Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kidney in Detail: Standard Grade Biology
Kidney in Detail: Standard Grade Biology
Uploaded by
Harshil Patel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
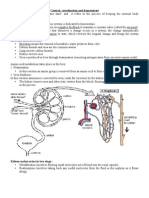
5 views16 pagesThe kidney filters blood to remove waste and regulate water levels. Each kidney contains millions of nephrons, the filtering units of the kidney. In each nephron, blood enters the glomerulus where filtration occurs under pressure, producing a glomerular filtrate containing water, glucose, salts, and urea. Protein and blood cells are too large to pass through. The filtrate then travels through the tubule where glucose, water and salts are reabsorbed, with the final urine containing excess water, salts, and waste urea. The kidneys regulate water concentration in the blood through negative feedback control.
Original Description:
Original Title
Kidneys
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe kidney filters blood to remove waste and regulate water levels. Each kidney contains millions of nephrons, the filtering units of the kidney. In each nephron, blood enters the glomerulus where filtration occurs under pressure, producing a glomerular filtrate containing water, glucose, salts, and urea. Protein and blood cells are too large to pass through. The filtrate then travels through the tubule where glucose, water and salts are reabsorbed, with the final urine containing excess water, salts, and waste urea. The kidneys regulate water concentration in the blood through negative feedback control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views16 pagesKidney in Detail: Standard Grade Biology
Kidney in Detail: Standard Grade Biology
Uploaded by
Harshil PatelThe kidney filters blood to remove waste and regulate water levels. Each kidney contains millions of nephrons, the filtering units of the kidney. In each nephron, blood enters the glomerulus where filtration occurs under pressure, producing a glomerular filtrate containing water, glucose, salts, and urea. Protein and blood cells are too large to pass through. The filtrate then travels through the tubule where glucose, water and salts are reabsorbed, with the final urine containing excess water, salts, and waste urea. The kidneys regulate water concentration in the blood through negative feedback control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 16
Kidney in Detail
Standard Grade Biology
Excretion by the Kidney
• Urea
-nitrogenous waste
-made by liver
-excess amino acids in blood
-toxic
• Why must nitrogenous waste be excreted?
1 – Filtration by the Kidney
•Supplied with blood
from renal artery
Renal
Lets have a
artery look at a
•Inside it splits into nephron!!!
many fine capillaries
Renal
•Each capillary vein
supplies blood to
hundreds of
thousands of tiny
filtration units called
Ureter
nephrons
1. Glomerulus brings a large
surface area of blood
capillaries in close contact Blood from
with Bowman’s capsule renal artery
enters wide
capillary
2. Liquid filtered from blood
under pressure (filtration)
3. Glomerular filtrate produced
Blood travels
containing:
through
-water narrow
-glucose Filtration capillary
-salts towards rena
-urea vein
Glomerular
filtrate
(Protein molecules and red blood
cells do not pass into tubule as
they are TOO BIG!!!!)
Think…
• Which feature of the glomerulus helps the
process of filtration?
• Which 4 components of unfiltered blood
appear in the glomerular filtrate?
• Why do blood cells and protein molecules
not appear in the glomerular filtrate?
Key Words!!
Nephron: structure in the kidney that acts as a
microscopic filtration unit
Glomerulus: dense mass of very fine blood capillaries at
the nephron that act as a filter
Bowman’s capusle:cup-shaped part of the nephron that
holds a glomerulus and collects the products of
filtration from it
Glomerular filtrate: liquid removed from the blood by
filtration in the kidney
2 – Reabsorption by the Kidney
• Once the main components of glomerulur filtrate
enter the bloodstream
-they are no longer in bloodstream
• If nothing more happened in the nephron then all
the useful stuff would be lost in the urine!
• Therefore, glucose, water and some salts need
to be reabsorbed!
More water
reabsorbed
Glucose
reabsorbed Final urine
containing:
-excess water
-unneeded salts
-waste urea
Variable amounts of water
and salts reabsorbed and
filtrate gradually turning into
urine
Think….
• Which three components of the glomerular
filtrate are reabsorbed?
• Why is it important for these to be
reabsorbed?
• Which substances are present in the final
urine?
• Summary of kidney function
2 – Controlling Water
Concentration
• Blood
-important part of internal environment
-constantly changing water concentration
-e.g. exercising
drinking lots of water
• The body uses negative feedback control
to regulate water content of the blood
How does it work?
• Control of Water animation
This powerpoint was kindly donated to
www.worldofteaching.com
http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a
thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a
completely free site and requires no registration. Please
visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.
You might also like
- Young People Faces More Challenges TodayDocument2 pagesYoung People Faces More Challenges TodayThena78% (23)
- Kiln Start Up Procedures PDFDocument12 pagesKiln Start Up Procedures PDFfaheemqc100% (2)
- Manual A-10 ANTI TANK AIRCRAFTDocument36 pagesManual A-10 ANTI TANK AIRCRAFTrcman779100% (2)
- Excretory Products & Their Elimination PowernotesDocument2 pagesExcretory Products & Their Elimination PowernotesSushmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Ch. 14 Vander's Human Physiology Book NotesDocument6 pagesCh. 14 Vander's Human Physiology Book Noteskts50% (2)
- How To Use This Sheet:: Life Design List © Andrew Leedham 2019Document10 pagesHow To Use This Sheet:: Life Design List © Andrew Leedham 2019Dustin CampNo ratings yet
- Kidney in Detail: Standard Grade BiologyDocument16 pagesKidney in Detail: Standard Grade BiologyCizre BotanNo ratings yet
- Kidney in Detail: Standard Grade BiologyDocument16 pagesKidney in Detail: Standard Grade BiologyCarl Agape DavisNo ratings yet
- Excretion NotesDocument5 pagesExcretion NoteskuluNo ratings yet
- (BIO) Chapter 9 - Excretion in HumansDocument14 pages(BIO) Chapter 9 - Excretion in Humansanya desilvaNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument36 pagesExcretory SystemOlamide AyindeNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products AND Their EliminationDocument43 pagesExcretory Products AND Their EliminationBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- Excretion and KidneysDocument39 pagesExcretion and KidneyselizabethNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their EliminationDocument9 pagesExcretory Products and Their EliminationBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- BBT221 Lec 18 - Urinary SystemDocument22 pagesBBT221 Lec 18 - Urinary Systemiamraiyan123No ratings yet
- Osmoregulation 1Document19 pagesOsmoregulation 1Cate SandersonNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument47 pagesExcretory Systemalice mamaNo ratings yet
- ORALREVALIDADocument2 pagesORALREVALIDAalthea jade villadongaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Urine FormationDocument35 pagesMechanism of Urine Formationgotiy6001No ratings yet
- 3 - Excretion NotesDocument33 pages3 - Excretion NotesJenny YoonNo ratings yet
- Notes For HomeostasisDocument21 pagesNotes For Homeostasisfreednemon83% (6)
- Topic 2b - Homeostasis-Student v2Document52 pagesTopic 2b - Homeostasis-Student v2Angel LimNo ratings yet
- Group 10 Urine FormationDocument27 pagesGroup 10 Urine FormationgracechamdimbaNo ratings yet
- EXCRETIONDocument9 pagesEXCRETIONMaira CanashinNo ratings yet
- Kidney 1Document41 pagesKidney 1Miguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Kidney Function - ExcretionDocument15 pagesKidney Function - Excretionznayune82No ratings yet
- What Are AntibioticsDocument29 pagesWhat Are AntibioticsLouie BruanNo ratings yet
- Share Mszo113 - Animal-Wps OfficeDocument29 pagesShare Mszo113 - Animal-Wps OfficeRoopa Ram MundhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 - Urinary SystemDocument64 pagesLecture 11 - Urinary SystemmaecabauatanNo ratings yet
- ANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021Document58 pagesANAT 1053 Unit 6 Urinary System Prof Slides Fall 2021abextekNo ratings yet
- 12 ExcretionDocument4 pages12 ExcretionvedikaNo ratings yet
- The Urinary and Reproductive System (J.R) - Policarpio MAT Gen. Sci.Document60 pagesThe Urinary and Reproductive System (J.R) - Policarpio MAT Gen. Sci.john ronald PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Excretion Unit 2Document20 pagesExcretion Unit 2SashidaeNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys and Formation of Urine 3 New 0Document22 pagesThe Kidneys and Formation of Urine 3 New 0Iph anyiNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument36 pagesUrinary SystemguintogeorgetteNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesUrinary Systemydnic alykPNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Excretory System PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 9 Excretory System PDFErica Ann Ical100% (1)
- DR DedyDocument61 pagesDR DedyFerry PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Urine FormationsDocument20 pagesMechanism of Urine FormationsGAURAVNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: by Eka BebasariDocument47 pagesUrinary System: by Eka BebasariMuhammad Reza SaputraNo ratings yet
- Excretion - Excretion Is The Removal of The Metabolic Wastes of An Organism. Wastes That AreDocument10 pagesExcretion - Excretion Is The Removal of The Metabolic Wastes of An Organism. Wastes That ArejoelNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System 2013Document52 pagesThe Urinary System 2013adystiNo ratings yet
- Module ΙV Urinary systemDocument41 pagesModule ΙV Urinary systemkeerthi krishnaNo ratings yet
- KidneyoutlineDocument33 pagesKidneyoutlineapi-273417637No ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument56 pagesHomeostasisn2gtmbbpcpNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of The Urine Production (2021)Document80 pagesThe Physiology of The Urine Production (2021)Shelly NobelNo ratings yet
- PDF Document 2Document14 pagesPDF Document 2Vari MafiaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Term 3 Week 5 - 2020Document12 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Term 3 Week 5 - 2020YONDELA MbandezeloNo ratings yet
- K1 - Fisiologi Sistem Urinaria blokNU-15Document35 pagesK1 - Fisiologi Sistem Urinaria blokNU-15chandra drNo ratings yet
- 3 Renal SystemDocument30 pages3 Renal SystemgsnehaaNo ratings yet
- Ultrafiltration and Selective ReabsorptionDocument22 pagesUltrafiltration and Selective ReabsorptionKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument32 pagesThe Urinary SystemriniambarwatiNo ratings yet
- Excretion IDocument27 pagesExcretion Ierinjoy77No ratings yet
- Urinary System: Functions of Renal SystemDocument28 pagesUrinary System: Functions of Renal SystemAubrey Cissé MwakayeNo ratings yet
- +1 Kite Class 36 ExcretionDocument5 pages+1 Kite Class 36 Excretionsolamanmathew127No ratings yet
- AUBFDocument8 pagesAUBFIssha CasañasNo ratings yet
- 032 Urinary SystemDocument25 pages032 Urinary SystemIntresting FactsNo ratings yet
- Renal PhysiologyDocument52 pagesRenal Physiologypetronellahkangombe0No ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Student Version The Urinary System 2020.ppt (1402)Document20 pagesChapter 15 Student Version The Urinary System 2020.ppt (1402)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- URINARY SYSTEM ReviewerDocument9 pagesURINARY SYSTEM Reviewer4th otosakaNo ratings yet
- System UriDocument48 pagesSystem UriStef FieNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument37 pagesExcretory SystemPatrick DeeNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument84 pagesUrinary SystemCheghe PerezNo ratings yet
- Kidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandKidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- SCLP Samaj School Year 10 Chemistry Revision WorksheetDocument11 pagesSCLP Samaj School Year 10 Chemistry Revision WorksheetHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Pravesh 1Document10 pagesPravesh 1Harshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Science Class 5 NotesDocument27 pagesScience Class 5 NotesHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Form One Biology NotesDocument89 pagesForm One Biology NotesHarshil Patel100% (2)
- (L4) - Digestion and Absorption - 25th MayDocument75 pages(L4) - Digestion and Absorption - 25th MayHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - The Mole: 10.1 Measuring MatterDocument96 pagesChapter 10 - The Mole: 10.1 Measuring MatterHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- The Excretory SystemDocument15 pagesThe Excretory SystemHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Science - The Human BodyDocument31 pagesScience - The Human BodyHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Form 3 BiologyDocument78 pagesForm 3 BiologyHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Form One Business StudiesDocument145 pagesForm One Business StudiesHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 3notesDocument151 pagesBiology Form 3notesHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Form 1 1 MicroscopeDocument46 pagesForm 1 1 MicroscopeHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Form One Physics HandbookDocument141 pagesForm One Physics HandbookHarshil Patel100% (1)
- Form One Computer NotesDocument73 pagesForm One Computer NotesHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- 1 - Intro To ApDocument14 pages1 - Intro To ApHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- The River of Life Blood Chapter 17Document31 pagesThe River of Life Blood Chapter 17Harshil PatelNo ratings yet
- 24 - Respiratory SystemDocument18 pages24 - Respiratory SystemHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- The Blood: Overview of Blood CirculationDocument14 pagesThe Blood: Overview of Blood CirculationHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- Uop Butamer Process: Nelson A. CusherDocument8 pagesUop Butamer Process: Nelson A. CusherBharavi K SNo ratings yet
- Dropwise and Filmwise Condensation PDFDocument5 pagesDropwise and Filmwise Condensation PDFmustafa100% (2)
- ADS FiltragrDocument68 pagesADS FiltragrAnonymous nRt5PwXhQ100% (1)
- Guide To Use Kismac For Advanced Wifi FunctionsDocument31 pagesGuide To Use Kismac For Advanced Wifi Functionsmandeepmails100% (1)
- Huawei g630 Repair ManualDocument40 pagesHuawei g630 Repair Manualأبو عبد الرحمان زهيرNo ratings yet
- W1A1Document2 pagesW1A1Arul PrasaadNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceJuvy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management Journal PDFDocument21 pagesStrategic Management Journal PDFselvyNo ratings yet
- Flexi Scope GuideDocument15 pagesFlexi Scope Guide69nino69No ratings yet
- Einstein II DgsDocument2 pagesEinstein II DgsHasanNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and DesignDocument11 pagesSystem Analysis and DesignGuruKPO100% (1)
- DLL - Tle-Ia 6 - Q3 - W4Document3 pagesDLL - Tle-Ia 6 - Q3 - W4RUTCHE TABANAONo ratings yet
- VCS IO FencingDocument44 pagesVCS IO FencingnysaNo ratings yet
- BAIL 16008 Catalogue Update DE5 PROOF Issuu v2Document38 pagesBAIL 16008 Catalogue Update DE5 PROOF Issuu v2Chris LuiNo ratings yet
- Gall's ProjectionDocument3 pagesGall's ProjectionBiki KunduNo ratings yet
- Financial CompensationDocument55 pagesFinancial CompensationJerome TimolaNo ratings yet
- Strategic PlanningDocument22 pagesStrategic PlanningLoloyNo ratings yet
- M1 Practice Problems - 2Document1 pageM1 Practice Problems - 2gnathwNo ratings yet
- 11 Quality Management - FDocument15 pages11 Quality Management - FdumNo ratings yet
- List of Companies Using Solar PowerDocument12 pagesList of Companies Using Solar PowerSahista IqbalNo ratings yet
- CO-EXISTENCE AND INTERNATIONAL LAW - TunkinDocument83 pagesCO-EXISTENCE AND INTERNATIONAL LAW - TunkinthayanneNo ratings yet
- IdealDocument8 pagesIdealAzza Sundus AntartikaNo ratings yet
- Executive Summary of The Primer On Automobile Fuel Efficiency and EmissionsDocument2 pagesExecutive Summary of The Primer On Automobile Fuel Efficiency and Emissionsdmorin10% (1)
- DP Sound ADI 15025 DriversDocument218 pagesDP Sound ADI 15025 DriversJuan Carlos Gonzalez LNo ratings yet
- Pemanfaatan Ekstrak Daun Mangrove (Rhizophora Bahan Aktif Sediaan Farmasi Terapi Anti KankerDocument7 pagesPemanfaatan Ekstrak Daun Mangrove (Rhizophora Bahan Aktif Sediaan Farmasi Terapi Anti KankerIsnawati 26No ratings yet
- Meeting PeopleDocument2 pagesMeeting PeopleJose AssisNo ratings yet