Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 viewsE-Commerce: Business. Technology. Society
E-Commerce: Business. Technology. Society
Uploaded by
Rahul MuralyCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Marketing Channel Strategy 8th Edition Palmatier Test BankDocument26 pagesMarketing Channel Strategy 8th Edition Palmatier Test BankStacyCarrgpjkb100% (61)
- Ternion Pitch Deck A RoundDocument18 pagesTernion Pitch Deck A RoundRish JeyamohanNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyDocument47 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietykkkonicNo ratings yet
- Slide 1-1Document49 pagesSlide 1-1Oladapo GbemisolaNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce 2014: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio TraverDocument27 pagesE-Commerce 2014: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Travervivek gupta100% (1)
- Laudon-Traver - Ec10 - PPT - ch01 - IndDocument30 pagesLaudon-Traver - Ec10 - PPT - ch01 - IndTri Azi GepNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyDocument29 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyrinishamrenishNo ratings yet
- E Commerce Ch01Document30 pagesE Commerce Ch01Joseph KandalaftNo ratings yet
- The Revolution Is Just BeginningDocument27 pagesThe Revolution Is Just Beginningabeni mesfinNo ratings yet
- Laudon Ec9e PP 1 GEDocument24 pagesLaudon Ec9e PP 1 GEVasanthi MuniasamyNo ratings yet
- Lesson One - CH01 RevisedDocument31 pagesLesson One - CH01 RevisedAndres RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Overview of Electronic Commerce Technology of E-BusinessDocument36 pagesOverview of Electronic Commerce Technology of E-BusinessManavAgarwalNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyDocument46 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyLuluk SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Revolution Is Just BeginningDocument24 pagesChapter 1 The Revolution Is Just BeginningOthman MuhamedNo ratings yet
- Turban Ec2012 PP 01Document36 pagesTurban Ec2012 PP 01RawdaNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio TraverDocument30 pagesE-Commerce: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio TraversonamrishikapoorNo ratings yet
- Laudon-Traver Ec10 PPT ch01Document31 pagesLaudon-Traver Ec10 PPT ch01Widya PranantaNo ratings yet
- Laudon-Traver Ec10 PPT Ch01Document29 pagesLaudon-Traver Ec10 PPT Ch01Khurram Adeel ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Introduction of E - CommerceDocument22 pagesIntroduction of E - CommerceAhmed Jan DahriNo ratings yet
- Turban Ec2012 PP 01Document36 pagesTurban Ec2012 PP 01FatinAzizNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyDocument33 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyHassan AliNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce - Chapter 1Document39 pagesE-Commerce - Chapter 1Thanh Lê Ngọc LanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Overview of Electronic CommerceDocument36 pagesChapter 01 Overview of Electronic CommerceDoan Thanh Chung (K17 HL)No ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyDocument26 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyTejasNo ratings yet
- The Revolution Is Just Beginning: Slide 1-1Document32 pagesThe Revolution Is Just Beginning: Slide 1-1Xuân LộcNo ratings yet
- IS-346 Unit-1 (ch01)Document28 pagesIS-346 Unit-1 (ch01)Abrar Al-OtaibiNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce - Chapter 1Document35 pagesE-Commerce - Chapter 1Như Phan Thị QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To e CommerceDocument47 pagesIntroduction To e Commerceindrawan trisaputraNo ratings yet
- The Revolution Is Just Beginning: Slide 1-1Document50 pagesThe Revolution Is Just Beginning: Slide 1-1Rachit Kumar SinghalNo ratings yet
- Overview of Electronic CommerceDocument16 pagesOverview of Electronic CommercehulahopNo ratings yet
- EC Final CourseDocument104 pagesEC Final CourseTahir NadeemNo ratings yet
- Overview of Electronic CommerceDocument36 pagesOverview of Electronic CommerceSANDUN KAVINDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document29 pagesChapter 01Hamza Farooq KoraiNo ratings yet
- Slides 01 - E ComDocument23 pagesSlides 01 - E Comhamza khanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Electronic CommerceDocument40 pagesOverview of Electronic CommerceBlack UnicornNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document35 pagesChapter 1abeeraNo ratings yet
- Turban - Ec2012Document36 pagesTurban - Ec2012Boro HammanNo ratings yet
- Laudon-Traver Ec11 PPT Ch01 ReviewedDocument10 pagesLaudon-Traver Ec11 PPT Ch01 ReviewedDinesh NathanNo ratings yet
- Ecom 1Document12 pagesEcom 1Isha PandeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To E-CommerceDocument8 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To E-CommerceJillian Grace DoteNo ratings yet
- Module 1 and 2 E-CommerceDocument15 pagesModule 1 and 2 E-CommerceGERBGARCIANo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Learning Objectives: The Revolution Is Just BeginningDocument9 pagesLearning Objectives Learning Objectives: The Revolution Is Just Beginningcssunny88No ratings yet
- Chapter1 PDFDocument36 pagesChapter1 PDFRicha JhaNo ratings yet
- 01 E Commerce OverviewDocument33 pages01 E Commerce OverviewAnonymous pssmjuNo ratings yet
- Turban Ec2012 PP 01 (Compatibility Mode)Document123 pagesTurban Ec2012 PP 01 (Compatibility Mode)Son HangNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce 2014: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio TraverDocument10 pagesE-Commerce 2014: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traverabdulbaset alselwiNo ratings yet
- The Revolution Is Just BeginningDocument31 pagesThe Revolution Is Just BeginningMacaraeg NicoleNo ratings yet
- Ch01 Laudon-Traver - Ec10 - PPT by JGADocument39 pagesCh01 Laudon-Traver - Ec10 - PPT by JGAJihad AounNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Chapter 1Document32 pagesE-Commerce Chapter 1Lam GiangNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Chapter 1Document32 pagesE-Commerce Chapter 1Ngọc Hà BảoNo ratings yet
- EC Chapter 1Document31 pagesEC Chapter 1RahafNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1nilanjan_kar_2No ratings yet
- CH 1. Intro. To EBuss & ECommDocument48 pagesCH 1. Intro. To EBuss & ECommAdrian DanielNo ratings yet
- E-Cormmerce RevolutionDocument25 pagesE-Cormmerce RevolutionRicky NavidonNo ratings yet
- Impact of E-Commerce On Supply Chain ManagementFrom EverandImpact of E-Commerce On Supply Chain ManagementRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Keeping the Digital Simple: A Handbook for Telco Digital TransformationFrom EverandKeeping the Digital Simple: A Handbook for Telco Digital TransformationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Evaluating The Business To Business Ecommerce Systems Of Dell & CiscoFrom EverandEvaluating The Business To Business Ecommerce Systems Of Dell & CiscoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Lync 2013 Unified Communications: From Telephony to Real-Time Communication in the Digital AgeFrom EverandMicrosoft Lync 2013 Unified Communications: From Telephony to Real-Time Communication in the Digital AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Group Paper Report Marketing Management: Case Study I: Reinventing EricssonDocument5 pagesGroup Paper Report Marketing Management: Case Study I: Reinventing Ericssonadedj99No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 External AuditDocument46 pagesChapter 7 External AuditIman NessaNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Management Kozhikode Post Graduate Programme in ManagementDocument5 pagesIndian Institute of Management Kozhikode Post Graduate Programme in ManagementAnchal BhalotiaNo ratings yet
- RWJ FCF11e Chap 02Document25 pagesRWJ FCF11e Chap 02kaylakshmiNo ratings yet
- Business History-ParleDocument18 pagesBusiness History-ParleRiya Dutta100% (1)
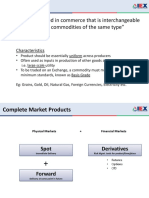
- Difference Between Money Market and Capital MarketDocument4 pagesDifference Between Money Market and Capital MarketSanjoy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Its Origins and Strategic ApplicationsDocument34 pagesConsumer Behavior Its Origins and Strategic ApplicationsbalabloomsNo ratings yet
- School of Business and Economics Department of Accounting and FinanceDocument8 pagesSchool of Business and Economics Department of Accounting and FinancetinntinnNo ratings yet
- KPMM Risiko Pasar Pbi-5!12!03 - EngDocument19 pagesKPMM Risiko Pasar Pbi-5!12!03 - EngvirzatcNo ratings yet
- SuperbizDocument11 pagesSuperbizeng20072007No ratings yet
- The Structure of StrategyDocument6 pagesThe Structure of StrategyGuillermo UribeNo ratings yet
- ENGG1320 1B CE Project Group 8Document26 pagesENGG1320 1B CE Project Group 8Kyle WongNo ratings yet
- Malerba 2002 - Sectoral Systems of InnovationDocument18 pagesMalerba 2002 - Sectoral Systems of Innovationapi-27028656No ratings yet
- Paper - 3: Cost Accounting and Financial Management: 2015 (In Lakhs) 2016 (In Lakhs)Document25 pagesPaper - 3: Cost Accounting and Financial Management: 2015 (In Lakhs) 2016 (In Lakhs)Apeksha ChilwalNo ratings yet
- NTPC PPT UpdateDocument52 pagesNTPC PPT UpdateSanjay SatyajitNo ratings yet
- FMPMC 411 Module 1Document11 pagesFMPMC 411 Module 1Aliah de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Case Study by PMDocument3 pagesCase Study by PMRI Shawon100% (1)
- A Study of Consumer Satisfaction and Perception Towards Cosmetic Products of AmwayDocument4 pagesA Study of Consumer Satisfaction and Perception Towards Cosmetic Products of AmwayChhaya ThakorNo ratings yet
- Hubspot PresentationDocument14 pagesHubspot PresentationNael Nasir Chiragh100% (2)
- Nature of Development EconomicsDocument1 pageNature of Development EconomicsCindy Ortiz GastonNo ratings yet
- Questions 2016 FRM1 PracticeExamDocument37 pagesQuestions 2016 FRM1 PracticeExamPaul Antonio Rios MurrugarraNo ratings yet
- Inventory Manager CertificationDocument6 pagesInventory Manager CertificationVskills CertificationNo ratings yet
- Direct Marketing To SM Mall in Customer ServiceDocument3 pagesDirect Marketing To SM Mall in Customer Serviceelaine bertumenNo ratings yet
- IBT 1-2 WeeksDocument7 pagesIBT 1-2 WeeksNicolle Curammeng100% (1)
- Mkt501 - 3 - Midterm Paper Solved by Silentlips.... NewDocument6 pagesMkt501 - 3 - Midterm Paper Solved by Silentlips.... Newzahidwahla1No ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange QuotesDocument4 pagesForeign Exchange QuotesVishant ChopraNo ratings yet
- Ias 2 InventoriesDocument5 pagesIas 2 InventoriesGohar MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Retail Management: A Strategic ApproachDocument47 pagesRetail Management: A Strategic Approachkalla_aslNo ratings yet
E-Commerce: Business. Technology. Society
E-Commerce: Business. Technology. Society
Uploaded by
Rahul Muraly0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views15 pagesOriginal Title
e Commerce
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views15 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. Society
E-Commerce: Business. Technology. Society
Uploaded by
Rahul MuralyCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 15
E-commerce
business. technology. society.
Second Edition
Kenneth C. Laudon
Carol Guercio Traver
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-1
E-commerce Defined
E-commerce involves digitally enabled
commercial transactions between and among
organizations and individuals
Digitally enabled transactions include all
transactions mediated by digital technology
Commercial transactions involve the
exchange of value across organizational or
individual boundaries in return for products or
services
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-2
E-commerce vs. E-business
Debate among consultants and academics
about meanings and limitations of terms e-
commerce and e-business
We use the term e-business to refer primarily
to the digital enablement of transactions and
processes within a firm, involving information
systems under the control of the firm
E-business does not include commercial
transactions involving an exchange of value
across organizational boundaries
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-3
The Difference between
E-commerce and E-business
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-4
Seven Unique Features of E-commerce
Technology and Their Significance
Is ubiquitous (available everywhere, all the time)
Offers global reach (across cultural/national boundaries)
Operates according to universal standards (lowers market
entry for merchants and search costs for consumers, price
discovery becomes easier)
Less information richness (less powerful selling environment)
Is interactive (can simulate face-to-face experience, but on
global scale)
Increases information density (amount and quality of
information available to all market participants)
Permits personalization/customization
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-5
Seven Unique Features of E-commerce Technology
Table 1.2,
Page 12
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-6
Types of E-commerce
Classified by nature of market relationship
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
Business-to-Business (B2B)
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
Classified by type of technology used
Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
Mobile commerce (M-commerce)
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-7
Major Types of E-commerce
Table 1.3, Page 17
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-8
Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
E-commerce
Involves online businesses attempting to
reach individual consumers
Many types of business models within this
category including online retailers, content
providers, portals, transaction brokers,
service providers, market creators and
community providers
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-9
Business-to-Business (B2B)
E-commerce
Involves businesses focusing on selling to
other businesses
Business models within B2B:
e-distributors, B2B service providers,
matchmakers, etc
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-10
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
E-commerce
Provides a way for consumers to sell to
each other, with the help of an online
market maker
eBay most well-known example
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-11
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) E-commerce
Uses peer-to-peer technology, which enables
Internet users to share files and computer
resources without having to go through a
central Web server
Napster most well-known example until put
out of business for copyright infringement
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-12
M-commerce
Use of wireless digital devices such as cell
phones and handheld devices to enable
transactions on the Web
Most widely used in Japan and Europe
(especially Finland)
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-13
PORTALS
Offers powerful web search tools as well as an
integrated package of content and services all in
one place.
Eg. Yahoo.com, AOL.com, MSN.com
Do not sell anything directly
Generate revenue
AOL and MSN : ISPs that provide access to
internet and web
Horizontal and vertical portals
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 1-14
e-DISTRIBUTOR
Company that supplies products and services
directly to individual businesses
Owned by one company seeking to serve
many customers
Examples:
Grainger.com
GE Electric Aircraft Engines (geae.com)
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide 2-15
You might also like
- Marketing Channel Strategy 8th Edition Palmatier Test BankDocument26 pagesMarketing Channel Strategy 8th Edition Palmatier Test BankStacyCarrgpjkb100% (61)
- Ternion Pitch Deck A RoundDocument18 pagesTernion Pitch Deck A RoundRish JeyamohanNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyDocument47 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietykkkonicNo ratings yet
- Slide 1-1Document49 pagesSlide 1-1Oladapo GbemisolaNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce 2014: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio TraverDocument27 pagesE-Commerce 2014: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Travervivek gupta100% (1)
- Laudon-Traver - Ec10 - PPT - ch01 - IndDocument30 pagesLaudon-Traver - Ec10 - PPT - ch01 - IndTri Azi GepNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyDocument29 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyrinishamrenishNo ratings yet
- E Commerce Ch01Document30 pagesE Commerce Ch01Joseph KandalaftNo ratings yet
- The Revolution Is Just BeginningDocument27 pagesThe Revolution Is Just Beginningabeni mesfinNo ratings yet
- Laudon Ec9e PP 1 GEDocument24 pagesLaudon Ec9e PP 1 GEVasanthi MuniasamyNo ratings yet
- Lesson One - CH01 RevisedDocument31 pagesLesson One - CH01 RevisedAndres RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Overview of Electronic Commerce Technology of E-BusinessDocument36 pagesOverview of Electronic Commerce Technology of E-BusinessManavAgarwalNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyDocument46 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyLuluk SuryaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Revolution Is Just BeginningDocument24 pagesChapter 1 The Revolution Is Just BeginningOthman MuhamedNo ratings yet
- Turban Ec2012 PP 01Document36 pagesTurban Ec2012 PP 01RawdaNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio TraverDocument30 pagesE-Commerce: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio TraversonamrishikapoorNo ratings yet
- Laudon-Traver Ec10 PPT ch01Document31 pagesLaudon-Traver Ec10 PPT ch01Widya PranantaNo ratings yet
- Laudon-Traver Ec10 PPT Ch01Document29 pagesLaudon-Traver Ec10 PPT Ch01Khurram Adeel ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Introduction of E - CommerceDocument22 pagesIntroduction of E - CommerceAhmed Jan DahriNo ratings yet
- Turban Ec2012 PP 01Document36 pagesTurban Ec2012 PP 01FatinAzizNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyDocument33 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyHassan AliNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce - Chapter 1Document39 pagesE-Commerce - Chapter 1Thanh Lê Ngọc LanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 Overview of Electronic CommerceDocument36 pagesChapter 01 Overview of Electronic CommerceDoan Thanh Chung (K17 HL)No ratings yet
- E-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyDocument26 pagesE-Commerce: Business. Technology. SocietyTejasNo ratings yet
- The Revolution Is Just Beginning: Slide 1-1Document32 pagesThe Revolution Is Just Beginning: Slide 1-1Xuân LộcNo ratings yet
- IS-346 Unit-1 (ch01)Document28 pagesIS-346 Unit-1 (ch01)Abrar Al-OtaibiNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce - Chapter 1Document35 pagesE-Commerce - Chapter 1Như Phan Thị QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Introduction To e CommerceDocument47 pagesIntroduction To e Commerceindrawan trisaputraNo ratings yet
- The Revolution Is Just Beginning: Slide 1-1Document50 pagesThe Revolution Is Just Beginning: Slide 1-1Rachit Kumar SinghalNo ratings yet
- Overview of Electronic CommerceDocument16 pagesOverview of Electronic CommercehulahopNo ratings yet
- EC Final CourseDocument104 pagesEC Final CourseTahir NadeemNo ratings yet
- Overview of Electronic CommerceDocument36 pagesOverview of Electronic CommerceSANDUN KAVINDANo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document29 pagesChapter 01Hamza Farooq KoraiNo ratings yet
- Slides 01 - E ComDocument23 pagesSlides 01 - E Comhamza khanNo ratings yet
- Overview of Electronic CommerceDocument40 pagesOverview of Electronic CommerceBlack UnicornNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document35 pagesChapter 1abeeraNo ratings yet
- Turban - Ec2012Document36 pagesTurban - Ec2012Boro HammanNo ratings yet
- Laudon-Traver Ec11 PPT Ch01 ReviewedDocument10 pagesLaudon-Traver Ec11 PPT Ch01 ReviewedDinesh NathanNo ratings yet
- Ecom 1Document12 pagesEcom 1Isha PandeNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To E-CommerceDocument8 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To E-CommerceJillian Grace DoteNo ratings yet
- Module 1 and 2 E-CommerceDocument15 pagesModule 1 and 2 E-CommerceGERBGARCIANo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives Learning Objectives: The Revolution Is Just BeginningDocument9 pagesLearning Objectives Learning Objectives: The Revolution Is Just Beginningcssunny88No ratings yet
- Chapter1 PDFDocument36 pagesChapter1 PDFRicha JhaNo ratings yet
- 01 E Commerce OverviewDocument33 pages01 E Commerce OverviewAnonymous pssmjuNo ratings yet
- Turban Ec2012 PP 01 (Compatibility Mode)Document123 pagesTurban Ec2012 PP 01 (Compatibility Mode)Son HangNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce 2014: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio TraverDocument10 pagesE-Commerce 2014: Kenneth C. Laudon Carol Guercio Traverabdulbaset alselwiNo ratings yet
- The Revolution Is Just BeginningDocument31 pagesThe Revolution Is Just BeginningMacaraeg NicoleNo ratings yet
- Ch01 Laudon-Traver - Ec10 - PPT by JGADocument39 pagesCh01 Laudon-Traver - Ec10 - PPT by JGAJihad AounNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Chapter 1Document32 pagesE-Commerce Chapter 1Lam GiangNo ratings yet
- E-Commerce Chapter 1Document32 pagesE-Commerce Chapter 1Ngọc Hà BảoNo ratings yet
- EC Chapter 1Document31 pagesEC Chapter 1RahafNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document28 pagesLecture 1nilanjan_kar_2No ratings yet
- CH 1. Intro. To EBuss & ECommDocument48 pagesCH 1. Intro. To EBuss & ECommAdrian DanielNo ratings yet
- E-Cormmerce RevolutionDocument25 pagesE-Cormmerce RevolutionRicky NavidonNo ratings yet
- Impact of E-Commerce On Supply Chain ManagementFrom EverandImpact of E-Commerce On Supply Chain ManagementRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Keeping the Digital Simple: A Handbook for Telco Digital TransformationFrom EverandKeeping the Digital Simple: A Handbook for Telco Digital TransformationRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Evaluating The Business To Business Ecommerce Systems Of Dell & CiscoFrom EverandEvaluating The Business To Business Ecommerce Systems Of Dell & CiscoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Lync 2013 Unified Communications: From Telephony to Real-Time Communication in the Digital AgeFrom EverandMicrosoft Lync 2013 Unified Communications: From Telephony to Real-Time Communication in the Digital AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Group Paper Report Marketing Management: Case Study I: Reinventing EricssonDocument5 pagesGroup Paper Report Marketing Management: Case Study I: Reinventing Ericssonadedj99No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 External AuditDocument46 pagesChapter 7 External AuditIman NessaNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Management Kozhikode Post Graduate Programme in ManagementDocument5 pagesIndian Institute of Management Kozhikode Post Graduate Programme in ManagementAnchal BhalotiaNo ratings yet
- RWJ FCF11e Chap 02Document25 pagesRWJ FCF11e Chap 02kaylakshmiNo ratings yet
- Business History-ParleDocument18 pagesBusiness History-ParleRiya Dutta100% (1)
- Difference Between Money Market and Capital MarketDocument4 pagesDifference Between Money Market and Capital MarketSanjoy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Its Origins and Strategic ApplicationsDocument34 pagesConsumer Behavior Its Origins and Strategic ApplicationsbalabloomsNo ratings yet
- School of Business and Economics Department of Accounting and FinanceDocument8 pagesSchool of Business and Economics Department of Accounting and FinancetinntinnNo ratings yet
- KPMM Risiko Pasar Pbi-5!12!03 - EngDocument19 pagesKPMM Risiko Pasar Pbi-5!12!03 - EngvirzatcNo ratings yet
- SuperbizDocument11 pagesSuperbizeng20072007No ratings yet
- The Structure of StrategyDocument6 pagesThe Structure of StrategyGuillermo UribeNo ratings yet
- ENGG1320 1B CE Project Group 8Document26 pagesENGG1320 1B CE Project Group 8Kyle WongNo ratings yet
- Malerba 2002 - Sectoral Systems of InnovationDocument18 pagesMalerba 2002 - Sectoral Systems of Innovationapi-27028656No ratings yet
- Paper - 3: Cost Accounting and Financial Management: 2015 (In Lakhs) 2016 (In Lakhs)Document25 pagesPaper - 3: Cost Accounting and Financial Management: 2015 (In Lakhs) 2016 (In Lakhs)Apeksha ChilwalNo ratings yet
- NTPC PPT UpdateDocument52 pagesNTPC PPT UpdateSanjay SatyajitNo ratings yet
- FMPMC 411 Module 1Document11 pagesFMPMC 411 Module 1Aliah de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Case Study by PMDocument3 pagesCase Study by PMRI Shawon100% (1)
- A Study of Consumer Satisfaction and Perception Towards Cosmetic Products of AmwayDocument4 pagesA Study of Consumer Satisfaction and Perception Towards Cosmetic Products of AmwayChhaya ThakorNo ratings yet
- Hubspot PresentationDocument14 pagesHubspot PresentationNael Nasir Chiragh100% (2)
- Nature of Development EconomicsDocument1 pageNature of Development EconomicsCindy Ortiz GastonNo ratings yet
- Questions 2016 FRM1 PracticeExamDocument37 pagesQuestions 2016 FRM1 PracticeExamPaul Antonio Rios MurrugarraNo ratings yet
- Inventory Manager CertificationDocument6 pagesInventory Manager CertificationVskills CertificationNo ratings yet
- Direct Marketing To SM Mall in Customer ServiceDocument3 pagesDirect Marketing To SM Mall in Customer Serviceelaine bertumenNo ratings yet
- IBT 1-2 WeeksDocument7 pagesIBT 1-2 WeeksNicolle Curammeng100% (1)
- Mkt501 - 3 - Midterm Paper Solved by Silentlips.... NewDocument6 pagesMkt501 - 3 - Midterm Paper Solved by Silentlips.... Newzahidwahla1No ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange QuotesDocument4 pagesForeign Exchange QuotesVishant ChopraNo ratings yet
- Ias 2 InventoriesDocument5 pagesIas 2 InventoriesGohar MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Retail Management: A Strategic ApproachDocument47 pagesRetail Management: A Strategic Approachkalla_aslNo ratings yet