Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp.1-Distillation, Simple and Fractional
Exp.1-Distillation, Simple and Fractional
Uploaded by
zazoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp.1-Distillation, Simple and Fractional
Exp.1-Distillation, Simple and Fractional
Uploaded by
zazoCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEM 331-Lab
Organic Chemistry
Experiment 1
Distillation: Simple and Fractional
Department of Chemistry - Faculty of Science
Beirut Arab University
Fall 2020-2021
Aim of the Experiment
Separate a solution of two miscible liquids in
order to obtain a pure solvent by using a
simple distillation technique.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 2
Separation technique
Many different methods for separation of a mixture, such as:
filtration,
extraction,
distillation,
centrifugation,….etc.
Distillation is one of the topic to study in this Lab session.
Just as recrystallization is used to purify an organic solid, distillation is used to
purify an organic liquid compound.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 3
Purity of a Compound
A Pure element or compound contains only one substance,
with no other substances mixed in. while, Impure materials
may be mixtures of elements, mixtures of compounds, or
mixtures of elements and compounds.
Pure liquid compound will have sharp and narrow boiling
point, while Impure liquid compound has a broad and
depressed boiling point because the impurities decrease the
ability of water molecules to become vaporized during boiling,
so, greater amount of heat should be applied, which can be
purified by distillation.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 4
Distillation
Three types of distillation:
Simple Distillation Fractional Distillation Steam Distillation
Both are methods used for separation of
Process which purifies
mixture of a components based on their
temperature-sensitive
boiling point.
materials, such as natural
• For fractional distillation: b.p between
aromatic compounds in
liquids should be less than 25 °C.
the presence of water.
• While Simple distillation: b.p between
liquids should be greater than 25 °C.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 5
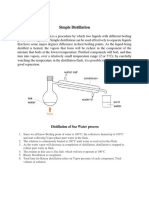
Simple Distillation
Simple distillation is used to separate and retain the solvent from a solution, is based on the principle that the
solvent which is more volatile evaporates first (volatile measures the tendency to vaporize, having the lower boiling
point)
The solvent that remains in the flask is called the residue.
The distilled product is called the distillate.
During the process as heat is applied, the solvent needed to be purified began to boil off and became water vapor
which rose up to the top of the flask.
The water vapor entered the condenser where cold water from the inlet caused the water to condense and run off
into the receiving flask.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 6
Fractional distillation
Is used in industrial scale in the separation of liquid air and the refining of crude oil.
Separation of two liquids based on the principle that one of the liquids is more volatile than the other (has a lower
boiling point and vaporizes first). For example, the boiling point of ethanol is 78° and pure water is 100°. So, As
the mixture of liquids was heated, the vapors rose up the fractionating column and continually condensed and
vaporized, with the lower boiling point liquid (the more volatile one), rising to the higher part of the column, this
liquid condensed first and was collected as the first fraction, the fractionating column is formed of small glass
beads each one will act as simple distillation . The thermometer measures the temperature of the vapor at the top
of the column and indicated what liquid is driven off. When the temperature reaches the boiling point of the
second liquid, that is then distilled into another container.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 7
Applications
Separation of volatile oil.
Purification of organic solvent.
Refining of petroleum products.
Separation of drug obtained from plant and animal.
Purification of drug from animal source.
Separation of crude oil.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 8
Boiling point
Boiling point is the temperature at which vapor pressure of the
liquid is equals to the atmospheric pressure. That is when liquid
and vapor are in equilibrium (liquids changes to vapor).
Thus if decreasing atmospheric pressure by evacuating the
system, the boiling point of the liquid increases.
Similarly when pressurizing the system, the boiling point will
increase.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 9
Distillation steps
There are three steps involved in the distillation:
1. 2. 3.
Vaporization of liquid Condensation of vapors Collection of distillate
Involves two steps: Vapors start to condense due to When vapors are cooled in a
1. Evaporation Process of the low temperature at the condenser and change back
liquid transforming from condensation zone. So all the into liquid, a pure liquid is
liquid state to gaseous vapors are converted into liquid collected which is called the
state due to the increase in again by cooling, away from the distillate and is collected in a
temperature or pressure. distillation flask. The temperature new, clean, and dry flask.
2. Boiling Occurring when remain constant until all the
liquid heated to its boiling molecules of a first liquid
point. converted into vapors and moves
into the condenser.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 10
Such example
If an open container is used
Molecules of vapors escape to the atmosphere to be replaced by molecules escaping from liquid.
This process is called evaporation which take place below the boiling point of the liquid.
If the container is closed system
An equilibrium is reached in which air space above the liquid is saturated with the molecules of the
vapor, the pressure is called vapor pressure (V.p), which is constant at a given temperature and not
affected by atmospheric pressure. We will illustrate two cases:
1. If the liquid have higher V.p at particular temperature, molecules are escaping easily, where the
intermolecular forces between molecules are weak, so, we should not have to supply so much
heat to break them and boil the liquid. So, liquid with higher V.p has lower boiling point.
2. If a liquid has lower V.p, molecules are not escaping easily, strong intermolecular forces, so, we
need to supply much heat. So, liquid with lower V.p has higher boiling point.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 11
Ideal Solution and Raoult’s Law
Ideal Solution
When two liquids are mixed together it is known as binary mixture. Ideal Solution is binary mixture of liquid
components and there is no change in properties of other substance. Heat is nether evolved nor absorbed
during mixture formation.
Raoult’s Law
Raoult’s law states that, "the partial vapour pressure of each volatile constituent in an ideal mixture is equal to
vapour pressure of pure constituents multiplied by its mole fraction"
Compound A : PA = P0 A . XA
Partial vapor pressure of a liquid, Vapor pressure of pure Mole fraction of
which is the pressure of that gas if it substance substance, which is equal
is alone occupied the entire volume to number of mole of
of the original mixture at the same compound A over number
temperature of mole of total
compounds in a mixture.
XA =
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 12
Dalton’s Law
Dalton’s law states that, the total pressure exerted by mixture of
ideal gas may be considered as sum of partial vapour pressure of
each gas (if alone were present and occupied same volume).
P T = PA + P B
PT = P0 A.XA + P0 B.XB
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 13
Application of Law
Application of Law is for component having higher vapour
pressure (lighter component) will be distilled first.
This principle is used in simple distillation, separation of
volatile liquid from non-volatile liquid. While fractional
distillation used for a mixture of volatile liquids.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 14
Safety Precautions
As in all laboratory exercises:
• Safety glasses, mask, and gloves must be worn at all
times.
• Avoid skin and eye contact with any chemical reagent.
• In case of skin contact, rinse the area with water for
several minutes.
• For eye contact, flush eyes with water and seek
immediate medical advice.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 15
Procedure
Heat gently When the first drop falls into the
receiver record the temperature
(b.p (ethanol) = 78 °C)
25 mL of 96% ethanol + 10 1. Continue heating with rate of 2
mL water + boiling stones drops/min, until all pure ethanol is
(used to regulate collected.
2. Record the volume of pure ethanol
temperature and prevent Attach the apparatus carefully by using a cylinder, should be
bumping) approximately the same used at the
beginning.
3. Record the volume of residue in the
round bottom flask which is related
to water.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 16
Calculation
96 % ethanol is used , which means that:
96 mL ethanol 100 mL
Volume (ethanol) /25 mL solution
??? 25 mL
And,
4 mL water 100 mL
??? 25 mL Total Volume (water) /25 mL solution
+ 10 mL water is added to the mixture.
So, The calculated value should be approximately the same of that
obtained.
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 17
Distillation: Simple and Fractional | Fall 2020-2021 18
You might also like
- Frequency Converter English ManualDocument33 pagesFrequency Converter English Manualproduccion multipack100% (2)
- BMS Sequence of OperationsDocument18 pagesBMS Sequence of OperationsRa Ar100% (2)
- Mitsubishi Full PUHY P700YSGM ADocument108 pagesMitsubishi Full PUHY P700YSGM AmpelperNo ratings yet
- Steam Distillation Separation of A Mixture of P-DichlorobenzeneDocument19 pagesSteam Distillation Separation of A Mixture of P-Dichlorobenzeneشهد إيادNo ratings yet
- Simple and Steam Distillation Exp3.Document5 pagesSimple and Steam Distillation Exp3.paoloNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Perfume Production - A Selection of Vintage Articles on the Methods and Ingredients of PerfumeryFrom EverandA Guide to Perfume Production - A Selection of Vintage Articles on the Methods and Ingredients of PerfumeryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Data Sheet Indirect Fired Heater NapkjsDocument12 pagesData Sheet Indirect Fired Heater Napkjsahmad santosoNo ratings yet
- Exp.1-Distillation Simple and FractionalDocument18 pagesExp.1-Distillation Simple and Fractionalsisi slayNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Different TestDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry Different TestNera AyonNo ratings yet
- Distillation: by Assistant Professor Jntua-Otpri AnantapurDocument39 pagesDistillation: by Assistant Professor Jntua-Otpri AnantapurRAJESHPAVANNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL CHEMISTRY Lecture # 2Document21 pagesINDUSTRIAL CHEMISTRY Lecture # 2Ali Abbas Aslam Ali Abbas AslamNo ratings yet
- Speaking Practice Questions Answers PDFDocument85 pagesSpeaking Practice Questions Answers PDFkomal naeemNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument80 pagesDistillationAbdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- 6 - Simple DistillationDocument6 pages6 - Simple DistillationJade AsparinNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument4 pagesDistillationManoj KhanalNo ratings yet
- Distillationbyankitayagnik 180430073733Document80 pagesDistillationbyankitayagnik 180430073733Syeda K Shah KazmiNo ratings yet
- Seperation MethodsDocument7 pagesSeperation MethodsjjknarutotokyoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Laboratory: Basra University College of Science and Technology Pharmacy DepartmentDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistry Laboratory: Basra University College of Science and Technology Pharmacy DepartmentcrtgyhujikNo ratings yet
- Figure 1. Two Liquid-Vapor Equilibrium Diagram: Because Water and OrganicsDocument2 pagesFigure 1. Two Liquid-Vapor Equilibrium Diagram: Because Water and Organicsgerald domingoNo ratings yet
- Types of DistillationDocument6 pagesTypes of Distillationravi2007No ratings yet
- 3 Group: GEN ChemistryDocument28 pages3 Group: GEN ChemistryBea Hannah FarrenNo ratings yet
- Simple and Fractional DistillationDocument6 pagesSimple and Fractional Distillationralph_ong230% (1)
- Simple Distillation: Rovic Kevin N. MelladoDocument2 pagesSimple Distillation: Rovic Kevin N. MelladoRovic MelladoNo ratings yet
- Notes On Purification of Organic CompoundDocument24 pagesNotes On Purification of Organic CompoundChirAgNo ratings yet
- Purification of Liquid Organic Compounds: DistillationDocument7 pagesPurification of Liquid Organic Compounds: DistillationfauzNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument15 pagesDistillationRahul PalsNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistrygayathrigadicharlaapsbNo ratings yet
- Process Calculation: DistillationDocument15 pagesProcess Calculation: DistillationJohn RajNo ratings yet
- RefineryDocument41 pagesRefineryawad awadNo ratings yet
- Exp 3Document9 pagesExp 3tamanranya234No ratings yet
- Basics of DistillationDocument10 pagesBasics of DistillationAgus AkNo ratings yet
- Definition:: DistillationDocument2 pagesDefinition:: DistillationAirah De JesusNo ratings yet
- Chem 73.2 Binary LiquidsDocument10 pagesChem 73.2 Binary LiquidsErnie Mark Patosa MaratasNo ratings yet
- Worksheets Bpo HycDocument71 pagesWorksheets Bpo HycHrithik JerathNo ratings yet
- DISTILLATION UNIT 1 28.2.22 - WatermarkDocument26 pagesDISTILLATION UNIT 1 28.2.22 - WatermarkHardik ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Separation of DiDocument19 pagesSeparation of Dinikhvidwans16No ratings yet
- Official Report Practicum of Chemical Separation Principles Fracsination DestilationDocument22 pagesOfficial Report Practicum of Chemical Separation Principles Fracsination DestilationFitriyah AbidinNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report DistillationDocument3 pagesLaboratory Report DistillationQueenie Luib MapoyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6 - DistillationDocument5 pagesExperiment 6 - DistillationRohit BiswasNo ratings yet
- Lyrics of I Believe I Can Fly - Erik SantosDocument3 pagesLyrics of I Believe I Can Fly - Erik SantosRaz MahariNo ratings yet
- What Is Fractional DistillationDocument4 pagesWhat Is Fractional DistillationShubham WarseNo ratings yet
- Absorption Refrigeration SystemDocument32 pagesAbsorption Refrigeration SystemEngr ModestoNo ratings yet
- Fractional Distillation LabDocument7 pagesFractional Distillation LabOmar AlasNo ratings yet
- Scientific ReportDocument7 pagesScientific ReportKath VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesOrganic Chemistrykarrivaraprasad44No ratings yet
- Separation and PurificationDocument41 pagesSeparation and PurificationAlea PrillyNo ratings yet
- 2024 01 18 17 12Document4 pages2024 01 18 17 12fatenhmd551No ratings yet
- Distillation Basics: Dharmsinh Desai UniversityDocument20 pagesDistillation Basics: Dharmsinh Desai UniversityGilles DakouriNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument5 pagesDistillationfelescosorheaNo ratings yet
- DisstilationDocument6 pagesDisstilationMustafa KhanNo ratings yet
- DistillationDocument109 pagesDistillationAmna AnjumNo ratings yet
- Fractional DistillationDocument15 pagesFractional DistillationAlyan Srijaya0% (1)
- Organic Lab - Distillation PDFDocument2 pagesOrganic Lab - Distillation PDFDaryayBaharNo ratings yet
- 16 Distillation NotesDocument6 pages16 Distillation Notesyown silvaNo ratings yet
- DistilationDocument11 pagesDistilationMuhammad HusseinNo ratings yet
- Simple Distillation (Petroleum)Document8 pagesSimple Distillation (Petroleum)hayder alaliNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes CHP 21Document3 pagesChem Notes CHP 21Krishna BeriwalNo ratings yet
- Simple DistillationDocument5 pagesSimple DistillationJheian Christian TubleNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Pure?Document8 pagesIs Matter Pure?Aarti JainNo ratings yet
- PURIFICATION of Organic Compounds: 2. SublimationDocument1 pagePURIFICATION of Organic Compounds: 2. SublimationchinnagandiNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument39 pagesOrganic Chemistryh2312416No ratings yet
- DistillationDocument72 pagesDistillationYashfa YasinNo ratings yet
- Distillation ColumnDocument22 pagesDistillation Columndiyar cheNo ratings yet
- Southernstate FallHazardAwareness-in-oil-gas-industryDocument36 pagesSouthernstate FallHazardAwareness-in-oil-gas-industryzazoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Interactions Between Oilfield Chemicals and Reservoir RocksDocument20 pagesEvaluation of Interactions Between Oilfield Chemicals and Reservoir RockszazoNo ratings yet
- Caught BetweenDocument30 pagesCaught BetweenzazoNo ratings yet
- Struck byDocument24 pagesStruck byzazoNo ratings yet
- Material Balance EquationsDocument4 pagesMaterial Balance EquationszazoNo ratings yet
- MOC - Final - Paper - Moscow - Financial - Services Final2Document39 pagesMOC - Final - Paper - Moscow - Financial - Services Final2zazoNo ratings yet
- Personal Protective EquipmentDocument20 pagesPersonal Protective EquipmentzazoNo ratings yet
- 4 Eor4gasmethods 180113184248Document28 pages4 Eor4gasmethods 180113184248zazoNo ratings yet
- Is A Fancy Term For A One Sentence Summary of What The Main Purpose or Point of Your PaperDocument9 pagesIs A Fancy Term For A One Sentence Summary of What The Main Purpose or Point of Your PaperzazoNo ratings yet
- Mud Filtration: Supervised By: MR - Pshtewan Jaf MR - Sarhad MR - GoranDocument12 pagesMud Filtration: Supervised By: MR - Pshtewan Jaf MR - Sarhad MR - GoranzazoNo ratings yet
- Drilling Engineering I (PETE 308) : Soran University Faculty of Engineering Department of Petroleum EngineeringDocument8 pagesDrilling Engineering I (PETE 308) : Soran University Faculty of Engineering Department of Petroleum EngineeringzazoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Miscible and Immiscible CO2 InjectioDocument17 pagesEvaluation of Miscible and Immiscible CO2 InjectiozazoNo ratings yet
- Concept Quiz Mars at UmhbDocument58 pagesConcept Quiz Mars at UmhbzazoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Clean Random Variables and Probability Distributions NotesDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Clean Random Variables and Probability Distributions NoteszazoNo ratings yet
- Koya University: (Mud Filtration)Document13 pagesKoya University: (Mud Filtration)zazoNo ratings yet
- Koya University: (Viscosity & Yield Point)Document11 pagesKoya University: (Viscosity & Yield Point)zazoNo ratings yet
- Mud Rheology Test Using Fann VG-Meter: Al - Mahdi Salah AldeenDocument6 pagesMud Rheology Test Using Fann VG-Meter: Al - Mahdi Salah AldeenzazoNo ratings yet
- Exp.5-Reaction of Alkanes, Alkenes, and CycloalkanesDocument27 pagesExp.5-Reaction of Alkanes, Alkenes, and CycloalkaneszazoNo ratings yet
- Exp.6-Alkyl and Aryl HalidesDocument16 pagesExp.6-Alkyl and Aryl HalideszazoNo ratings yet
- Bicycle Wind Turbine PDFDocument7 pagesBicycle Wind Turbine PDFtokagkeloNo ratings yet
- N Detailed Modelling PDFDocument32 pagesN Detailed Modelling PDFhussain100% (1)
- Ee 435 2Document43 pagesEe 435 2EdamEdamNo ratings yet
- Design Two Phase SeperatorsDocument8 pagesDesign Two Phase SeperatorsabhmarsNo ratings yet
- SJPO Special Round 2011 Sample PDFDocument10 pagesSJPO Special Round 2011 Sample PDFziwei_from_chinaNo ratings yet
- Solar Photovoltaic System PT-SPS-N10 2Document1 pageSolar Photovoltaic System PT-SPS-N10 2efendi susantoNo ratings yet
- Line Protection BasicDocument54 pagesLine Protection BasicAshishKumarNo ratings yet
- Mars4solutionsongrid 6kwDocument5 pagesMars4solutionsongrid 6kwmaya phatakNo ratings yet
- Master Thesis Yiwei Cadaverine-SensorDocument77 pagesMaster Thesis Yiwei Cadaverine-SensorAndreas NeoNo ratings yet
- Tolteq Iseries NXT Directional ModuleDocument1 pageTolteq Iseries NXT Directional ModuleBen PontierNo ratings yet
- Proposed Solar PV Plant Labour Colony Area: Engineers & Consultants (FZC.,) Sharjah, UAEDocument1 pageProposed Solar PV Plant Labour Colony Area: Engineers & Consultants (FZC.,) Sharjah, UAEMuhammad NasarNo ratings yet
- ABB Motor (IE4)Document1 pageABB Motor (IE4)Lee DerekNo ratings yet
- TB12Document2 pagesTB12chiri003No ratings yet
- Specific Gravity For Phisical LabDocument2 pagesSpecific Gravity For Phisical LabMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Single Line Diagram of Raina 132Kv Sub-Station: 1 PH PTDocument1 pageSingle Line Diagram of Raina 132Kv Sub-Station: 1 PH PTSarfaraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Industrial Boiler and Burner Limit Control SwitchesDocument5 pagesIndustrial Boiler and Burner Limit Control SwitchesGordinhorsNo ratings yet
- Ch-9 Class-8 Q AnsDocument7 pagesCh-9 Class-8 Q AnsmeghaNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Theory Tutorial #2 (Initial Conditions) Bex/Bct/Bel Ii/IDocument2 pagesElectric Circuit Theory Tutorial #2 (Initial Conditions) Bex/Bct/Bel Ii/IJcb NitinNo ratings yet
- Yuasa NP10-6Document1 pageYuasa NP10-6Lumaksono WirastomoNo ratings yet
- Linked PDFDocument385 pagesLinked PDFroparts cluj100% (1)
- Formal Lab Report - Work and EnergyDocument4 pagesFormal Lab Report - Work and Energyapi-270086937No ratings yet
- D.E 6rd EditionDocument33 pagesD.E 6rd EditionkenNo ratings yet
- Sofarsolar Datasheet - 10-15KTL-G2 - en - 202003 - V2-20200312Document2 pagesSofarsolar Datasheet - 10-15KTL-G2 - en - 202003 - V2-20200312Umar MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Modifikasi Sistem Kendali Sepeda Listrik Listrik Hybrid: Nurul Huda, Fahrul KhamamiDocument6 pagesModifikasi Sistem Kendali Sepeda Listrik Listrik Hybrid: Nurul Huda, Fahrul KhamamifaisalNo ratings yet
- Energy ResourcesDocument26 pagesEnergy ResourcesAnum ObaidNo ratings yet
- EE-103: Electrical Engineering: Chap:6 (Part I) CapacitorsDocument27 pagesEE-103: Electrical Engineering: Chap:6 (Part I) CapacitorsZarak KhanNo ratings yet