Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
What Is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Uploaded by
MITUL PATEL0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views27 pagesSheet metal fabrication involves shaping metal sheets through processes like bending, cutting, and forming. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and other metals between 0.006-0.25 inches thick. Forming processes like bending and deep drawing deform the metal into shapes without removing material, while cutting processes like shearing, punching, and lasers remove material. Sheet metal is used widely in industries like construction, automotive, and aerospace for parts that require precise shapes.
Original Description:
d
Original Title
114921446-Sheet-Metal-Fabrication
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSheet metal fabrication involves shaping metal sheets through processes like bending, cutting, and forming. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and other metals between 0.006-0.25 inches thick. Forming processes like bending and deep drawing deform the metal into shapes without removing material, while cutting processes like shearing, punching, and lasers remove material. Sheet metal is used widely in industries like construction, automotive, and aerospace for parts that require precise shapes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views27 pagesWhat Is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
What Is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Uploaded by
MITUL PATELSheet metal fabrication involves shaping metal sheets through processes like bending, cutting, and forming. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and other metals between 0.006-0.25 inches thick. Forming processes like bending and deep drawing deform the metal into shapes without removing material, while cutting processes like shearing, punching, and lasers remove material. Sheet metal is used widely in industries like construction, automotive, and aerospace for parts that require precise shapes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 27
what is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Sheet metal fabrication is a classification of
manufacturing processes that shape a piece of sheet
metal into the desired part through material removal
and/or material deformation.
Sheet metal, which acts as the workpiece in these
processes, is one of the most common forms of raw
material stock.
The material thickness that classifies a workpiece as sheet
metal is not clearly defined. However, sheet metal is
generally considered to be a piece of stock between 0.006
and 0.25 inches thick.
A piece of metal much thinner is considered to be "foil"
and any thicker is referred to as a "plate".
The thickness of a piece of sheet metal is often referred to
as its gauge,
Gauge
The sheet metal gauge (sometimes spelled gage)
indicates the standard thickness of sheet metal for a
specific material.
For most materials, as the gauge number increases,
the material thickness decreases.
WHAT IS FOIL?
Foil (metal) a quite thin sheet of metal, usually
manufactured with a rolling mill machine
WHAT IS PLATE :
Plate, metal sheets thicker than 6 mm or 1⁄4 in
Sheet metal stock is available in a wide variety of materials,
which include the following:
Aluminum
Brass
Bronze
Copper
Magnesium
Nickel
Stainless steel
Steel
Tin
Titanium
Zinc
Sheet metal can be cut, bent, and stretched into a nearly any
shape. Material removal processes can create holes and
cutouts in any 2D geometric shape.
Deformation processes can bend the sheet numerous times
to different angles or stretch the sheet to create complex
contours.
These parts are found in a variety of industries, such as
aircraft, automotive, construction, consumer products,
HVAC, and furniture.
Sheet metal fabrication processes
Sheet metal fabrication processes can mostly be placed into two
categories –
Forming
cutting.
Forming processes are those in which the applied force causes
the material to plastically deform, but not to fail. Such processes
are able to bend or stretch the sheet into the desired shape
Cutting processes are those in which the applied force causes the
material to fail and separate, allowing the material to be cut or
removed
Forming
Bending
Roll forming
Spinning
Deep Drawing
Stretch forming
Cutting with shear
Shearing
Blanking
Punching
Cutting without shear
Laser beam cutting
Plasma cutting
Water jet cutting
Sheet Metal Forming
Sheet metal forming processes are those in which force is applied to a piece
of sheet metal to modify its geometry rather than remove any material
The applied force stresses the metal beyond its yield strength, causing the
material to plastically deform, but not to fail. By doing so, the sheet can be
bent or stretced into a variety of complex shapes.
Sheet metal forming processes include the following:
Bending
Roll forming
Spinning
Deep Drawing
Stretch forming
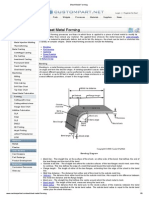
Bending
Bending is a metal forming process in which a force is applied
to a piece of sheet metal, causing it to bend at an angle and
form the desired shape.
A bending operation causes deformation along one axis, but a
sequence of several different operations can be performed to
create a complex part.
While using a press brake and standard die sets, there are
still a variety of techniques that can be used to bend the
sheet. The most common method is known as V-bending,
in which the punch and die are "V" shaped.
The punch pushes the sheet into the "V" shaped groove in
the V-die, causing it to bend.
If the punch does not force the sheet to the bottom of the
die cavity, leaving space or air underneath, it is called "air
bending".
If the punch forces the sheet to the bottom of the die
cavity, it is called "bottoming"
The act of bending results in both tension and compression in the
sheet metal. The outside portion of the sheet will undergo tension
and stretch to a greater length, while the inside portion experiences
compression and shortens. The neutral axis is the boundary line
inside the sheet metal, along which no tension or compression
forces are present. As a result, the length of this axis remains
constant. The changes in length to the outside and inside surfaces
can be related to the original flat length by two parameters, the
bend allowance and bend deduction, which are defined below
Bending is typically performed on a machine called a press brake,
which can be manually or automatically operated. For this reason,
the bending process is sometimes referred to as press brake
forming.
A press brake contains an upper tool called the punch and a lower
tool called the die, between which the sheet metal is located. The
sheet is carefully positioned over the die and held in place by the
back gauge while the punch lowers and forces the sheet to bend.
In an automatic machine, the punch is forced into the sheet under
the power of a hydraulic ram. The bend angle achieved is
determined by the depth to which the punch forces the sheet into
the die. This depth is precisely controlled to achieve the desired
bend.
In addition to V-bending, another common bending method is wipe
bending, sometimes called edge bending. Wipe bending requires the sheet
to be held against the wipe die by a pressure pad. The punch then presses
against the edge of the sheet that extends beyond the die and pad. The
sheet will bend against the radius of the edge of the wipe die.
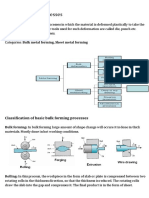
ROLL FORMING
Roll forming, sometimes, is a metal forming process in which
sheet metal is progressively shaped through a series of
bending operations
The process is performed on a roll forming line in which the
sheet metal stock is fed through a series of roll stations
. Each station has a roller, referred to as a roller die, positioned
on both sides of the sheet.
DEEP DRAWING
Deep drawing is a metal forming process in which
sheet metal is stretched into the desired part shape.
APPLICATIONS
Aluminium sheets are used extensively in an aircraft
industry. The wings of an airplane are made from
reinforced aluminium, and the frame is also made
from aluminium.
It can easily be welded and has good corrosion
resistance
An aluminium sheet finds application in a household
also
Sheet metal has applications in car bodies,
AGRO EQUIPMENTS
You might also like
- Dimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyFrom EverandDimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal FabricationDocument28 pagesSheet Metal Fabricationsamurai7_770% (2)
- Sheet Metal Forming PDFDocument9 pagesSheet Metal Forming PDFRakhesh Manchi100% (1)
- Sheet-Metal-Op N Bmberations-131023053838-Phpapp02Document40 pagesSheet-Metal-Op N Bmberations-131023053838-Phpapp02sbs271187No ratings yet
- Automatic Bending Machine Report-1Document70 pagesAutomatic Bending Machine Report-1ganeshNo ratings yet
- Sheetmetal IntroDocument48 pagesSheetmetal IntroBharat M GajeraNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Operations 131023053838 Phpapp02Document40 pagesSheet Metal Operations 131023053838 Phpapp02VEERAMANINo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal FormingDocument16 pagesSheet Metal FormingSabur Mythin Abdul AzeesNo ratings yet
- Cold FormingDocument7 pagesCold FormingglaxionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Sheet Metal Fabrication) With VideoDocument71 pagesChapter 4 (Sheet Metal Fabrication) With VideoSamrat BhattaraiNo ratings yet
- Module 5 PDFDocument93 pagesModule 5 PDFVishal Shanmuga SundramNo ratings yet
- Universal Grinding - Machine - Report-FinalDocument48 pagesUniversal Grinding - Machine - Report-FinalGopuNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Sheet Metal FormingDocument69 pagesWeek 8 Sheet Metal FormingashkansoheylNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal BasicsDocument69 pagesSheet Metal Basicskiran_wakchaure50% (2)
- Unit IV 180208091907Document153 pagesUnit IV 180208091907tamilselvan nNo ratings yet
- Die Basics 101: Intro To Stamping: Stamping (Metalworking) Stamping PressingDocument30 pagesDie Basics 101: Intro To Stamping: Stamping (Metalworking) Stamping PressingAmitNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming Processes - FullDocument5 pagesMetal Forming Processes - FullArjun NbNo ratings yet
- FMP 221 Lecture 9 Cold WorkingDocument34 pagesFMP 221 Lecture 9 Cold WorkingSarojKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Forming ProcessDocument5 pagesSheet Metal Forming ProcessAbdulbar kelilNo ratings yet
- Tool DesignDocument48 pagesTool DesignPAVIN ENGGNo ratings yet
- Types of Sheet Metal Press OperationsDocument4 pagesTypes of Sheet Metal Press OperationsRajat AhujaNo ratings yet
- MT 2nd AssignmentDocument72 pagesMT 2nd AssignmentDixitNo ratings yet
- Press & Press WorkDocument7 pagesPress & Press Workapi-19822628No ratings yet
- Metal Forming TechniquesDocument49 pagesMetal Forming TechniquesSachinBhagiNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal FormingDocument9 pagesSheet Metal FormingKhin Aung ShweNo ratings yet
- Plastic DeformationDocument3 pagesPlastic DeformationCleng LaynesNo ratings yet
- StampingDocument2 pagesStampingKapiel KatariaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal WorkingDocument26 pagesSheet Metal Workingvelavansu0% (1)
- BendingDocument8 pagesBendingShal DxtNo ratings yet
- 15 Sheet Metal Bending and Forming ProcessesDocument2 pages15 Sheet Metal Bending and Forming ProcessesHamada HamadaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal OperationsDocument27 pagesSheet Metal OperationsbmvinayNo ratings yet
- Mt1 Unit 4 NotesDocument11 pagesMt1 Unit 4 Notesvelavansu100% (1)
- Die BasicsDocument2 pagesDie BasicsCosmin TanaseNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal OperationDocument46 pagesSheet Metal Operationmada sadaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Forming and High Energy Rate FormingDocument68 pagesSheet Metal Forming and High Energy Rate FormingAbhishek TanguturiNo ratings yet
- Production-Technology-11 04 2020Document9 pagesProduction-Technology-11 04 2020Selvaraj SimiyonNo ratings yet
- Unit IV OrigionalDocument25 pagesUnit IV OrigionalPrakash SinghNo ratings yet
- Classification of Forming & Shaping Processes & EquipmentDocument51 pagesClassification of Forming & Shaping Processes & EquipmentFarman AliNo ratings yet
- Design of Sheet Metal Working ToolsDocument38 pagesDesign of Sheet Metal Working ToolsAsef ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Rolling (Bulk Deformation Process)Document27 pagesRolling (Bulk Deformation Process)Kazal ArefinNo ratings yet
- Bulk Deformatin Processes and EquipmentDocument46 pagesBulk Deformatin Processes and EquipmentarhlboyNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Press ToolsDocument9 pages01 Introduction To Press ToolsAngelo De DominicisNo ratings yet
- Bending PrincipleDocument12 pagesBending PrincipleDevanand RNo ratings yet
- PP PP PP PPDocument37 pagesPP PP PP PPJagdish Kolte100% (1)
- Bend Radius Bend Angle: Bending Is A Metal Forming Process in Which A Force Is Applied To A Piece of Sheet MetalDocument8 pagesBend Radius Bend Angle: Bending Is A Metal Forming Process in Which A Force Is Applied To A Piece of Sheet MetalSassyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Process CHETANDocument34 pagesManufacturing Process CHETANChetanraj D PatilNo ratings yet
- Press Working Operation NOTESDocument6 pagesPress Working Operation NOTESZakyNo ratings yet
- GR GNT 00166580000000717Document25 pagesGR GNT 00166580000000717ashoku24007No ratings yet
- Metal Forming Processes: PresentationDocument16 pagesMetal Forming Processes: PresentationBashu Dev SanjelNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document3 pagesAssignment 6Ishaan IslamNo ratings yet
- V BendingDocument4 pagesV BendingSufyan ZaighumNo ratings yet
- Metal ForgingDocument17 pagesMetal ForgingcemekaobiNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming ProcessesDocument40 pagesMetal Forming ProcessesRyat AtmadjaNo ratings yet
- Bending (Metalworking) : ProcessDocument9 pagesBending (Metalworking) : ProcessSubhransu Sekhar SahooNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming Processes: PresentationDocument16 pagesMetal Forming Processes: PresentationBahrul HayatNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Forming ProcessesDocument38 pagesSheet Metal Forming ProcessesRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Presstool MasterDocument111 pagesPresstool MasterRajesh Kumar100% (2)
- Classic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersFrom EverandClassic Handplanes and Joinery: Essential Tips and Techniques for WoodworkersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- What Is A Bearing? Types of BearingsDocument15 pagesWhat Is A Bearing? Types of BearingsMITUL PATELNo ratings yet
- MED-Unit-1-2 (1) (Autosaved)Document60 pagesMED-Unit-1-2 (1) (Autosaved)MITUL PATELNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal FormingDocument25 pagesSheet Metal FormingMITUL PATELNo ratings yet
- Measurement of SurfaceDocument42 pagesMeasurement of SurfaceMITUL PATELNo ratings yet
- What Are Fasteners?Document16 pagesWhat Are Fasteners?MITUL PATELNo ratings yet
- Units Conversions: It Is Absolutely Essential To Report Units With The Number AnswersDocument31 pagesUnits Conversions: It Is Absolutely Essential To Report Units With The Number AnswersMITUL PATELNo ratings yet
- Measures-English, Metric, and EquivalentsDocument1 pageMeasures-English, Metric, and EquivalentsMITUL PATELNo ratings yet
- Measures (English, Metric, and Equivalents)Document1 pageMeasures (English, Metric, and Equivalents)MITUL PATELNo ratings yet
- PFERD Tool Manual Catalogue 1 Int enDocument60 pagesPFERD Tool Manual Catalogue 1 Int enAndakara Edo WardhanaNo ratings yet
- Service Accessories: CatalogDocument32 pagesService Accessories: CatalogdummaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Sealing and Encapsulation: Jason Shin Derek LindbergDocument31 pagesFundamentals of Sealing and Encapsulation: Jason Shin Derek LindbergAmritanshuSarangiNo ratings yet
- QC10-H-043 M03 Cement Mortar Lining-Rev2Document25 pagesQC10-H-043 M03 Cement Mortar Lining-Rev2GousePeerzadeNo ratings yet
- DJJ30082 Worksheet Milling ReportDocument9 pagesDJJ30082 Worksheet Milling ReportSakinah KamalNo ratings yet
- TZe Tapes Technical DataDocument13 pagesTZe Tapes Technical Databukan jasaNo ratings yet
- Viton Selection GuideDocument17 pagesViton Selection Guidedcrypto2022No ratings yet
- PaintsCoatings - Catalogue - 2023 FormuleDocument19 pagesPaintsCoatings - Catalogue - 2023 FormuleAchour BouchefraNo ratings yet
- Grinding and Finishing Processes: Unit 6Document49 pagesGrinding and Finishing Processes: Unit 6Sudharshan IyengarNo ratings yet
- MOS-CVL-11 Concrete Repair MOSDocument2 pagesMOS-CVL-11 Concrete Repair MOSWaqar Ahmad MalikNo ratings yet
- Simufact Improves Quality With New Dedicated Simulation Solution For Direct Energy Deposition 3D PrintingDocument2 pagesSimufact Improves Quality With New Dedicated Simulation Solution For Direct Energy Deposition 3D PrintingChandrasekarNo ratings yet
- Alcon Metal Detector For Alu Foil PackagedDocument2 pagesAlcon Metal Detector For Alu Foil PackagedPrima AdyNo ratings yet
- Wiring Cable StandardDocument6 pagesWiring Cable StandardAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Sigmazinc™: Zinc Primer RangeDocument8 pagesSigmazinc™: Zinc Primer RangeRoberto_PrrNo ratings yet
- Shankar's Resume-3Document6 pagesShankar's Resume-3Green FarmersNo ratings yet
- North Direction: Makkah: Steel Structural PlatformDocument8 pagesNorth Direction: Makkah: Steel Structural PlatformDer3'am Al m7armehNo ratings yet
- Army Institute of Business Administration A Report OnDocument16 pagesArmy Institute of Business Administration A Report OnMirKhalidSaifullahNo ratings yet
- TDS Byk-012 enDocument2 pagesTDS Byk-012 enThái NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Pure Substances Year 8Document20 pagesMixtures and Pure Substances Year 8b2.dakurahNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Welding Sewing MachineDocument24 pagesUltrasonic Welding Sewing Machineaqsa imranNo ratings yet
- Industry Directory 2019 NEWDocument123 pagesIndustry Directory 2019 NEWfescfacturasNo ratings yet
- A 962 - A 962M - 01 Qtk2mi0wmueDocument7 pagesA 962 - A 962M - 01 Qtk2mi0wmueCalib TestNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Concrete Compressive Strength of River Bed and Crusher Run Coarse Aggregate in Pokhara ValleyDocument5 pagesComparative Analysis of Concrete Compressive Strength of River Bed and Crusher Run Coarse Aggregate in Pokhara ValleyAswini NRNo ratings yet
- TRAINING-ACTIVITY-MATRIX - Housekeeping Profed10Document6 pagesTRAINING-ACTIVITY-MATRIX - Housekeeping Profed10Lusanta, Jessa Mae B.No ratings yet
- Secondary Paint Process Qualification FormDocument13 pagesSecondary Paint Process Qualification FormRajwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout - IDocument16 pagesPlant Layout - ITanya rajNo ratings yet
- Correlation Among Crystalline Morphology of PEEK Interface Bond Strength andDocument14 pagesCorrelation Among Crystalline Morphology of PEEK Interface Bond Strength and高亚男No ratings yet
- 12 Major Causes of Foaming On Copper Plating of The PCB BoardDocument8 pages12 Major Causes of Foaming On Copper Plating of The PCB BoardjackNo ratings yet
- Cost CurvesDocument64 pagesCost CurvesChiranjitNo ratings yet
- Cooper Hybrid: Collaborative Welding SystemDocument2 pagesCooper Hybrid: Collaborative Welding SystemAugusto BlancoNo ratings yet