Services 1moonnaNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Symbolic Math ToolboxDocument300 pagesMATLAB Symbolic Math ToolboxelfrichNo ratings yet
- PCR 27 ManualDocument193 pagesPCR 27 Manualsteve100% (1)
- 1 Basic Facts About PerliteDocument2 pages1 Basic Facts About PerliteAllen WellsNo ratings yet
- Back TitrationDocument20 pagesBack TitrationChristopher SeerajNo ratings yet
- PT 111 - N Chapter 6: BandagingDocument61 pagesPT 111 - N Chapter 6: BandagingJan Crizza Dale R. FrancoNo ratings yet
- Sysweld Welding ReportDocument23 pagesSysweld Welding ReportAsiahKuzaimanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Shading of Buildings As A Preventive Measure For Passive Cooling and Energy Conservation in BuildingsDocument4 pagesA Study On Shading of Buildings As A Preventive Measure For Passive Cooling and Energy Conservation in BuildingsMohammad Arif KamalNo ratings yet
- x99 75 Manual PDFDocument108 pagesx99 75 Manual PDFYonni AroussiNo ratings yet
- Arjuna-Carboxylic Acids and AminesDocument66 pagesArjuna-Carboxylic Acids and AminesNirjhar KhetoNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Facemask and Respirator Filtration Test MethodsDocument13 pagesA Comparison of Facemask and Respirator Filtration Test MethodsDJSeidelNo ratings yet
- SCH 5Document1 pageSCH 5csilva_356601No ratings yet
Study of Ultrastructural Pathology of Microtubules and Microfilaments in Various Cell Types (Electronograms)
Study of Ultrastructural Pathology of Microtubules and Microfilaments in Various Cell Types (Electronograms)
Uploaded by
shyngys0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views8 pagesThe document discusses the study of ultrastructural pathology of microtubules and microfilaments in various cell types. It provides details on microtubules and microfilaments, which are intracellular structures that form part of the cytoskeleton. Microtubules are hollow cylinders composed of tubulin dimers. They play an important structural role in many cellular processes and transport particles along their surface using motor proteins. The study examines microtubule and microfilament structures at the ultrastructural level in different cell types to understand pathology using electron microscopy.
Original Description:
Original Title
Pathology12
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the study of ultrastructural pathology of microtubules and microfilaments in various cell types. It provides details on microtubules and microfilaments, which are intracellular structures that form part of the cytoskeleton. Microtubules are hollow cylinders composed of tubulin dimers. They play an important structural role in many cellular processes and transport particles along their surface using motor proteins. The study examines microtubule and microfilament structures at the ultrastructural level in different cell types to understand pathology using electron microscopy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views8 pagesStudy of Ultrastructural Pathology of Microtubules and Microfilaments in Various Cell Types (Electronograms)
Study of Ultrastructural Pathology of Microtubules and Microfilaments in Various Cell Types (Electronograms)
Uploaded by
shyngysThe document discusses the study of ultrastructural pathology of microtubules and microfilaments in various cell types. It provides details on microtubules and microfilaments, which are intracellular structures that form part of the cytoskeleton. Microtubules are hollow cylinders composed of tubulin dimers. They play an important structural role in many cellular processes and transport particles along their surface using motor proteins. The study examines microtubule and microfilament structures at the ultrastructural level in different cell types to understand pathology using electron microscopy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
Study of ultrastructural pathology of
microtubules and microfilaments in
various cell types (electronograms)
ZHEXENBIN SHYNGGYS BB-1908
IN THE SUBJECT: PATHOLOGY OF CELLS
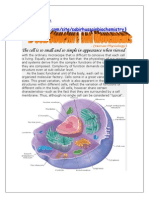
The study of ultrastructural pathology of microtubules and microfilaments in various types of cells is an
important task.In an electron microscope, numerous structures (organelles) necessary for cell metabolism are
determined. Part of the cells in conditions of pathology contains formations that are not involved in metabolic
processes and are not structurally homogeneous with the cytoplasm — these are inclusions (fat, glycogen,
pigments, etc.). Mitochondria are indicators of the functional state of cells that are most sensitive to
aggression. The destruction (destruction) of an excessive number of mitochondria is carried out by the
processes of autophagy by vacuoles, which play the role of secondary lysosomes.
As has long been known, the study of ultrastructural pathology of microtubules and microfilaments in
various cell types is closely related to Golgi.
Golgi structures are formed by flattened sacs (vacuoles) containing secretory granules and anastomoses
that are interconnected with the endoplasmic reticulum. In them, proteins intended for secretion are
conjugated with carbohydrate groups. Morphological manifestations of secretory function disorders are
expressed either in the form of hyperplasia of the lamellar complex, i.e. an increase in the area of its
membranes and the number of secretory granules, or in the form of atrophy of the lamellar complex,
which is accompanied by reduction (reduction) of vacuoles and loss of secretory granules.
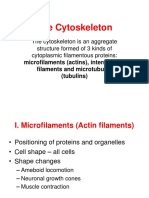
Microtubules are protein intracellular structures that
are part of the cytoskeleton.Microtubules are hollow
cylinders with a diameter of 25 nm. Their length can
be from a few micrometers to probably several
millimeters in the axons of nerve cells. Their wall is
formed by tubulin dimers. Microtubules, like actin
microfilaments, are polar: microtubule self—
assembly occurs at one end, disassembly occurs at
the other. In cells, microtubules play a structural role
in many cellular processes.
Microtubules are structures in which 13 protofilaments[ consisting of α- and β-tubulin
heterodimers are stacked around the circumference of a hollow cylinder. The outer
diameter of the cylinder is about 25 nm, the inner diameter is about 15.One of the
ends of the microtubule, called the plus-end, constantly attaches free tubulin to itself.
From the opposite end — the minus end - tubulin units are split off.β-tubulinThere are
three phases in the formation of microtubules:The delayed phase, or nucleation. This
is the stage of microtubule nucleation, when tubulin molecules begin to combine into
larger formations. Such a connection occurs slower than the attachment of the tubulin
to the already assembled microtubule, which is why the phase is called delayed.The
polymerization phase, or elongation. If the concentration of free tubulin is high, its
polymerization occurs faster than depolymerization at the negative end, due to which
the microtubule lengthens. As it grows, the concentration of tubulin drops to a critical
level, and the growth rate slows down until entering the next phase.Stable state phase.
Depolymerization balances polymerization, and microtubule growth stops.Laboratory
studies show that the assembly of microtubules from tubulins occurs only in the
presence of guanosine triphosphate and magnesium ions.
The study of ultrastructural pathology of microtubules and microfilaments in various
types of cells also concerns the microtubules themselves.Microtubules in the cell are
used as "rails" for transporting particles. Membrane vesicles and mitochondria can
move along their surface. The transport of microtubules is carried out by proteins
called motor proteins. These are high-molecular compounds consisting of two heavy
(weighing about 300 kDa) and several light chains. In heavy chains, the head and tail
domains are isolated. The two head domains bind to microtubules and are themselves
engines, and the tail domains bind to organelles and other intracellular formations to
be transported.
Study of ultrastructural pathology of microtubules and microfilaments
in various cell types (electronograms)pharmaceutical technologies
include microorganisms, cells and tissuesof plant and animal origin,
their structural components andmetabolites. Microorganisms are used
for the production of antibiotics,amino acids, enzymes, vitamins,
recombinant proteins, vaccines andprobiotics, the development of
diagnostic test systems (biochips,polymerase chain reaction, enzyme
immunoassay). Human stem cells are used in cell therapy and tissue
engineering, sexualThe cells are used in in vitro fertilization
technology.
References
1. http://www.niboch.nsc.ru/lib
2. http://webirbis.kgmu.kz
3. https://usma.ru/wp-content/uploads/=
4.http://stgmu.ru/userfiles/depts/histology_embryology/CITOLOGIYa_Pravka__6-2-17.pdf
You might also like
- Edward de Bono - 5 Day Course in ThinkingDocument158 pagesEdward de Bono - 5 Day Course in ThinkingNway Moe Saung100% (2)
- BSCS Final CN 2021 Spring 6th ADocument2 pagesBSCS Final CN 2021 Spring 6th AwaheedNo ratings yet
- Histology: Lecture NotesDocument97 pagesHistology: Lecture Notessky100% (4)
- From Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.From EverandFrom Tubulin to Thought: The Nexus of Cytoskeleton Microtubules and Brain Complexity.No ratings yet
- Assignment 1594125502 SmsDocument4 pagesAssignment 1594125502 Smsanulorance98No ratings yet
- 2cytology Cytoskel Receptor Transp (3) 1Document43 pages2cytology Cytoskel Receptor Transp (3) 1m.mansoor3377No ratings yet
- Microtubules: Organization: Single Microtubules Are Distributed Within The Cytoplasm. Also, MicrotubulesDocument6 pagesMicrotubules: Organization: Single Microtubules Are Distributed Within The Cytoplasm. Also, MicrotubulesArif NabeelNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument65 pagesCytoskeletonSapana SubediNo ratings yet
- CELLDocument31 pagesCELLtan shin meiNo ratings yet
- MicrotubuleDocument4 pagesMicrotubuleAbhishek DasNo ratings yet
- BCH 4107 - Plant BiochemistryDocument13 pagesBCH 4107 - Plant BiochemistryOLUWASEGUN K AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 CellDocument17 pagesChapter 2 CellSirWin AmidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Cell Structure and FunctionDocument42 pagesChapter 3: Cell Structure and FunctionHanifa ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Prepared By:-: Priyanka Yadav M.Sc. Life Sciences Ist SemDocument37 pagesPrepared By:-: Priyanka Yadav M.Sc. Life Sciences Ist SemleartaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - CytoskeletonDocument38 pagesLecture 6 - CytoskeletonNL DearestNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton Actividad 28-03 PDFDocument9 pagesCytoskeleton Actividad 28-03 PDFCatalina YáñezNo ratings yet
- Assignment II: Macaranas, Mar SDocument7 pagesAssignment II: Macaranas, Mar SMar MacaranasNo ratings yet
- MicrotubulesDocument39 pagesMicrotubulesAdnan QureshiNo ratings yet
- CytoskeletonDocument9 pagesCytoskeletonGordon YapNo ratings yet
- 1 7 CytoskeletonDocument31 pages1 7 CytoskeletonAditya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Cytoskeleton STDocument18 pagesLecture 6 - Cytoskeleton STminhph.23bi14469No ratings yet
- Week 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021Document4 pagesWeek 7. Reading Materials - Cell Structure and Function 2021yui kirigayayuukiNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles 2Document42 pagesCell Organelles 2James IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.animal Cell StructureDocument25 pagesTopic 2.animal Cell StructureJanine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- The Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellDocument9 pagesThe Cytoskeleton Is A Network of Filament and Tubules That Extends Throughout A CellHania GulNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 006 Chapter 3Document7 pagesZoology Notes: 006 Chapter 3humanupgrade100% (1)
- Name: Course: Registration Number: Assignment One: Describe The Structure Function and Adaptation of Animal CellsDocument5 pagesName: Course: Registration Number: Assignment One: Describe The Structure Function and Adaptation of Animal CellsDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton (1) HBHHHHGGH, HGDocument24 pagesCytoskeleton (1) HBHHHHGGH, HGrohanv4712No ratings yet
- Enumerating The Structure of Major Protein, Describe The Eukaryotic CytoskeletonDocument10 pagesEnumerating The Structure of Major Protein, Describe The Eukaryotic CytoskeletonTathagata ChakravarttyNo ratings yet
- Microtubules - The Cell - NCBI BookshelfDocument5 pagesMicrotubules - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelfanulorance98No ratings yet
- Biomed 05Document12 pagesBiomed 05api-3706483No ratings yet
- February 27, 2012 - Chapter 7: Inside The CellDocument4 pagesFebruary 27, 2012 - Chapter 7: Inside The CellVincent Troy SantosNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Prepared by Dr. Sana AslamDocument41 pagesCell Structure: Prepared by Dr. Sana Aslamsajjad Ali balouch100% (1)
- Cell Organelles - Biology Class 11 - NEETDocument18 pagesCell Organelles - Biology Class 11 - NEETsanjNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: How Are Eukaryotic Cells Organized Into Smaller Parts?Document6 pagesUnit 3: How Are Eukaryotic Cells Organized Into Smaller Parts?juan mondaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 CytoplasmmDocument46 pagesLecture 2 Cytoplasmmdiyarberwari15No ratings yet
- Cell CytoskeletonDocument7 pagesCell Cytoskeletonandersonmack047No ratings yet
- MicrotubuleDocument12 pagesMicrotubuleGordon YapNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Section 4-2, Parts of The Eukaryotic CellDocument20 pagesImmunology: Section 4-2, Parts of The Eukaryotic CellJoia De LeonNo ratings yet
- The CytoskeletonDocument3 pagesThe CytoskeletonMark Lorenz LorillaNo ratings yet
- Flagellar Restoration in C. ReinhardiDocument8 pagesFlagellar Restoration in C. Reinhardinasek22No ratings yet
- BIOL 202 Lab 2 Animal Cells and Tissues: Cell StructureDocument15 pagesBIOL 202 Lab 2 Animal Cells and Tissues: Cell StructureKate Anne Montallana RamosNo ratings yet
- Intro, Cell, TissueDocument29 pagesIntro, Cell, Tissueanisa930804No ratings yet
- Biochem AssignmentDocument2 pagesBiochem AssignmentAngel GoNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton DADocument35 pagesCytoskeleton DAAnonymous NVBCqKWHNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton: Jetro P. MagnayonDocument66 pagesCytoskeleton: Jetro P. MagnayonChristian Santiago100% (1)
- CytoskeletonDocument9 pagesCytoskeletonQuoc KhanhNo ratings yet
- Cyto SkeletonDocument3 pagesCyto SkeletonRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-The CellDocument43 pagesLecture 2-The CellMatende husseinNo ratings yet
- Microtubule Oranizing CenterDocument5 pagesMicrotubule Oranizing CenterSasha GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 14 The CytoskeletonDocument7 pages14 The Cytoskeletonsatriamanullang880No ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Plant CellDocument3 pagesParts and Function of Plant CellAmy A. OgnayonNo ratings yet
- Study of Ultrastructural Pathology of Mitochondria and Changes in Cell Bioenergetics (Electronograms)Document9 pagesStudy of Ultrastructural Pathology of Mitochondria and Changes in Cell Bioenergetics (Electronograms)shyngysNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 BioA 3201Document6 pagesAssign 2 BioA 3201Princess CabardoNo ratings yet
- Biology For The IB Diploma Chapter 1 SummaryDocument8 pagesBiology For The IB Diploma Chapter 1 SummaryDana PorterNo ratings yet
- Keerthana H PDocument22 pagesKeerthana H PVidya shree GNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton 2Document7 pagesCytoskeleton 2Basil Francis AlajidNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure by Sabir.h.nDocument15 pagesCell Structure by Sabir.h.nprinceaimy.bestNo ratings yet
- Cellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsDocument9 pagesCellular Ultrastructure: Eukaryotic CellsPiriyatharshini RamanathNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Cell and Molecular Biology 1Document38 pagesLecture 1 Cell and Molecular Biology 1Martin HangasNo ratings yet
- Cell OrgenellesDocument10 pagesCell OrgenellesShruti TiwariNo ratings yet
- Liver Disease Modelling: Zhexenbin Shynggys BB-1908 in The Subject: Differentiation of CellsDocument8 pagesLiver Disease Modelling: Zhexenbin Shynggys BB-1908 in The Subject: Differentiation of CellsshyngysNo ratings yet
- Organoids in Developmental Biology Research and ApplicationDocument8 pagesOrganoids in Developmental Biology Research and ApplicationshyngysNo ratings yet
- Study of Ultrastructural Pathology of Mitochondria and Changes in Cell Bioenergetics (Electronograms)Document9 pagesStudy of Ultrastructural Pathology of Mitochondria and Changes in Cell Bioenergetics (Electronograms)shyngysNo ratings yet
- Study of Cellular Processes (Proliferation, Polyploidy, Hypertrohy) During Reparative Regeneration of Various OrgansDocument8 pagesStudy of Cellular Processes (Proliferation, Polyploidy, Hypertrohy) During Reparative Regeneration of Various OrgansshyngysNo ratings yet
- FELCOM 12 Operator's Manual M2 1-22-03Document182 pagesFELCOM 12 Operator's Manual M2 1-22-03smartstepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PDFDocument37 pagesChapter 13 PDFZerlyndaBunga'alloNo ratings yet
- Multi Storey Steel Building 01Document19 pagesMulti Storey Steel Building 01Dan AlexandrescuNo ratings yet
- RSSI-Based Indoor Localization With The Internet of ThingsDocument13 pagesRSSI-Based Indoor Localization With The Internet of ThingsEmi SaharaNo ratings yet
- The Molecules of LifeDocument13 pagesThe Molecules of LifeZen Garcia100% (1)
- Dcm292 Dock For Iphone/ Ipod Sleek Micro SystemDocument17 pagesDcm292 Dock For Iphone/ Ipod Sleek Micro SystemRafael SuarezNo ratings yet
- Mtap 2015Document10 pagesMtap 2015irec100% (2)
- General Circulation: Thermal Circulation and Earth's RotationDocument3 pagesGeneral Circulation: Thermal Circulation and Earth's RotationGie AndalNo ratings yet
- Map Design PDFDocument35 pagesMap Design PDFShahin NescoNo ratings yet
- Elasticity WireDocument8 pagesElasticity WiremksayshiNo ratings yet
- Sast Vs Dast Vs Iast Infographic FinalDocument1 pageSast Vs Dast Vs Iast Infographic Finalpunzango73No ratings yet
- The CircleDocument9 pagesThe CircleavislgNo ratings yet
- Example:: Practice Personal Hygiene Protocols at All Times. 1Document11 pagesExample:: Practice Personal Hygiene Protocols at All Times. 1Christopher GunsatNo ratings yet
- Standard Base Course Soil ModulusDocument14 pagesStandard Base Course Soil ModulusphatmatNo ratings yet
- College Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3rd Edition Knight Test BankDocument39 pagesCollege Physics A Strategic Approach Technology Update 3rd Edition Knight Test Bankgretchenmilesdxeh3100% (13)
- Various Cases and Studies of Direct Stroke Lightning Protection On Different Substation IJERTV5IS040692 PDFDocument4 pagesVarious Cases and Studies of Direct Stroke Lightning Protection On Different Substation IJERTV5IS040692 PDFHasnain AwanNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Fixtures & Appliances: Building Services 1Document12 pagesPlumbing Fixtures & Appliances: Building Services 1moonnaNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Symbolic Math ToolboxDocument300 pagesMATLAB Symbolic Math ToolboxelfrichNo ratings yet
- PCR 27 ManualDocument193 pagesPCR 27 Manualsteve100% (1)
- 1 Basic Facts About PerliteDocument2 pages1 Basic Facts About PerliteAllen WellsNo ratings yet
- Back TitrationDocument20 pagesBack TitrationChristopher SeerajNo ratings yet
- PT 111 - N Chapter 6: BandagingDocument61 pagesPT 111 - N Chapter 6: BandagingJan Crizza Dale R. FrancoNo ratings yet
- Sysweld Welding ReportDocument23 pagesSysweld Welding ReportAsiahKuzaimanNo ratings yet
- A Study On Shading of Buildings As A Preventive Measure For Passive Cooling and Energy Conservation in BuildingsDocument4 pagesA Study On Shading of Buildings As A Preventive Measure For Passive Cooling and Energy Conservation in BuildingsMohammad Arif KamalNo ratings yet
- x99 75 Manual PDFDocument108 pagesx99 75 Manual PDFYonni AroussiNo ratings yet
- Arjuna-Carboxylic Acids and AminesDocument66 pagesArjuna-Carboxylic Acids and AminesNirjhar KhetoNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of Facemask and Respirator Filtration Test MethodsDocument13 pagesA Comparison of Facemask and Respirator Filtration Test MethodsDJSeidelNo ratings yet
- SCH 5Document1 pageSCH 5csilva_356601No ratings yet