Professional Documents
Culture Documents
STORAGE OF SPERM ERECTION OF Penis
STORAGE OF SPERM ERECTION OF Penis
Uploaded by
Akhand Pratap0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views12 pagesThe document summarizes the processes of sperm storage, erection, and ejaculation in men. Sperm is stored and matured in the epididymis. During an erection, sensory stimulation causes blood vessels to relax and fill the corpora cavernosa of the penis. Ejaculation involves contractions that push sperm from the epididymis through the urethra, where semen is expelled from the body in two phases.
Original Description:
Original Title
STORAGE OF SPERM ERECTION OF penis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the processes of sperm storage, erection, and ejaculation in men. Sperm is stored and matured in the epididymis. During an erection, sensory stimulation causes blood vessels to relax and fill the corpora cavernosa of the penis. Ejaculation involves contractions that push sperm from the epididymis through the urethra, where semen is expelled from the body in two phases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views12 pagesSTORAGE OF SPERM ERECTION OF Penis
STORAGE OF SPERM ERECTION OF Penis
Uploaded by
Akhand PratapThe document summarizes the processes of sperm storage, erection, and ejaculation in men. Sperm is stored and matured in the epididymis. During an erection, sensory stimulation causes blood vessels to relax and fill the corpora cavernosa of the penis. Ejaculation involves contractions that push sperm from the epididymis through the urethra, where semen is expelled from the body in two phases.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pptx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
STORAGE OF SPERM ,
ERECTION OF PENIS AND
EJACULATION
STORAGE OF SPERM
• The epididymis is the organ responsible for
the sperm transport , concentration,
storage, and maturation.
Epididymis has three anatomic parts
- CAPUT ( head)
- CORPUS (body)
-CAUDA (tail)
functions of epididymes -
. Collect newly born spermatozoa
. Provide passage to spermatozoa
. Helps in transport of sperm
.Storage facility to sperm
. Nutrition to spermatozoa
. Absorption of unwanted testiucular fluid
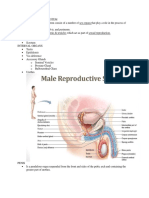
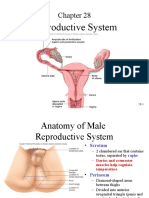
ERECTION OF PENIS
• Penis is the copulatory male organ.
- it is made of 3 part
- Root
- Body
- Glans penis
Body made up of large cavernosum penis
which is enclosed by fibrous capsule , tunica
albuginea.
ventral to this is corpus spongeosum.
they are spongy in nature and divided into
many spaces.
• An erection begins with sensory and
mental stimulation. During sexual arousal,
nerve messages begin to stimulate the
penis. Impulses from the brain and local
nerves cause the muscles of the corpora
cavernosa to relax, allowing blood to flow
in and fill the open spaces. The blood
creates pressure in the corpora cavernosa,
making the penis expand and creating an
erection.
• The arteries relax and open up to let more
blood flow in; at the same time, the veins
close up. Once blood is in the penis,
• The tunica albuginea (the membrane
surrounding the corpora cavernosa), helps to
trap the blood in the corpora cavernosa,
sustaining the erection. Erection is reversed
when muscles in the penis contract, stopping
the inflow of blood and opening outflow
channels.These spaces are continuous
with veins of penis.
• Erection is caused when these spaces are
filled and distended with blood.
• erection is under control of parasympathetic
system.
• reflex stimulation causes erection.
EJACULATION
• After gradual increase in intensity of sexual
rythmic movement , there is discharge
from male urethral orifice into female
genitalia.
• Sexual stimulation and friction provide the
impulses that are delivered to the spinal
cord and into the brain.
• Ejaculation is a reflex action controlled by
the central nervous system. It is triggered
when the sexual act reaches a critical level
•
• Process strarts from epididymis , travel
along ductus deferens .
• At the moment of ejaculation the walls of
the epididymis contract (squeeze) to create
peristaltic waves that push sperm into the
vas deferens.
• At the same time sex glands contracts ,
their content are forced into urethra.
• Ejaculation takes place in two phases: in
the first, or emission stage, sperm are
moved from the testes and the epididymis
(where the sperm are stored) to the
beginning of the urethra, in the second
stage, ejaculation proper, the semen is
moved through the urethra and expelled
from the body.
• During the emission phase, the muscles
around the epididymis and ductus deferens
(the tube extending from the epididymis)
contract to push the sperm into the prostate
and urethra.
• oxytocin is released which cause transport
of semen .
• rythmic contraction of urethral ,
ischiocavernosus and bulbocavernosus
muscles cause release of semen from
urethra.
• maximum lenthening of penis during
ejaculation.
You might also like
- Maternal & Child Care Nursing ReviewDocument37 pagesMaternal & Child Care Nursing Reviewɹǝʍdןnos98% (130)
- Biology SS2 3RD Term e NotesDocument45 pagesBiology SS2 3RD Term e NotesAdio Babatunde Abiodun Cabax100% (2)
- A. Menstrual Cycle Here Are Important Events During The Menstrual CycleDocument2 pagesA. Menstrual Cycle Here Are Important Events During The Menstrual CycleRosiro33% (3)
- Patho Physiology Ovarian CystDocument3 pagesPatho Physiology Ovarian CystSig Deliso100% (1)
- 5a. Male & Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument119 pages5a. Male & Female Reproductive AnatomyvictorNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument63 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Anatomy - KWDocument26 pagesMale Reproductive Anatomy - KWabyannaybaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument70 pagesAnatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDaniel HikaNo ratings yet
- Male ReproductiveDocument59 pagesMale ReproductiveChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument47 pagesMale Reproductive SystemLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument47 pagesReproductive System - Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemGeorge MunyendoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument219 pagesReproductive Systemtzushka_vipNo ratings yet
- Oleza Cannery S. Reproductive SystemDocument16 pagesOleza Cannery S. Reproductive SystemCannery OlezaNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document158 pagesWeek 4Qossay WaxNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument10 pagesReproductive SystemMatt MasilonganNo ratings yet
- SEC C MedLab - GUT&Lymphatics - ABCDE GroupDocument113 pagesSEC C MedLab - GUT&Lymphatics - ABCDE GroupLynx Kee BayatingNo ratings yet
- Chap 19 - The Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesChap 19 - The Reproductive SystemHATLERNo ratings yet
- Biomedicalperspective in Gender and Sexuality: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionDocument29 pagesBiomedicalperspective in Gender and Sexuality: Anatomy and Physiology of ReproductionBrian CastañedaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument31 pagesMale Reproductive SystemGeorge Allen VisperasNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument52 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAjay D100% (1)
- Gender and Society. Unit Ii. Rep 1Document21 pagesGender and Society. Unit Ii. Rep 1alexa dawatNo ratings yet
- Male Pelvic Viscera: NaeemiDocument36 pagesMale Pelvic Viscera: Naeemijed larsen capulong gavinoNo ratings yet
- Science Presentation: By: Beam BorachoDocument33 pagesScience Presentation: By: Beam BorachoPEMAR ACOSTANo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Human Reproduction: Prepared By: Kriti BanstolaDocument78 pagesUnit 1: Human Reproduction: Prepared By: Kriti BanstolaKriti BanstolaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive SystemKim, Seyoung Cristine G.No ratings yet
- The Urinary Bladder: MusculatureDocument2 pagesThe Urinary Bladder: MusculatureSanjay KishoreNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesMale Reproductive SystemEugene RalaNo ratings yet
- 3Q W1 Reproductive Systems 1Document41 pages3Q W1 Reproductive Systems 1chikmxzcNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument81 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Male Reproductive SystemMj BrionesNo ratings yet
- Final LectureDocument162 pagesFinal Lecturemohmmad-0-50No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Physiology 2021Document188 pagesMale Reproductive Physiology 2021Elijah Kihiu18No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument63 pagesUntitledShalom OsayandeNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesThe Male Reproductive Systemmbok diyirNo ratings yet
- Basic Human AnatomyDocument43 pagesBasic Human AnatomyZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- 18 Urinary SystemDocument39 pages18 Urinary SystemSimply MiniNo ratings yet
- Spermatic Cord: Human Body MapsDocument6 pagesSpermatic Cord: Human Body MapsSelim HanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument63 pagesUntitledShalom OsayandeNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument71 pagesReproductive SystemDEBORAH JUBILEE MABAYAGNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemAbbasi KahumaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Male Reproductive OrganDocument5 pagesAnatomy - Male Reproductive OrganJoie ConceptNo ratings yet
- Rhsi, LSDocument56 pagesRhsi, LSMary AkellaNo ratings yet
- Lect4 PelvisDocument26 pagesLect4 PelvisasakingofhNo ratings yet
- Sistem Reproduksi PriaDocument87 pagesSistem Reproduksi PriaAnonymous uLcvBr5ywNo ratings yet
- Parenthood and Family RelationsDocument2 pagesParenthood and Family RelationsSakshi TyagiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemDocument31 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemYUAN CAÑAS100% (1)
- Lecture Notes 6 PDFDocument14 pagesLecture Notes 6 PDFRachelle SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive CyclesDocument52 pagesHuman Reproductive Physiology and Reproductive Cyclesestefania_vlNo ratings yet
- Revisit of Male & Female Genital Tracts Semester VIIDocument50 pagesRevisit of Male & Female Genital Tracts Semester VIIDr. AyshaNo ratings yet
- YL Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesYL Anatomy of The Male Reproductive SystemdrnyolNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesThe Male Reproductive SystemHoney MalabuteNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesReproductive SystemPrincess Nicole HernaezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ReportDocument7 pagesAnatomy Reportمحمود الموسويNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System - Bio 2Document56 pagesReproductive System - Bio 220181539No ratings yet
- Chapt28 LectureDocument44 pagesChapt28 Lecturemelissa_sunNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument22 pagesMale Reproductive SystemKBS100% (1)
- Male Reproductive AnatomyDocument25 pagesMale Reproductive Anatomyisimmonn0% (1)
- Mechanism of Erection & EjaculationDocument15 pagesMechanism of Erection & Ejaculationmeez rameezNo ratings yet
- Bovine Male GenitaliaDocument48 pagesBovine Male Genitaliaಮನೋಜ್ ಭಾರದ್ವಾಜ್No ratings yet
- Male Repro SystemDocument21 pagesMale Repro Systemdoreen03No ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument42 pagesThe Reproductive SystemAries BautistaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument7 pagesReproductive Systemcollege code - 5No ratings yet
- Penis: Abdomen Skin CircumcisionDocument4 pagesPenis: Abdomen Skin CircumcisionTatadarz Auxtero LagriaNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemDocument30 pagesMale Reproductive SystemChinju Jose SajithNo ratings yet
- Repeat Breeding DiagnosisDocument35 pagesRepeat Breeding DiagnosisAkhand PratapNo ratings yet
- College of Veterinary Science & Animal Husbandry MhowDocument23 pagesCollege of Veterinary Science & Animal Husbandry MhowAkhand PratapNo ratings yet
- CHIMERA and ImmunomodulationDocument20 pagesCHIMERA and ImmunomodulationAkhand PratapNo ratings yet
- College of Veterinary Science & Animal Husbandry Mhow: TopicDocument20 pagesCollege of Veterinary Science & Animal Husbandry Mhow: TopicAkhand PratapNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia - Semen Analysis (CHECKED)Document8 pagesWikipedia - Semen Analysis (CHECKED)vitruvianxyzNo ratings yet
- UterusDocument3 pagesUterusBernadette FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Topic: Fertilization: Print Self Learning MaterialDocument9 pagesTopic: Fertilization: Print Self Learning MaterialNihalNo ratings yet
- Swine PPT 2012Document99 pagesSwine PPT 2012ዘንገና ቲዩብNo ratings yet
- 06 Perineum GenitaliaDocument24 pages06 Perineum GenitaliaRoger ViloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1995 PDFDocument239 pagesAnatomy 1995 PDFDaniel SisniegasNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument8 pagesMenstrual Cyclejeni antonyNo ratings yet
- Digos City National High School Senior High School Quarter 2 (Week 2) Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesDigos City National High School Senior High School Quarter 2 (Week 2) Earth and Life Sciencejanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- GynaecologyDocument123 pagesGynaecologyKiranNo ratings yet
- Normal Ovaries On UltrasoundDocument1 pageNormal Ovaries On UltrasoundDr Pankaj TalwarNo ratings yet
- Macario Biology W1Document6 pagesMacario Biology W1Roberto MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1st Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiDocument17 pages1st Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Oogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in TheDocument7 pagesOogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in ThebarbacumlaudeNo ratings yet
- Abdul Qudus PatologiDocument37 pagesAbdul Qudus PatologiAgus SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Maternal Newborn Nursing ExamDocument3 pagesMaternal Newborn Nursing Examrevathidadam55555No ratings yet
- PT - SCIENCE 5 EditedDocument7 pagesPT - SCIENCE 5 EditedANALOU CAPILLONo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infection and Semen Characteristics in Infertile MenDocument6 pagesBacterial Infection and Semen Characteristics in Infertile Menalia eltayebNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics & Gynecology: Original Review & Revision HyderabadDocument739 pagesObstetrics & Gynecology: Original Review & Revision Hyderabad24k.avinashNo ratings yet
- Sex at The Anatomical LevelDocument46 pagesSex at The Anatomical LevelkavehNo ratings yet
- Urology 36 Undescended TestisDocument33 pagesUrology 36 Undescended TestistasyaNo ratings yet
- Sperm Wars - Robin Baker: Chapter 1: The Generation GameDocument6 pagesSperm Wars - Robin Baker: Chapter 1: The Generation GameGustavo PernaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproduction SystemDocument37 pagesFemale Reproduction SystemSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- MusaedAlsayadi (GynaecologmcqsDr. Farouk Haseeb)Document65 pagesMusaedAlsayadi (GynaecologmcqsDr. Farouk Haseeb)a7332773No ratings yet
- HormonesDocument2 pagesHormonesVirzle ValenciaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Periodic Test Science 10Document2 pages3rd Periodic Test Science 10Anonymous xagGSIdNo ratings yet
- Ambiguous GenitaliaDocument2 pagesAmbiguous Genitaliamimit sasmitaNo ratings yet