Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochem, Chapter 1 Slide
Biochem, Chapter 1 Slide
Uploaded by
Galata Bane0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views8 pagesBiochemical engineering links biological science with chemical engineering principles to conduct biological processes on an industrial scale. It applies science and engineering to processing materials or treating biological materials biologically to produce goods and services. Biotechnology uses living organisms or their components to make or modify products, and is applied in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, environmental applications, and more. A typical biological process involves upstream preparation and inoculation, the bioprocess or fermentation itself, and downstream product recovery and purification.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBiochemical engineering links biological science with chemical engineering principles to conduct biological processes on an industrial scale. It applies science and engineering to processing materials or treating biological materials biologically to produce goods and services. Biotechnology uses living organisms or their components to make or modify products, and is applied in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, environmental applications, and more. A typical biological process involves upstream preparation and inoculation, the bioprocess or fermentation itself, and downstream product recovery and purification.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views8 pagesBiochem, Chapter 1 Slide
Biochem, Chapter 1 Slide
Uploaded by
Galata BaneBiochemical engineering links biological science with chemical engineering principles to conduct biological processes on an industrial scale. It applies science and engineering to processing materials or treating biological materials biologically to produce goods and services. Biotechnology uses living organisms or their components to make or modify products, and is applied in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, environmental applications, and more. A typical biological process involves upstream preparation and inoculation, the bioprocess or fermentation itself, and downstream product recovery and purification.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ppt, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 8
Introduction to Biochemical
Engineering
Biochemical Engineering is concerned with
the conducting biological processes on an
industrial scale. This area links biological
science with chemical engineering
Biotechnology
• Biotechnology can be broadly defined as
“Commercial techniques that use living
organisms, or substances from those organisms, to
make or modify a product, including techniques
used for the improvement of the characteristics of
economically important plants and animals and for
the development of microorganisms to act on the
environment
It is the application of science and
engineering principles to the processing of
materials by biological agents or direct
treatment of biological materials for the
production of goods and services
• Recombinant DNA and Cell fusion are the best
examples of biotechnology.
Recombinant DNA: allows the direct manipulation of
genetic material of individual cells, which may be used to
develop microorganisms that produce new products as well as
useful organisms.
Cell fusion: is a process to form a single hybrid cell with
nuclei and cytoplasm from two different types of cells in order
to combine the desirable characteristics of the two.
Applications of biotechnology
• Pharmaceuticals: To produce antibiotics, antigens, human growth
hormone, insulin, vaccines…….
• Animal agriculture: For the developments of disease free seed
stocks and Healthier, higher yielding food animals.
• Plant agriculture : For transfer of stress, Herbicide, development
of plants with the increased abilities of photosynthesis or nitrogen
fixation, for the developments of biological insecticides…….
• Environmental applications: For mineral leaching, metal
concentration, pollution control, toxic was degradation, and enhanced oil
recovery.
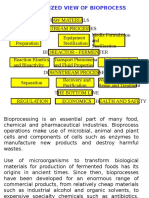
Typical biological process
Preparation of inoculums and medium,
Inoculum scale up,
Inoculating the inoculums in the culture
Upstream media/bioreactor,
process Controlling of pH and temperature
Production of:
Bioprocess Microbial cells (biomass) e.g bakery yeast, SCP
(Fermentation) Microbial metabolites e.g alcohols, organic acids
Microbial enzymes e.g invertase, lipase
Recombinant products
Removal of insolubles
Downstream
Product isolation, purification and polishing
process
Effluent treatment
You might also like
- OPENSTAX MICROBIOLOGY TEST BANK OpenStax Microbiology THIS TEST BANK COVERS ALL CHAPTERS 1-26 OF THE BOOK Complete GuideDocument32 pagesOPENSTAX MICROBIOLOGY TEST BANK OpenStax Microbiology THIS TEST BANK COVERS ALL CHAPTERS 1-26 OF THE BOOK Complete Guidemarcuskenyatta275No ratings yet
- Textbook of Gynaecological OncologyDocument58 pagesTextbook of Gynaecological OncologyMarco Vinicio Benavides Osorto100% (2)
- Strain Variation in The Mycobacterium Its Role in Biology, Epidemiology and ControlDocument319 pagesStrain Variation in The Mycobacterium Its Role in Biology, Epidemiology and Controlraj kumarNo ratings yet
- FGIKReplication Student HandoutDocument16 pagesFGIKReplication Student Handoutnj saim100% (1)
- Introduction To Pharmacoinformatics: DR Dzul Azri Mohamed Noor Dzulazri@usm - MyDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacoinformatics: DR Dzul Azri Mohamed Noor Dzulazri@usm - MyLakshmanan ValliappanNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Power Point Chapter OneDocument22 pagesBiochemical Power Point Chapter OneEstifa negashNo ratings yet
- Generalized View of BioprocessDocument20 pagesGeneralized View of BioprocessTamoor TariqNo ratings yet
- What Is Bioprocess?Document28 pagesWhat Is Bioprocess?sanyukta sinhaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering: Dr. Syed Nadir HussainDocument46 pagesBiochemical Engineering: Dr. Syed Nadir Hussainumairgul841No ratings yet
- Environmental Biotechnology (BBT427) Spring 2020: Prepared by Dr. Ishrat JabeenDocument23 pagesEnvironmental Biotechnology (BBT427) Spring 2020: Prepared by Dr. Ishrat JabeenEarfanNo ratings yet
- Environmental Biotechnology (BBT427) Spring 2020: Prepared by Dr. Ishrat JabeenDocument23 pagesEnvironmental Biotechnology (BBT427) Spring 2020: Prepared by Dr. Ishrat JabeenEarfanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Bioreactor and Bioprocess EngineeringDocument18 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Bioreactor and Bioprocess EngineeringRaad AlesayiNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess TechnologyDocument33 pagesBioprocess TechnologyAMALAY RAFFLI ARNOLDYNo ratings yet
- Scope of MicroDocument32 pagesScope of MicroShehram QazafiNo ratings yet
- Bioprocess Engineering (BT 508) : Credits-4 Units - 6 Total Marks - 150Document26 pagesBioprocess Engineering (BT 508) : Credits-4 Units - 6 Total Marks - 150Savita100% (1)
- App Chem AsigDocument9 pagesApp Chem Asighafiz_qamarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document14 pagesLecture 1Tadiwanashe MagombeNo ratings yet
- BT6304 BibtDocument77 pagesBT6304 Bibt18UGBT055 Surya PrabhaNo ratings yet
- Modern Techniques in Plant Breeding 3 (2-1)Document13 pagesModern Techniques in Plant Breeding 3 (2-1)Aiman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Biochemical EngineeringDocument28 pagesBiochemical Engineeringsurajagtap010% (1)
- Q2 BiotechhandoutDocument8 pagesQ2 BiotechhandoutJustANormalDevツ (Devy)No ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document15 pagesLecture 01Tanvir FahimNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Fermentation ProcessesDocument18 pagesAn Introduction To Fermentation ProcessesPhú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document7 pagesChapter 1workisaNo ratings yet
- Scope of BiotechnologyDocument15 pagesScope of Biotechnologyrameenakhtar993No ratings yet
- Basics of Fermentation Technology and Fermentor Design 3795Document32 pagesBasics of Fermentation Technology and Fermentor Design 3795PatelrajaniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiotechnologyDocument335 pagesIntroduction To BiotechnologySamson TizazuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Biotechnology1Document46 pagesIntroduction To Biotechnology1Chloe AgolitoNo ratings yet
- Colors of BiotechnologyDocument66 pagesColors of Biotechnologyasdfgh0% (1)
- Abag, Mary Eisle E. Acosta, Charrisma A. Beron, Danica D. Camsol, Kristina CDocument55 pagesAbag, Mary Eisle E. Acosta, Charrisma A. Beron, Danica D. Camsol, Kristina CRen H. RoxasNo ratings yet
- BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument8 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGYvijaysecondmailNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiotechnologyDocument46 pagesIntroduction To BiotechnologySunita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Ppt1Document45 pagesBiochemical Ppt1DanishNo ratings yet
- BIOTECHNOLOGYDocument5 pagesBIOTECHNOLOGYkeidieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document32 pagesChapter 1eire_dankeNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology q4Document6 pagesBiotechnology q4viendalisay27No ratings yet
- U1 Capítulo 1 - Introduction (Fundamentals of Biochemical Engineering, Rajiv Dutta) PDFDocument7 pagesU1 Capítulo 1 - Introduction (Fundamentals of Biochemical Engineering, Rajiv Dutta) PDFGisele Cescutti100% (1)
- Biotech Product DevDocument24 pagesBiotech Product DevAbdul BasitNo ratings yet
- 3 230325101018 bcf55df7Document28 pages3 230325101018 bcf55df7Dawit GetahunNo ratings yet
- Microbial BiotechnologyL1Document24 pagesMicrobial BiotechnologyL1Swarna15No ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument26 pagesBiotechnologyJ. DiroshikaNo ratings yet
- Lec01 - Concepts MicroorganismsDocument16 pagesLec01 - Concepts MicroorganismsBhavna MuthyalaNo ratings yet
- Biotech Lec 1 IntrodDocument5 pagesBiotech Lec 1 Introdnareman hassanNo ratings yet
- Biotech Lec 1 Introd PDFDocument5 pagesBiotech Lec 1 Introd PDFnareman hassanNo ratings yet
- Principle of Biochemical Engineering: Manam Walait Lecturer FLS, UCP LahoreDocument23 pagesPrinciple of Biochemical Engineering: Manam Walait Lecturer FLS, UCP LahoreJawadNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Intro To Bioproducts and BioseparationsDocument30 pagesTopic 1 Intro To Bioproducts and BioseparationsPamela Aboytes100% (2)
- Rakib L1 - Introduction To Microbial BiotechnologyDocument22 pagesRakib L1 - Introduction To Microbial BiotechnologySadia Afrin OshinNo ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument9 pagesBiotechnologyhikarychan122No ratings yet
- Biotechnology Group 1 Introduction and UsesDocument2 pagesBiotechnology Group 1 Introduction and UsesAniqa JavedNo ratings yet
- Application of Biotechnology in Food, Pharmaceuticals and Agriculture IndustriesDocument22 pagesApplication of Biotechnology in Food, Pharmaceuticals and Agriculture IndustriesLov SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument22 pagesBiotechnology Recombinant DNA TechnologyRenien Khim BahayaNo ratings yet
- Introduksi Bioteknologi Dan Teknobiologi: Oleh Dr. Drh. Heru Nurcahyo, M.KesDocument38 pagesIntroduksi Bioteknologi Dan Teknobiologi: Oleh Dr. Drh. Heru Nurcahyo, M.KesAmin Khusnadiyah aminkhusnadiyah.2020No ratings yet
- CH 28 Applied and Industril MicrobiologyDocument35 pagesCH 28 Applied and Industril Microbiologyramonlennon1980No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Biochemical Engineering (Biot. 4132) Course ECTS: 3Document61 pagesFundamentals of Biochemical Engineering (Biot. 4132) Course ECTS: 3Andebet HabtamNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Bioproduk - VEENA VASHEENE VK - 061611133280 - ADocument9 pagesSpesifikasi Bioproduk - VEENA VASHEENE VK - 061611133280 - Aanwini kumNo ratings yet
- Mbio313 Assignment 2Document8 pagesMbio313 Assignment 2Razia UrmiNo ratings yet
- Overview BiotechDocument16 pagesOverview Biotechbasikal petakNo ratings yet
- Che514a IntroductionDocument30 pagesChe514a IntroductionGenevive S. de VeraNo ratings yet
- Week 1-Introduction of BioindustryDocument31 pagesWeek 1-Introduction of BioindustryFery HaidirNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Processes (Section 2) : What Is Biochemical Process?Document8 pagesBiochemical Processes (Section 2) : What Is Biochemical Process?Ren H. RoxasNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Biotechnology PDFDocument15 pagesFermentation Biotechnology PDFsadatrafia100% (1)
- Annual Plant Reviews, Biochemistry of Plant Secondary MetabolismFrom EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Biochemistry of Plant Secondary MetabolismNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology and Bioinformatics: From Gene Editing to Personalized MedicineFrom EverandBiotechnology and Bioinformatics: From Gene Editing to Personalized MedicineNo ratings yet
- Absorption & StrippingDocument17 pagesAbsorption & StrippingGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- 2 Design of Isothermal Ideal ReactorsDocument28 pages2 Design of Isothermal Ideal ReactorsGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- Plant Design &economicsDocument55 pagesPlant Design &economicsGalata Bane100% (1)
- Metu University Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument38 pagesMetu University Faculty of Engineering and Technology Department of Chemical EngineeringGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- Nationaly Harmonised B.Sc. Chemical Engineering ProgramDocument2 pagesNationaly Harmonised B.Sc. Chemical Engineering ProgramGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- Fast Food Industry Purchase Process: - A Study On Sustainability and Healthy FoodDocument82 pagesFast Food Industry Purchase Process: - A Study On Sustainability and Healthy FoodGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- Binyam TeshomeDocument146 pagesBinyam TeshomeGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: 1.1 BackgroundDocument56 pagesChapter One: 1.1 BackgroundGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- Simplex Algorithm - WikipediaDocument20 pagesSimplex Algorithm - WikipediaGalata BaneNo ratings yet
- Ot Culture NGDocument3 pagesOt Culture NGAniruddha ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 OrientationDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology 1 OrientationJeM LobiLabNo ratings yet
- Molecular Cytogenetics in The Era of ChromosomicsDocument9 pagesMolecular Cytogenetics in The Era of ChromosomicsK CruzNo ratings yet
- Haematol 2016 149476 FullDocument31 pagesHaematol 2016 149476 FullNurul Huda KowitaNo ratings yet
- Tsukushi Functions As An Organizer Inducer by Inhibition of - 2004 - DevelopmenDocument12 pagesTsukushi Functions As An Organizer Inducer by Inhibition of - 2004 - Developmenhalil sahanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Internet LessonDocument3 pagesMitosis Internet LessonGLENMAR VINEGASNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Animal Handling Basic Information of Pharmacology PracticumDocument14 pagesModule 1 - Animal Handling Basic Information of Pharmacology PracticummadelineNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Stem Cell Research and TherapyDocument6 pagesEthics in Stem Cell Research and TherapySwathi sampathkumarNo ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual ReproductionDocument20 pagesAsexual and Sexual ReproductionJanet Laride100% (1)
- Extraction of Dna From Calf Thymus CellsDocument24 pagesExtraction of Dna From Calf Thymus CellsdansuperNo ratings yet
- DNA WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA WorksheetH DNo ratings yet
- UNIT1 MilestoneDocument16 pagesUNIT1 MilestoneTanya AlkhaliqNo ratings yet
- BHU HospitalDocument8 pagesBHU HospitalAzka FatimaNo ratings yet
- Uni ProtDocument6 pagesUni Protwilliam919No ratings yet
- Hubungan Kuantitatif Struktur Aktivitas Obat Antibiotik, AnalgetikDocument62 pagesHubungan Kuantitatif Struktur Aktivitas Obat Antibiotik, AnalgetikAdelia KhaerunisaNo ratings yet
- Role of Bioinformatics in AgricultureDocument6 pagesRole of Bioinformatics in AgriculturevipinqiaNo ratings yet
- Bio 10th - How Do Organism Reproduce - Revision WorksheetDocument10 pagesBio 10th - How Do Organism Reproduce - Revision WorksheetDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- PML23 000845 - Soriano Maria Corazon Muñoz - RT PCR 1Document1 pagePML23 000845 - Soriano Maria Corazon Muñoz - RT PCR 1Dpmmh Lab DeptNo ratings yet
- (Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine) Marco Tatullo (Eds.) - MSCs and Innovative Biomaterials in Dentistry-Humana Press (2017)Document199 pages(Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine) Marco Tatullo (Eds.) - MSCs and Innovative Biomaterials in Dentistry-Humana Press (2017)chenNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Biology Mechanisms of InheritanceDocument22 pagesGrade 12 Biology Mechanisms of Inheritanceapi-635512040No ratings yet
- BCMB2X01 MEDS2003 2024 L17 MolecularBiologyIntroDocument33 pagesBCMB2X01 MEDS2003 2024 L17 MolecularBiologyIntrohyy370815No ratings yet
- Research Paper On Recombinant Dna TechnologyDocument7 pagesResearch Paper On Recombinant Dna Technologyvagipelez1z2100% (1)
- Quiz 1 - BIOL 420 U - Advanced Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 - BIOL 420 U - Advanced Cell and Molecular BiologyCumNo ratings yet
- Solgent Co.,Ltd.: Diaplexq™ Novel Coronavirus Detection KitDocument2 pagesSolgent Co.,Ltd.: Diaplexq™ Novel Coronavirus Detection KitBenny OhorellaNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Intro To DrugsDocument23 pagesCh1 Intro To DrugsLalita SutcharitkulNo ratings yet